Abstract
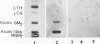
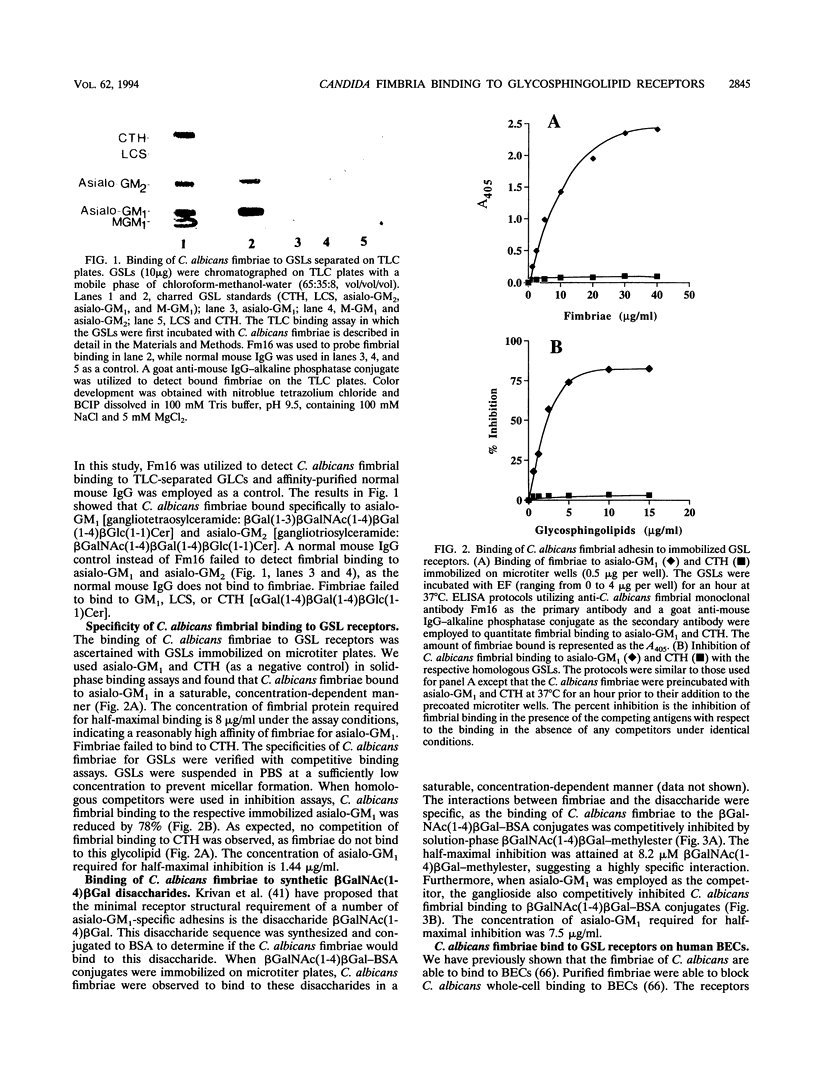
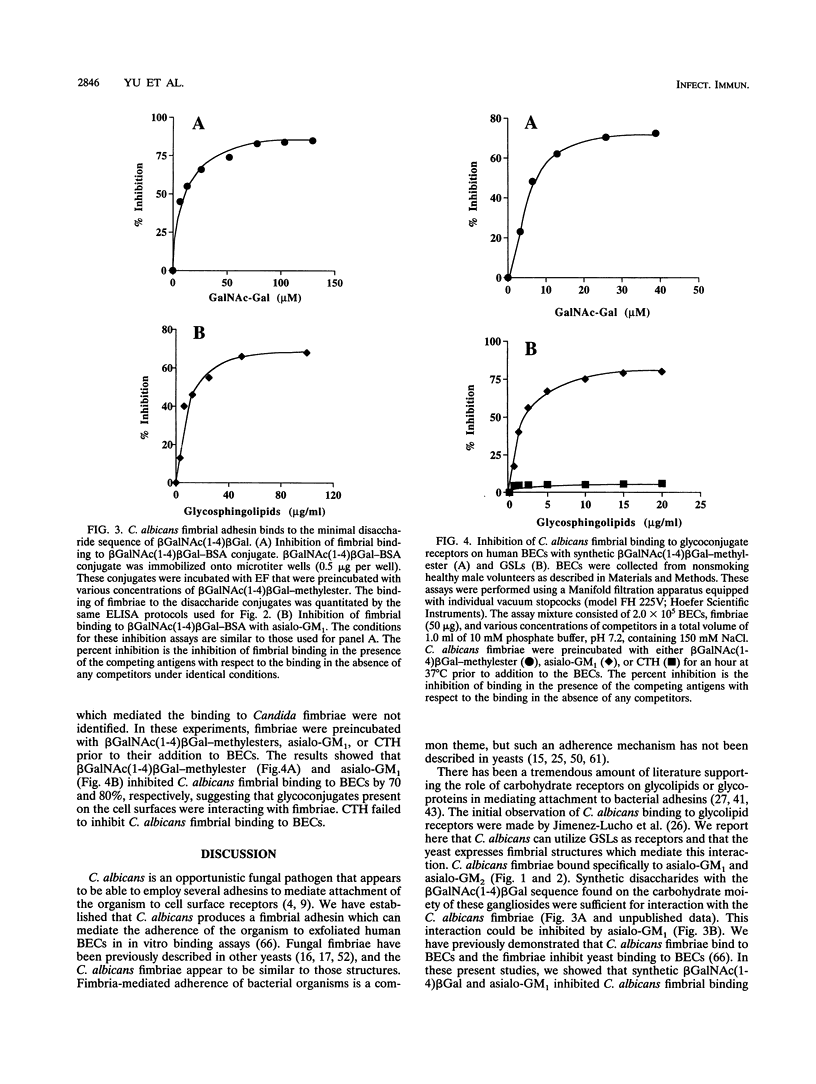
Candida albicans is an opportunist fungal pathogen that has the ability to adhere to host cell surface receptors via a number of adhesins. Yu et al. (L. Yu, K. K. Lee, K. Ens, P. C. Doig, M. R. Carpenter, W. Staddon, R. S. Hodges, W. Paranchych, and R. T. Irvin, Infect. Immun. 62:2834-2842, 1994) described the purification and initial characterization of a fimbrial adhesin from C. albicans. In this paper, we show that C. albicans fimbriae also bind to asialo-GM1 [gangliotetraosylceramide: beta Gal(1-3)beta GalNAc(1-4) beta Gal(1-4)beta Glc(1-1)Cer] immobilized on microtiter plates in a saturable and concentration-dependent manner. C. albicans fimbrial binding to exfoliated human buccal epithelial cells (BECs) was inhibited by asialo-GM1 in in vitro binding assays. The fimbriae interact with the glycosphingolipid receptors via the carbohydrate portion of the receptors, since fimbriae were observed to bind to synthetic beta GalNAc(1-4)beta Gal-protein conjugates and the disaccharide was able to inhibit binding of fimbriae to BECs in in vitro binding assays. We conclude from these results that the C. albicans yeast form expresses a fimbrial adhesin that binds to glycosphingolipids displayed on the surface of human BECs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker N. R., Minor V., Deal C., Shahrabadi M. S., Simpson D. A., Woods D. E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S is an adhesion. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2859–2863. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2859-2863.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg M., Rüchel R. Expression of extracellular acid proteinase by proteolytic Candida spp. during experimental infection of oral mucosa. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):626–631. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.626-631.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawner D. L., Cutler J. E. Variability in expression of cell surface antigens of Candida albicans during morphogenesis. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):337–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.337-343.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R. A., Braun P. C. Adherence and receptor relationships of Candida albicans. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):1–20. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.1-20.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova M., Lopez-Ribot J. L., Monteagudo C., Llombart-Bosch A., Sentandreu R., Martinez J. P. Identification of a 58-kilodalton cell surface fibrinogen-binding mannoprotein from Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4221–4229. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4221-4229.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centeno A., Davis C. P., Cohen M. S., Warren M. M. Modulation of Candida albicans attachment to human epithelial cells by bacteria and carbohydrates. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1354–1360. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1354-1360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins-Lech C., Kalbfleisch J. H., Franson T. R., Sohnle P. G. Inhibition by sugars of Candida albicans adherence to human buccal mucosal cells and corneocytes in vitro. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):831–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.831-834.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley I. A., Douglas L. J. Isolation and partial characterization of an adhesin from Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):629–636. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E. Putative virulence factors of Candida albicans. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:187–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas L. J. Adhesion of Candida species to epithelial surfaces. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;15(1):27–43. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. E., Jr, Mayer C. L., Filler S. G., Wadsworth E., Calderone R. A. Cell extracts of Candida albicans block adherence of the organisms to endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3087–3091. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3087-3091.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghannoum M. A., Burns G. R., Elteen K. A., Radwan S. S. Experimental evidence for the role of lipids in adherence of Candida spp. to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):189–193. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.189-193.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghannoum M., Abu Elteen K. Correlative relationship between proteinase production, adherence and pathogenicity of various strains of Candida albicans. J Med Vet Mycol. 1986 Oct;24(5):407–413. doi: 10.1080/02681218680000621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson K. S., Vercellotti G. M., Bendel C. M., Hostetter M. K. Molecular mimicry in Candida albicans. Role of an integrin analogue in adhesion of the yeast to human endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):1896–1902. doi: 10.1172/JCI115214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen K. C., Brawner D. L., Riesselman M. H., Jutila M. A., Cutler J. E. Differential adherence of hydrophobic and hydrophilic Candida albicans yeast cells to mouse tissues. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):907–912. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.907-912.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen K. C., Lay J. G., Hazen B. W., Fu R. C., Murthy S. Partial biochemical characterization of cell surface hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3469–3476. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3469-3476.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen K. C. Participation of yeast cell surface hydrophobicity in adherence of Candida albicans to human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1894–1900. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1894-1900.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez-Lucho V., Ginsburg V., Krivan H. C. Cryptococcus neoformans, Candida albicans, and other fungi bind specifically to the glycosphingolipid lactosylceramide (Gal beta 1-4Glc beta 1-1Cer), a possible adhesion receptor for yeasts. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2085–2090. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2085-2090.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K. A. Animal glycosphingolipids as membrane attachment sites for bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:309–350. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.001521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearns M. J., Davies P., Smith H. Variability of the adherence of Candida albicans strains to human buccal epithelial cells: inconsistency of differences between strains related to virulence. Sabouraudia. 1983 Jun;21(2):93–98. doi: 10.1080/00362178385380161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. J., Rogers A. L., Hanselmen L. R., Soll D. R., Yancey R. J., Jr Variation in adhesion and cell surface hydrophobicity in Candida albicans white and opaque phenotypes. Mycopathologia. 1988 Jun;102(3):149–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00437397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. J., Rogers A. L., Yancey R. J., Jr Environmental alteration and phenotypic regulation of Candida albicans adhesion to plastic. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3876–3881. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3876-3881.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. J., Volz P. A. Ecology of Candida albicans gut colonization: inhibition of Candida adhesion, colonization, and dissemination from the gastrointestinal tract by bacterial antagonism. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):654–663. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.654-663.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura L. H., Pearsall N. N. Adherence of Candida albicans to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):64–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.64-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura L. H., Pearsall N. N. Relationship between germination of Candida albicans and increased adherence to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):464–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.464-468.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. D., Lee J. C., Morris A. L. Adherence of Candida albicans and other Candida species to mucosal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):667–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.667-674.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A. Adherence of Candida albicans to components of the subendothelial extracellular matrix. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Mar 15;56(3):249–254. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1097(05)80049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A., Drutz D. J., Harrison J. L., Huppert M. Adherence and penetration of vascular endothelium by Candida yeasts. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):374–384. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.374-384.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A. Fungal adherence to the vascular compartment: a critical step in the pathogenesis of disseminated candidiasis. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):340–347. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A., Smith R. L. A fibronectin receptor on Candida albicans mediates adherence of the fungus to extracellular matrix. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):604–610. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivan H. C., Roberts D. D., Ginsburg V. Many pulmonary pathogenic bacteria bind specifically to the carbohydrate sequence GalNAc beta 1-4Gal found in some glycolipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6157–6161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., King R. D. Characterization of Candida albicans adherence to human vaginal epithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1024–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1024-1030.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Gibbons R. J. Suppression of Candida albicans by human oral streptococci in gnotobiotic mice. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):846–849. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.846-849.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisch P. A., Calderone R. A. Adherence of Candida albicans to a fibrin-platelet matrix formed in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):650–656. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.650-656.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer C. L., Filler S. G., Edwards J. E., Jr Candida albicans adherence to endothelial cells. Microvasc Res. 1992 Mar;43(2):218–226. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(92)90018-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCourtie J., Douglas L. J. Extracellular polymer of Candida albicans: isolation, analysis and role in adhesion. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Mar;131(3):495–503. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-3-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCourtie J., Douglas L. J. Relationship between cell surface composition of Candida albicans and adherence to acrylic after growth on different carbon sources. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1234–1241. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1234-1241.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paranchych W., Frost L. S. The physiology and biochemistry of pili. Adv Microb Physiol. 1988;29:53–114. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persi M. A., Burnham J. C., Duhring J. L. Effects of carbon dioxide and pH on adhesion of Candida albicans to vaginal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):82–90. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.82-90.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon N. H., Day A. W. Fungal fimbriae. I. Structure, origin, and synthesis. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Apr;21(4):537–546. doi: 10.1139/m75-076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. L., Digre K. B., Payne C. D. Adherence of Candida species to human epidermal corneocytes and buccal mucosal cells: correlation with cutaneous pathogenicity. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Jul;83(1):37–41. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12261661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. L., Payne C. D. Scanning electron microscopy of epidermal adherence and cavitation in murine candidiasis: a role for Candida acid proteinase. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1942–1949. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1942-1949.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Calderone R. A., Edwards J. E., Jr Adherence of Candida species to host tissues and plastic surfaces. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jan-Feb;8(1):73–85. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Edwards J. E., Jr, Gibson T. R., Moore J. C., Cohen A. H., Green I. Adherence of Candida to cultured vascular endothelial cells: mechanisms of attachment and endothelial cell penetration. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1264–1274. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandin R. L., Rogers A. L., Beneke E. S., Fernandez M. I. Influence of mucosal cell origin on the in vitro adherence of Candida albicans: are mucosal cells from different sources equivalent? Mycopathologia. 1987 May;98(2):111–119. doi: 10.1007/BF00437297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Savage D. C. Adhesion of Candida albicans to mouse intestinal mucosa in vitro: development of the assay and test of inhibitors. J Med Vet Mycol. 1986 Dec;24(6):477–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D., Myers P. G., Kaye D., Levison M. E. Adherence of Candida albicans to human vaginal and buccal epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jan;143(1):76–82. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon W., Todd T., Irvin R. T. Equilibrium analysis of binding of Candida albicans to human buccal epithelial cells. Can J Microbiol. 1990 May;36(5):336–340. doi: 10.1139/m90-058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosh F. D., Douglas L. J. Characterization of a fucoside-binding adhesin of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4734–4739. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4734-4739.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L., Lee K. K., Ens K., Doig P. C., Carpenter M. R., Staddon W., Hodges R. S., Paranchych W., Irvin R. T. Partial characterization of a Candida albicans fimbrial adhesin. Infect Immun. 1994 Jul;62(7):2834–2842. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.7.2834-2842.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]