Abstract
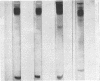
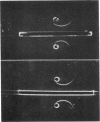
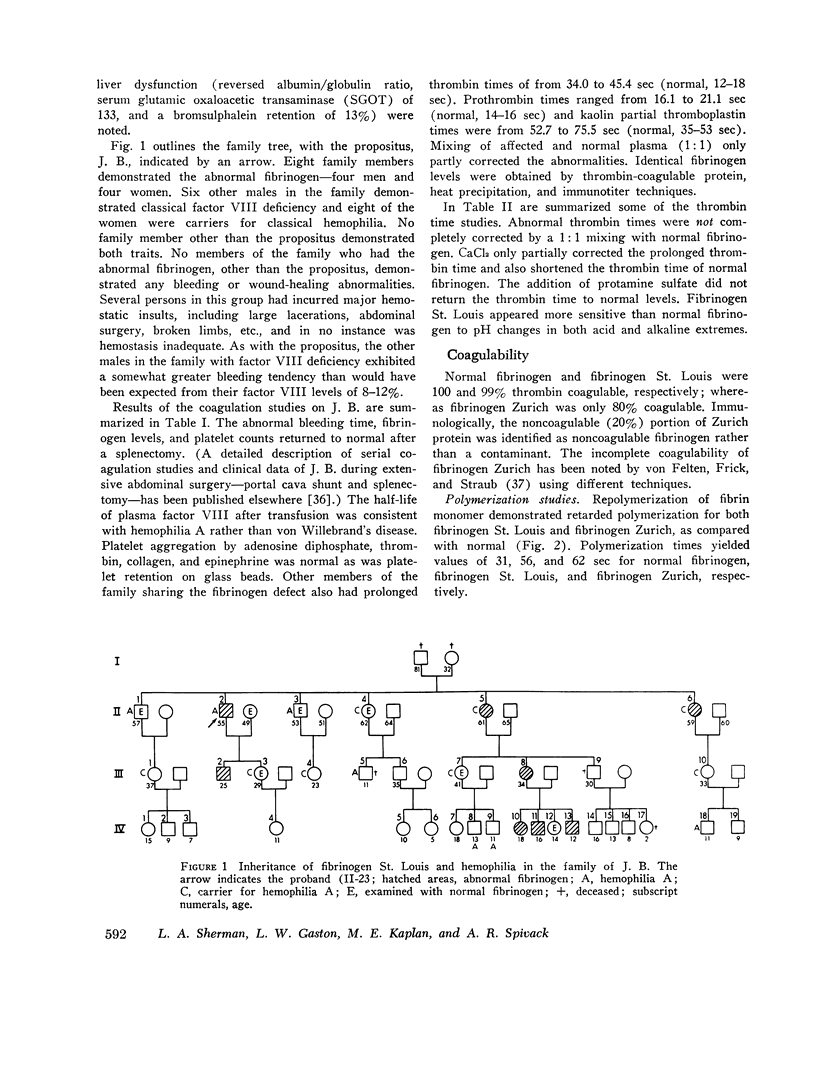
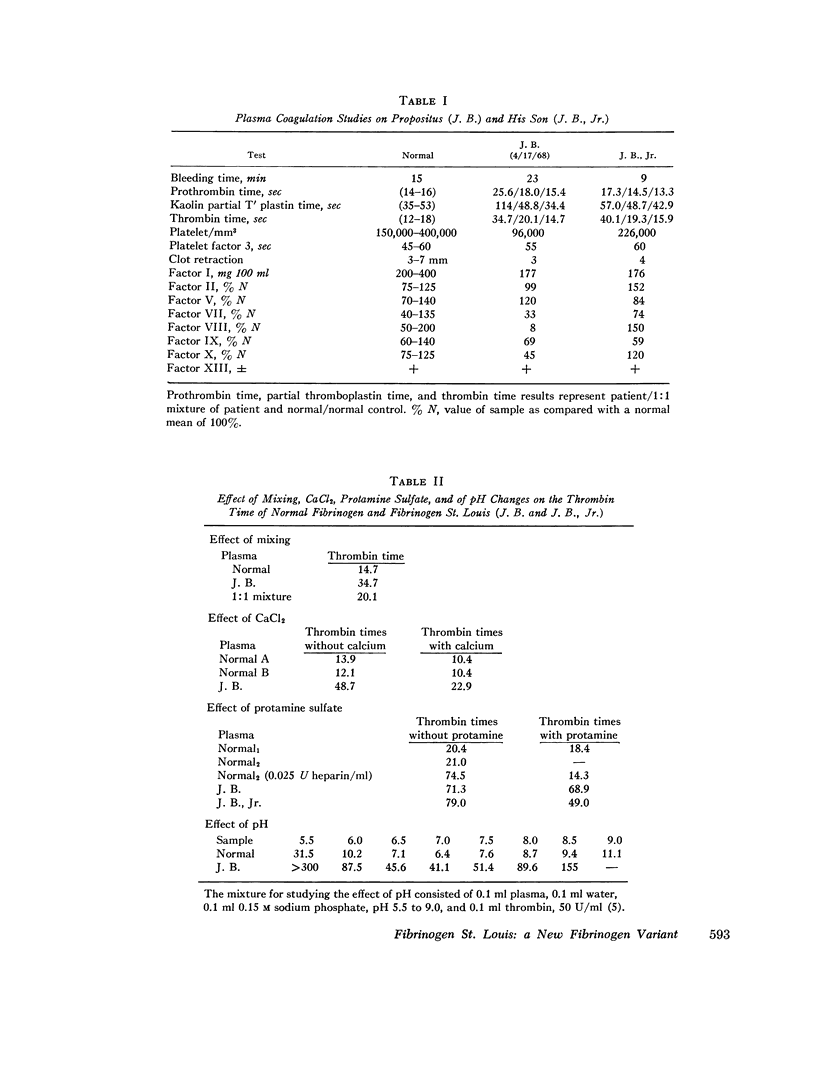
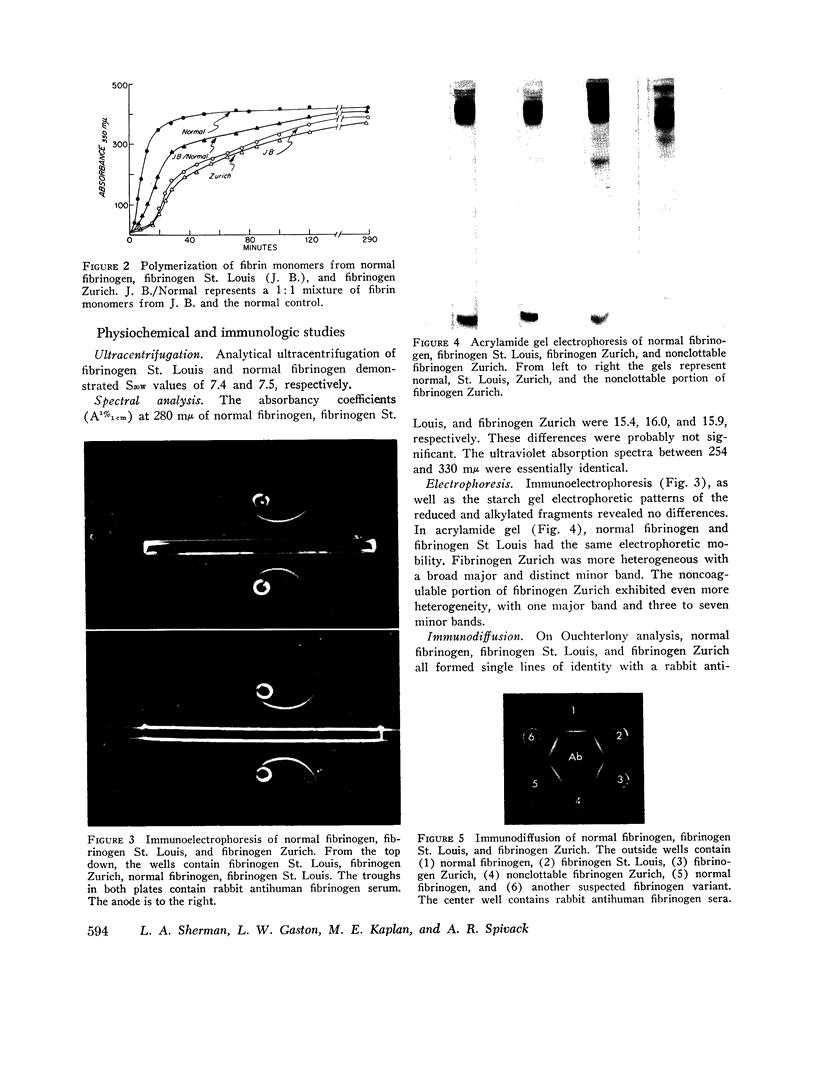
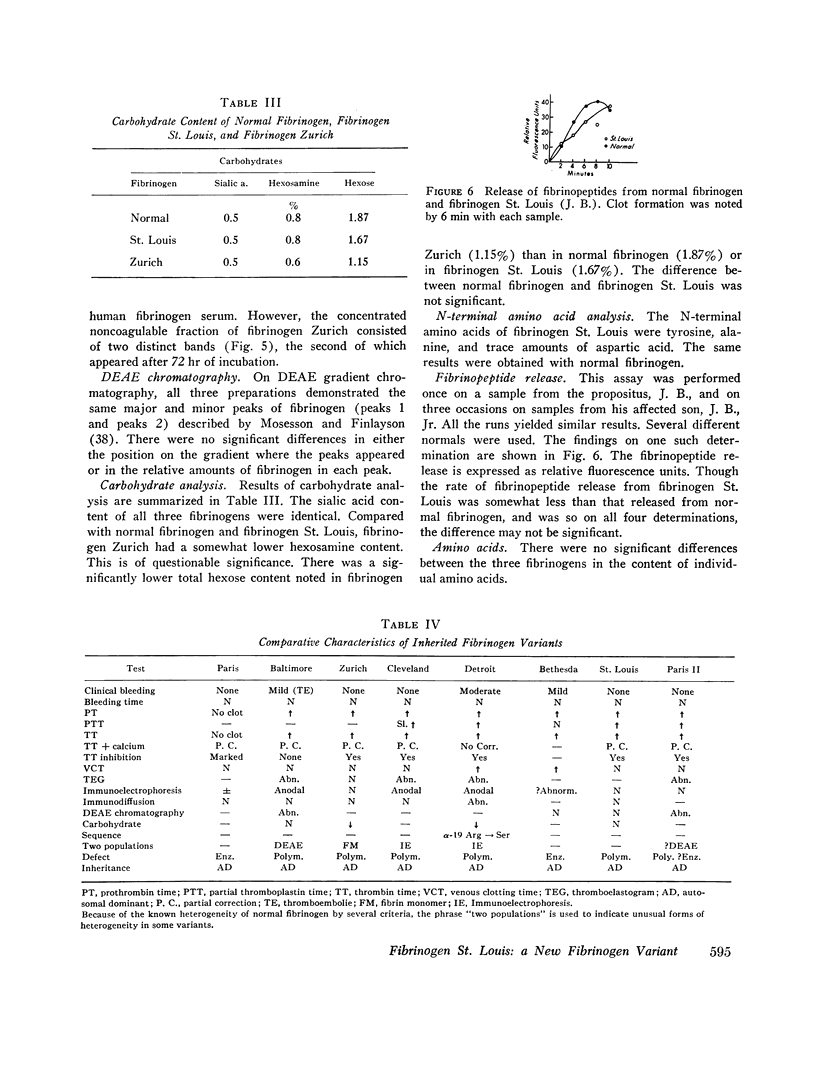
A patient with classical hemophilia (factor VIII deficiency) was found to have a new abnormal fibrinogen (fibrinogen St. Louis). Other family members exhibited either defect alone. Fibrinogen St. Louis was inherited as an autosomal dominant and was not associated with clinical bleeding. When compared with normal fibrinogen, fibrinogen St. Louis was found to have defective fibrin polymerization and possibly a slower release of fibrinopeptides. The prolonged thrombin times were partially corrected by calcium chloride and protamine sulfate. Ultracentrifugal sedimentation, electrophoretic mobility, DEAE chromatographic pattern, carbohydrate content, N-terminal amino acids, immunodiffusion, and immunoelectrophoretic patterns and electrophoresis of reduced and alkylated fragments were all normal. In contrast to fibrinogen St. Louis, the most similar other fibrinogen variant (fibrinogen Zurich) was found to be heterogeneous by several criteria and to have reduced hexose content.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck E. A., Mosesson M. W., Charache P., Jackson D. P. Hämorrhagische Diathese mit dominantem Erbgang, verursacht durch ein anomales Fibrinogen (Fibrinogen Baltimore) Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1966 Sep 17;96(37):1196–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Gall W. E., Waxdal M. J., Konigsberg W. H. The covalent structure of a human gamma G-immunoglobulin. I. Isolation and characterization of the whole molecule, the polypeptide chains, and the tryptic fragments. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1950–1958. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman W. B., Ratnoff O. D., Boyer M. H. An inherited qualitative abnormality in plasma fibrinogen: fibrinogen Cleveland. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Sep;72(3):455–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston L. W., Baue A. E., Pfaff D. A., Wise L. Spleno-renal shunt, cholecystectomy, and appendectomy in a patient with hemophilia A, and abnormal fibrinogen, and thrombocytopenia. Ann Surg. 1971 Feb;173(2):234–237. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197102000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston L. W., Brooks J. E., Blumenthal H. J., Miller C. E. A study of blood coagulation following an acute stroke. Stroke. 1971 Jan-Feb;2(1):81–87. doi: 10.1161/01.str.2.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston L. W., Spivack A. R. Preparation of canine factor VII deficient substrate plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Oct;72(4):548–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASSELBACK R., MARION R. B., THOMAS J. W. Congenital hypofibrinogenemia in five members of a family. Can Med Assoc J. 1963 Jan 5;88:19–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IMPERATO C., DETTORI A. G. Ipofibrinogenemia congenita con fibrinoastenia. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1958 Oct;13(4):380–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen C. L., Vreeken J. Fibrinogen Amsterdam, another hereditary abnormality of fibrinogen. Br J Haematol. 1971 Mar;20(3):287–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb07039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAKI K. The polymerization of proteins; the action of thrombin on fibrinogen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Jul;32(2):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90277-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LATALLO Z. S., FLETCHER A. P., ALKJAERSIG N., SHERRY S. Influence of pH, ionic strength, neutral ions, and thrombin on fibrin polymerization. Am J Physiol. 1962 Apr;202:675–680. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.4.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mammen E. F., Prasad A. S., Barnhart M. I., Au C. C. Congenital dysfibrinogenemia: fibrinogen Detroit. J Clin Invest. 1969 Feb;48(2):235–249. doi: 10.1172/JCI105980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mester L., Szabados L. Structure défectueuse et biosynthèse des fractions glucidiques dans les variantes pathologiques du fibrinogène. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1970 Sep-Oct;10(5):679–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Alkjaersig N., Sweet B., Sherry S. Human fibrinogen of relatively high solubility. Comparative biophysical, biochemical, and biological studies with fibrinogen of lower solubility. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3279–3287. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCTOR R. R., RAPAPORT S. I. The partial thromboplastin time with kaolin. A simple screening test for first stage plasma clotting factor deficiencies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1961 Sep;36:212–219. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/36.3.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., MENZIE C. A new method for the determination of fibrinogen in small samples of plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Feb;37(2):316–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIFFMAN G., KABAT E. A., THOMPSON W. IMMUNOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON BLOOD GROUPS. XXX. CLEAVAGE OF A, B, AND H BLOOD-GROUP SUBSTANCES BY ALKALI. Biochemistry. 1964 Jan;3:113–120. doi: 10.1021/bi00889a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samama M., Soria J., Soria C., Bousser J. Dysfibrinogénémie congénitale et familiale sans tendance hémorragique. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1969 Nov-Dec;9(6):817–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L. A., Mosesson M. W., Sherry S. Isolation and characterization of the clottable low molecular weight fibrinogen derived by limited plasmin hydrolysis of human fraction I-4. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1515–1523. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straughn W., 3rd, Wagner R. H. A simple method for preparing fibrinogen. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 Jul 31;16(1):198–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Felten A., Duckert F., Frick P. G. Familial disturbance of fibrin monomer aggregation. Br J Haematol. 1966 Nov;12(6):667–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1966.tb00152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIEME R. J. An improved technique of agar-gel electrophoresis on microscope slides. Clin Chim Acta. 1959 May;4(3):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(59)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin E. T., Wessler S. Bovine thrombin and activated factor X. Separation and purification. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):112–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Felten A., Frick P. G., Straub P. W. Studies on fibrin monomer aggregation in congenital dysfibrinogenaemia (fibrinogen "Zürich"): separation of a pathological from a normal fibrin fraction. Br J Haematol. 1969 Apr;16(4):353–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb00412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]