Abstract
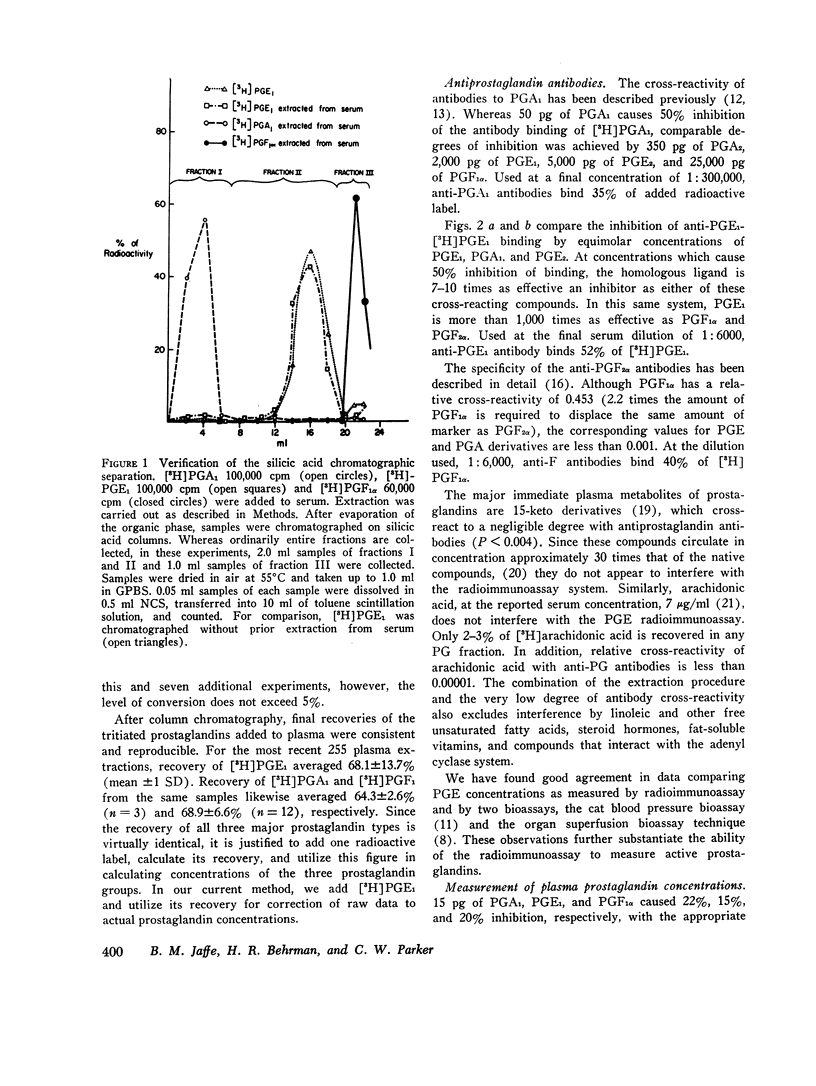
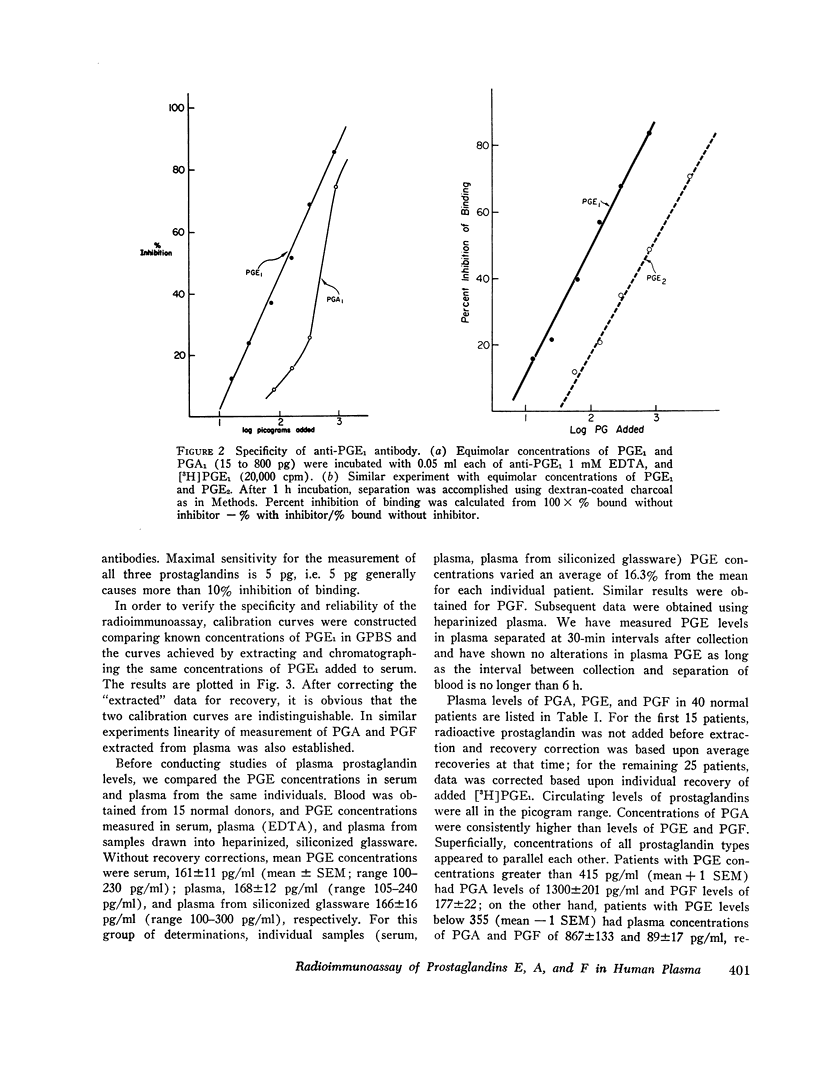
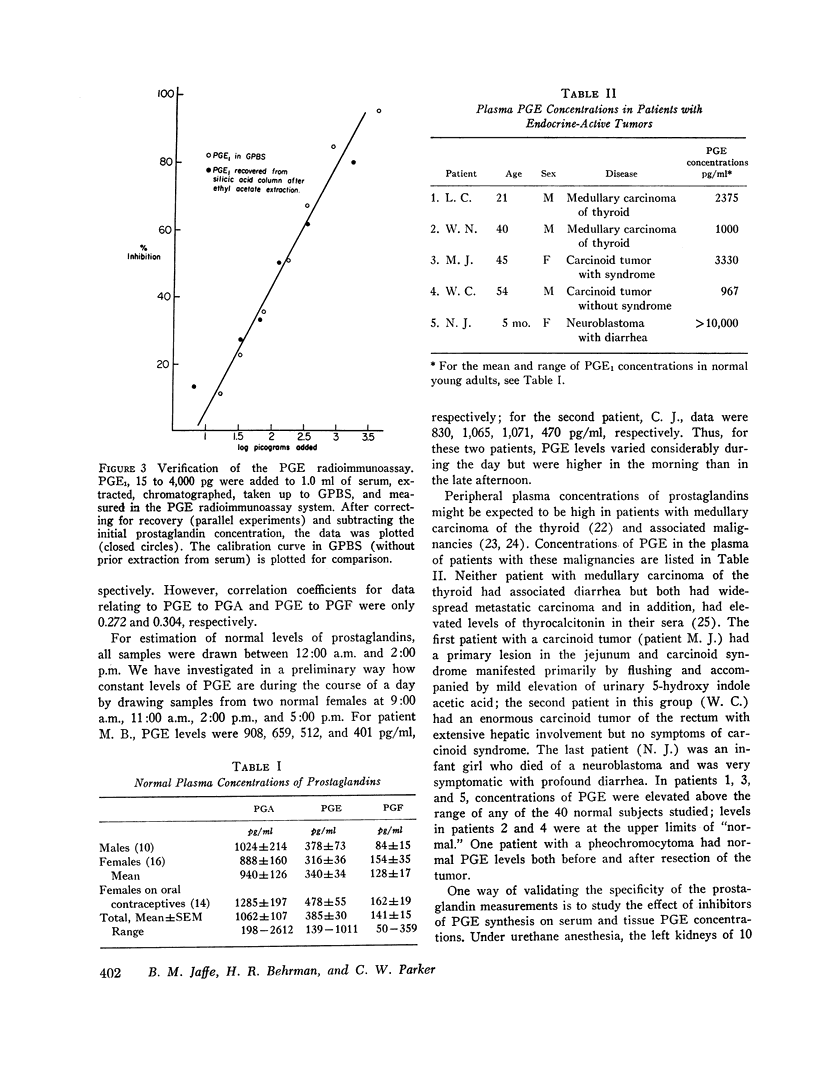
The details of a radioimmunoassay capable of measuring as 5 pg of prostaglandin A, E, and F (PGA, PGE, and PGF) in human and rat plasma are described. Plasma samples are extracted (with 4000 cpm [3H] PGE1 added for calculation of recovery) with an organic solvent system at an apparent pH of 5.8 and then chromatographed on silicic acid columns with increasing concentrations of methanol to separate PGA, PGE, and PGF. Each chromatographed sample is measured by radioimmunoassay, using the homologous antibody and tritiated marker. 40 normal individuals had mean plasma concentrations of PGA, PGE, and PGF of 1062±107 pg/ml, 385±30 pg/ml, and 141±15 pg/ml, respectively. Elevated PGE levels were measured in the plasma of patients with medullary carcinoma of the thyroid, carcinoid, and neuroblastoma. Treatment of rats with indomethacin decreased serum PGE levels by 67%. The radioimmunoassay appears to be of considerable experimental as well as clinical interest.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen N. H. Dehydration of prostaglandins: study by spectroscopic method. J Lipid Res. 1969 May;10(3):320–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anggård E., Samuelsson B. Biosynthesis of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid in guinea pig lung. Prostaglandins and related factors. 38. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3518–3521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axen U., Gréen K., Hörlin D., Samuelsson B. Mass spectrometric determination of picomole amounts of prostaglandins E 2 and F 2 using synthetic deuterium labeled carriers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Oct 15;45(2):519–525. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90850-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYGDEMAN M., SAMUELSSON B. QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF PROSTAGLANDINS IN HUMAN SEMEN. Clin Chim Acta. 1964 Dec;10:566–568. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(64)90198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrman H. R., Yoshinaga K., Wyman H., Greep R. O. Effects of prostaglandin on ovarian steroid secretion and biosynthesis during pregnancy. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jul;221(1):189–193. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.1.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Carlson L. A., Weeks J. R. The prostaglandins: a family of biologically active lipids. Pharmacol Rev. 1968 Mar;20(1):1–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. A., Jackson C. E., Tashjian A. H., Jr Medullary thyroid carcinoma detected by serum calcitonin assay. Arch Surg. 1972 Apr;104(4):579–586. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1972.04180040193033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell B. V., Burstein S., Brock W. A., Speroff L. Radioimmunoassay of the F prostaglandins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Aug;33(2):171–175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell B. V., Tillson S. A., Brock W. A., Speroff L. The effects of exogenous progesterone and estradiol on prostaglandin F levels in ovariectomized ewes. Prostaglandins. 1972 Mar;1(3):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(72)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakins K. E., Karim S. M., Miller J. D. Antagonism of some smooth muscle actions of prostaglandins by polyphloretin phosphate. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;39(3):556–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Indomethacin and aspirin abolish prostaglandin release from the spleen. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):237–239. doi: 10.1038/newbio231237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins: their disappearance from and release into the circulation. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):868–873. doi: 10.1038/216868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN K., SAMUELSSON B. SYNTHESIS OF TRITIUM-LABELED PROSTAGLANDIN E-2 AND STUDIES ON ITS METABOLISM IN GUINEA PIG LUNG. 37. PROSTAGLANDINS AND RELATED FACTORS. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:1932–1940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez Cernosek R. M., Morrill L. M., Levine L. Prostaglandin F2alpha levels in peripheral sera of man. Prostaglandins. 1972 Jan;1(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(72)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez-Cernosek R. M., Zuckerman J., Levine L. Prostaglandin F2alpha levels in sera during human pregnancy. Prostaglandins. 1972 Apr;1(4):331–337. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(72)80010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. On the metabolism of prostaglandins E 1 and E 2 in man. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6713–6721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton E. W., Jones R. L. Prostaglandins A1,A2 and 19-hydroxy A1; their actions on smooth muscle and their inactivation on passage through the pulmonary and hepatic portal vascular beds. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Nov;37(3):705–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb08509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe B. M., Parker C. W., Marshall G. R., Needleman P. Renal concentrations of prostaglandin E in acute and chronic renal ischemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 1;49(3):799–805. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90481-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe B. M., Parker C. W., Philpott G. W. Immunochemical measurement of prostaglandin or prostaglandin-like activity from normal and neoplastic cultured tissue. Surg Forum. 1971;22:90–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe B. M., Smith J. W., Newton W. T., Parker C. W. Radioimmunoassay for prostaglandins. Science. 1971 Feb 5;171(3970):494–496. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3970.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannegiesser H., Lee J. B. Difference in haemodynamic response to prostaglandins A and E. Nature. 1971 Feb 12;229(5285):498–500. doi: 10.1038/229498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim S. M. The identification of prostaglandins in human umbilical cord. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Feb;29(2):230–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb01955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirton K. T., Cornette J. C., Barr K. L. Characterization of antibody to prostaglandin F 2a . Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):903–909. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90578-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE J. B., HICKLER R. B., SARAVIS C. A., THORN G. W. SUSTAINED DEPRESSOR EFFECT OF RENAL MEDULLARY EXTRACT IN THE NORMOTENSIVE RAT. Circ Res. 1963 Oct;13:359–366. doi: 10.1161/01.res.13.4.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L., Gjtierrez Cernosek R. M., Van Vunakis H. Specificities of prostaglandins B 1 , F 1 , and F 2 antigen-antibody reactions. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6782–6785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L., Van Vunakis H. Antigenic activity of prostaglandins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 9;41(5):1171–1177. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90209-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Terragno N. A., Strand J. C., Lee J. B., Lonigro A. J., Ng K. K. Selective passage of prostaglandins across the lung. Nature. 1969 Aug 16;223(5207):742–745. doi: 10.1038/223742b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oates J. A., Butler T. C. Pharmacologic and endocrine aspects of carcinoid syndrome. Adv Pharmacol. 1967;5:109–128. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60656-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orczyk G. P., Behrman H. R. Ovulation blockade by aspirin or indomethacin--in vivo evidence for a role of prostaglandin in gonadotrophin secretion. Prostaglandins. 1972 Jan;1(1):3–20. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(72)90061-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P. J., Vane J. R., Wyllie J. H. Inactivation of prostaglandins by the lungs. Nature. 1970 Feb 14;225(5233):600–604. doi: 10.1038/225600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podos S. M., Jaffe B. M., Becker B. Prostaglandins and glaucoma. Br Med J. 1972 Oct 28;4(5834):232–232. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5834.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polet H., Levine L. Serum prostaglandin A isomerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Dec 3;45(5):1169–1176. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMUELSSON B. PROSTAGLANDINS AND RELATED FACTORS. 28. METABOLISM OF PROSTAGLANDIN E1 IN GUINEA PIG LUNG: THE STRUCTURES OF TWO METABOLITES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4097–4102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHRADE W., BIEGLER R., BOEHLE E. Fatty-acid distribution in the lipid fractions of healthy persons of different age, patients with atherosclerosis and patients with idiopathic hyperlipidaemia. J Atheroscler Res. 1961 Jan-Feb;1:47–61. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1319(61)80053-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. E., Ramwell P. W. Separation, identification, and estimation of prostaglandins. Methods Biochem Anal. 1969;17:325–371. doi: 10.1002/9780470110355.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Willis A. L. Aspirin selectively inhibits prostaglandin production in human platelets. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):235–237. doi: 10.1038/newbio231235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. J., Los M., Horton E. W. The separation, identification and estimation of prostaglandins in nanogram quantities by combined gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Life Sci I. 1970 Sep 1;9(17):983–988. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. The release and fate of vaso-active hormones in the circulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Feb;35(2):209–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams E. D., Karim S. M., Sandler M. Prostaglandin secretion by medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. A possible cause of the associated idarrhoea. Lancet. 1968 Jan 6;1(7532):22–23. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. M., Wyllie J. H. Prostaglandins and glaucoma. Br Med J. 1971 Sep 11;3(5775):615–617. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5775.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. C., Chang L., Burke G. Thyrotropin increases prostaglandin levels in isolated thyroid cells. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):1038–1042. doi: 10.1172/JCI106864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


