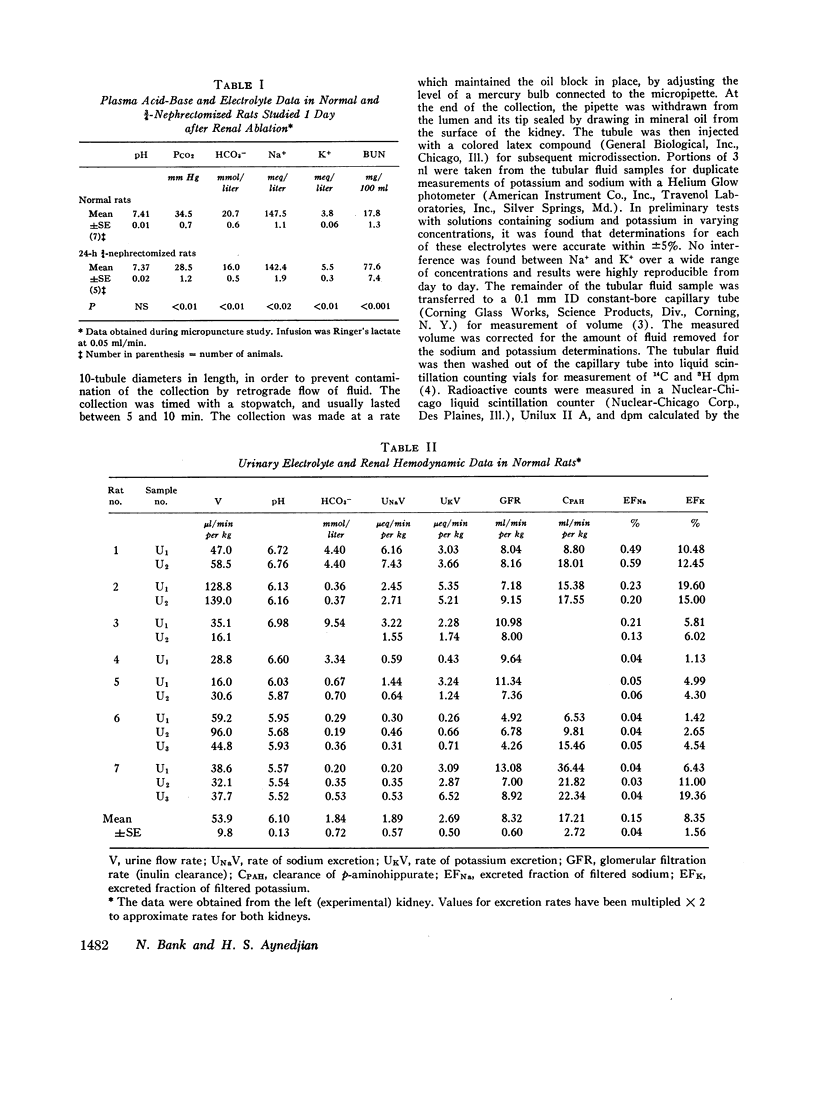
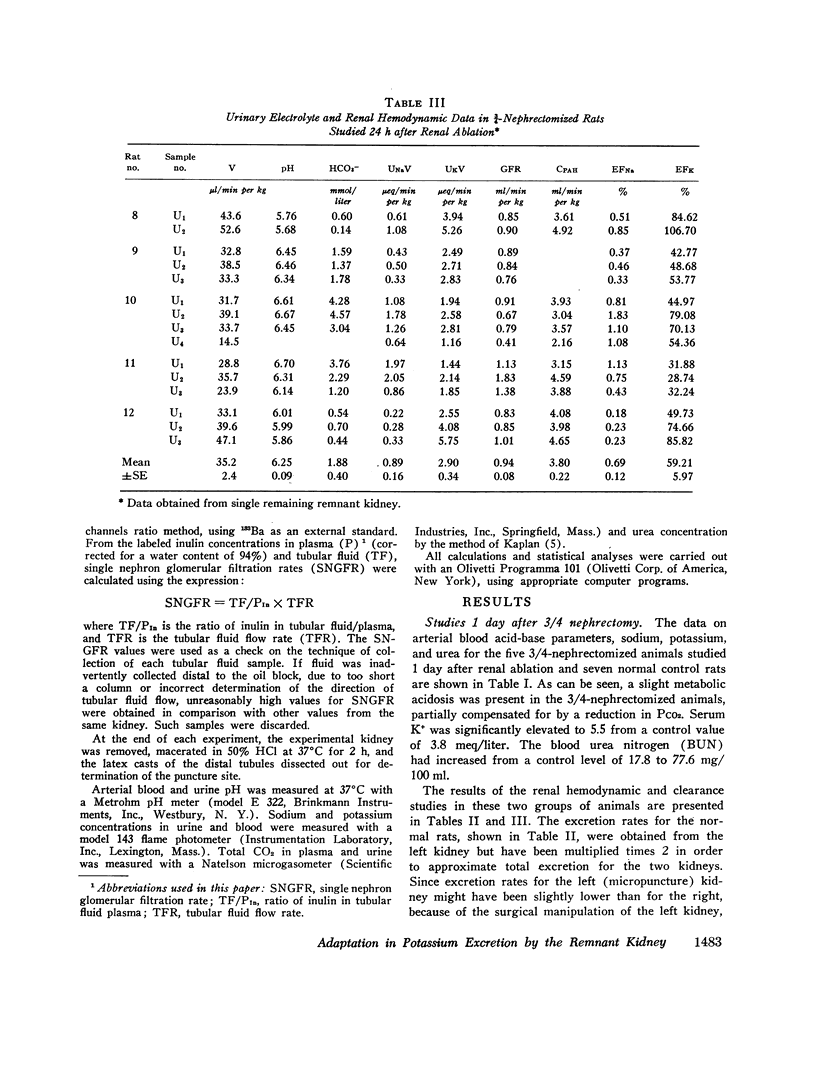
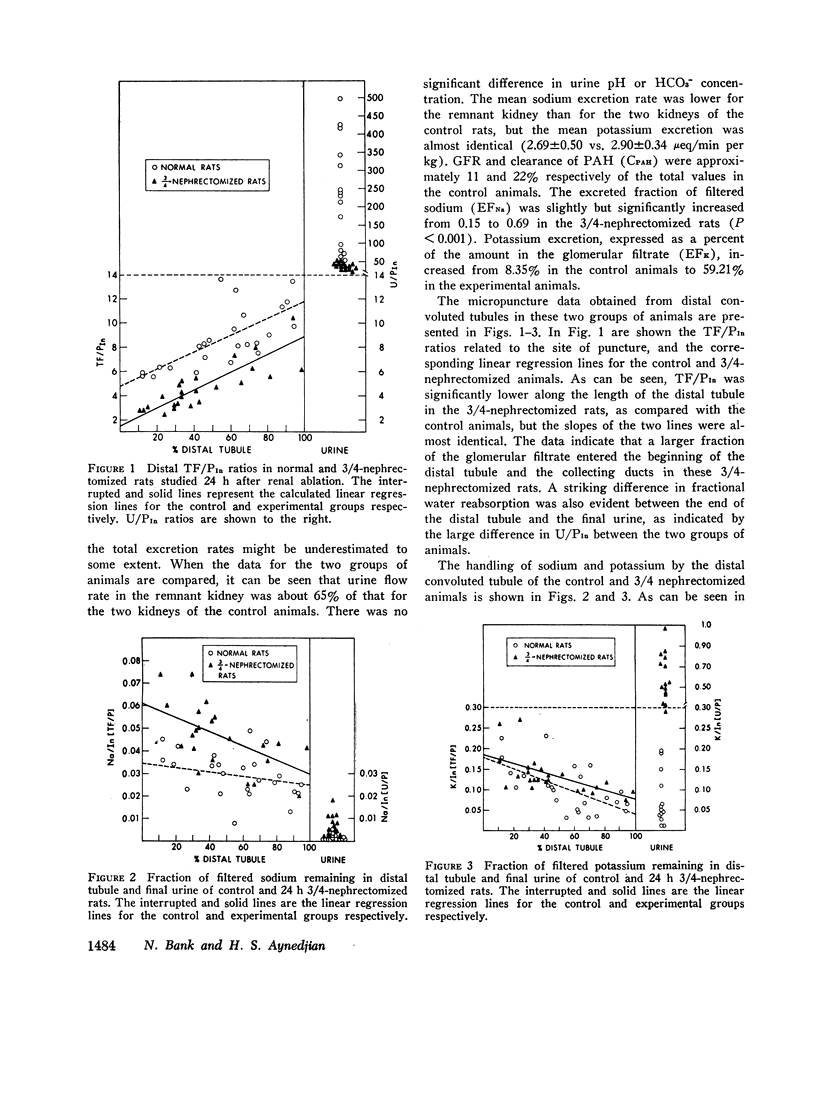
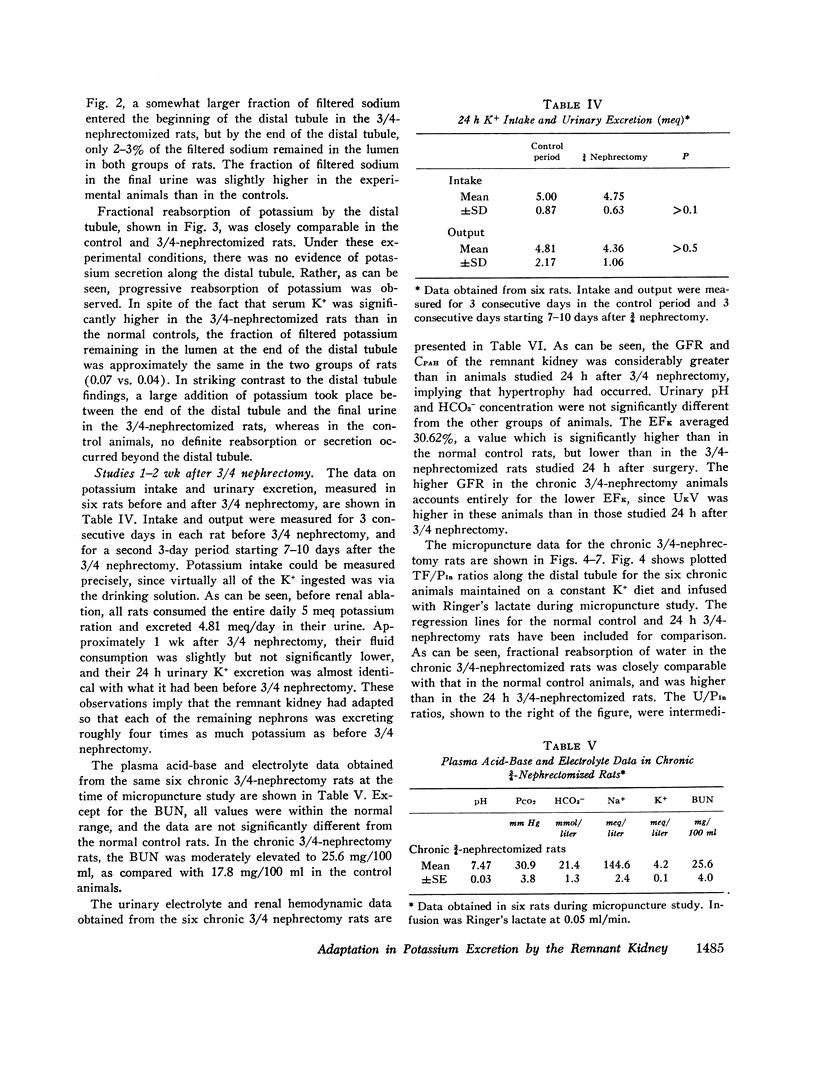
Abstract
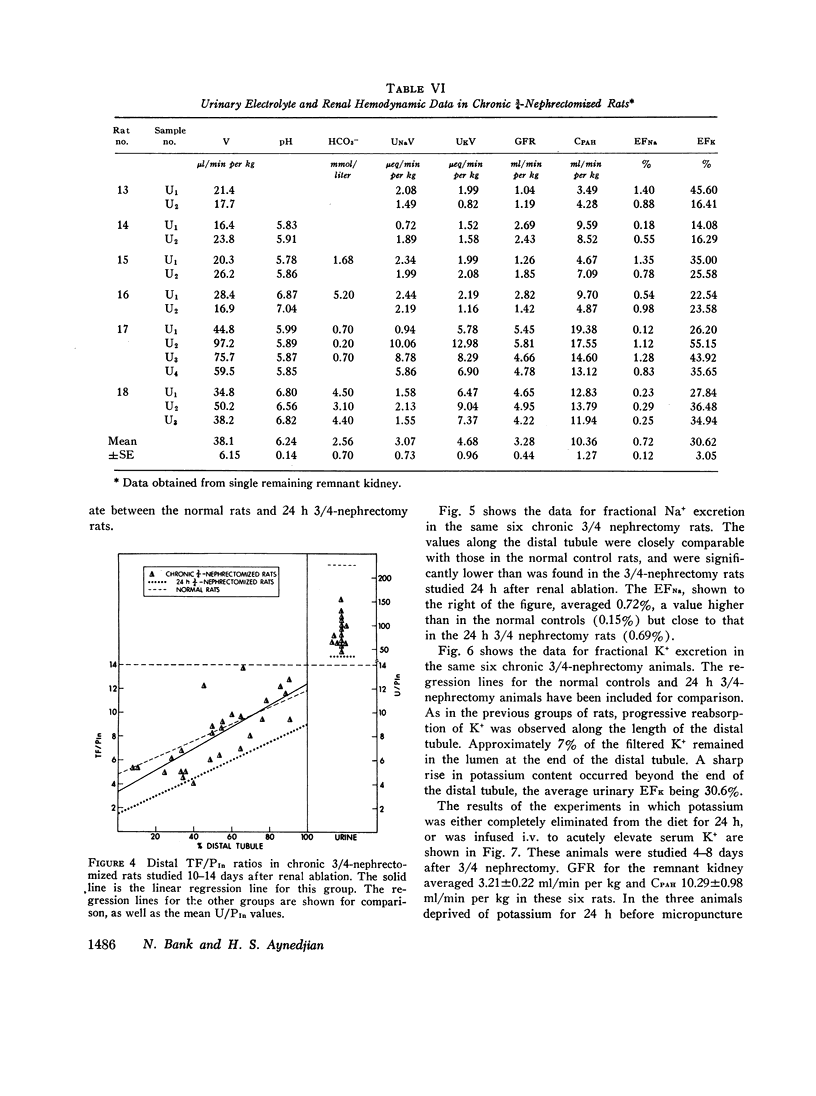
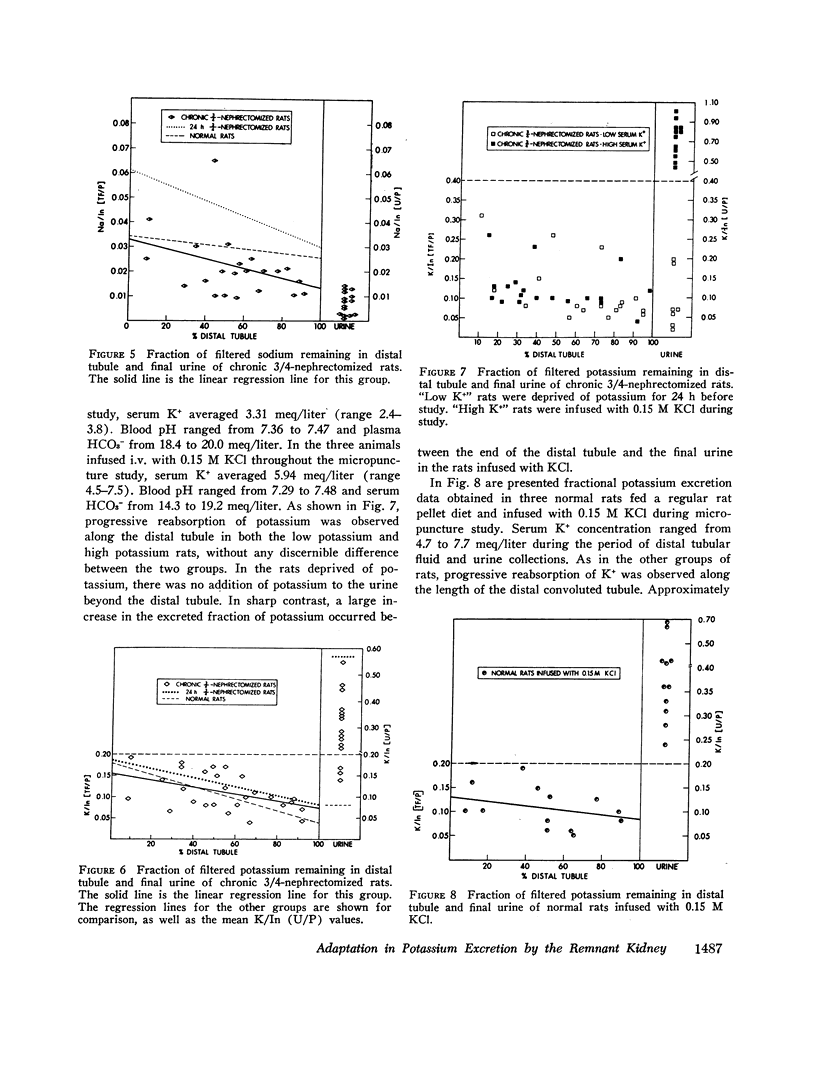
In order to study the mechanism of enhanced potassium excretion by the remaining nephrons of the remnant kidney, micropuncture and clearance experiments were carried out in rats after surgical ablation of 3/4 of the total renal mass. The potassium intake in all animals was approximately 5 meq/day. Animals were studied 24 h and 10-14 days after 3/4 nephrectomy. Balance measurements in the chronic animals before micropuncture study indicated that 24 h K+ excretion by the remnant kidney was equal to that of the two kidneys before ablation of renal mass. Measurements of distal tubular inulin and potassium concentrations revealed progressive reabsorption of potassium in this segment of the nephron in both the 24-h and chronic 3/4-nephrectomized rats, as well as in normal control rats. A large increase in tubular fluid potassium content occurred between the end of the distal tubule and the final urine in the 3/4-nephrectomized rats, but not in the normal controls. These observations suggest that the segment of the nephron responsible for enhanced potassium excretion by remaining nephrons was the collecting duct.
In additional experiments, potassium was completely eliminated from the diet of chronic 3/4-nephrectomized rats before micropuncture study. In these animals, no addition of K+ occurred beyond the distal tubules. Normal rats infused with 0.15 M KCl to acutely elevate serum K+ concentration, demonstrated reabsorption of K+ in the distal tubule and a large addition of K+ to the urine beyond the distal tubule.
We conclude that the collecting duct is the major site of regulation of urinary potassium excretion in normal rats and is responsible for the adaptation to nephron loss by the remnant kidney.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Grantham J. J., Kurg M. B., Obloff J. The nature of transtubular Na and K transport in isolated rabbit renal collecting tubules. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1815–1826. doi: 10.1172/JCI106399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIERHOLZER K. Secretion of potassium and acidification in collecting ducts of mammalian kidney. Am J Physiol. 1961 Aug;201:318–324. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.2.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALNIC G., KLOSE R. M., GIEBISCH G. MICROPUNCTURE STUDY OF RENAL POTASSIUM EXCRETION IN THE RAT. Am J Physiol. 1964 Apr;206:674–686. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.4.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., De Mello Aires M., Giebisch G. Potassium transport across renal distal tubules during acid-base disturbances. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):1192–1208. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., Klose R. M., Giebisch G. Micropuncture study of distal tubular potassium and sodium transport in rat nephron. Am J Physiol. 1966 Sep;211(3):529–547. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultze R. G., Taggart D. D., Shapiro H., Pennell J. P., Caglar S., Bricker N. S. On the adaptation in potassium excretion associated with nephron reduction in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1061–1068. doi: 10.1172/JCI106577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDHAGER E. E., GIEBISCH G. Micropuncture study of renal tubular transfer of sodium chloride in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1961 Mar;200:581–590. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.3.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright F. S., Strieder N., Fowler N. B., Giebisch G. Potassium secretion by distal tubule after potassium adaptation. Am J Physiol. 1971 Aug;221(2):437–448. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.2.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarger W. E., Aynedjian H. S., Bank N. A micropuncture study of postobstructive diuresis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):625–637. doi: 10.1172/JCI106852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


