Abstract
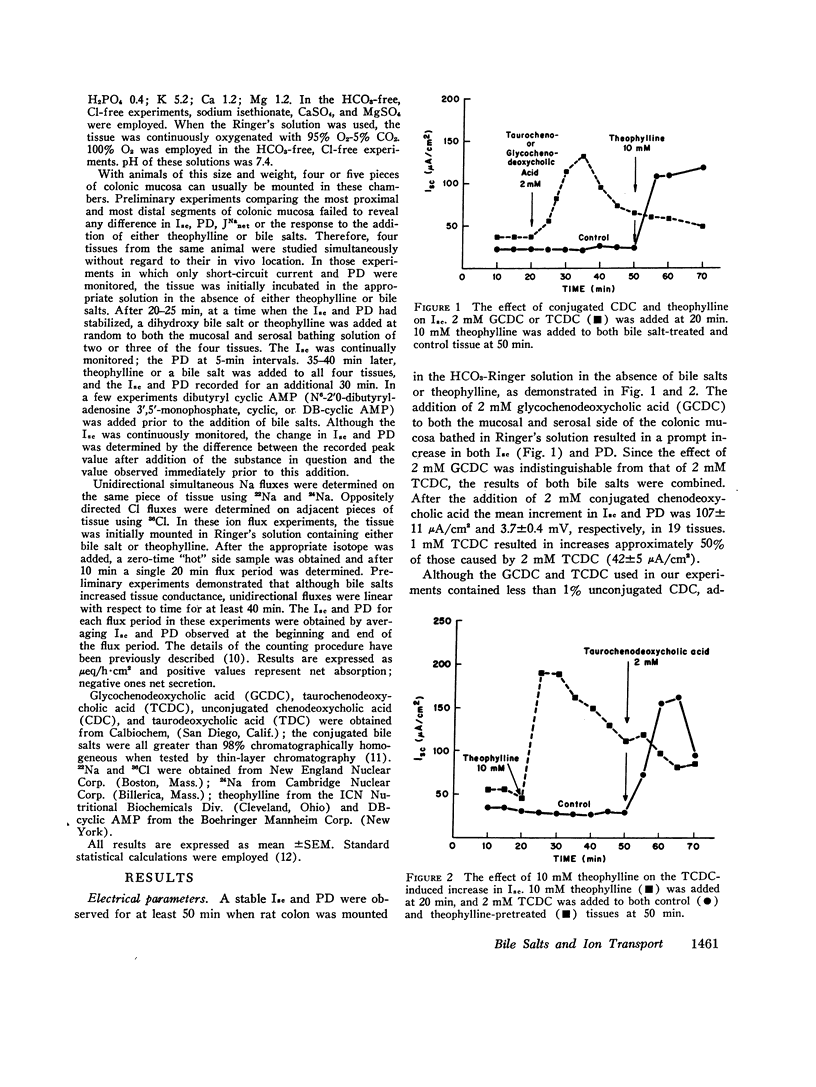
The mechanism by which excess quantities of bile salts in the colon produce diarrhea is not known. Therefore, experiments were performed in which the effect of conjugated dihydroxy bile salts on ion transport was evaluated in the in vitro short-circuited rat colon. 2 mM glycochenodeoxycholic acid (GCDC), taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDC), or taurodeoxycholic acid caused a prompt increase in short-circuit current (Isc) and electrical potential difference (PD). Similar results were obtained when theophylline was added. Removal of HCO2 and C1 prevented the effects of both bile salts and theophylline. Pretreatment with theophylline blocked the increase in Isc and PD produced by TCDC and pretreatment with either TCDC or GCDC inhibited the expected theophylline response. Na fluxes in the presence of both TCDC and theophylline demonstrated a decrease in net absorption; and TCDC decreased net C1 absorption and theophylline caused a reversal of net C1 absorption to net C1 secretion. It is proposed that the diarrhea associated with cholerheic enteropathy is produced by active anion secretion possibly mediated by cyclic AMP.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Field M: Intestinal secretion: effect of cyclic AMP and its role in cholera. N Engl J Med. 1971 May 20;284(20):1137–1144. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197105202842008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Fromm D., McColl I. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. I. Na and Cl fluxes and short-circuit current. Am J Physiol. 1971 May;220(5):1388–1396. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.5.1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Fromm D., al-Awqati Q., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effect of cholera enterotoxin on ion transport across isolated ileal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):796–804. doi: 10.1172/JCI106874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. II. Effects of cyclic 3', 5'-AMP. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):992–997. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Plotkin G. R., Silen W. Effects of vasopressin, theophylline and cyclic adenosine monophosphate on short-circuit current across isolated rabbit ileal mucosa. Nature. 1968 Feb 3;217(5127):469–471. doi: 10.1038/217469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forth W., Rummel W., Glasner H. Zur resorptionshemmenden Wirkung von Gallensäuren. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol Exp Pathol. 1966;254(4):364–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Schultz S. G. Effect of bile salts on transport across brush border of rabbit ileum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 15;211(3):589–592. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H., Hofmann A. F. Breath test for altered bile-acid metabolism. Lancet. 1971 Sep 18;2(7725):621–625. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)80068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix T. R., Bayless T. M. Digestion: intestinal secretion. Annu Rev Physiol. 1970;32:139–164. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.32.030170.001035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepner G. W., Hofmann A. F., Thomas P. J. Metabolism of steroid and amino acid moieties of conjugated bile acids in man. I. Cholylglycine. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1889–1897. doi: 10.1172/JCI106991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepner G. W., Hofmann A. F., Thomas P. J. Metabolism of steroid and amino acid moieties of conjugated bile acids in man. II. Glycine-conjugated dihydroxy bile acids. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1898–1905. doi: 10.1172/JCI106992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Poley J. R. Cholestyramine treatment of diarrhea associated with ileal resection. N Engl J Med. 1969 Aug 21;281(8):397–402. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196908212810801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Poley J. R. Role of bile acid malabsorption in pathogenesis of diarrhea and steatorrhea in patients with ileal resection. I. Response to cholestyramine or replacement of dietary long chain triglyceride by medium chain triglyceride. Gastroenterology. 1972 May;62(5):918–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F. The syndrome of ileal disease and the broken enterohepatic circulation: cholerheic enteropathy. Gastroenterology. 1967 Apr;52(4):752–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekhjian H. S., Phillips S. F. Perfusion of the canine colon with unconjugated bile acids. Effect on water and electrolyte transport, morphology, and bile acid absorption. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jul;59(1):120–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekjian H. S., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Colonic secretion of water and electrolytes induced by bile acids: perfusion studies in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1569–1577. doi: 10.1172/JCI106644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oye I., Sutherland E. W. The effect of epinephrine and other agents on adenyl cyclase in the cell membrane of avian erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 31;127(2):347–354. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90389-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson D. K., Ebel H., DiBona D. R., Sharp G. W. Localization of the action of cholera toxin on adenyl cyclase in mucosal epithelial cells of rabbit intestine. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2292–2298. doi: 10.1172/JCI107039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins J. P., Moore M. M. Adenyl cyclase of rat cerebral cortex. Activation of sodium fluoride and detergents. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):62–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W., Binder H. J., Curran P. F. Electrolyte secretion by the guinea pig ileum in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1972 Sep;223(3):531–537. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.3.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., ZALUSKY R. ION TRANSPORT IN ISOLATED RABBIT ILEUM. I. SHORT-CIRCUIT CURRENT AND NA FLUXES. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Jan;47:567–584. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer D. E., Lust W. D., Sircar B., Goldberg N. D. Elevated concentration of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in intestinal mucosa after treatment with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):851–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Hynie S. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by cholera toxin. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):266–269. doi: 10.1038/229266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. H., Fromm H., Hofmann A. F. Acquired hyperoxaluria, nephrolithiasis, and intestinal disease. Description of a syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jun 29;286(26):1371–1375. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197206292862601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


