Abstract
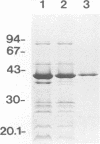
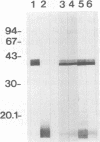
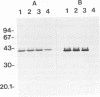
We purified the major outer membrane protein (MOMP), which is the most abundant OMP (with an apparent molecular mass of 40 kDa), from Haemophilus somnus strain 8025. The method involves solubilization of the MOMP with Zwittergent 3-14 and further purification accomplished by ion-exchange and molecular-sieve chromatographies. The amino-terminal sequence of the MOMP showed considerable similarity to those of porin proteins from other gram-negative bacteria. The MOMP of H. somnus is immunogenic to rabbits and calves. Hyperimmune sera from rabbits and calves reacted with both the MOMP and lipopolysaccharides in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunoblot analysis. The rabbit antiserum to the MOMP was cross-reactive with whole-cell preparations from strains 8025, D1238, NT2301, and 540 at a band with a molecular mass of 40 kDa in immunoblot analysis, although the reactivity of the rabbit antiserum with strain 540 was lower than those with the other strains tested. Two murine monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) to the MOMP were developed. ELISA with the OMP fractions as the antigens showed that one MAb was cross-reactive with the four strains but that the other MAb was reactive with the three strains other than strain 540. These results indicate that the MOMP of H. somnus possesses at least two antigenic determinants and that the MOMP of strain 540 is antigenically different from those of the other strains. The antigenic heterogeneity of the H. somnus MOMP has implications regarding the development of a serotyping system with MAbs that is based on the MOMP epitopes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Canto G. J., Biberstein E. L. Serological diversity in Haemophilus somnus. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1009–1015. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1009-1015.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Arthur J. E., Widders P. R., Smith J. W., Barbet A. F. Antigenic specificity of convalescent serum from cattle with haemophilus somnus-induced experimental abortion. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1381–1386. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1381-1386.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B. Molecular aspects of some virulence factors of Haemophilus somnus. Can J Vet Res. 1990 Apr;54 (Suppl):S57–S62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corboz L., Wild P. Epidemiologie der Haemophilus somnus-Infektion beim Rind: Vergleich von Stämmen in der Polyacrylamidgel-Elektrophorese (PAGE). Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1981 Feb;123(2):79–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolewski R. P., Kania S. A., Inzana T. J., Widders P. R., Liggitt H. D., Corbeil L. B. Protective ability and specificity of convalescent serum from calves with Haemophilus somnus pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1403–1411. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1403-1411.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Hansen E. J. Coprecipitation of lipopolysaccharide and the 39,000-molecular-weight major outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b by lipopolysaccharide-directed monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):819–827. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.819-827.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haid A., Suissa M. Immunochemical identification of membrane proteins after sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:192–205. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel J., Brodeur B. R., Larose Y., Tsang P. S., Belmaaza A., Montplaisir S. A monoclonal antibody directed against a serotype-specific, outer-membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Mar;23(2):163–170. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-2-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Hasemann C., Clausell A., Capra J. D., Orth K., Moomaw C. R., Slaughter C. A., Latimer J. L., Miller E. E. Primary structure of the porin protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b determined by nucleotide sequence analysis. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1100–1107. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1100-1107.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Chou M. Y., Inouye M. A comparative study on the genes for three porins of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. DNA sequence of the osmoregulated ompC gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6932–6940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Tolan R. W., Jr Molecular cloning, expression, and primary sequence of outer membrane protein P2 of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):88–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.88-94.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C. Human bactericidal antibody response to outer membrane protein P2 of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2673–2679. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2673-2679.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Nakae T. The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1979;20:163–250. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Aukema R., Murray L. J. Antigenic heterogeneity of Haemophilus somnus. Aust Vet J. 1987 Apr;64(4):113–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1987.tb09643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B. Ultrastructure of Haemophilus somnus, causative agent of bovine infectious thromboembolic meningoencephalitis. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Sep;42(9):1638–1640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Zak K., Heckels J. E. Monoclonal antibodies to gonococcal outer membrane protein IB: use in investigation of the potential protective effect of antibodies directed against conserved and type-specific epitopes. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jun;132(6):1621–1629. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-6-1621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]