Abstract
Group B streptococci (GBS) are the most common cause of neonatal sepsis and pneumonia. The pathogenesis of GBS disease is not completely defined. GBS-induced endothelial cell injury is suggested by histological findings at autopsy and in animal studies. We hypothesized that (i) type III GBS (COH-1) invade and injure human umbilical vein endothelial (HUVE) cells and (ii) isogenic mutations in GBS capsule synthesis would influence HUVE invasion. Confluent HUVE monolayers were infected for 0.5, 2, or 6 h. Media with penicillin plus gentamicin were added and incubated for 2 h to kill extracellular bacteria. Cells were washed and lysed, and the number of live intracellular bacteria was determined by plate counting. COH-1 invaded HUVE cells in a time-dependent manner at levels 1,000-fold higher than those of the noninvasive Escherichia coli strain but significantly lower than those of Staphylococcus aureus. There was no evidence for net intracellular replication of GBS within HUVE cells. COH-1 infection of HUVE cells caused the release of lactate dehydrogenase activity. GBS invasion was inhibited by cytochalasin D in a dose-dependent manner; GBS-induced lactate dehydrogenase release was attenuated by cytochalasin D. The isogenic strains COH 1-11, devoid of capsular sialic acid, and COH 1-13, devoid of all type III capsule, invaded HUVE cells three- to fivefold more than the parent COH-1 strain. The type III capsular polysaccharide and particularly the capsular sialic acid attenuate GBS invasion of HUVE cells. Electron micrographs of lung tissue from a GBS-infected newborn Macaca nemestrina also showed GBS within capillary endothelial cells. We conclude that endothelial cell invasion and injury are potential mechanisms in the pathogenesis of GBS disease.
Full text
PDF

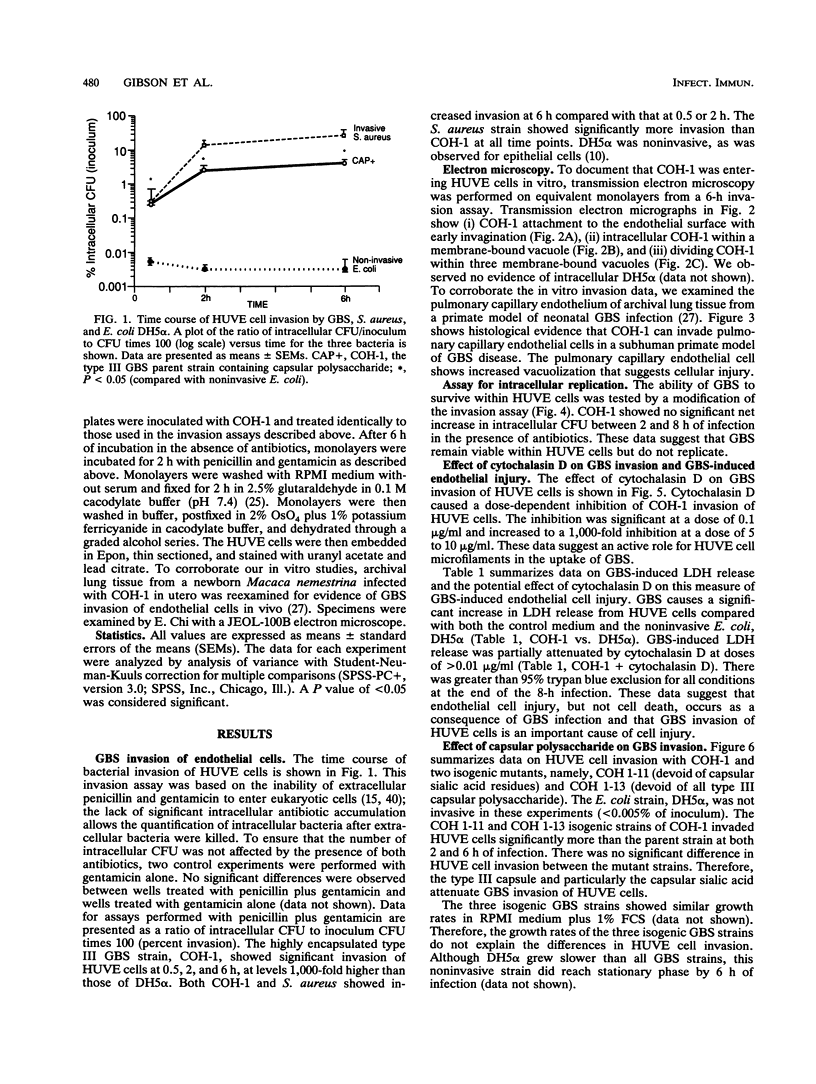
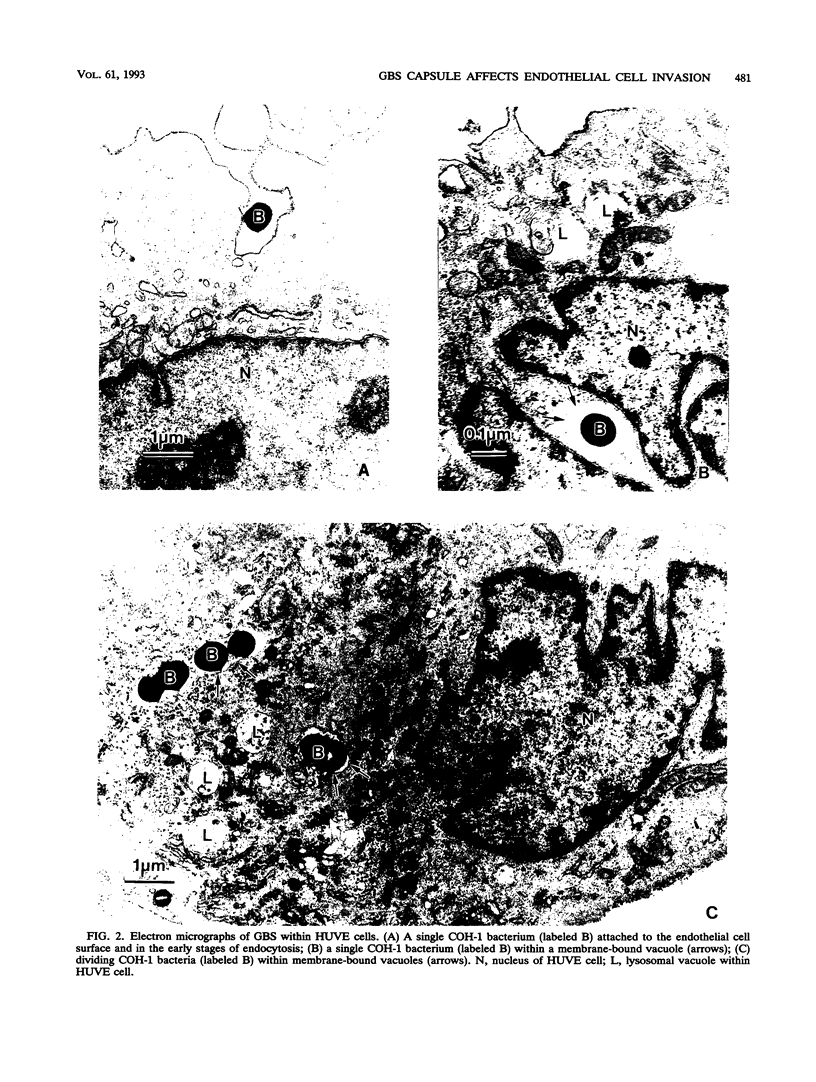
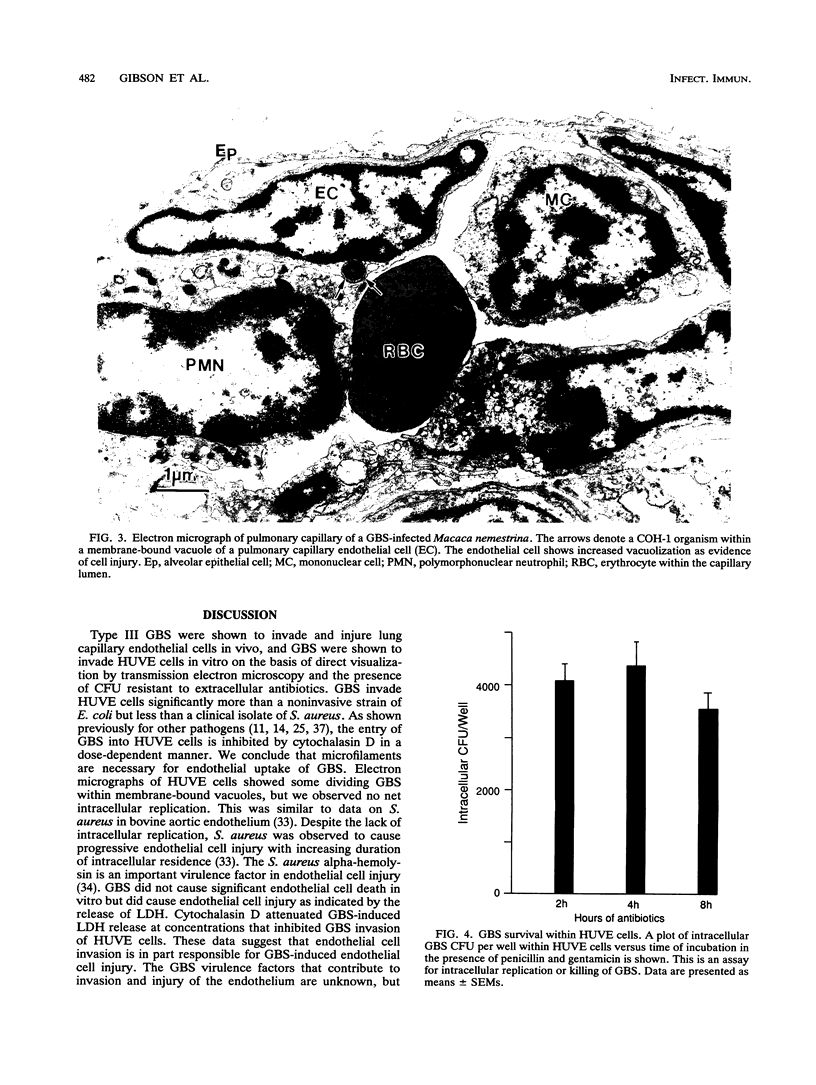


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ablow R. C., Driscoll S. G., Effmann E. L., Gross I., Jolles C. J., Uauy R., Warshaw J. B. A comparison of early-onset group B steptococcal neonatal infection and the respiratory-distress syndrome of the newborn. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jan 8;294(2):65–70. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197601082940201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Absolom D. R. The role of bacterial hydrophobicity in infection: bacterial adhesion and phagocytic ingestion. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Mar;34(3):287–298. doi: 10.1139/m88-054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayoub E. M., Swingle H. Pathogenic mechanisms in neonatal GBS infection. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1985;35:128–141. doi: 10.1159/000410368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Microcapsule of type III strains of group B Streptococcus: production and morphology. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):189–194. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.189-194.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becroft D. M., Farmer K., Mason G. H., Morris M. C., Stewart J. H. Perinatal infections by group B beta-haemolytic streptococci. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1976 Dec;83(12):960–966. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1976.tb00782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berendt A. R., Simmons D. L., Tansey J., Newbold C. I., Marsh K. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is an endothelial cell adhesion receptor for Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):57–59. doi: 10.1038/341057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EICKHOFF T. C., KLEIN J. O., DALY A. K., INGALL D., FINLAND M. NEONATAL SEPSIS AND OTHER INFECTIONS DUE TO GROUP B BETA-HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI. N Engl J Med. 1964 Dec 10;271:1221–1228. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196412102712401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrieri P. GBS enzymes, hemolysin, toxins and other products. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1985;35:57–70. doi: 10.1159/000410361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Gumbiner B., Falkow S. Penetration of Salmonella through a polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cell monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):221–230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOOD M., JANNEY A., DAMERON G. Beta hemolytic streptococcus group B associated with problems of the perinatal period. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1961 Oct;82:809–818. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)36146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill R. J., Vann J. M., Proctor R. A. Phagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus by cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells: model for postadherence events in endovascular infections. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):833–836. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.833-836.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemming V. G., McCloskey D. W., Hill H. R. Pneumonia in the neonate associated with group B streptococcal septicemia. Am J Dis Child. 1976 Nov;130(11):1231–1233. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1976.02120120065011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of microorganisms. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):104–123. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Falkow S. A single genetic locus encoded by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis permits invasion of cultured animal cells by Escherichia coli K-12. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):262–264. doi: 10.1038/317262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenstein A. L., Davis C., Braude A. Pulmonary changes in neonatal sepsis to group B beta-hemolytic Streptococcus: relation of hyaline membrane disease. J Infect Dis. 1976 Apr;133(4):430–435. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.4.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macneal W. J., Spence M. J., Slavkin A. E. Early Lesions of Experimental Endocarditis Lenta. Am J Pathol. 1943 Sep;19(5):735–749. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. R., Rubens C. E., Wilson C. B. Lung antibacterial defense mechanisms in infant and adult rats: implications for the pathogenesis of group B streptococcal infections in the neonatal lung. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):91–100. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. R., Ruzinski J. T., Rubens C. E., Chi E. Y., Wilson C. B. The effect of type-specific polysaccharide capsule on the clearance of group B streptococci from the lungs of infant and adult rats. J Infect Dis. 1992 Feb;165(2):306–314. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.2.306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Hoover R., Jones M. R., Berry L. C., Jr, Brigham K. L. In vitro effects of endotoxin on bovine and sheep lung microvascular and pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jan;138(1):165–174. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philips J. B., 3rd, Li J. X., Gray B. M., Pritchard D. G., Oliver J. R. Role of capsule in pulmonary hypertension induced by group B streptococcus. Pediatr Res. 1992 Apr;31(4 Pt 1):386–390. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199204000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirante J., Ceballos R., Cassady G. Group B beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection in the newborn. I. Early onset infection. Am J Dis Child. 1974 Nov;128(5):659–665. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110300069009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. D. Interactions of respiratory pathogens with host cell surface and extracellular matrix components. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Sep;3(3):181–186. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/3.3.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas J., Larsson L. E., Hellerqvist C. G., Brigham K. L., Gray M. E., Stahlman M. T. Pulmonary hemodynamic and ultrastructural changes associated with Group B streptococcal toxemia in adult sheep and newborn lambs. Pediatr Res. 1983 Dec;17(12):1002–1008. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198312000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Edwards J. E., Jr, Gibson T. R., Moore J. C., Cohen A. H., Green I. Adherence of Candida to cultured vascular endothelial cells: mechanisms of attachment and endothelial cell penetration. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1264–1274. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., Raff H. V., Jackson J. C., Chi E. Y., Bielitzki J. T., Hillier S. L. Pathophysiology and histopathology of group B streptococcal sepsis in Macaca nemestrina primates induced after intraamniotic inoculation: evidence for bacterial cellular invasion. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):320–330. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Schultz D. R., Goodwin J. D., Vann J. M., Selvaraj M. P., Hart M. A. Role of C1q in phagocytosis of Salmonella minnesota by pulmonary endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1356–1362. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1356-1362.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M. Selection and characterization of bovine aortic endothelial cells. In Vitro. 1978 Dec;14(12):966–980. doi: 10.1007/BF02616210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins D. C., Hatcher V. B., Patel D., Orr G. A., Higgins L. L., Lowy F. D. A human endothelial cell membrane protein that binds Staphylococcus aureus in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1248–1254. doi: 10.1172/JCI114560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vann J. M., Proctor R. A. Cytotoxic effects of ingested Staphylococcus aureus on bovine endothelial cells: role of S. aureus alpha-hemolysin. Microb Pathog. 1988 Jun;4(6):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vann J. M., Proctor R. A. Ingestion of Staphylococcus aureus by bovine endothelial cells results in time- and inoculum-dependent damage to endothelial cell monolayers. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2155–2163. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2155-2163.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollman J. H., Smith W. L., Ballard E. T., Light I. J. Early onset group B streptococcal disease: clinical, roentgenographic, and pathologic features. J Pediatr. 1976 Aug;89(2):199–203. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80447-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M., Wagner B. Immunoelectron microscopical demonstration of the cell wall and capsular antigens of GBS. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1985;35:119–127. doi: 10.1159/000410367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S. Rickettsial interactions with human endothelial cells in vitro: adherence and entry. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):205–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.205-210.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels M. R., Haft R. F., Heggen L. M., Rubens C. E. Identification of a genetic locus essential for capsule sialylation in type III group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):392–400. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.392-400.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels M. R., Pozsgay V., Kasper D. L., Jennings H. J. Structure and immunochemistry of an oligosaccharide repeating unit of the capsular polysaccharide of type III group B Streptococcus. A revised structure for the type III group B streptococcal polysaccharide antigen. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8262–8267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Jacobs R. F., Smith A. L. Cellular antibiotic pharmacology. Semin Perinatol. 1982 Apr;6(2):205–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]