Abstract
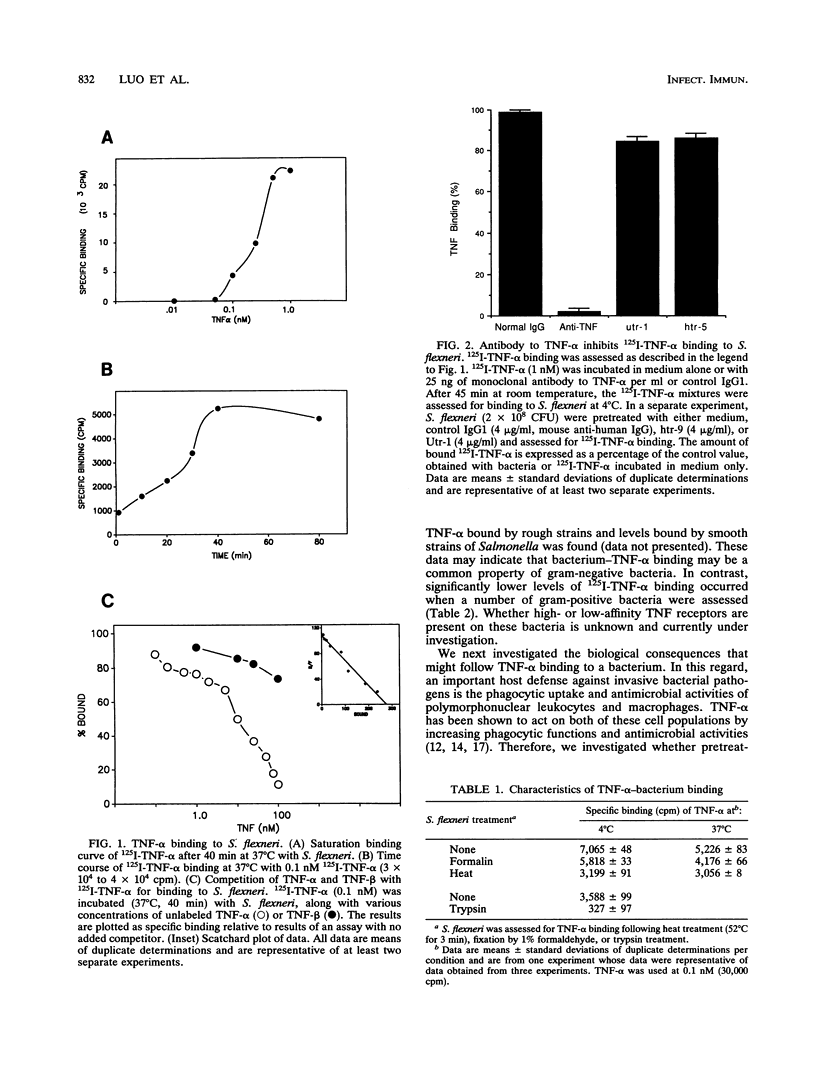
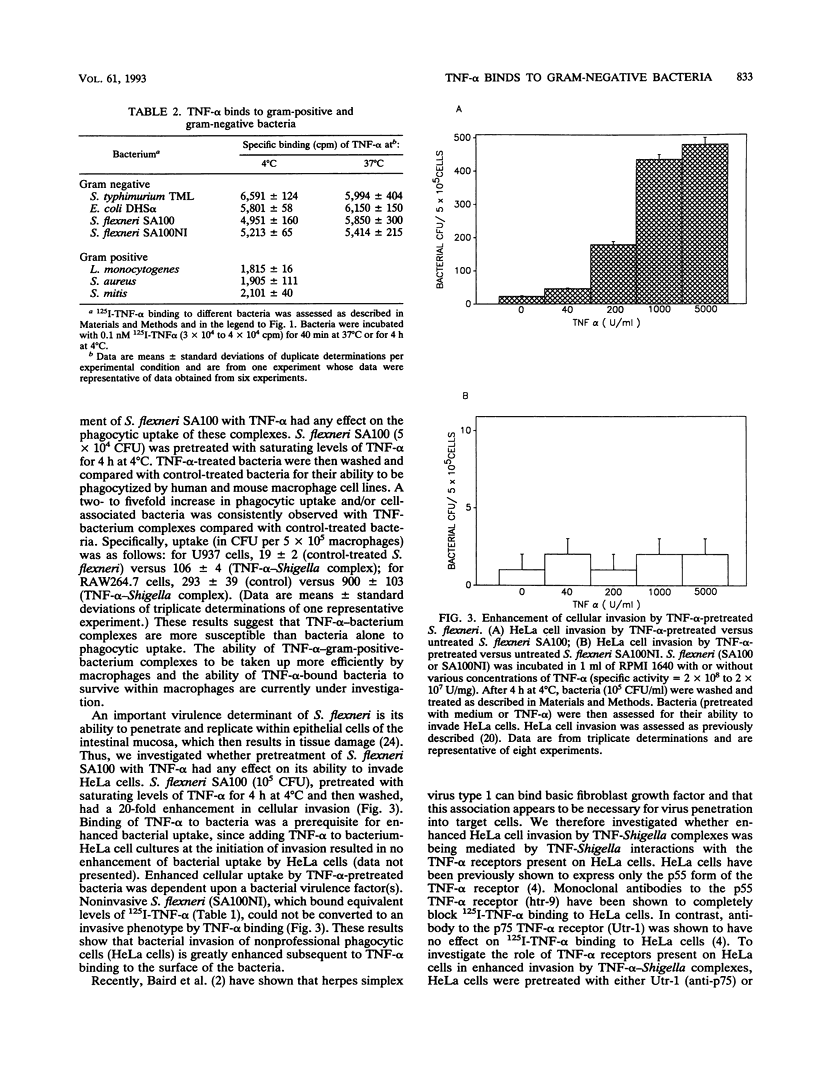
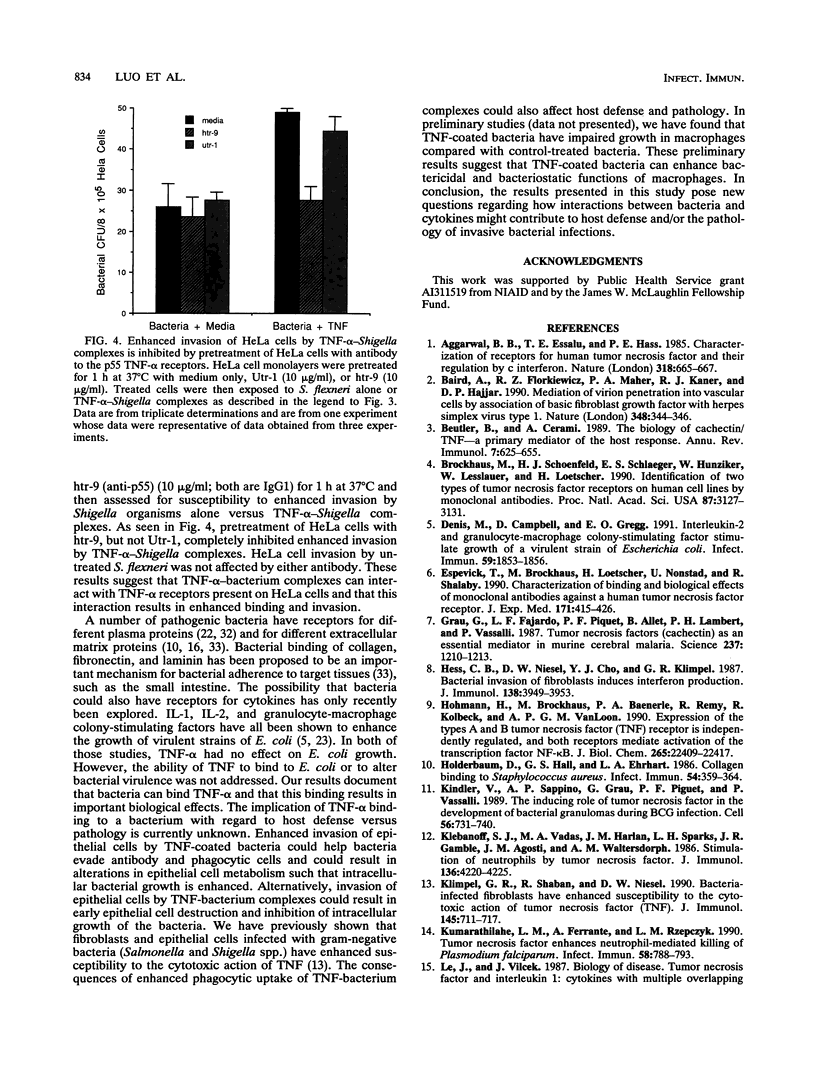
Human and murine receptors for tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) are present on most somatic cells and have been characterized and cloned. In contrast, very little is currently known about whether TNF-alpha can bind to pathogens and whether such binding results in important biological consequences for the infected host. We now report that a number of gram-negative bacteria have receptors for TNF-alpha. Using 125I-labeled TNF-alpha, we show that Shigella flexneri has 276 receptors for TNF-alpha, with a Kd of 2.5 nM. The binding of labeled TNF-alpha to these bacterial receptors can be inhibited by cold TNF-alpha but not by cold TNF-beta. Binding of 125I-TNF-alpha to S. flexneri was inhibited by trypsin treatment of bacterial cells or incubation at 52 degrees C for 3 min. Monoclonal antibody to either the 55-kDa or the 75-kDa TNF-alpha receptor, which are present on different eukaryotic cells, had no effect on 125I-TNF-alpha binding to bacteria. A number of gram-negative bacteria were capable of binding 125I-TNF-alpha. Gram-positive bacteria bound significantly less 125I-TNF-alpha than gram-negative bacteria. Pretreatment of S. flexneri with TNF-alpha resulted in enhanced bacterial invasion of HeLa cells and enhanced uptake by human and murine macrophages. Pretreatment of HeLa cells with antibody to the 55-kDa TNF-alpha receptor abrogated enhanced invasion of HeLa cells by TNF-alpha-bacterium complexes. These results suggest that TNF-alpha-bacterium complexes can interact with TNF-alpha receptors present on eukaryotic cells. This report shows that gram-negative bacteria have receptors for TNF-alpha and that a virulence property of a bacterium is altered as a consequence of cytokine binding.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal B. B., Eessalu T. E., Hass P. E. Characterization of receptors for human tumour necrosis factor and their regulation by gamma-interferon. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):665–667. doi: 10.1038/318665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Florkiewicz R. Z., Maher P. A., Kaner R. J., Hajjar D. P. Mediation of virion penetration into vascular cells by association of basic fibroblast growth factor with herpes simplex virus type 1. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):344–346. doi: 10.1038/348344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockhaus M., Schoenfeld H. J., Schlaeger E. J., Hunziker W., Lesslauer W., Loetscher H. Identification of two types of tumor necrosis factor receptors on human cell lines by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3127–3131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Campbell D., Gregg E. O. Interleukin-2 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulate growth of a virulent strain of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1853–1856. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1853-1856.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Brockhaus M., Loetscher H., Nonstad U., Shalaby R. Characterization of binding and biological effects of monoclonal antibodies against a human tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Exp Med. 1990 Feb 1;171(2):415–426. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Fajardo L. F., Piguet P. F., Allet B., Lambert P. H., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) as an essential mediator in murine cerebral malaria. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1210–1212. doi: 10.1126/science.3306918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess C. B., Niesel D. W., Cho Y. J., Klimpel G. R. Bacterial invasion of fibroblasts induces interferon production. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3949–3953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann H. P., Brockhaus M., Baeuerle P. A., Remy R., Kolbeck R., van Loon A. P. Expression of the types A and B tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors is independently regulated, and both receptors mediate activation of the transcription factor NF-kappa B. TNF alpha is not needed for induction of a biological effect via TNF receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22409–22417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holderbaum D., Hall G. S., Ehrhart L. A. Collagen binding to Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):359–364. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.359-364.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A., Harlan J. M., Sparks L. H., Gamble J. R., Agosti J. M., Waltersdorph A. M. Stimulation of neutrophils by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4220–4225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel G. R., Shaban R., Niesel D. W. Bacteria-infected fibroblasts have enhanced susceptibility to the cytotoxic action of tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):711–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumaratilake L. M., Ferrante A., Rzepczyk C. M. Tumor necrosis factor enhances neutrophil-mediated killing of Plasmodium falciparum. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):788–793. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.788-793.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J. D., dos Reis M., Brentani R. R. Presence of laminin receptors in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.3160113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxey-Mims M. M., Simms H. H., Frank M. M., Lin E. Y., Gaither T. A. The effects of IL-1, IL-2, and tumor necrosis factor on polymorphonuclear leukocyte Fc gamma receptor-mediated phagocytosis. IL-2 down-regulates the effect of tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1823–1830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kato K. Endogenous tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is essential to host resistance against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2563–2569. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2563-2569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niesel D. W., Hess C. B., Cho Y. J., Klimpel K. D., Klimpel G. R. Natural and recombinant interferons inhibit epithelial cell invasion by Shigella spp. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):828–833. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.828-833.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen-Schaub L. B., Crump W. L., 3rd, Morin G. I., Grimm E. A. Regulation of lymphocyte tumor necrosis factor receptors by IL-2. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2236–2241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padda J. S., Schryvers A. B. N-linked oligosaccharides of human transferrin are not required for binding to bacterial transferrin receptors. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2972–2976. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2972-2976.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porat R., Clark B. D., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Enhancement of growth of virulent strains of Escherichia coli by interleukin-1. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):430–432. doi: 10.1126/science.1833820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Involvement of a plasmid in the invasive ability of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.852-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall T. J., Lewis M., Koller K. J., Lee A., Rice G. C., Wong G. H., Gatanaga T., Granger G. A., Lentz R., Raab H. Molecular cloning and expression of a receptor for human tumor necrosis factor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90816-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor exerts endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine control of inflammatory responses. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1269–1277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Davis T., Anderson D., Solam L., Beckmann M. P., Jerzy R., Dower S. K., Cosman D., Goodwin R. G. A receptor for tumor necrosis factor defines an unusual family of cellular and viral proteins. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1019–1023. doi: 10.1126/science.2160731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart C. A. Phylogenetic distance from man correlates with immunologic cross-reactivity among liver insulin receptors. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1986;84(2):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(86)90200-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Weber R. F., Figari I. S., Reynolds C., Palladino M. A., Jr, Goeddel D. V. The two different receptors for tumor necrosis factor mediate distinct cellular responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9292–9296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treseler C. B., Maziarz R. T., Levitz S. M. Biological activity of interleukin-2 bound to Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):183–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.183-188.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullberg M., Kronvall G., Karlsson I., Wiman B. Receptors for human plasminogen on gram-negative bacteria. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):21–25. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.21-25.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visai L., Speziale P., Bozzini S. Binding of collagens to an enterotoxigenic strain of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):449–455. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.449-455.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


