Abstract
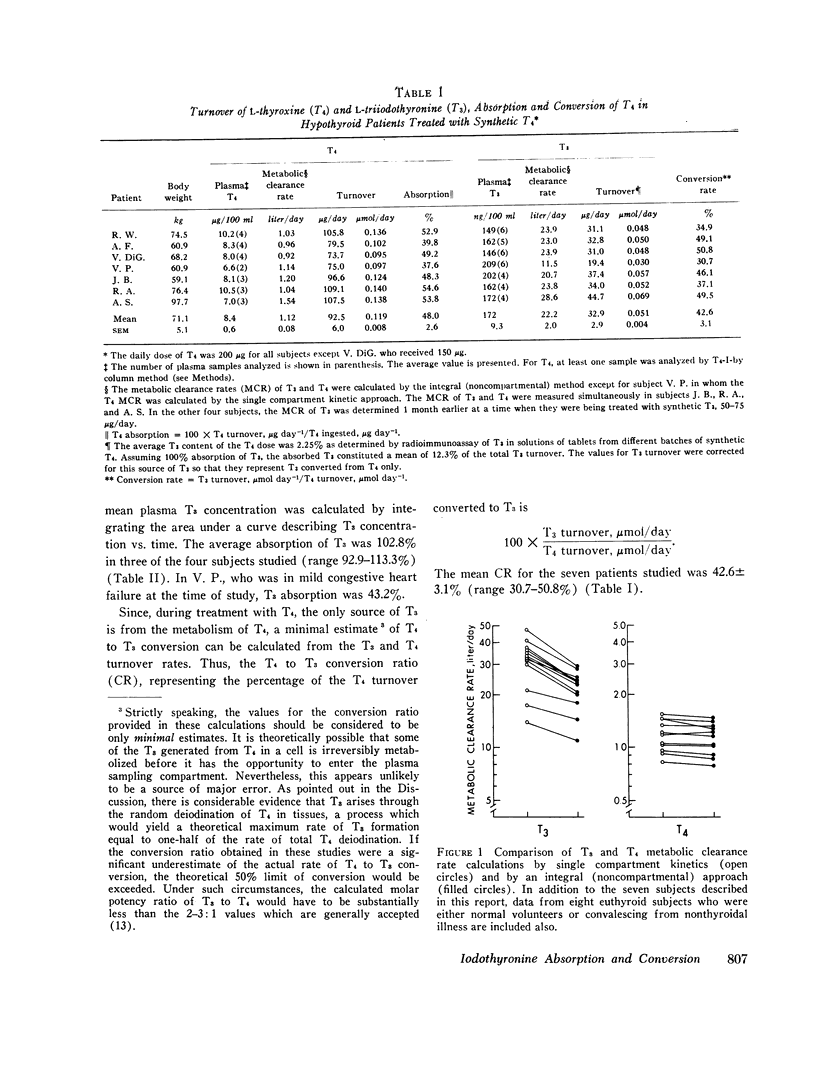
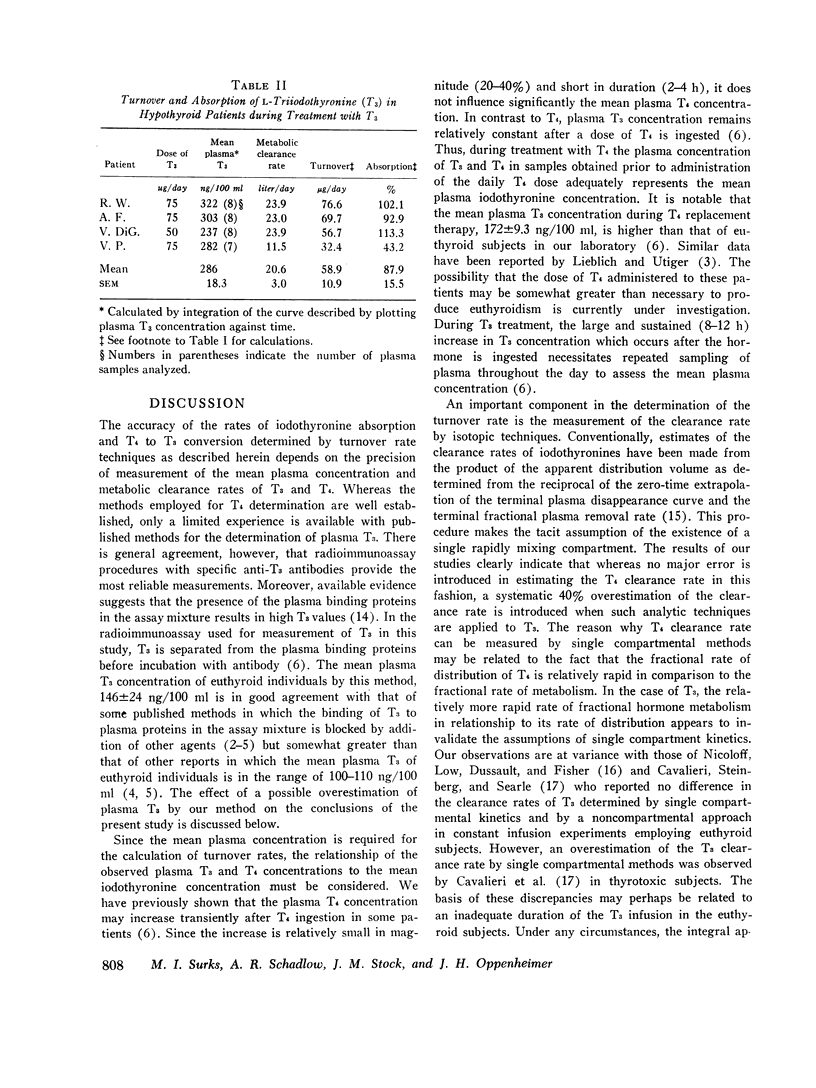
The absorption of L-thyroxine (T4) and L-triiodothyronine (T3) and the fractional rate of conversion of T4 to T3 were determined from the turnover rates of T4 and T3 in seven patients without endogenous thyroid function during separate treatment periods with these iodothyronines. Serum T3 concentration was measured by a radioimmunoassay procedure in which the iodothyronines are separated from the plasma proteins before incubation with anti-T3 antibody. Metabolic clearance rates were calculated by an integral (noncompartmental) approach since the use of single compartment kinetics led to a 40% overestimation of the metabolic clearance rate of T3. Based on the amount of hormone ingested and the observed hormonal turnover rates, the absorption of T4 and T3 (iodothyronine turnover/iodothyronine ingested) in man could be estimated. Absorption of T3 was complete in three subjects but decreased to 43% in a fourth who was suffering from mild congestive heart failure. Mean T4 absorption was 48.0±2.6% (SEM) for seven subjects. The mean fractional rate of T4 to T3 conversion determined during T4 replacement therapy (T3 turnover/T4 turnover) was 42.6% (range 30.7-50.8%). Thus, approximately one-half of the T4 which was deiodinated was converted to T3 suggesting that monodeiodination is an obligatory step in the peripheral metabolism of T4. Calculations based on these results together with other available data suggest that under normal physiologic circumstances the major portion of the T3 pool is derived from monodeiodination of T4.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S. Quantitative aspects of iodine metabolism: the exchangeable organic iodine pool, and the rates of thyroidal secretion, peripheral degradation and fecal excretion, of endogenously synthesized organically bound iodine. J Clin Invest. 1954 Nov;33(11):1533–1552. doi: 10.1172/JCI103032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACKBURN C. M., McCONAHEY W. M., KEATING F. R., Jr, ALBERT A. Calorigenic effects of single intravenous doses of L-triiodothyronine and L-thyroxine in myxedematous persons. J Clin Invest. 1954 Jun;33(6):819–824. doi: 10.1172/JCI102953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOMSTEDT B., PLANTIN L. O. THE EXTRATHYROIDAL DISTRIBUTION OF 131-I THYROXINE. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1965 Apr;48:536–546. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0480536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman L. E., Ingbar S. H., Sterling K. Conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3) in athyreotic human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):855–864. doi: 10.1172/JCI106304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri R. R., Steinberg M., Searle G. L. Metabolic clearance rate of L-triiodothyronine in man: a comparison of results by single-injection and constant infusion methods. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Oct;33(4):624–629. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-4-624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNN J. T., STANBURY J. B. The metabolism of 3:3':5'-triiodothyronine in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1958 Jul;18(7):713–720. doi: 10.1210/jcem-18-7-713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., PITT-RIVERS R. 3:5:3'-triiodothyronine. 2. Physiological activity. Biochem J. 1953 Mar;53(4):652–657. doi: 10.1042/bj0530652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharib H., Mayberry W. E., Ryan R. J. Radioimmunoassay for triiodothyronine: A preliminary report. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Dec;31(6):709–712. doi: 10.1210/jcem-31-6-709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharib H., Ryan R. J., Mayberry W. E., Hockert T. Radioimmunoassay for triiodothyronine (T 3 ): I. Affinity and specificity of the antibody for T 3 . J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Sep;33(3):509–516. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-3-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer M. A., Grimm Y., Studer H. Qualitative changes in the secretion of thyroid hormones induced by iodine deficiency. Endocrinology. 1968 Dec;83(6):1193–1198. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-6-1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays M. T. Absorption of oral thyroxine in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Jun;28(6):749–756. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-6-749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays M. T. Absorption of triiodothyronine in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 May;30(5):675–676. doi: 10.1210/jcem-30-5-675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., FREINKEL N. Simultaneous estimation of rates of thyroxine degradation and thyroid hormone synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jun;34(6):808–819. doi: 10.1172/JCI103136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. R. Direct immunoassay of triiodothyronine in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):1939–1949. doi: 10.1172/JCI107000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieblich J., Utiger R. D. Triiodothyronine radioimmunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):157–166. doi: 10.1172/JCI106786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY B. E., PATTEE C. J. DETERMINATION OF THYROXINE UTILIZING THE PROPERTY OF PROTEIN-BINDING. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Feb;24:187–196. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuma T., Nihei N., Gershengorn M. C., Hollander C. S. Serum triiodothyronine: measurements in human serum by radioimmunoassay with corroboration by gas-liquid chromatography. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2679–2688. doi: 10.1172/JCI106769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagataki S., Uchimura H., Masuyama Y., Nakao K., Ito K. Triiodothyronine and thyroxine in thyroid glands of euthyroid Japanese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jul;35(1):18–23. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-1-18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoloff J. T., Low J. C., Dussault J. H., Fisher D. A. Simultaneous measurement of thyroxine and triiodothyronine peripheral turnover kinetics in man. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):473–483. doi: 10.1172/JCI106835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ODDIE T. H., FISHER D. A., ROGERS C. WHOLE-BODY COUNTING OF I-131-LABELED THYROXINE. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Jul;24:628–637. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-7-628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oddie T. H., Fisher D. A., Epperson D. Effect of exogenous thyroxine on thyroid accumulation and secretion in euthyroid subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Sep;25(9):1196–1206. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-9-1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell W. D., Wilber J. F., Utiger R. D. Studies of thyrotropin physiology by means of radioimmunoassay. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1967;23:47–85. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9826-2.50005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Koerner D., Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I. Specific nuclear triiodothyronine binding sites in rat liver and kidney. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Aug;35(2):330–333. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-2-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Shapiro H. C., Bernstein G., Surks M. I. Differences in primary cellular factors influencing the metabolism and distribution of 3,5,3'-L-triiodothyronine and L-thyroxine. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):1016–1024. doi: 10.1172/JCI106301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I. Propylthiouracil inhibits the conversion of L-thyroxine to L-triiodothyronine. An explanation of the antithyroxine effect of propylthiouracil and evidence supporting the concept that triiodothyronine is the active thyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2493–2497. doi: 10.1172/JCI107063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PILEGGI V. J., LEE N. D., GOLUB O. J., HENRY R. J. Determination of iodine compounds in serum. I. Serum thyroxine in the presence of some iodine contaminants. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1961 Oct;21:1272–1279. doi: 10.1210/jcem-21-10-1272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman C. S., Chambers J. B., Jr, Read V. H. The extrathyroidal conversion rate of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1187–1196. doi: 10.1172/JCI106596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERLING K., CHODOS R. B. Radiothyroxine turnover studies in myxedema, thyrotoxicosis, and hypermetabolism without endocrine disease. J Clin Invest. 1956 Jul;35(7):806–813. doi: 10.1172/JCI103333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schadlow A. R., Surks M. I., Schwartz H. L., Oppenheimer J. H. Specific triiodothyronine binding sites in the anterior pituitary of the rat. Science. 1972 Jun 16;176(4040):1252–1254. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4040.1252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. Quantitation of extrathyroidal conversion of L-thyroxine to 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1124–1130. doi: 10.1172/JCI106584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Brenner M. A., Newman E. S. Conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in normal human subjects. Science. 1970 Sep 11;169(3950):1099–1100. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3950.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. Metabolism of phenolic- and tyrosyl-ring labeled L-thyroxine in human beings and rats. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Oct;33(4):612–618. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-4-612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Schadlow A. R., Oppenheimer J. H. A new radioimmunoassay for plasma L-triiodothyronine: measurements in thyroid disease and in patients maintained on hormonal replacement. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3104–3113. doi: 10.1172/JCI107137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAIT J. F. REVIEW: THE USE OF ISOTOPIC STEROIDS FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF PRODUCTION RATES IN VIVO. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1963 Dec;23:1285–1297. doi: 10.1210/jcem-23-12-1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


