Abstract
It has been suggested that prostaglandins may be involved in the control of sodium homeostasis. Prostaglandin A and prostaglandin E have been shown to increase renal blood flow and urinary sodium excretion and prostaglandin A has been shown to stimulate aldosterone release. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of chronic sodium loading and sodium restriction on plasma prostaglandin A, E, and F concentrations.
Seven normal human volunteers were placed on three sodium intake diets: (a) ad lib. sodium intake, (b) high sodium intake, and (c) low sodium intake. Plasma prostaglandin A, E, and F concentrations were measured by radioimmunoassay.
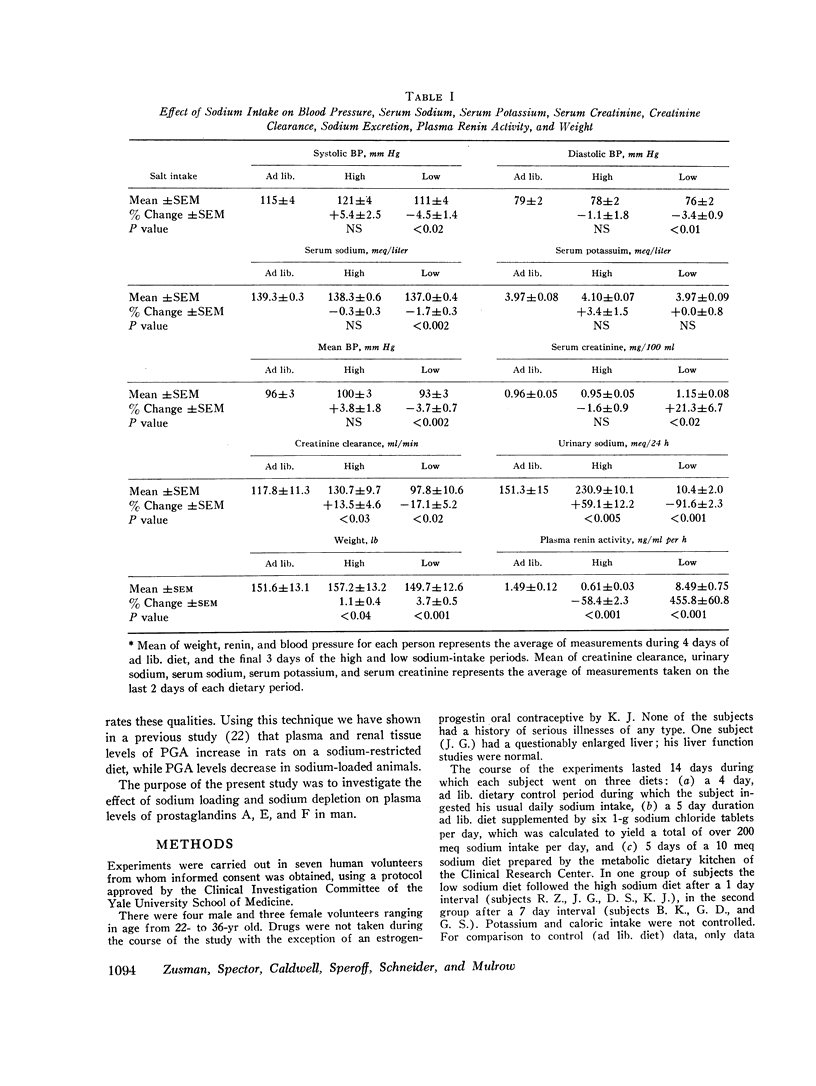
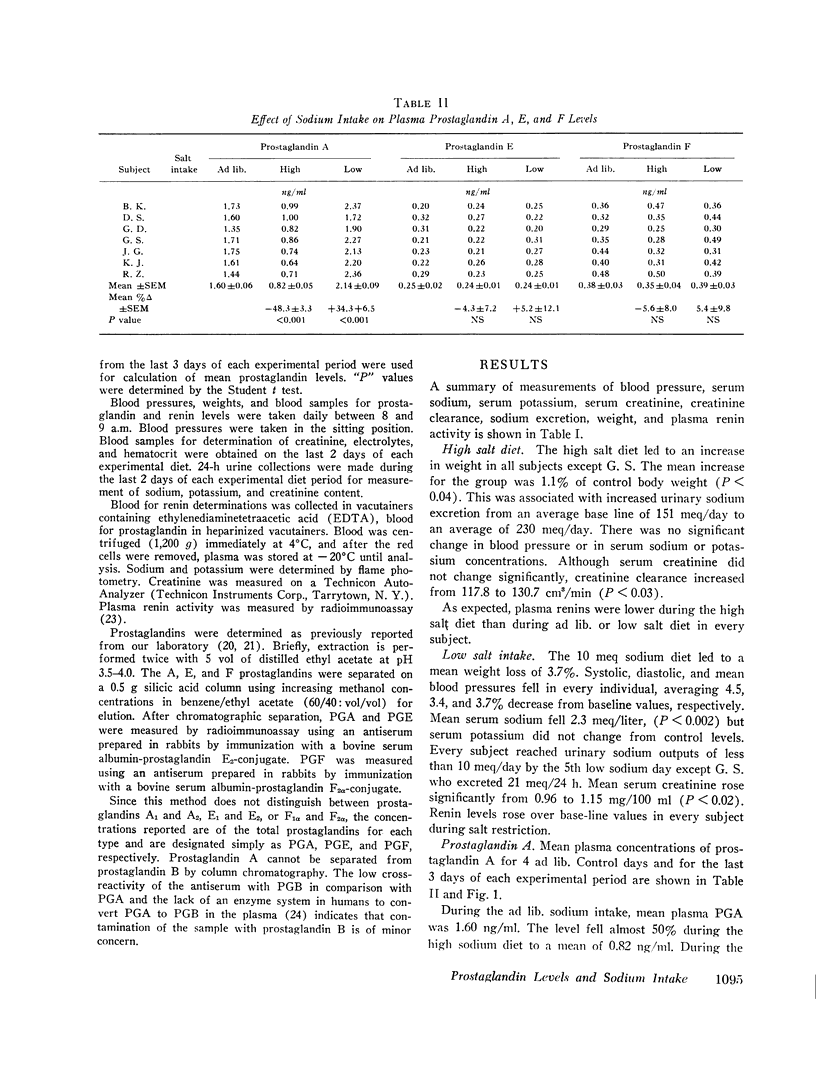
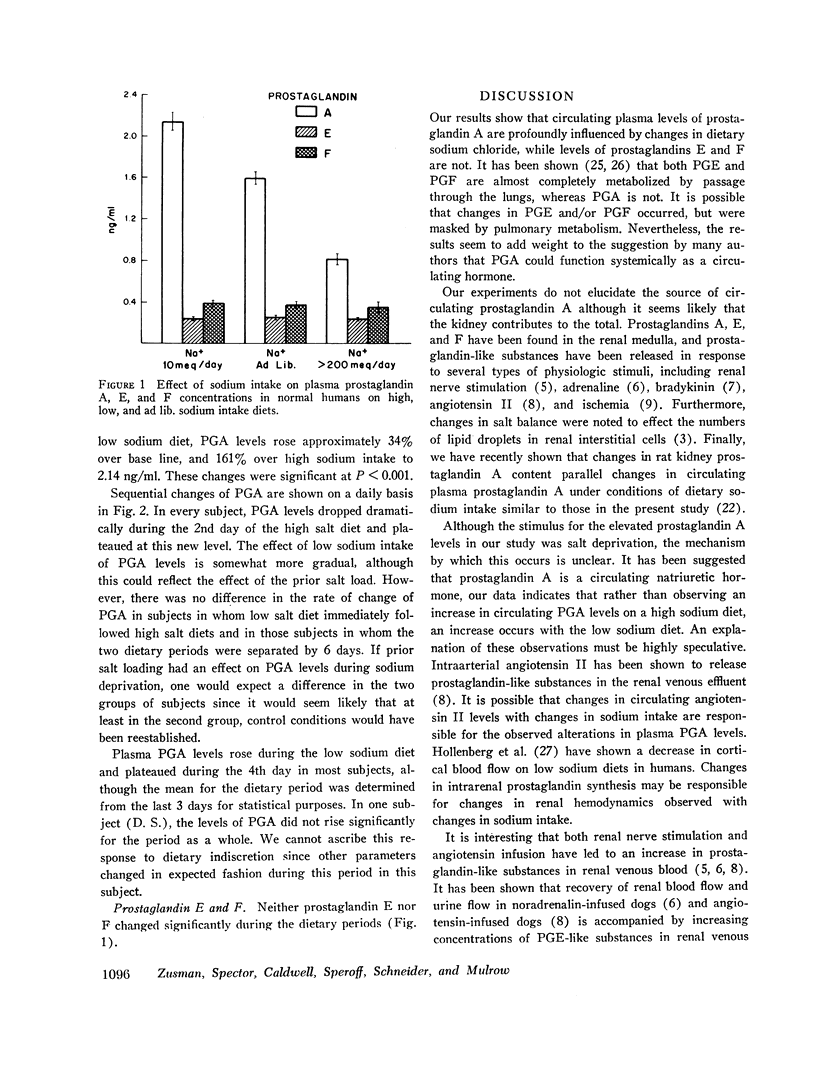
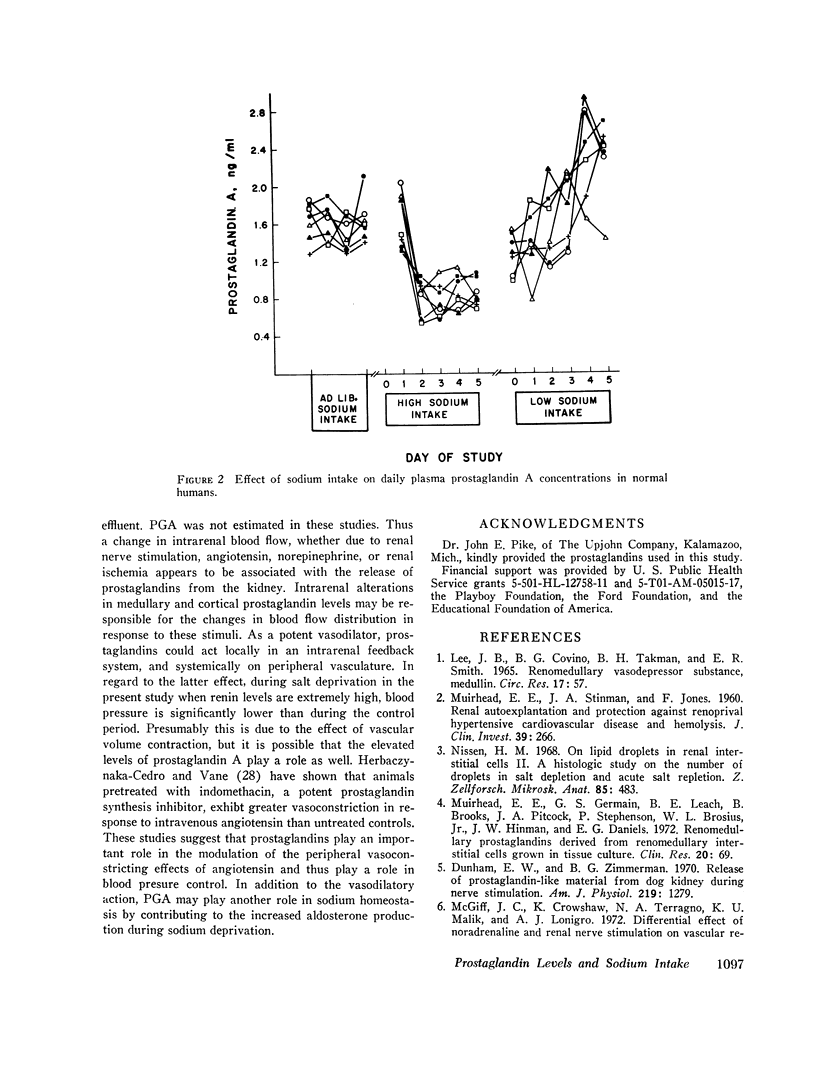
Mean prostaglandin A levels on the ad lib. diet were 1.60 ng/ml. Prostaglandin A levels decreased 49% to 0.82 ng/ml on the high sodium intake and increased 34% to 2.14 ng/ml on the low sodium intake. Prostaglandin A levels increased 161% on the low sodium diet in comparison with levels on the high sodium diet. Plasma prostaglandin E and F concentrations did not change significantly during variation in sodium intake.
These results show that dietary sodium content markedly effects plasma prostaglandin A levels and that prostaglandins may play a role in the physiologic mechanism of sodium homeostasis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caldwell B. V., Burstein S., Brock W. A., Speroff L. Radioimmunoassay of the F prostaglandins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Aug;33(2):171–175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr A. A. Hemodynamic and renal effects of a prostaglandin, PGA 1, in subjects with essential hypertension. Am J Med Sci. 1970 Jan;259(1):21–26. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197001000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrière S., Friborg J., Guay J. P. Vasodilators, intrarenal blood flow, and natriuresis in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jul;221(1):92–98. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.1.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham E. W., Zimmerman B. G. Release of prostaglandin-like material from dog kidney during nerve stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1970 Nov;219(5):1279–1285. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.5.1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichman M. P., Littenburg G., Brooker G., Horton R. Effect of prostaglandin A 1 on renal and adrenal function in man. Circ Res. 1972 Sep;31(9 Suppl):19–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E., Koerner T., Page L. B., Kliman B., Purnode A. Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Oct;29(10):1349–1355. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-10-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg N. K., Epstein M., Guttmann R. D., Conroy M., Basch R. I., Merrill J. P. Effect of sodium balance on intrarenal distribution of blood flow in normal man. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Mar;28(3):312–317. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.28.3.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton E. W., Jones R. L. Prostaglandins A1,A2 and 19-hydroxy A1; their actions on smooth muscle and their inactivation on passage through the pulmonary and hepatic portal vascular beds. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Nov;37(3):705–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb08509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston H. H., Herzog J. P., Lauler D. P. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on renal hemodynamics, sodium and water excretion. Am J Physiol. 1967 Oct;213(4):939–946. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.4.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karatzas N. B., Noble M. I., Saunders K. B., McIlroy M. B. Transmission of the blood flow pulse through the pulmonary arterial tree of the dog. Circ Res. 1970 Jul;27(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.27.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karatzas N. B., Noble M. I., Saunders K. B., McIlroy M. B. Transmission of the blood flow pulse through the pulmonary arterial tree of the dog. Circ Res. 1970 Jul;27(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.27.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE J. B., COVINO B. G., TAKMAN B. H., SMITH E. R. RENOMEDULLARY VASODEPRESSOR SUBSTANCE, MEDULLIN: ISOLATION, CHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION AND PHYSIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES. Circ Res. 1965 Jul;17:57–77. doi: 10.1161/01.res.17.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. J., Johnson J. G., Smith C. J., Hatch F. E. Renal effects of prostaglandin A1 in patients with essential hypertension. Kidney Int. 1972 Apr;1(4):254–262. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonigro A. J., Terragno N. A., Malik K. U., McGiff J. C. A prostaglandin may mediate the renal vasodilator action of bradykinin. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Dec;78(6):1016–1017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIRHEAD E. E., STIRMAN J. A., JONES F. Renal autoexplantation and protection against renoprival hypertensive cardiovascular disease and hemolysis. J Clin Invest. 1960 Feb;39:266–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI104037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Maldonado M., Tsaparas N., Eknoyan G., Suki W. N. Renal actions of prostaglandins: comparison with acetylcholine and volume expansion. Am J Physiol. 1972 May;222(5):1147–1152. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.5.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Crowshaw K., Terragno N. A., Lonigro A. J., Strand J. C., Williaon M. A., Lee J. B., Ng K. K. Prostaglandin-like substances appearing in canine renal venous blood during renal ischemia. Their patial characterization by pharmacologic and chromatographic procedures. Circ Res. 1970 Nov;27(5):765–782. doi: 10.1161/01.res.27.5.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Terragno N. A., Strand J. C., Lee J. B., Lonigro A. J., Ng K. K. Selective passage of prostaglandins across the lung. Nature. 1969 Aug 16;223(5207):742–745. doi: 10.1038/223742b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen H. M. On lipid droplets in renal interstitial cells. II. A histological study on the number of droplets in salt depletion and acute salt repletion. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;85(4):483–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polet H., Levine L. Serum prostaglandin A isomerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Dec 3;45(5):1169–1176. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Direct effects of prostaglandin on renal function and renin release in anesthetized dog. Am J Physiol. 1968 Feb;214(2):218–221. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman R. M., Caldwell B. V., Speroff L., Behrman H. R. Radioimmunoassay of the A prostaglandins. Prostaglandins. 1972 Jul;2(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(72)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


