Abstract
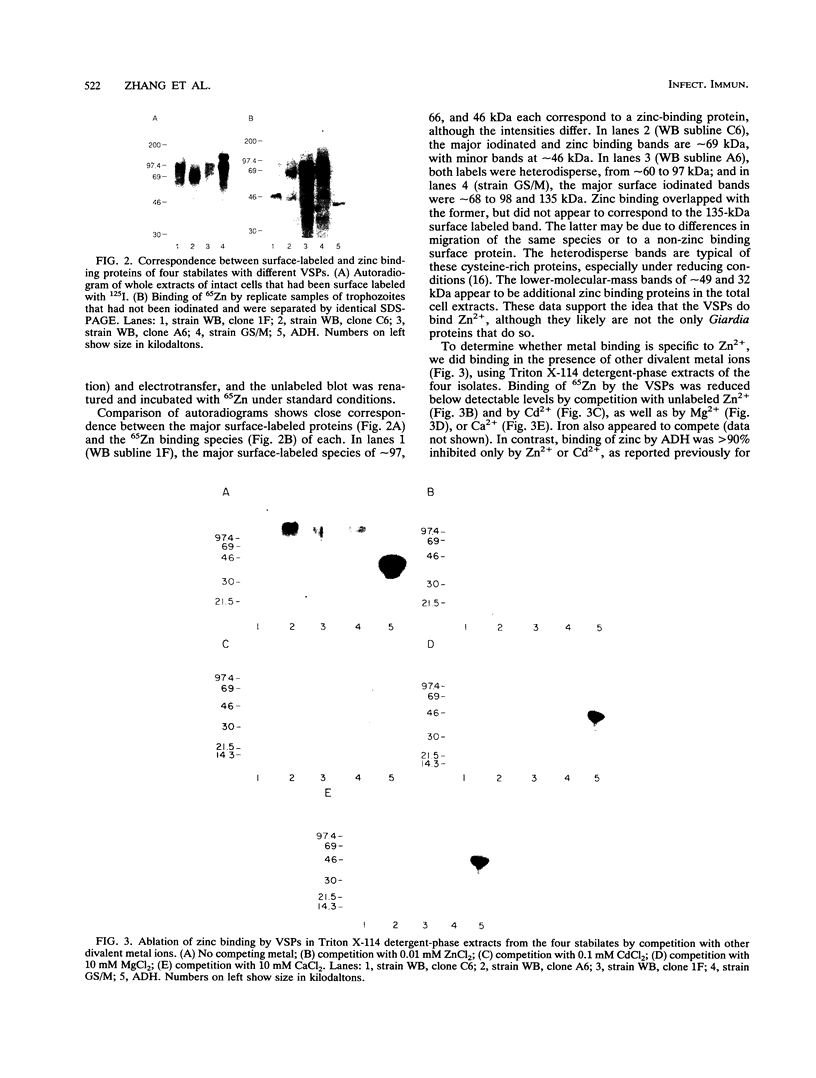
The abundant, highly variable surface proteins (VSPs) which cover the surface of Giardia lamblia trophozoites compose a group of extremely cysteine (C)-rich proteins in which more than half of the cysteines are in the motif CXXC. Because of the constancy of these features among the known VSPs and the prominence of cysteine and particularly CXXC in proteins that bind zinc and other metals, we asked whether G. lamblia VSPs bind zinc in vitro. VSPs are the major protein component of Triton X-114 detergent-phase extracts of G. lamblia trophozoites and can be readily identified by surface iodination of intact cells. The partitioning of 65Zn binding into the Triton X-114 detergent phase and the correspondence between surface iodination and zinc binding patterns of four G. lamblia strains or sublines with different VSPs support the idea that VSPs bind zinc. The requirement for renaturation of blots with a reducing agent indicates that Zn2+ is coordinated by cysteine residues, rather than by other amino acids. Binding did not appear to be specific to zinc since it was inhibited by competition with other divalent metal ions. The abundance of the VSPs and the prevalence of metal binding motifs among all known variants suggest that they may play an important role in trophozoite survival and colonization in the host.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam R. D., Aggarwal A., Lal A. A., de La Cruz V. F., McCutchan T., Nash T. E. Antigenic variation of a cysteine-rich protein in Giardia lamblia. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):109–118. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa M. S., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. Papillomavirus polypeptides E6 and E7 are zinc-binding proteins. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1404–1407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1404-1407.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. E. Zinc proteins: enzymes, storage proteins, transcription factors, and replication proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:897–946. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D. Giardia lamblia: the role of conjugated and unconjugated bile salts in killing by human milk. Exp Parasitol. 1987 Feb;63(1):74–83. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(87)90080-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Hagblom P., Harwood J., Aley S. B., Reiner D. S., McCaffery M., So M., Guiney D. G. Isolation and expression of the gene for a major surface protein of Giardia lamblia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4463–4467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempe J. M., Cousins R. J. Cysteine-rich intestinal protein binds zinc during transmucosal zinc transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9671–9674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowatt M. R., Aggarwal A., Nash T. E. Carboxy-terminal sequence conservation among variant-specific surface proteins of Giardia lamblia. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Dec;49(2):215–227. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90065-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtagh J. J., Jr, Mowatt M. R., Lee C. M., Lee F. J., Mishima K., Nash T. E., Moss J., Vaughan M. Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins in the intestinal parasite Giardia lamblia. Isolation of a gene encoding an approximately 20-kDa ADP-ribosylation factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9654–9662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E. Antigenic variation in Giardia lamblia. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Feb;68(2):238–241. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Herrington D. A., Levine M. M., Conrad J. T., Merritt J. W., Jr Antigenic variation of Giardia lamblia in experimental human infections. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4362–4369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Merritt J. W., Jr, Conrad J. T. Isolate and epitope variability in susceptibility of Giardia lamblia to intestinal proteases. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1334–1340. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1334-1340.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. Surface antigen variability and variation in Giardia lamblia. Parasitol Today. 1992 Jul;8(7):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(92)90119-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimenta P. F., da Silva P. P., Nash T. Variant surface antigens of Giardia lamblia are associated with the presence of a thick cell coat: thin section and label fracture immunocytochemistry survey. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3989–3996. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3989-3996.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner D. S., Gillin F. D. Human secretory and serum antibodies recognize environmentally induced antigens of Giardia lamblia. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):637–643. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.637-643.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff L. A., Nibert M. L., Fields B. N. Characterization of a zinc blotting technique: evidence that a retroviral gag protein binds zinc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4195–4199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley S. L., Jr, Becker A., Kunz-Jenkins C., Foster L., Li E. Cloning and expression of a membrane antigen of Entamoeba histolytica possessing multiple tandem repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4976–4980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster L. C., Zhang K., Chance B., Ayene I., Culp J. S., Huang W. J., Wu F. Y., Ricciardi R. P. Conversion of the E1A Cys4 zinc finger to a nonfunctional His2,Cys2 zinc finger by a single point mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9989–9993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbach E. C., Claggett C. E., Keister D. B., Diamond L. S., Kon H. Respiratory metabolism of Giardia lamblia. J Parasitol. 1980 Apr;66(2):347–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]