Abstract
Catecholamines have several physiological effects on the kidney. These include: (a) stimulation of renin synthesis in the cortex: (b) antidiuresis by beta adrenergic agents; and (c) diuresis by alpha adrenergic stimulation. The role of cyclic 3′,5′-adenosine monophosphate (cyclic AMP) in the renal actions of catecholamines was evaluated by measuring the effects of several adrenergic agents on cyclic AMP concentration in the dog kidney.
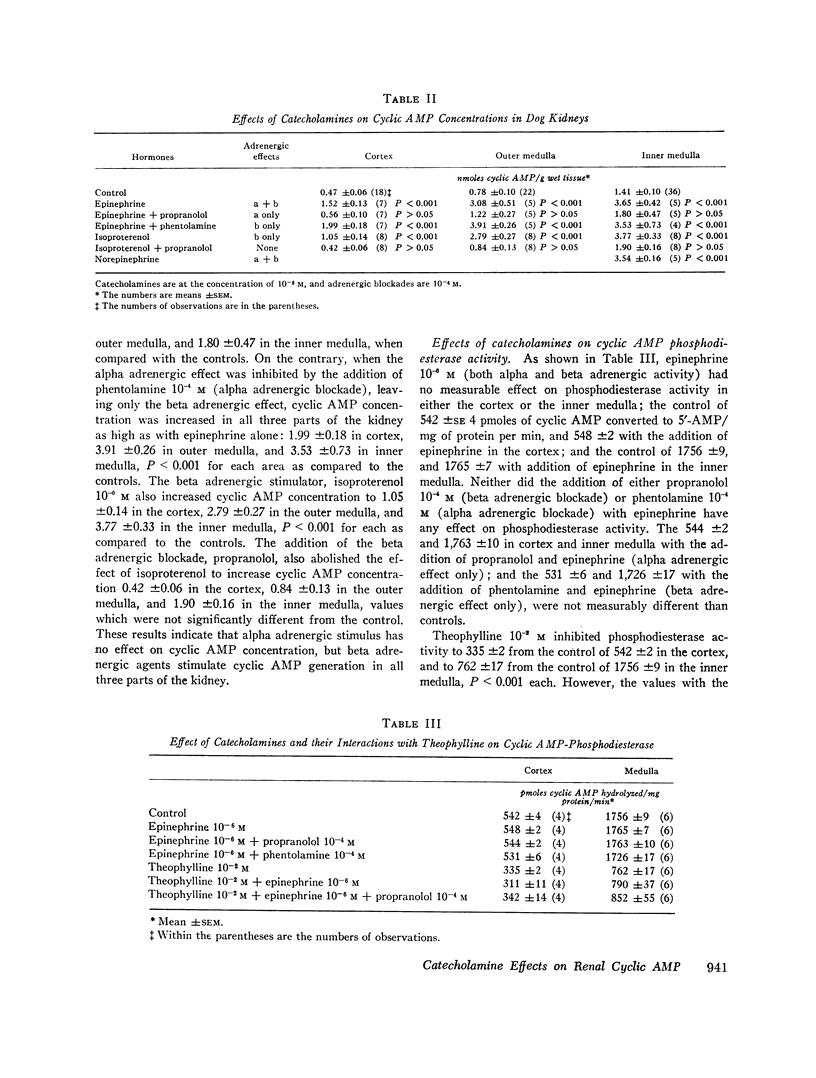
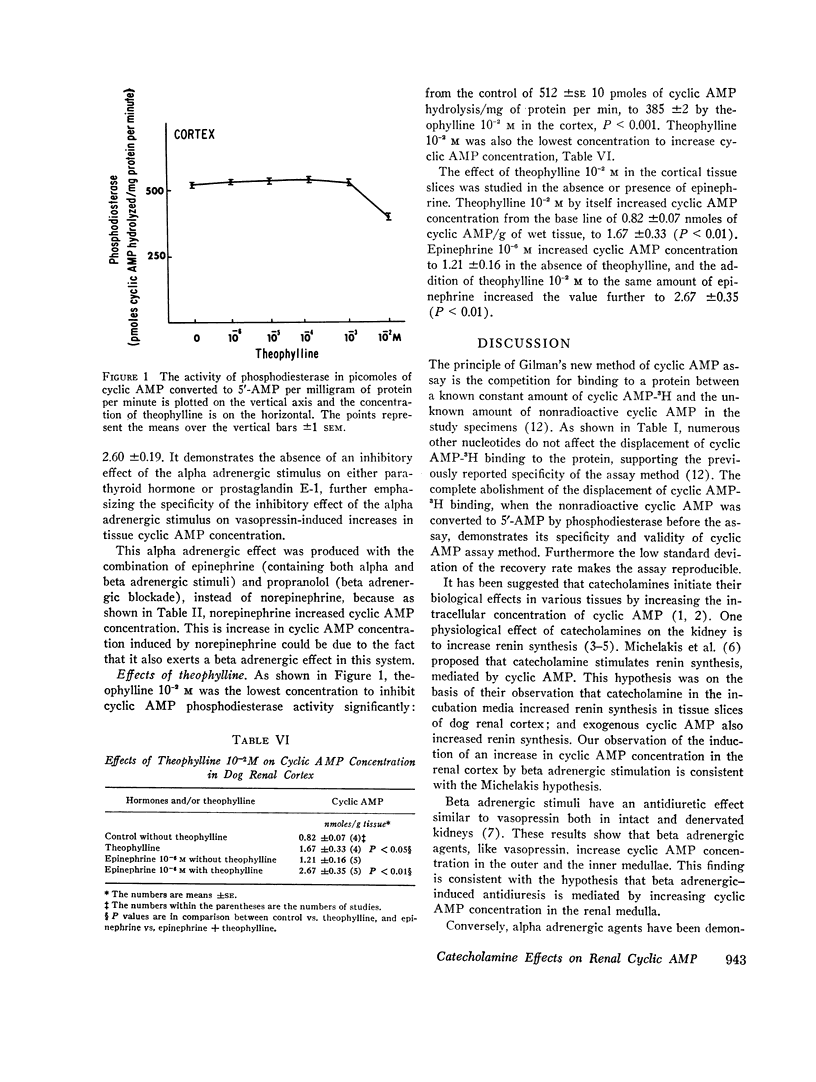
Beta adrenergic activity increased cyclic AMP concentration in the renal cortex, a finding consistent with the hypothesis that beta-adrenergic stimulation augments renin synthesis by increasing cyclic AMP generation.
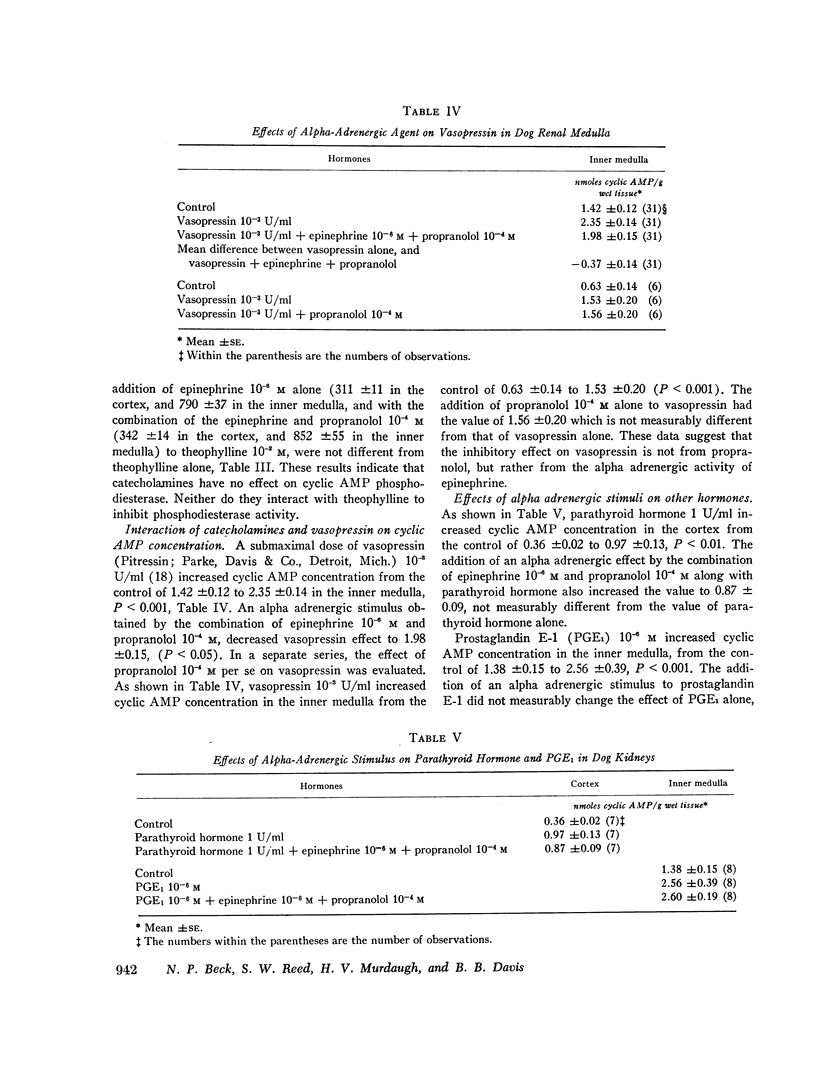
Beta adrenergic stimulation, like vasopressin, increased cyclic AMP concentration in the renal medulla. This suggests that beta adrenergic stimulation causes antidiuresis by augmenting cyclic AMP generation in the renal medulla.
Alpha adrenergic activity inhibited the effect of vasopressin to stimulate cyclic AMP generation. These results support the hypothesis that the diuretic effect of alpha adrenergic stimulation is mediated by inhibition of the effect of vasopressin to increase cyclic AMP generation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALDWIN D. S., GOMBOS E. A., CHASIS H. Changes in sodium and water excretion induced by epinephrine and I-norepinephrine in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 May;61:832–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Properties of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1967 Apr;6(4):1079–1087. doi: 10.1021/bi00856a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A. Norepinephrine inhibition of vasopressin antidiuresis. J Clin Invest. 1968 Mar;47(3):540–547. doi: 10.1172/JCI105750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. D., Küchel O., Liddle G. W., Island D. P. Role of the sympathetic nervous system in regulating renin and aldosterone production in man. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):599–605. doi: 10.1172/JCI105561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handler J. S., Bensinger R., Orloff J. Effect of adrenergic agents on toad bladder response to ADH, 3',5'-AMP, and theophylline. Am J Physiol. 1968 Nov;215(5):1024–1031. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.5.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G., Weiss B., Brodie B. B. A simple, sensitive method for the assay of adenyl cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Oct;163(2):379–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberman B., Klein L. A., Kleeman C. R. Effect of adrenergic blocking agents on the vasopressin inhibiting action of norepinephrine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jan;133(1):131–134. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M., Caudle J., Liddle G. W. In vitro stimulation of renin production by epinephrine, norepinephrine, and cyclic AMP. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Mar;130(3):748–753. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto E., Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. 3. Purification and properties of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6395–6402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata N., Rasmussen H. Renal gluconeogenesis: effects of Ca2+ and H+. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 21;215(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90382-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland E. W., Robison G. A. The role of cyclic-3',5'-AMP in responses to catecholamines and other hormones. Pharmacol Rev. 1966 Mar;18(1):145–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Effect of catecholamines and the renal nerves on renin secretion in anesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1965 Sep;209(3):659–662. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.3.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen R. L., Kingsbury W. S., Stouder D. A., Schneider E. G., Rostorfer H. H. Effects of infusion of catecholamines and angiotensin II on renin release in anesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1965 Nov;209(5):1012–1024. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.5.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


