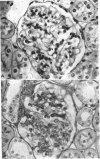
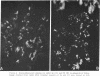
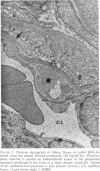
Abstract
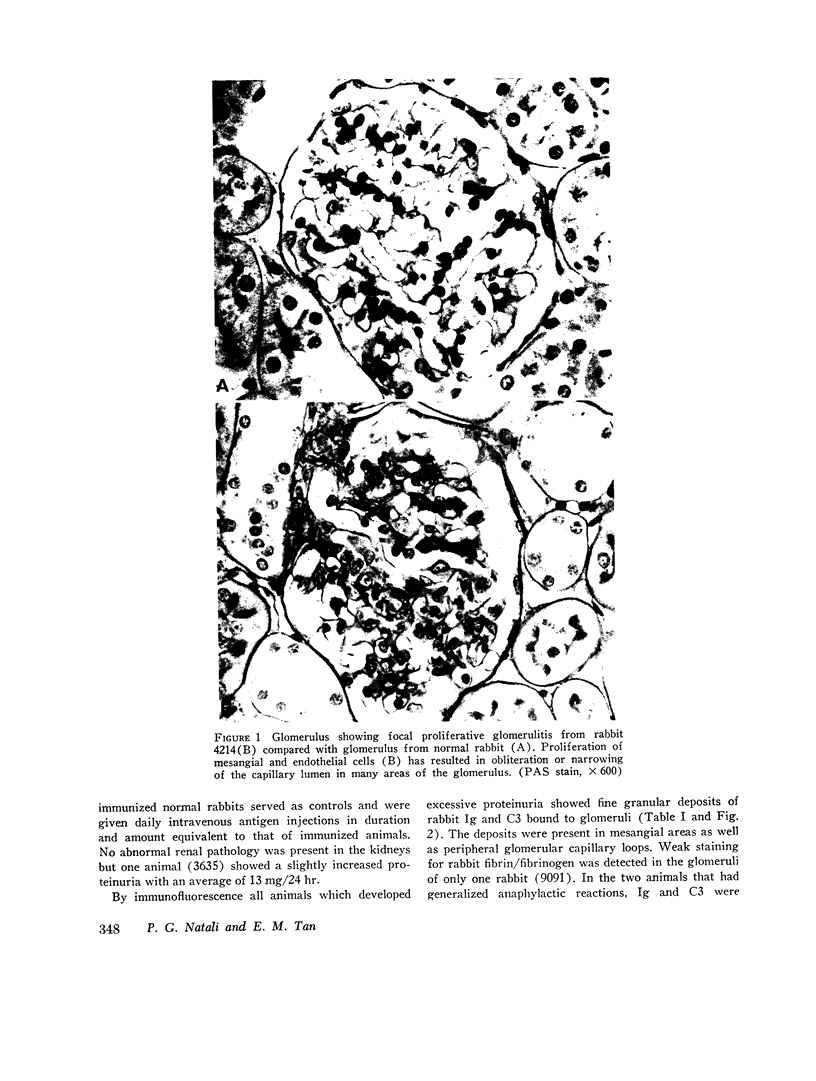
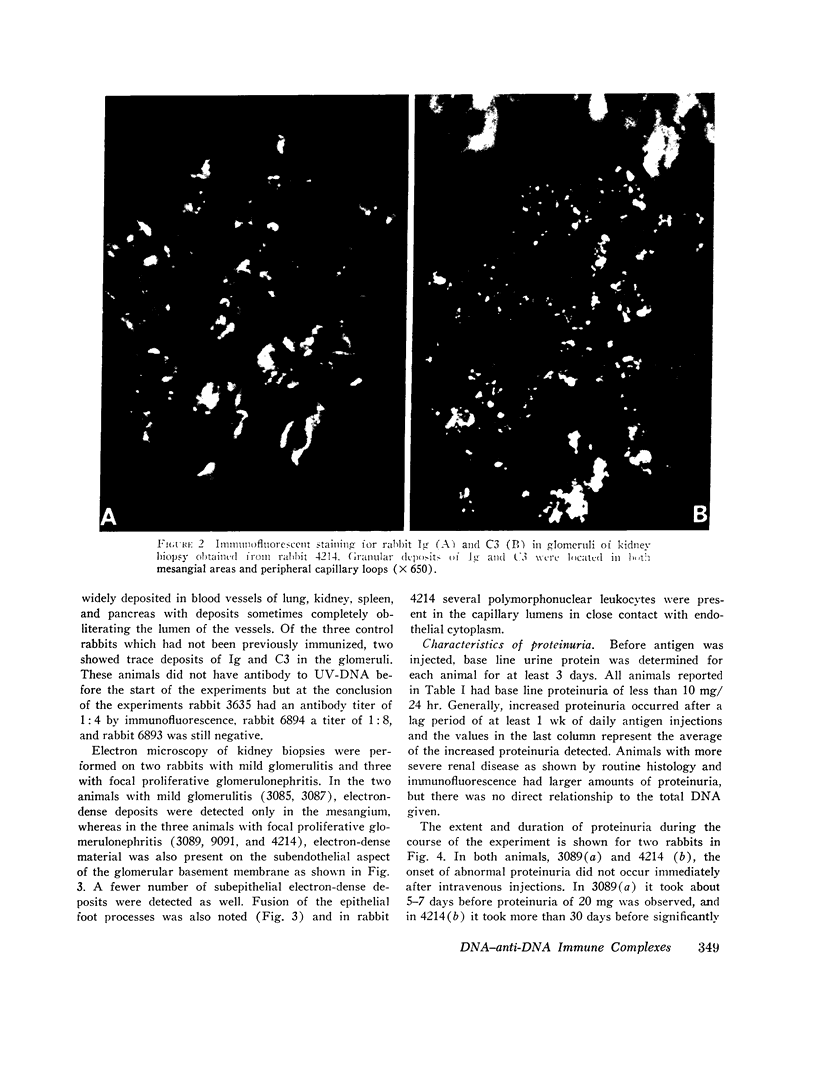
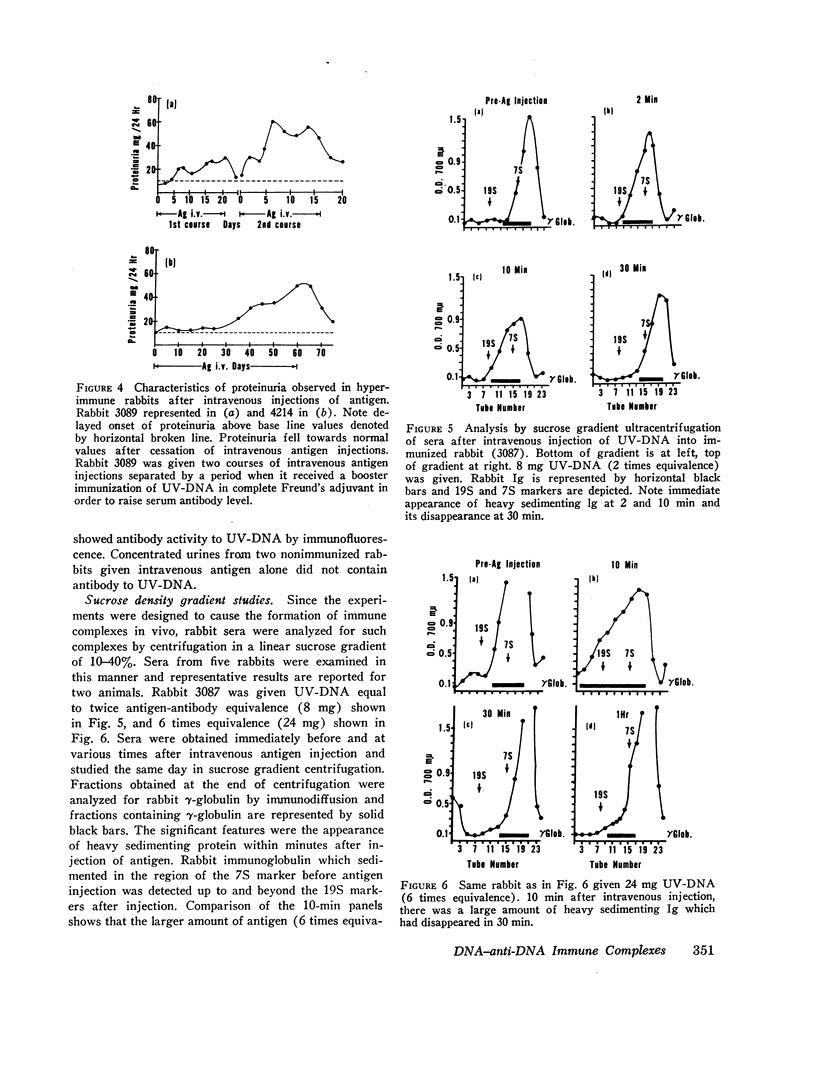
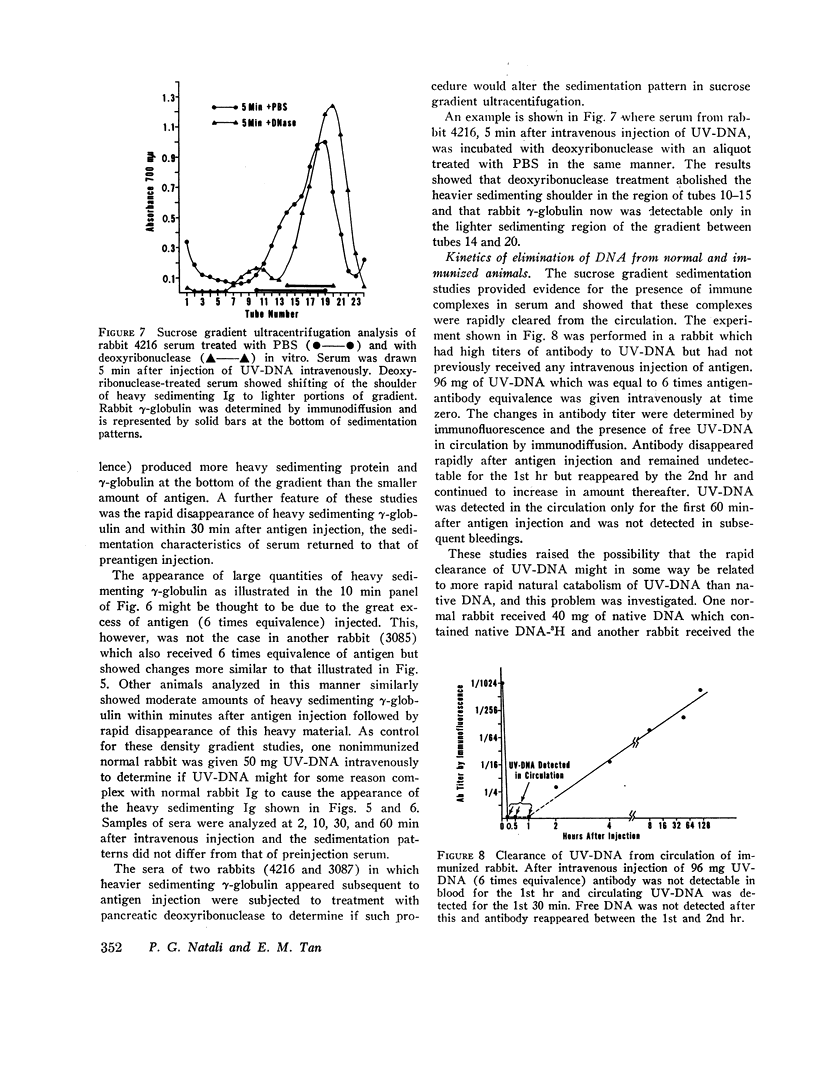
Rabbits immunized with ultraviolet-irradiated DNA (UV-DNA) produced high titers of serum antibody. This experimental model was studied to determine if injection of antigen (UV-DNA) intravenously into immunized animals would induce glomerulonephritis and proteinuria. Proteinuria was observed several days after the start of daily intravenous injections into immunized animals and was sustained as long as injections were continued, but fell to normal values after stopping antigen administration. The kidneys showed glomerulitis sometimes associated with focal proliferative lesions, and immunofluorescence showed rabbit Ig and C3 in glomeruli. By electron microscopy, electron-dense subendothelial deposits were seen. Sucrose density gradient analyses of sera immediately after antigen injections suggested the presence of immune complexes of DNA and antibody since both heavy sedimenting and 7S Ig were detected. After digestion with deoxyribonuclease rabbit Ig could be found only in the 7S sedimenting fractions. Intravenous injection of UV-DNA into normal, nonimmune animals did not produce heavy sedimenting Ig or abnormal sedimentation patterns. These studies with an experimental model might provide insight into pathogenetic mechanisms operating in systemic lupus erythematosus where the importance of DNA—anti-DNA immune complexes have been documented. The studies suggested that gradual accumulation of DNA immune complexes in glomeruli might be one mechanism causing renal functional abnormalities.
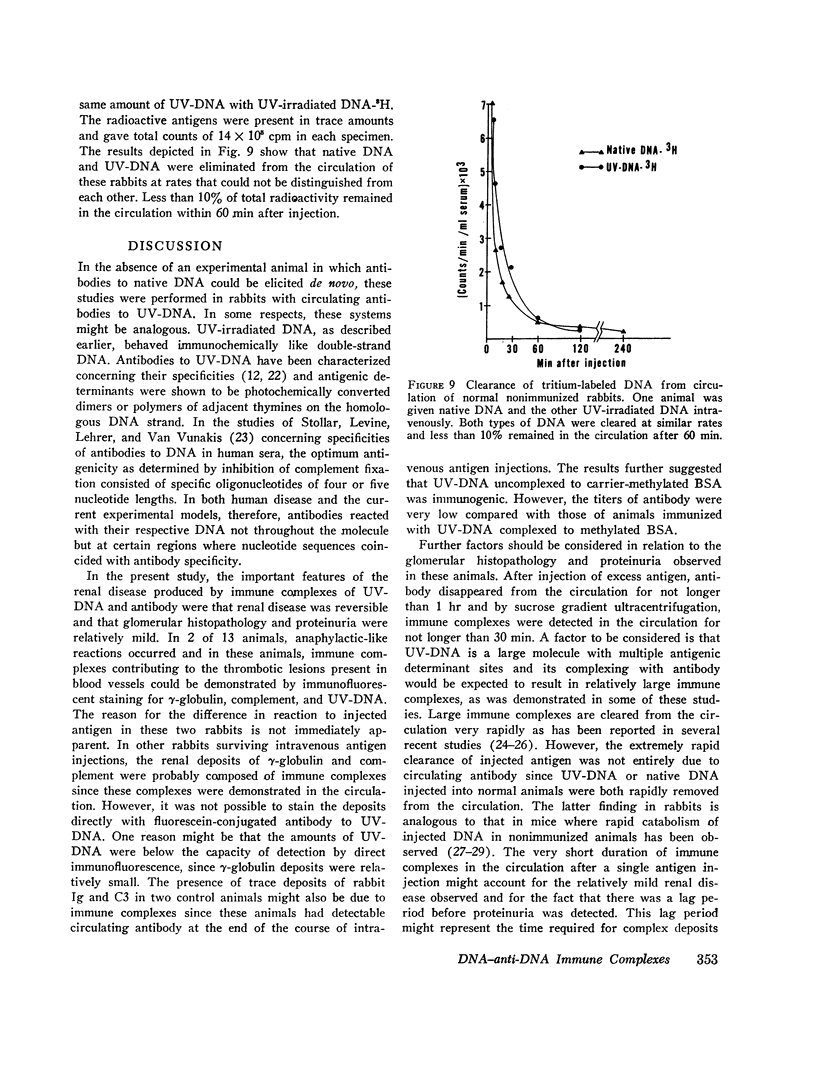
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres G. A., Accinni L., Beiser S. M., Christian C. L., Cinotti G. A., Erlanger B. F., Hsu K. C., Seegal B. C. Localization of fluorescein-labeled antinucleoside antibodies in glomeruli of patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus nephritis. J Clin Invest. 1970 Nov;49(11):2106–2118. doi: 10.1172/JCI106428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENDICH A., WILCZOK T., BORENFREUND E. CIRCULATING DNA AS A POSSIBLE FACTOR IN ONCOGENESIS. Science. 1965 Apr 16;148(3668):374–376. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3668.374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck J. S., Oakley C. L., Rowell N. R. Transplacental passage of antinuclear antibody. Study in infants of mothers with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol. 1966 Jun;93(6):656–663. doi: 10.1001/archderm.93.6.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Hawkins D. Studies on circulating immune complexes. 3. Factors governing the ability of circulating complexes to localize in blood vessels. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):137–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., VAZQUEZ J. J., WEIGLE W. O., COCHRANE C. G. Pathogenesis of serum sickness. AMA Arch Pathol. 1958 Jan;65(1):18–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDMAN P., MARKOWITZ A. S. Isolation of antibody-like gamma-globulin from lupus glomeruli. Br Med J. 1962 Apr 28;1(5286):1175–1178. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5286.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friou G. J. Antinuclear antibodies: diagnostic significance and methods. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Apr;10(2):151–159. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost P. G., Lachmann P. J. The relationship of desoxyribonuclease inhibitor levels in human sera to the occurrence of antinuclear antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Jun;3(5):447–455. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUPTA S., HERRIOTT R. M. Nucleases and their inhibitors in the cellular components of human blood. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Apr;101:88–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90538-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEKWICK R. A., MACKAY M. E., NANCE M. H., RECORD B. R. The purification of human fibrinogen. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):671–683. doi: 10.1042/bj0600671b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Schur P. H., Kunkel H. G. Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):607–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan C., Kaplan M. H. Immunopathologic studies of systemic lupus erythematosus. II. Antinuclear reaction of gamma-globulin eluted from homogenates and isolated glomeruli of kidneys from patients with lupus nephritis. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):569–579. doi: 10.1172/JCI105558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledoux L. Uptake of DNA by living cells. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1965;4:231–267. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60790-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L., Seaman E., Hammerschlag E., Van Vunakis H. Antibodies to photoproducts of deoxyribonucleic acids irradiated with ultraviolet light. Science. 1966 Sep 30;153(3744):1666–1667. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3744.1666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot R. W., Jr, Drusin R. E., Christian C. L. Properties of soluble immune complexes. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1493–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARDINEY M. R., Jr, MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. MOUSE BETA-1C-GLOBULIN: PRODUCTION OF ANTISERUM AND CHARACTERIZATION IN THE COMPLEMENT REACTION. J Immunol. 1965 Jun;94:877–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannik M., Arend M. P., Hall A. P., Gilliland B. C. Studies on antigen-antibody complexes. I. Elimination of soluble complexes from rabbit circulation. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):713–739. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmont A. M. The transfusion of active LE plasma into nonlupus recipients, with a note on the LE-like cell. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun 30;124(2):838–851. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb19006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natali P. G., Tan E. M. Immunological detection of thymidine photoproduct formation in vivo. Radiat Res. 1971 Jun;46(3):506–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLESCIA O. J., BRAUN W., PALCZUK N. C. PRODUCTION OF ANTIBODIES TO DENATURED DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID (DNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:279–285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP F. Localization of antinuclear factors from lupus erythematosus sera in tissue culture. J Immunol. 1962 Jun;88:732–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELIGMANN M. DNA ANTIBODIES. Arthritis Rheum. 1963 Aug;6:SUPPL–557. doi: 10.1002/art.1780060427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOLLAR D., LEVINE L., LEHRER H. I., VAN VUNAKIS H. The antigenic determinants of denatured DNA reactive with lupus erythematosus serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 May 15;48:874–880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.5.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Sandson J. Immunologic factors and clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1968 Mar 7;278(10):533–538. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196803072781004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. C., Irvin W. S., LaRoque R. L., Velez C., Daly V., Kaiser A. D., Holman H. R. Association of autoantibodies to different nuclear antigens with clinical patterns of rheumatic disease and responsiveness to therapy. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):350–359. doi: 10.1172/JCI106502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUMITA T., IWANAGA M. Fate of injected deoxyribonucleic acid in mice. Nature. 1963 Jun 15;198:1088–1089. doi: 10.1038/1981088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Kunkel H. G. Characteristics of a soluble nuclear antigen precipitating with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):464–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Schur P. H., Carr R. I., Kunkel H. G. Deoxybonucleic acid (DNA) and antibodies to DNA in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1732–1740. doi: 10.1172/JCI105479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Stoughton R. B. Ultraviolet light alteration of cellular deoxyribonucleic acid in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):708–714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAZQUEZ J. J., DIXON F. J. Immunohistochemical study of lesions in rheumatic fever, systemic lupus ervthematosus, and rheumatoid arthritis. Lab Invest. 1957 May-Jun;6(3):205–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD J. R., CLOUD R. S., TURNER L. M., Jr NON-CYTOTOXICITY OF "NUCLEAR ANTIBODIES" FROM LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS SERA IN TISSUE CULTURE. Ann Rheum Dis. 1964 Sep;23:381–388. doi: 10.1136/ard.23.5.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood B. T., Thompson S. H., Goldstein G. Fluorescent antibody staining. 3. Preparation of fluorescein-isothiocyanate-labeled antibodies. J Immunol. 1965 Aug;95(2):225–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]