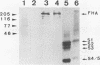
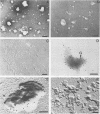
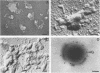
Abstract
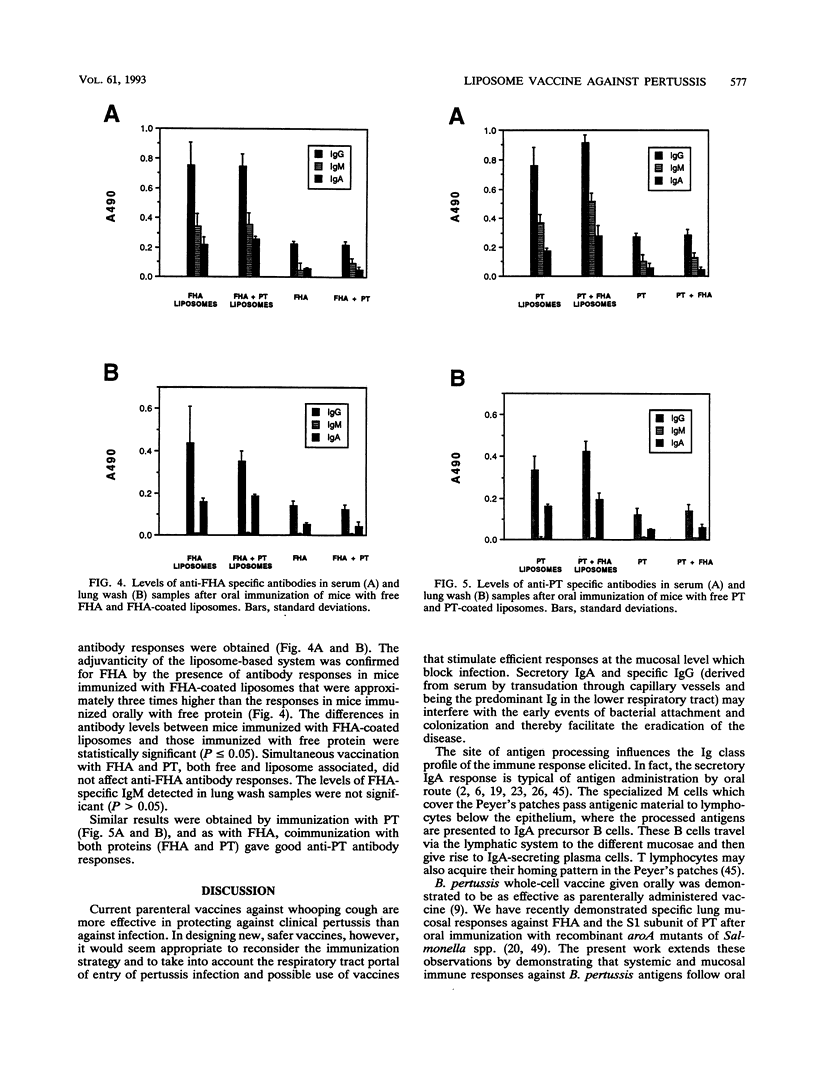
Mice were orally vaccinated with liposomes coated with filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA) and detoxified pertussis toxin (PT) of Bordetella pertussis. FHA- and PT-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) was detected in serum, and both IgG and IgA were detected in lung washes following the immunization. Antibody responses in mice immunized with liposomes coated with FHA and PT were significantly higher than those in mice immunized with free FHA and PT, which demonstrated the adjuvanticity of the liposome carrier. The results indicate the potential usefulness of this approach for eliciting immune responses against FHA and PT (and perhaps other pertussis antigens) in humans and its possible utility in large-scale vaccination to protect against both B. pertussis infection and disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. G., Gregoriadis G. Liposomes as immunological adjuvants. Nature. 1974 Nov 15;252(5480):252–252. doi: 10.1038/252252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienenstock J., Befus A. D. Mucosal immunology. Immunology. 1980 Oct;41(2):249–270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow R., Boothroyd J. C. Protection of mice from fatal Toxoplasma gondii infection by immunization with p30 antigen in liposomes. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 15;147(10):3496–3500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C., Prince S. J., Michalek S. M., Jackson S., Russell M. W., Moldoveanu Z., McGhee J. R., Mestecky J. IgA antibody-producing cells in peripheral blood after antigen ingestion: evidence for a common mucosal immune system in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2449–2453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Magistris M. T., Romano M., Nuti S., Rappuoli R., Tagliabue A. Dissecting human T cell responses against Bordetella species. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1351–1362. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desiderio J. V., Campbell S. G. Immunization against experimental murine salmonellosis with liposome-associated O-antigen. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):658–663. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.658-663.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk W., Höfler K. H., Rosanelli K., Kurz R. Gegenwart und Zukunft der oralen Pertussis-Schutzimpfung. Fortschr Med. 1981 Sep 10;99(34):1363–1366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine P. E., Clarkson J. A. Reflections on the efficacy of pertussis vaccines. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Sep-Oct;9(5):866–883. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.5.866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fountain M. W., Ganjam V. K., Schultz R. D. Liposome carrier vehicle for triiodothryonine. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1982 Jan-Feb;9(1):101–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1982.tb00784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis M. J., Fry C. M., Rowlands D. J., Brown F., Bittle J. L., Houghten R. A., Lerner R. A. Immunological priming with synthetic peptides of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Nov;66(Pt 11):2347–2354. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-11-2347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. W., Parker C. D. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Bordetella pertussis. J Biol Stand. 1984 Oct;12(4):353–365. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(84)80060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing A. J., Bird C. R., Redhead K., Thomas M. Human cellular immune responses to Bordetella pertussis infection. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1989 Mar;1(4):205–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1989.tb02384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giammanco A., Chiarini A., Stroffolini T., De Mattia D., Chiaramonte M., Moschen M. E., Mura I., Rigo G., Taormina S., Sarzana A. Seroepidemiology of pertussis in Italy. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Nov-Dec;13(6):1216–1220. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.6.1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman Y. E., Wort A. J., Jackson F. L. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of pertussis immunoglobulin A in nasopharyngeal secretions as an indicator of recent infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):286–292. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.286-292.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriadis G. Immunological adjuvants: a role for liposomes. Immunol Today. 1990 Mar;11(3):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory R. L., Michalek S. M., Richardson G., Harmon C., Hilton T., McGhee J. R. Characterization of immune response to oral administration of Streptococcus sobrinus ribosomal preparations in liposomes. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):780–786. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.780-786.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán C. A., Brownlie R. M., Kadurugamuwa J., Walker M. J., Timmis K. N. Antibody responses in the lungs of mice following oral immunization with Salmonella typhimurium aroA and invasive Escherichia coli strains expressing the filamentous hemagglutinin of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4391–4397. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4391-4397.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán C. A., Walker M. J., Rohde M., Timmis K. N. Direct expression of Bordetella pertussis filamentous hemagglutinin in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium aroA. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3787–3795. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3787-3795.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howson C. P., Fineberg H. V. Adverse events following pertussis and rubella vaccines. Summary of a report of the Institute of Medicine. JAMA. 1992 Jan 15;267(3):392–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen H. K., Høiby N., Pedersen S. S. Experimental immunization with Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate induces IgA and IgG antibody responses. APMIS. 1991 Dec;99(12):1061–1068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahl L. P., Lelchuk R., Scott C. A., Beesley J. Characterization of Leishmania major antigen-liposomes that protect BALB/c mice against cutaneous leishmaniasis. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3233–3241. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3233-3241.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahl L. P., Scott C. A., Lelchuk R., Gregoriadis G., Liew F. Y. Vaccination against murine cutaneous leishmaniasis by using Leishmania major antigen/liposomes. Optimization and assessment of the requirement for intravenous immunization. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4441–4449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantele A., Arvilommi H., Kantele J. M., Rintala L., Mäkelä P. H. Comparison of the human immune response to live oral, killed oral or killed parenteral Salmonella typhi TY21A vaccines. Microb Pathog. 1991 Feb;10(2):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90072-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Mountzouros K. T., Relman D. A., Falkow S., Cowell J. L. Bordetella pertussis filamentous hemagglutinin: evaluation as a protective antigen and colonization factor in a mouse respiratory infection model. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):7–16. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.7-16.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Alderslade R., Ross E. M. Whooping cough and whooping cough vaccine: the risks and benefits debate. Epidemiol Rev. 1982;4:1–24. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller A. S., Leeuwenburg J., Pratt D. S. Pertussis: epidemiology and control. Bull World Health Organ. 1986;64(2):321–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Arai H., Cole R. L. Mouse-protecting and histamine-sensitizing activities of pertussigen and fimbrial hemagglutinin from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):243–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.243-250.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N. Location and chemical synthesis of a pre-S gene coded immunodominant epitope of hepatitis B virus. Science. 1984 Apr 27;224(4647):392–395. doi: 10.1126/science.6200931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny P., Chubb A. P., Cownley K., Charles I. G. Biologic and protective properties of the 69-kDa outer membrane protein of Bordetella pertussis: a novel formulation for an acellular pertussis vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):114–122. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olander R. M., Muotiala A., Karvonen M., Kuronen T., Runeberg-Nyman K. Serum antibody response to B. pertussis Tn5 mutants, purified PT and FHA in two different mouse strains and passive protection in the murine intranasal infection model. Microb Pathog. 1990 Jan;8(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90006-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Sacci J. B., Jr, Alving C. R., Richardson E. C. Enhancement by lipid A of mucosal immunogenicity of liposome-associated cholera toxin. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):563–566. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podda A., Nencioni L., De Magistris M. T., Di Tommaso A., Bossù P., Nuti S., Pileri P., Peppoloni S., Bugnoli M., Ruggiero P. Metabolic, humoral, and cellular responses in adult volunteers immunized with the genetically inactivated pertussis toxin mutant PT-9K/129G. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):861–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhalem A., Bourdieu C., Luffau G., Pery P. Vaccination of mice with liposome-entrapped adult antigens of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1988 Mar-Apr;139(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0769-2625(88)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. L., Hayre M. D., Hockmeyer W. T., Alving C. R. Liposomes, lipid A, and aluminum hydroxide enhance the immune response to a synthetic malaria sporozoite antigen. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):682–686. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.682-686.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. G., Alexander J. Effective immunization against cutaneous leishmaniasis with defined membrane antigens reconstituted into liposomes. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1274–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Cowell J. L., Sato H., Burstyn D. G., Manclark C. R. Separation and purification of the hemagglutinins from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):313–320. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.313-320.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahin R. D., Brennan M. J., Li Z. M., Meade B. D., Manclark C. R. Characterization of the protective capacity and immunogenicity of the 69-kD outer membrane protein of Bordetella pertussis. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):63–73. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snippe H., van Dam J. E., van Houte A. J., Willers J. M., Kamerling J. P., Vliegenthart J. F. Preparation of a semisynthetic vaccine to Streptococcus pneumoniae type 3. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):842–844. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.842-844.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter R. W., Cochi S. L. Pertussis hospitalizations and mortality in the United States, 1985-1988. Evaluation of the completeness of national reporting. JAMA. 1992 Jan 15;267(3):386–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. G., Ashworth L. A., Miller E., Lambert H. P. Serum IgG, IgA, and IgM responses to pertussis toxin, filamentous hemagglutinin, and agglutinogens 2 and 3 after infection with Bordetella pertussis and immunization with whole-cell pertussis vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;160(5):838–845. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.5.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Jr Mechanisms of immune regulation at mucosal surfaces. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S784–S792. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine R. C., Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. XII. Electron microscopy of the enzyme from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2143–2152. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmann D., Klein J. P., Scholler M., Ogier J., Ackermans F., Frank R. M. Serum and salivary antibody responses in rats orally immunized with Streptococcus mutans carbohydrate protein conjugate associated with liposomes. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):408–413. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.408-413.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. J., Rohde M., Timmis K. N., Guzmán C. A. Specific lung mucosal and systemic immune responses after oral immunization of mice with Salmonella typhimurium aroA, Salmonella typhi Ty21a, and invasive Escherichia coli expressing recombinant pertussis toxin S1 subunit. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4260–4268. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4260-4268.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. J., Rohde M., Wehland J., Timmis K. N. Construction of minitransposons for constitutive and inducible expression of pertussis toxin in bvg-negative Bordetella bronchiseptica. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4238–4248. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4238-4248.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. J., Wehland J., Timmis K. N., Raupach B., Schmidt M. A. Characterization of murine monoclonal antibodies that recognize defined epitopes of pertussis toxin and neutralize its toxic effect on Chinese hamster ovary cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4249–4251. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4249-4251.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zealey G. R., Loosmore S. M., Yacoob R. K., Cockle S. A., Herbert A. B., Miller L. D., Mackay N. J., Klein M. H. Construction of Bordetella pertussis strains that overproduce genetically inactivated pertussis toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):208–214. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.208-214.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]