Abstract
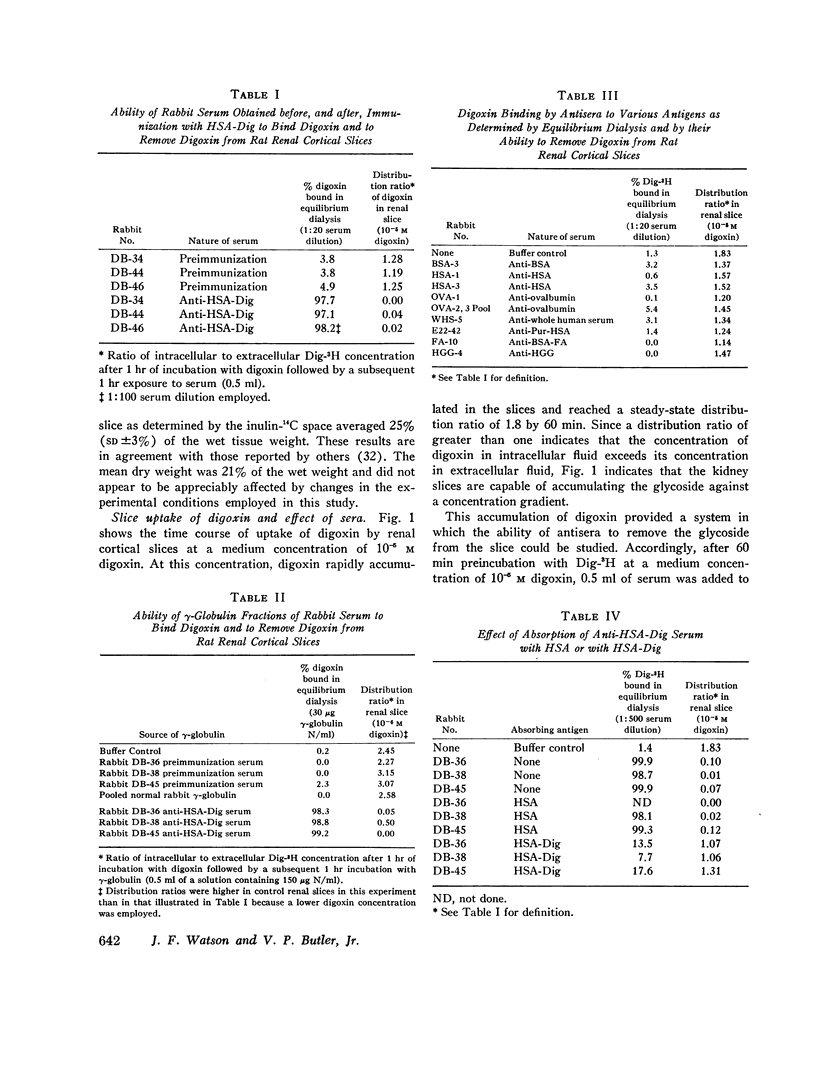
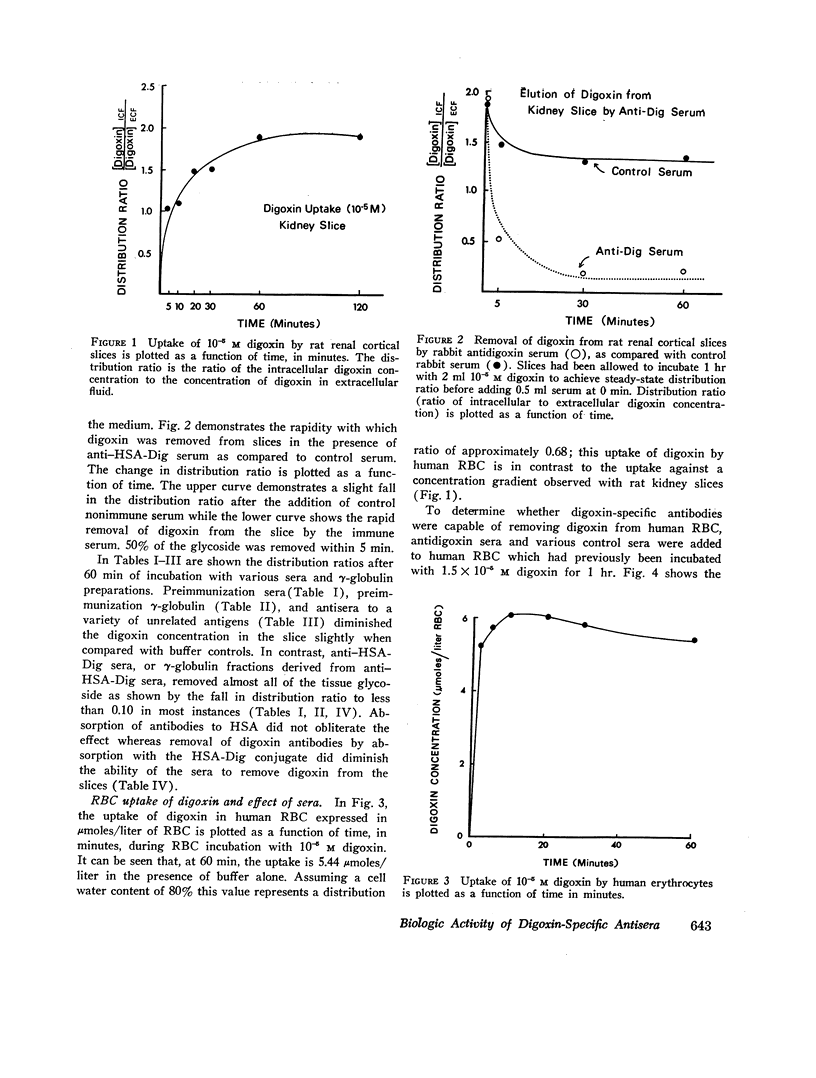
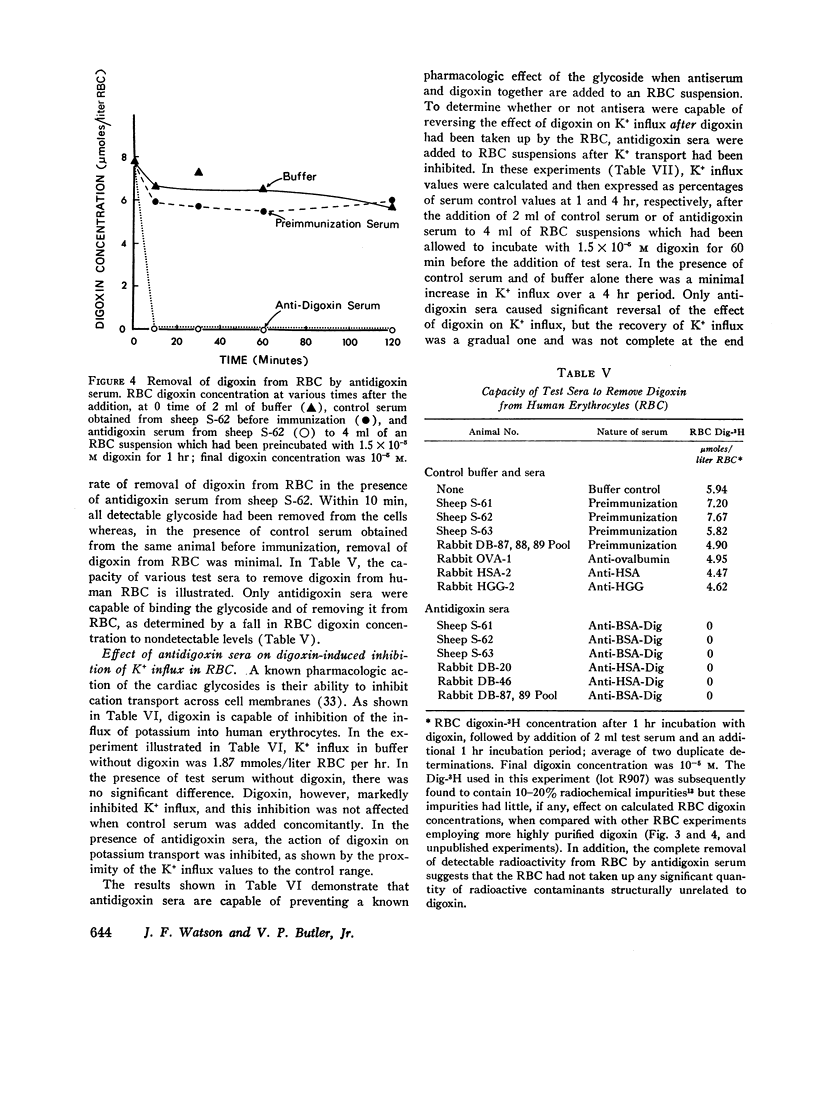
Digoxin-specific antibodies are capable of removing essentially all intracellular digoxin from rat renal cortical slices or from human erythrocytes. In removing digoxin from erythrocytes, these antibodies are capable of reversing an effect of the drug on cellular potassium transport. This study provides direct evidence that antibodies are capable of removing, and thereby reversing the biological effect of, physiologically active low molecular weight substances after they have been taken up by mammalian cells. This biologic property of digoxin-specific antibodies suggests that autidigoxin sera may prove useful in the reversal of digoxin toxicity.
Rapid and essentially quantitative removal of digoxin from red cells by antibody is not accompanied by an immediate restoration of patassium influx to normal levels. Identification of the mechanism of this phenomenon may provide useful information concerning the mode of action not only of digoxin, but also of the cation transport system of human erythrocytes.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTLER V. P., Jr, BEISER S. M., ERLANGER B. F., TANENBAUM S. W., COHEN S., BENDICH A. Purine-specific antibodies which react with deoxvribonucleic acid (DNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Sep 15;48:1597–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.9.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER V. P., Jr, TANENBAUM S. W., BEISER S. M. A STUDY OF THE CROSS-REACTIVITY OF ANTIPURIN-6-OYL SERUM WITH DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID (DNA). J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:19–38. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler V. P., Jr, Chen J. P. Digoxin-specific antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jan;57(1):71–78. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSBY W. H., MUNN J. I., FURTH F. W. Standardizing a method for clinical hemoglobinometry. U S Armed Forces Med J. 1954 May;5(5):693–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOHERTY J. E., PERKINS W. H., MITCHELL G. K. Tritiated digoxin studies in human subjects. Arch Intern Med. 1961 Oct;108:531–539. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1961.03620100023004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. R., Goodfriend T. L. Neutralization of airway effects on bradykinin by antibodies. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jul;217(1):73–77. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. R., Meade K. M. Biologically active antibodies to histamine. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):360–360. doi: 10.1038/226360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty J. E., Perkins W. H. Tissue concentration and turnover of tritiated digoxin in dogs. Am J Cardiol. 1966 Jan;17(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(66)90259-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISEN H. N. EQUILIBRIUM DIALYSIS FOR MEASUREMENT OF ANTIBODY-HAPTEN AFFINITIES. Methods Med Res. 1964;10:106–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERLANGER B. F., BEISER S. M. ANTIBODIES SPECIFIC FOR RIBONUCLEOSIDES AND RIBONUCLEOTIDES AND THEIR REACTION WITH DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:68–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. THE ACTION OF CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES ON ION MOVEMENTS. Pharmacol Rev. 1964 Dec;16:381–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODFRIEND L., SEHON A. H. Antibodies to estrone-protein conjugates. II. Endocrinological studies. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1961 May;39:961–965. doi: 10.1139/o61-094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macknight A. D. The extracellular space in rat renal cortical slices incubated at 0.5 degrees and 25 degrees. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug;163(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui H., Schwartz A. Mechanism of cardiac glycoside inhibition of the (Na+-K+)-dependent ATPase from cardiac tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 25;151(3):655–663. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NERI R. O., TOLKSDORF S., BEISER S. M., ERLANGER B. F., AGATE F. J., Jr, LIEBERMAN S. FURTHER STUDIES ON THE BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF PASSIVE IMMUNIZATION WITH ANTIBODIES TO STEROID-PROTEIN CONJUGATES. Endocrinology. 1964 Apr;74:593–598. doi: 10.1210/endo-74-4-593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng C. W., Gregory K. F. Antibody to lactate dehydrogenase. II. Uptake, accumulation and specific intracellular action in malignant cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 12;170(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90159-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oken D. E., Biber T. U. Biologically effective immunization against angiotensin. Am J Physiol. 1968 Apr;214(4):791–795. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.4.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON M. S., GREENE R. C. MEASUREMENT OF LOW ENERGY BETA-EMITTERS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION BY LIQUID SCINTILLATION COUNTING OF EMULSIONS. Anal Chem. 1965 Jun;37:854–857. doi: 10.1021/ac60226a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Roth J., Macchia V. Binding of hormone to tissue: the first step in polypeptide hormone action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1802–1809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG L. E., BLAIR A., SEGAL S. Transport of amino acids by slices of rat-kidney cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Dec 23;54:479–488. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG L. E., DOWNING S. J., SEGAL S. Extracellular space estimation in rat kidney slices using C saccharides and phlorizin. Am J Physiol. 1962 Apr;202:800–804. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.4.800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranadive N. S., Sehon A. H. Antibodies to serotonin. Can J Biochem. 1967 Nov;45(11):1701–1710. doi: 10.1139/o67-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R., Welt L. G. The concentration dependence of active potassium transport in the human red blood cell. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):65–76. doi: 10.1172/JCI105512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt D. H., Butler V. P., Jr Reversal of digoxin toxicity with specific antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1738–1744. doi: 10.1172/JCI106663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., Butler V. P., Jr, Haber E. Characterization of antibodies of high affinity and specificity for the digitalis glycoside digoxin. Biochemistry. 1970 Jan 20;9(2):331–337. doi: 10.1021/bi00804a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., Butler V. P., Jr, Haber E. Determination of therapeutic and toxic serum digoxin concentrations by radioimmunoassay. N Engl J Med. 1969 Nov 27;281(22):1212–1216. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196911272812203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., Haber E. Digoxin intoxication: the relationship of clinical presentation to serum digoxin concentration. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2377–2386. doi: 10.1172/JCI106457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMASI T., KUNKEL H. G. ISOLATION OF 7S AND 19S GAMMA GLOBULINS. Methods Med Res. 1964;10:80–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar-Waron H., Sela M. Pyridoxal-specific antibodies obtained with a synthetic pyridoxal-polypeptide conjugate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jul 27;124(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90322-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


