Abstract
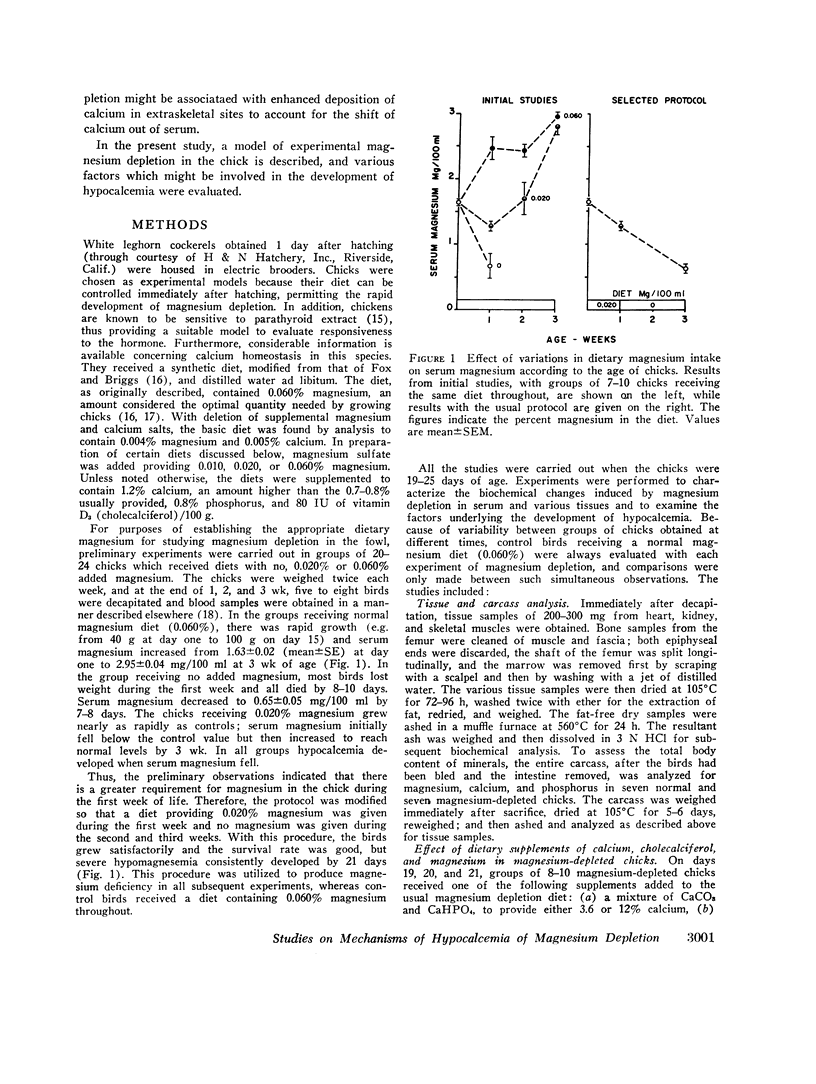
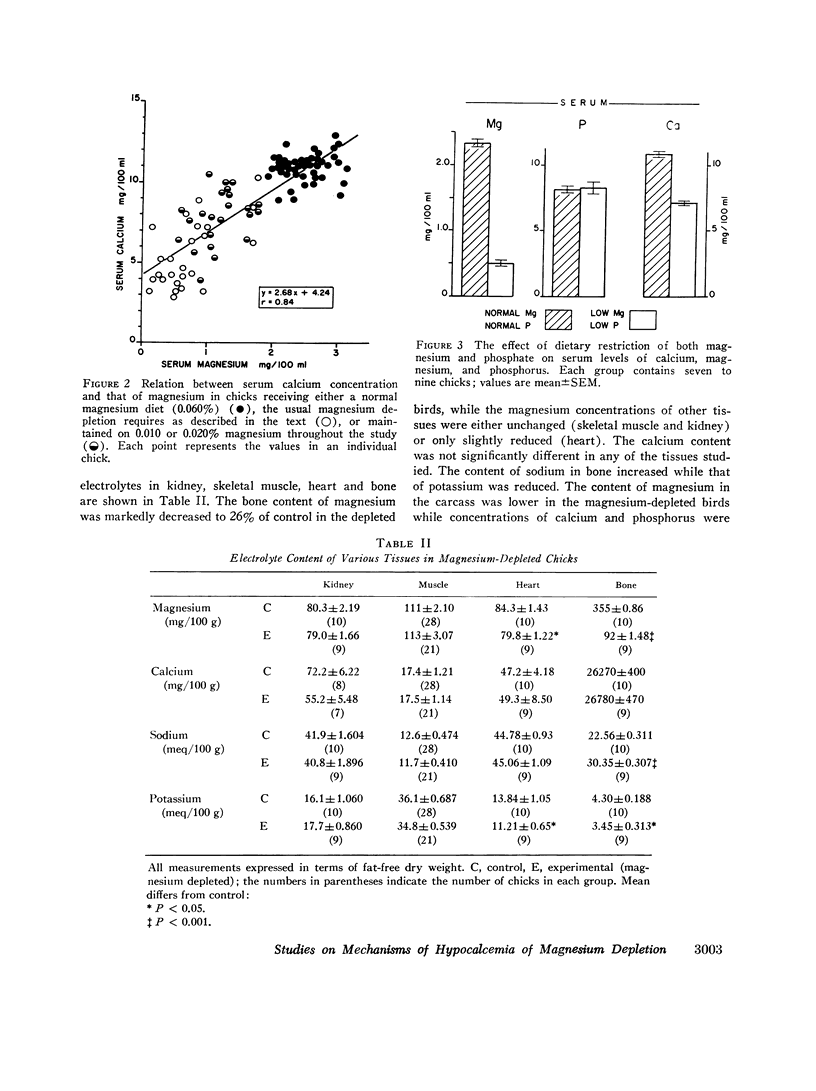
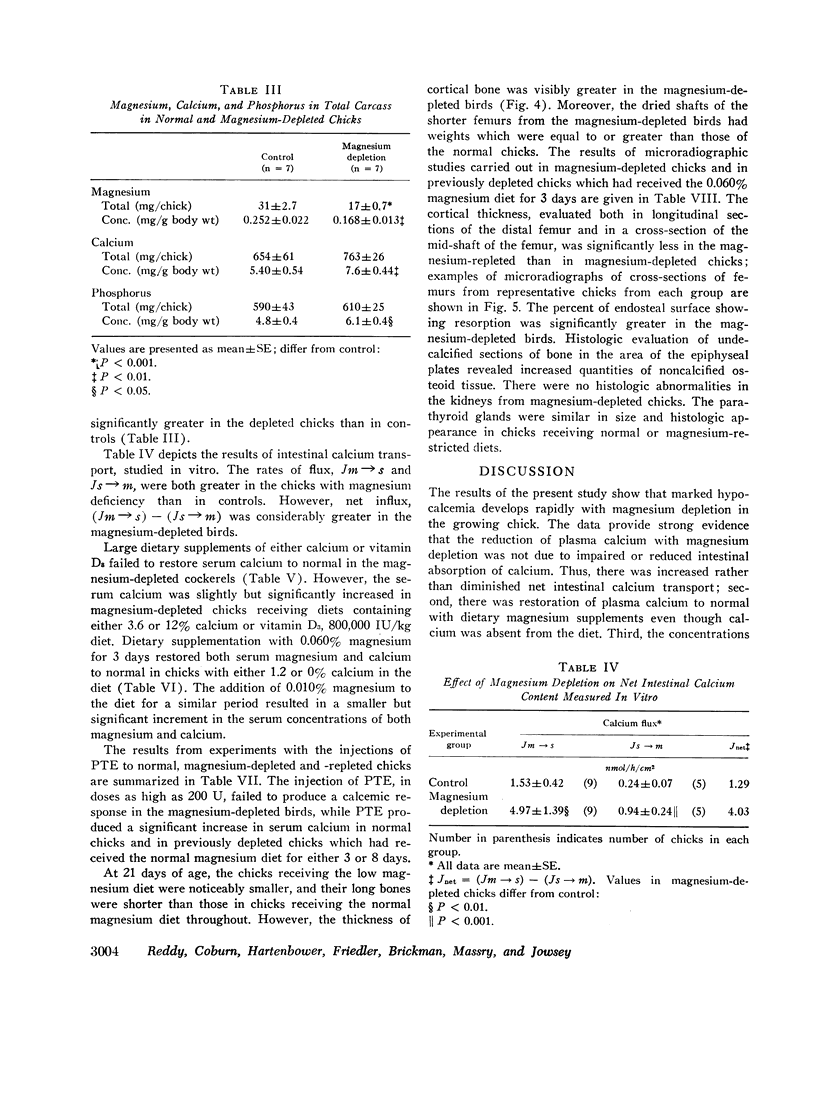
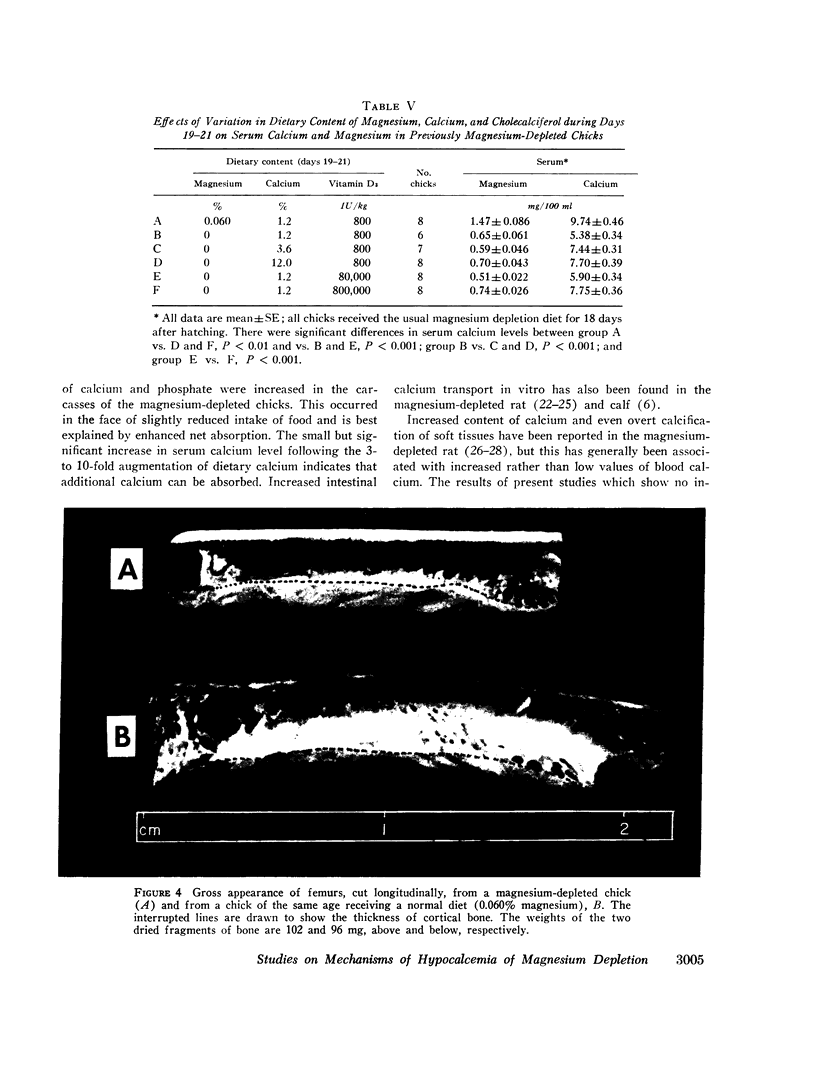
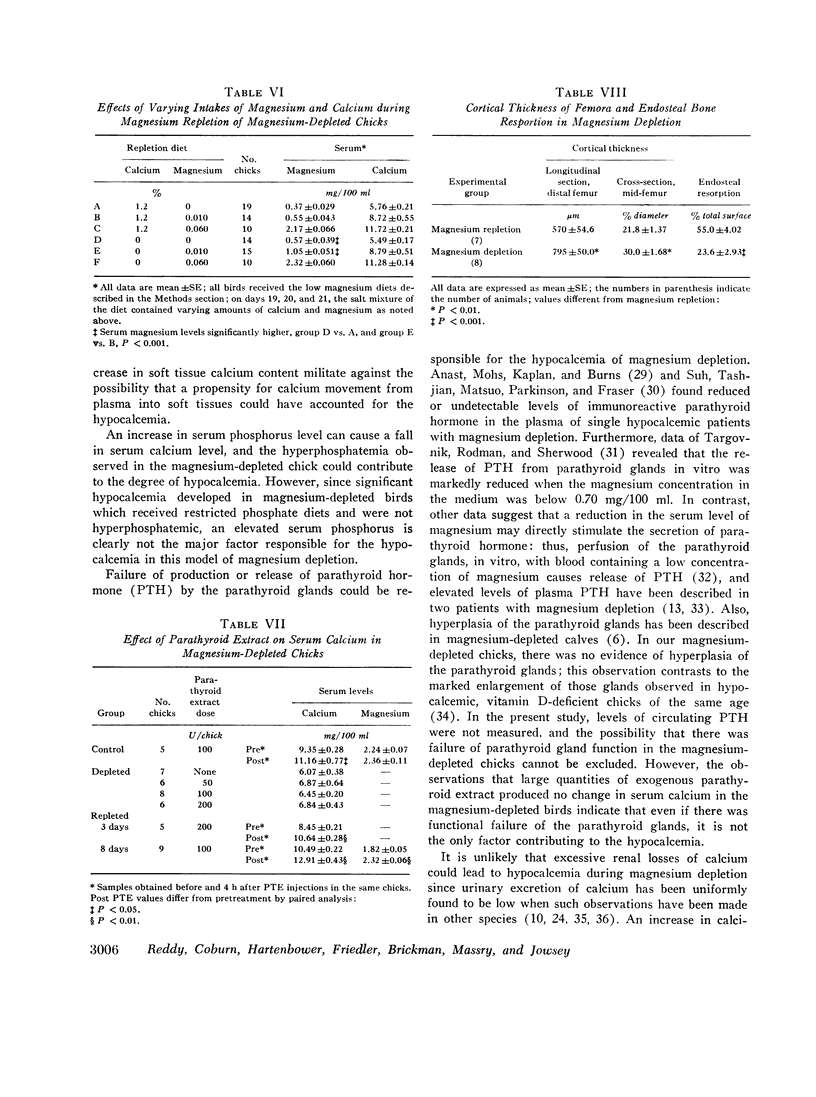
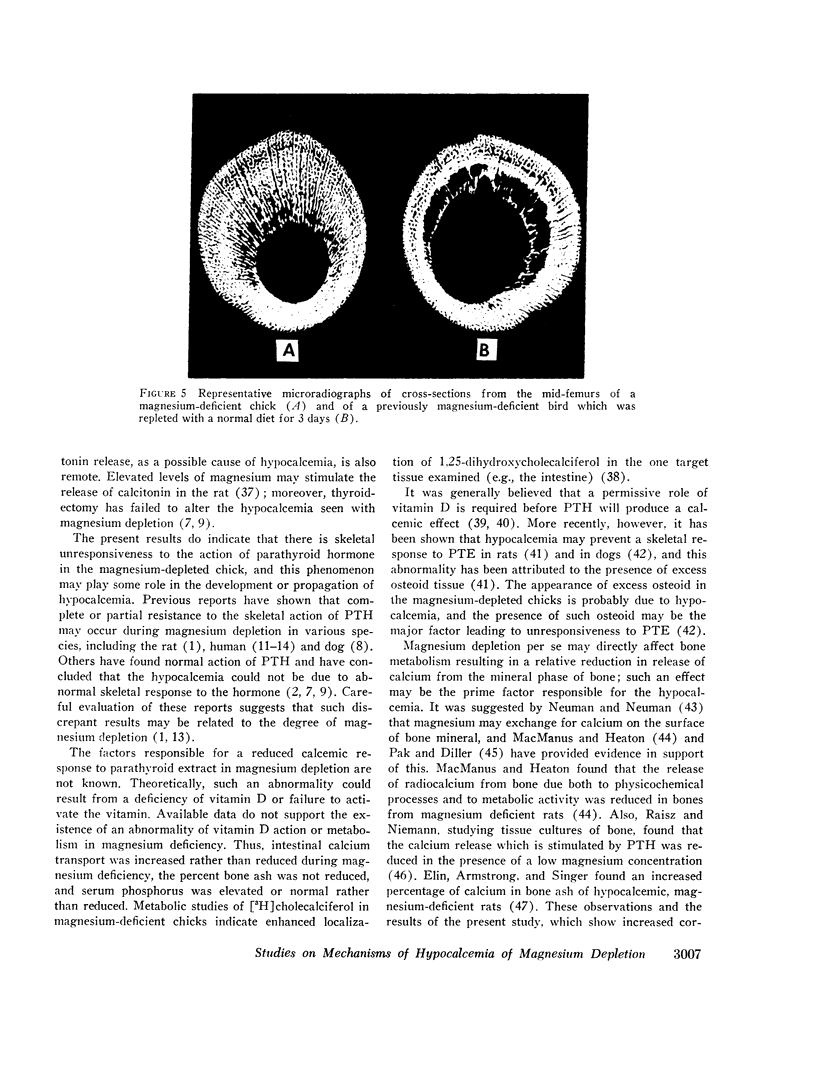
Studies were carried out to evaluate the mechanism of hypocalcemia in magnesium depletion. Day old chicks fed a magnesium deficient diet developed marked hypocalcemia, with a direct relation between serum calcium (y) and magnesium (x): y = 2.68 x + 4.24, r = 0.84 (both in mg/100 ml). Injections of parathyroid extract that increased serum calcium 2-3 mg/100 ml in normals had no effect in Mg-depleted birds. Very large dietary supplements of calcium or vitamin D3 increased mean serum calcium only from 5.3 to 7.7 and 7.8 mg/100 ml, respectively, while a normal magnesium diet for 3 days increased calcium from 5.3 to 9.9 mg/100 ml despite absence of dietary calcium. Intestinal calcium transport, studied in vitro, and the calcium concentration of the carcass was significantly increased in magnesium-depleted chicks, making it unlikely that reduced intestinal absorption of calcium caused the hypocalcemia. In magnesium-deficient chicks, the bone content of magnesium was decreased by 74%, the calcium content was unchanged, and the cortical thickness of bone was markedly increased. After 3 days of magnesium-repletion, cortical thickness was reduced with increased endosteal resorption. There was an increase in unmineralized osteoid tissue in the magnesium-depleted chicks. Parathyroid gland size and histology did not differ in magnesium-depleted and control birds. The results suggest that hypocalcemia develops due to altered equilibrium of calcium between extracellular fluid and bone, favoring increased net movement into the latter. Failure of parathyroid gland function could also exist, and unresponsiveness to parathyroid hormone (PTH) may also contribute to the hypocalcemia. However, failure of PTH action is probably due to the presence of excess osteoid tissue rather than a primary event leading to hypocalcemia.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALCOCK N., MACINTYRE I. Inter-relation of calcium and magnesium absorption. Clin Sci. 1962 Apr;22:185–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams T. H., Norman A. W. Studies on the mechanism of action of calciferol. I. Basic parameters of vitamin D-mediated calcium transport. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4421–4431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anast C. S., Mohs J. M., Kaplan S. L., Burns T. W. Evidence for parathyroid failure in magnesium deficiency. Science. 1972 Aug 18;177(4049):606–608. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4049.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Au W. Y., Raisz L. G. Restoration of parathyroid responsiveness in vitamin D-deficient rats by parenteral calcium or dietary lactose. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1572–1578. doi: 10.1172/JCI105648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckle R. M., Care A. D., Cooper C. W., Gitelman H. J. The influence of plasma magnesium concentration on parathyroid hormone secretion. J Endocrinol. 1968 Dec;42(4):529–534. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0420529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHUTKOW J. G. STUDIES ON THE METABOLISM OF MAGNESIUM IN THE MAGNESIUM-DEFICIENT RAT. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Jun;65:912–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coburn J. W., Massry S. G. Changes in serum and urinary calcium during phosphate depletion: studies on mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1073–1087. doi: 10.1172/JCI106323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor T. B., Toskes P., Mahaffey J., Martin L. G., Williams J. B., Walser M. Parathyroid function during chronic magnesium deficiency. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1972 Aug;131(2):100–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. J. Magnesium depletion in the rhesus monkey: induction of magnesium-dependent hypocalcaemia. Clin Sci. 1971 Oct;41(4):333–344. doi: 10.1042/cs0410333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Armstrong W. D., Singer L. Body fluid electrolyte composition of chronically magnesium-deficient and control rats. Am J Physiol. 1971 Feb;220(2):543–548. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.2.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estep H., Shaw W. A., Watlington C., Hobe R., Holland W., Tucker S. G. Hypocalcemia due to hypomagnesemia and reversible parathyroid hormone unresponsiveness. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Jun;29(6):842–848. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-6-842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX M. R., BRIGGS G. M. Salt mixtures for purified-type diets. III. An improved salt mixtures for chicks. J Nutr. 1960 Oct;72:243–250. doi: 10.1093/jn/72.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON H. C., HARRISON H. E., PARK E. A. Vitamin D and citrate metabolism; effect of vitamin D in rats fed diets adequate in both calcium and phosphorus. Am J Physiol. 1958 Feb;192(2):432–436. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.192.2.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATON F. W. THE PARATHYROID GLANDS AND MAGNESIUM METABOLISM IN THE RAT. Clin Sci. 1965 Jun;28:543–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn T. J., Chase L. R., Avioli L. V. Effect of magnesium depletion on responsiveness to parathyroid hormone in parathyroidectomized rats. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):886–891. doi: 10.1172/JCI106883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartenbower D. L., Coburn J. W. A model of renal insufficiency in the chick. Lab Anim Sci. 1972 Apr;22(2):258–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jowsey J. Calcium release from the skeletons of rachitic puppies. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):9–15. doi: 10.1172/JCI106802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KO K. W., FELLERS F. X., CRAIG J. M. Observations on magnesium deficiency in the rat. Lab Invest. 1962 Apr;11:294–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessner D. M., Epstein F. H. Effect of magnesium deficiency on gastrointestinal transfer of calcium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jul;122(3):721–725. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifshitz F., Harrison H. C., Harrison H. E. Intestinal transport of calcium and phosphate in experimental magnesium deficiency. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 May;125(1):19–25. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER E. R., ULLREY D. E., ZUTAUT C. L., BALTZER B. V., SCHMIDT D. A., HOEFER J. A., LUECKE R. W. MAGNESIUM REQUIREMENT OF THE BABY PIG. J Nutr. 1965 Jan;85:13–20. doi: 10.1093/jn/85.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Chu L. L., Hamilton J. W., Cohn D. V. Partial purification of parathyroid hormone from chicken parathyroid glands. Endocrinology. 1973 May;92(5):1312–1317. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-5-1312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacManus J., Heaton F. W., Lucas P. W. A decreased response to parathyroid hormone in magnesium deficiency. J Endocrinol. 1971 Feb;49(2):253–258. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0490253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacManus J., Heaton F. W. The effect of magnesium deficiency on calcium homeostasis in the rat. Clin Sci. 1969 Apr;36(2):297–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pak C. Y., Diller E. C. Ionic interaction with bone mineral. V. Effect of Mg2+, Citrate3-, F- and SO4 negative 2 ion on the solubility, dissolution and growth of bone mineral. Calcif Tissue Res. 1969 Aug 11;4(1):69–77. doi: 10.1007/BF02279107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RASMUSSEN H., DELUCA H., ARNAUD C., HAWKER C., VONSTEDINGK M. THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN VITAMIN D AND PARATHYROID HORMONE. J Clin Invest. 1963 Dec;42:1940–1946. doi: 10.1172/JCI104880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radde I. C., Wittermann E. R., Pensuwan S. Effect of thyroid and parathyroid on hypocalcemia occurring after a magnesium load. Endocrinology. 1968 Dec;83(6):1285–1292. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-6-1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raisz L. G., Niemann I. Effect of phosphate, calcium and magnesium on bone resorption and hormonal responses in tissue culture. Endocrinology. 1969 Sep;85(3):446–452. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-3-446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH W. O., BAXTER D. J., LINDNER A., GINN H. E., GUILES H. Effect of magnesium depletion on renal function in the rat. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Feb;59:211–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood L. M. Magnesium ion and parathyroid function. N Engl J Med. 1970 Mar 26;282(13):752–752. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197003262821315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh S. M., Csima A., Fraser D. Pathogenesis of hypocalcemia in magnesium depletion. Normal end-organ responsiveness to parathyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2668–2678. doi: 10.1172/JCI106768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh S. M., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Matsuo N., Parkinson D. K., Fraser D. Pathogenesis of hypocalcemia in primary hypomagnesemia: normal end-organ responsiveness to parathyroid hormone, impaired parathyroid gland function. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):153–160. doi: 10.1172/JCI107159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targovnik J. H., Rodman J. S., Sherwood L. M. Regulation of parathyroid hormone secretion in vitro: quantitative aspects of calcium and magnesium ion control. Endocrinology. 1971 Jun;88(6):1477–1482. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-6-1477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELT L. G. EXPERIMENTAL MAGNESIUM DEPLETION. Yale J Biol Med. 1964 Apr;36:325–349. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHANG R., WELT L. G. Observations in experimental magnesium depletion. J Clin Invest. 1963 Mar;42:305–313. doi: 10.1172/JCI104717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodard J. C., Webster P. D., Carr A. A. Primary hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia, diarrhea and insensitivity to parathyroid hormone. Am J Dig Dis. 1972 Jul;17(7):612–618. doi: 10.1007/BF02231747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]