Abstract
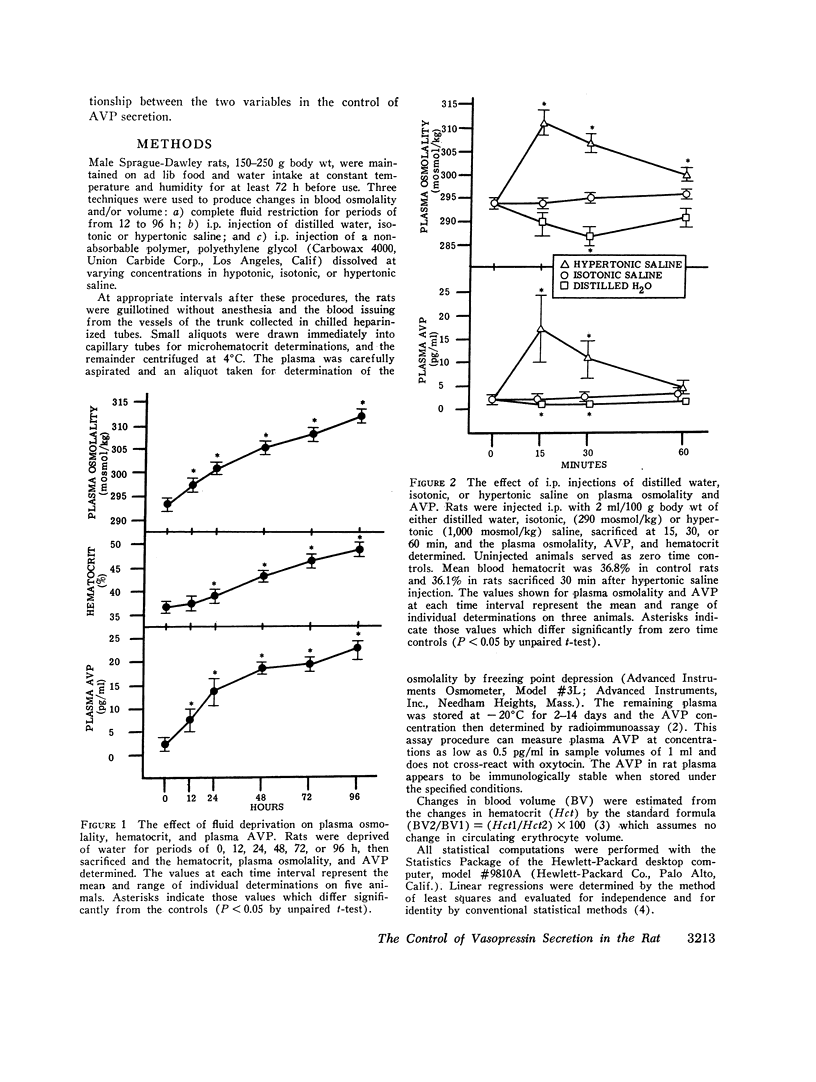
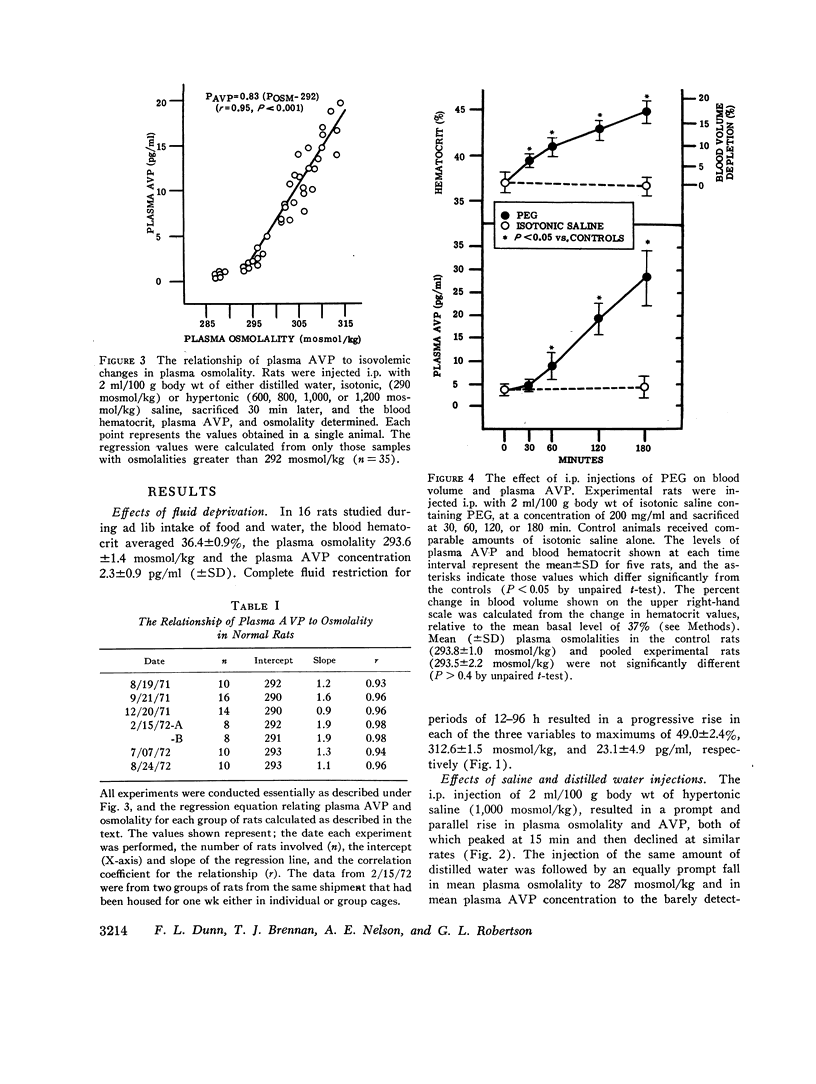
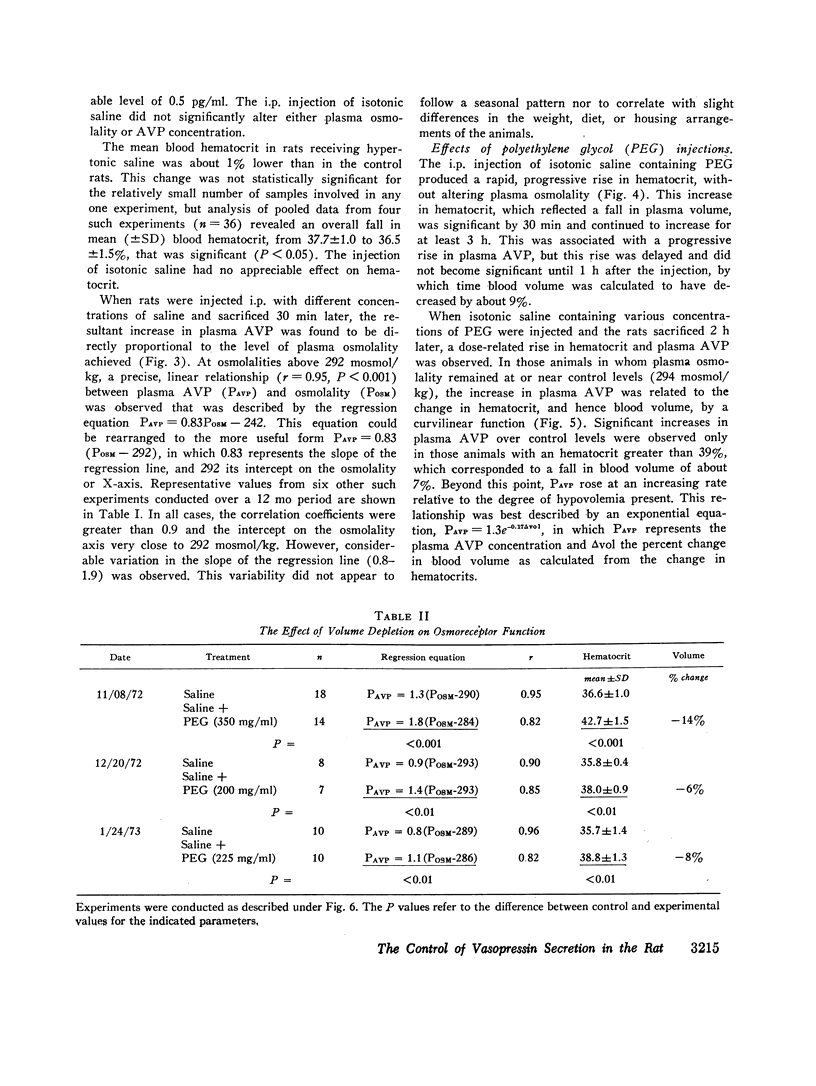
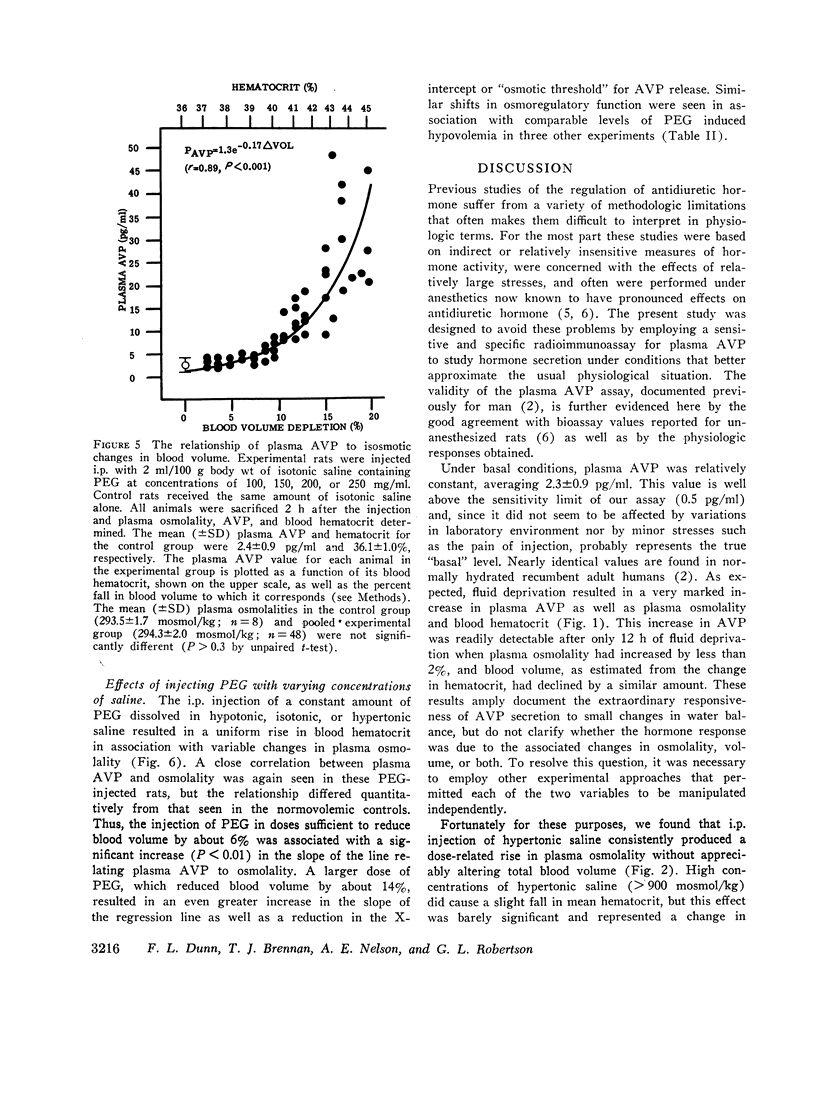
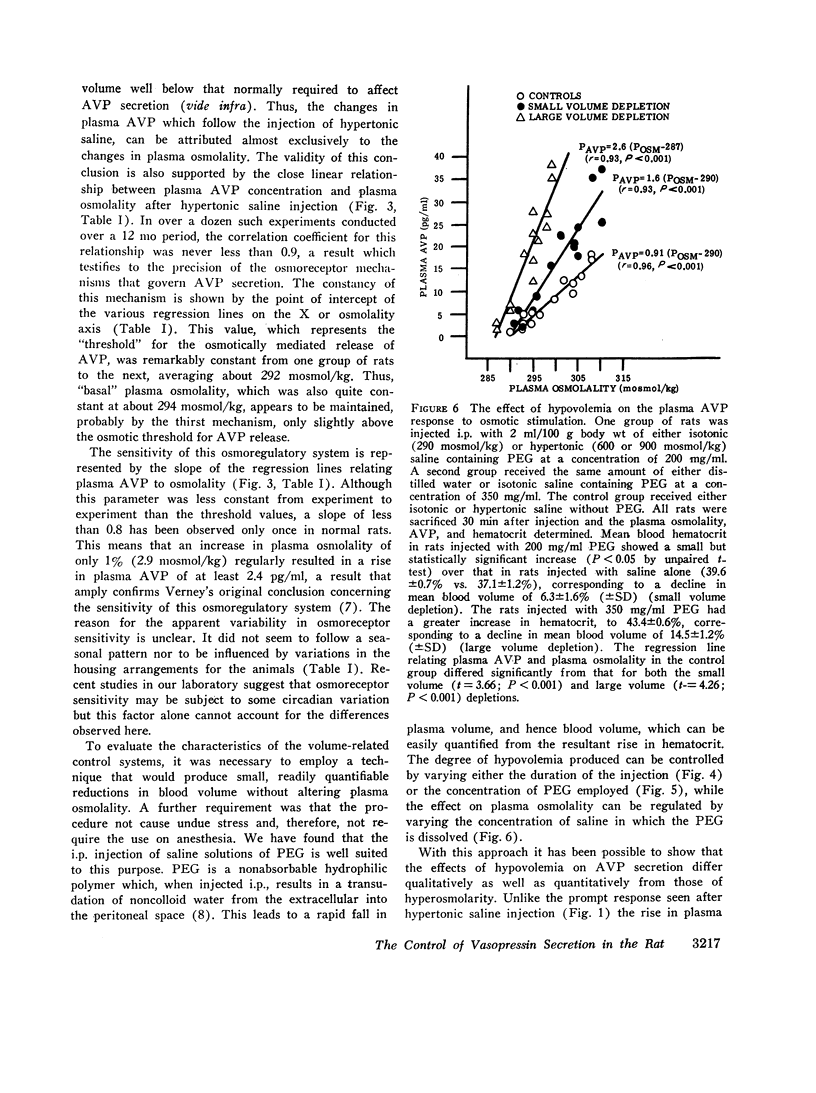
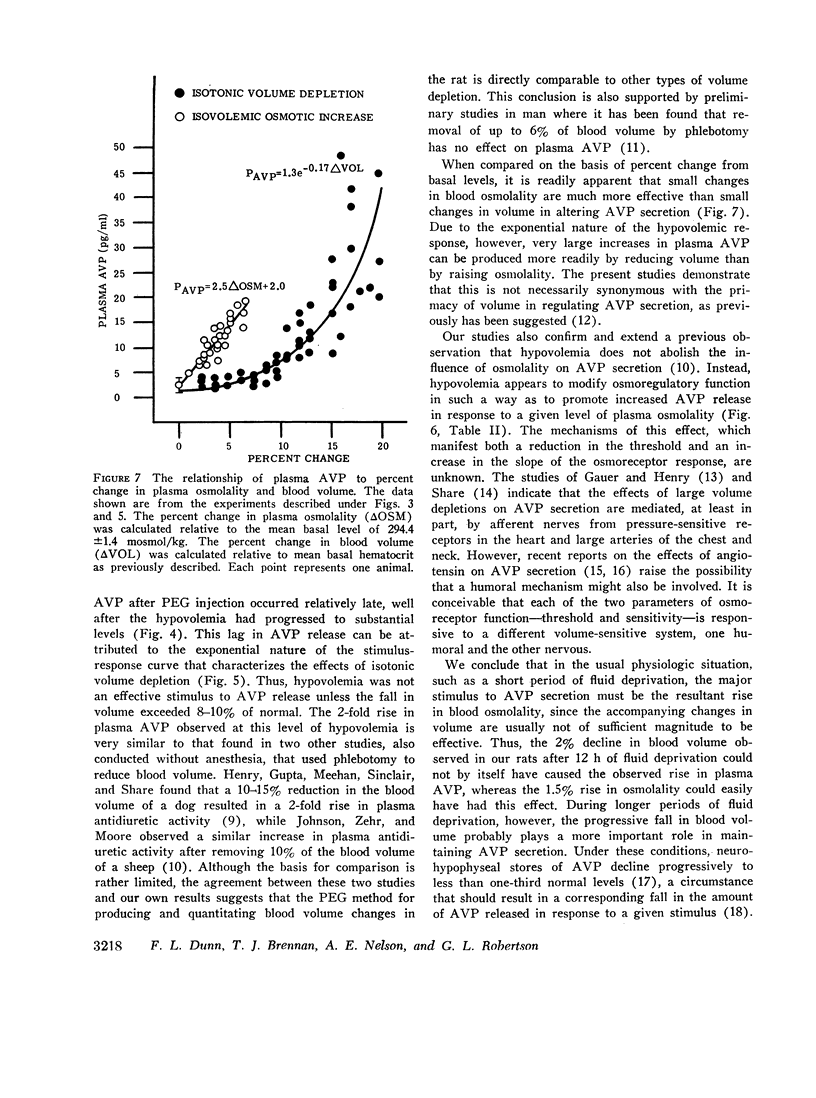
A sensitive and specific radioimmunoassay for plasma arginine vasopressin (AVP) has been used to study the effects of blood osmolality and volume in regulating AVP secretion in unanesthetized rats. Under basal conditions, plasma AVP and osmolality were relatively constant, averaging 2.3±0.9 (SD) pg/ml and 294±1.4 mosmol/kg, respectively. Fluid restriction, which increased osmolality and decreased volume, resulted in a progressive rise in plasma AVP to about 10 times basal levels after 96 h. A 2-3-fold increase in plasma AVP occurred as early as 12 h, when osmolality and volume had each changed by less than 2%. Intraperitoneal injections of hypertonic saline, which had no effect on blood volume, also produced a rise in plasma AVP that was linearly correlated with the rise in osmolality (r > 0.9) and quantitatively similar to that found during fluid restriction (plasma AVP increased 2-4-fold with each 1% increase in osmolality). Intraperitoneal injection of polyethylene glycol, which decreased blood volume without altering osmolality, also increased plasma AVP but this response followed an exponential pattern and did not become significant until volume had decreased by 8% or more. At these levels of hypovolemia, the osmoregulatory system continued to function but showed a lower threshold and increase sensitivity to osmotic stimulation. We conclude that AVP secretion is regulated principally by blood osmolality but that the responsiveness of this mechanism may be significantly altered by modest changes in blood volume.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson B., Westbye O. Synergistic action of sodium and angiotensin on brain mechanisms controlling fluid balance. Life Sci I. 1970 Jun 1;9(11):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90090-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN L. M., GINSBURG M. Effect of anaesthetics and haemorrhage on the release of neurohypophysial antidiuretic hormone. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1956 Sep;11(3):236–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1956.tb01060.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Berliner R. W. Relationship between extracellular volume and fluid reabsorption by the rat nephron. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jul;217(1):6–12. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAUER O. H., HENRY J. P. Circulatory basis of fluid volume control. Physiol Rev. 1963 Jul;43:423–481. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1963.43.3.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Zehr J. E., Moore W. W. Effects of separate and concurrent osmotic and volume stimuli on plasma ADH in sheep. Am J Physiol. 1970 May;218(5):1273–1280. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.5.1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLE J. B., RADFORD E. P., Jr BIO-ASSAY FOR ANTIDIURETIC ACTIVITY IN BLOOD OF UNDISTURBED RATS. J Appl Physiol. 1964 Mar;19:179–186. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malvin R. L. Possible role of the renin-angiotensin system in the regulation of antidiuretic hormone secretion. Fed Proc. 1971 Jul-Aug;30(4):1383–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M., Moses A. M. Radioimmunoassay of urinary antidiuretic hormone with application to study of the Brattleboro rat. Endocrinology. 1971 Jun;88(6):1389–1396. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-6-1389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. M., Miller M. Accumulation and release of pituitary vasopressin in rats heterozygous for hypothalamic diabetes insipidus. Endocrinology. 1970 Jan;86(1):34–41. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-1-34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson G. L., Mahr E. A., Athar S., Sinha T. Development and clinical application of a new method for the radioimmunoassay of arginine vasopressin in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;52(9):2340–2352. doi: 10.1172/JCI107423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito T., Yoshida S. Levels of antidiuretic hormone in plasma after hemorrhage and infusion of hypertonic saline in dogs. Endocrinology. 1971 Jun;88(6):1511–1513. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-6-1511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


