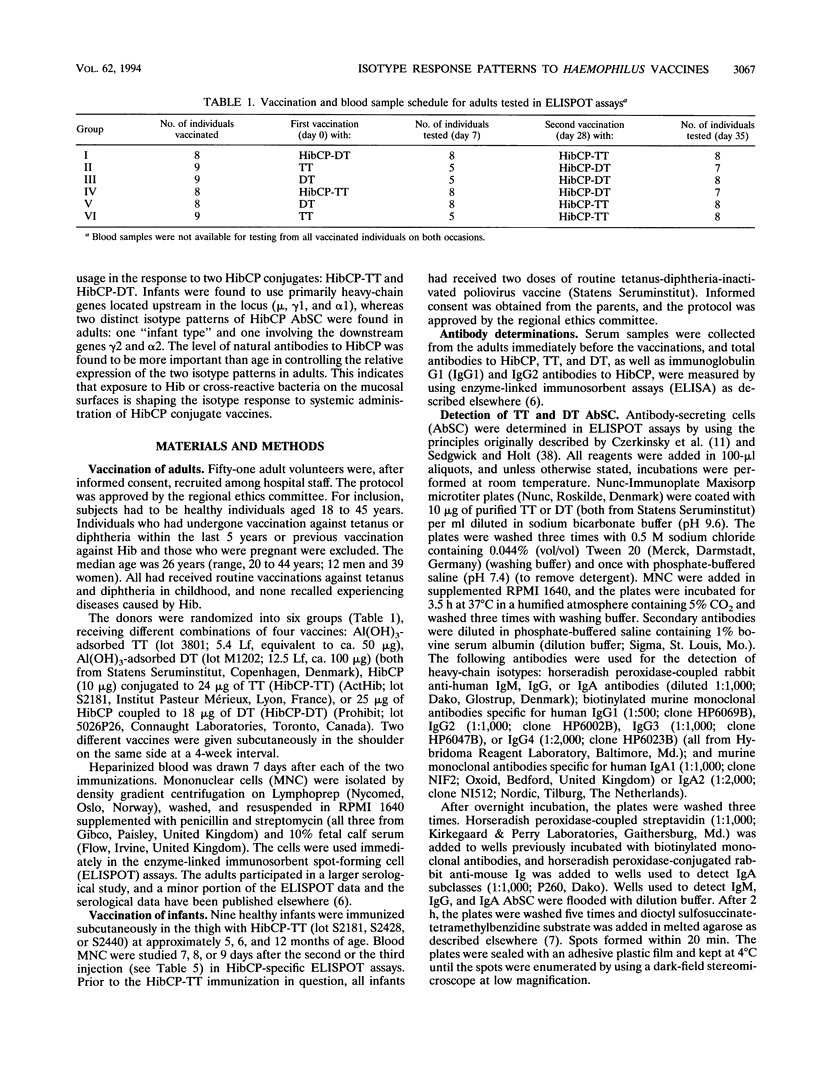
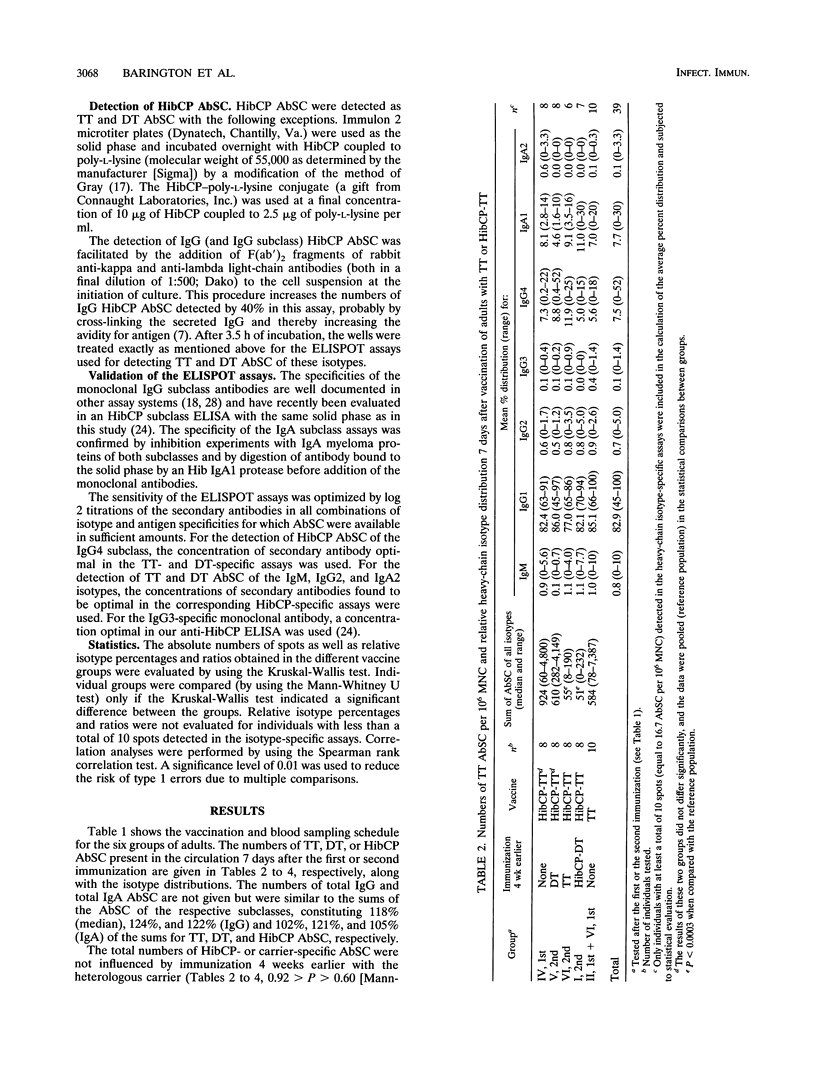
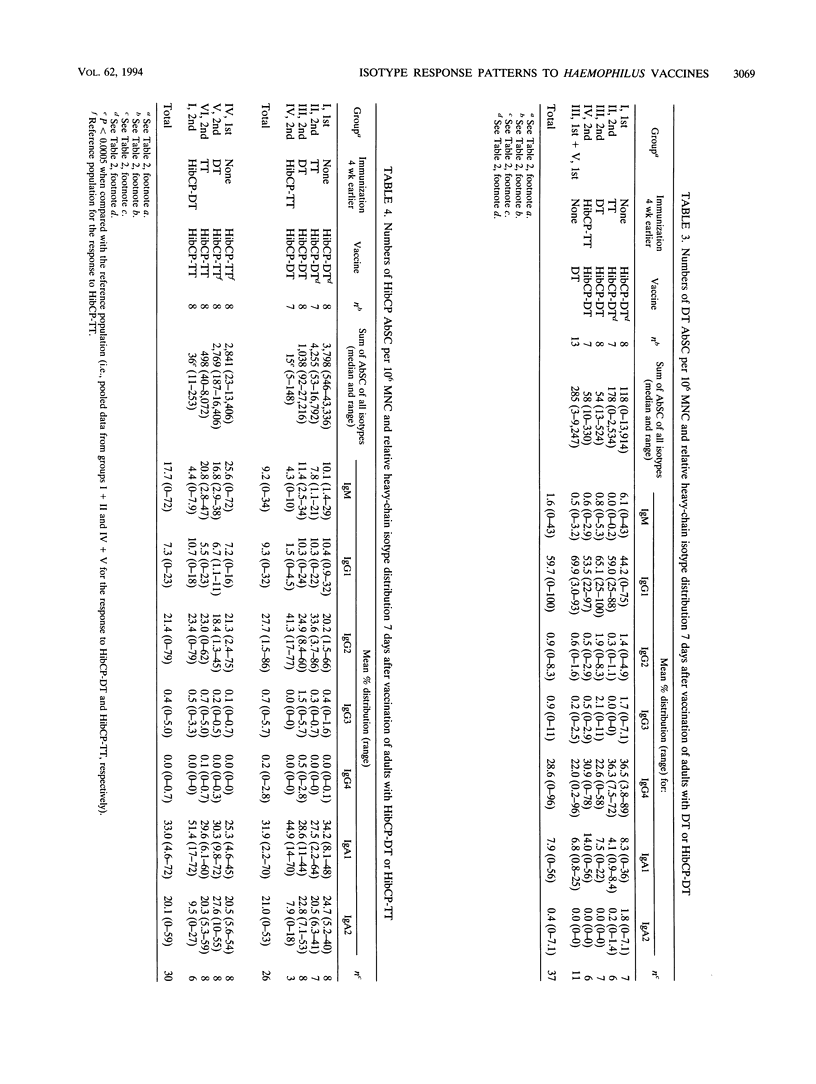
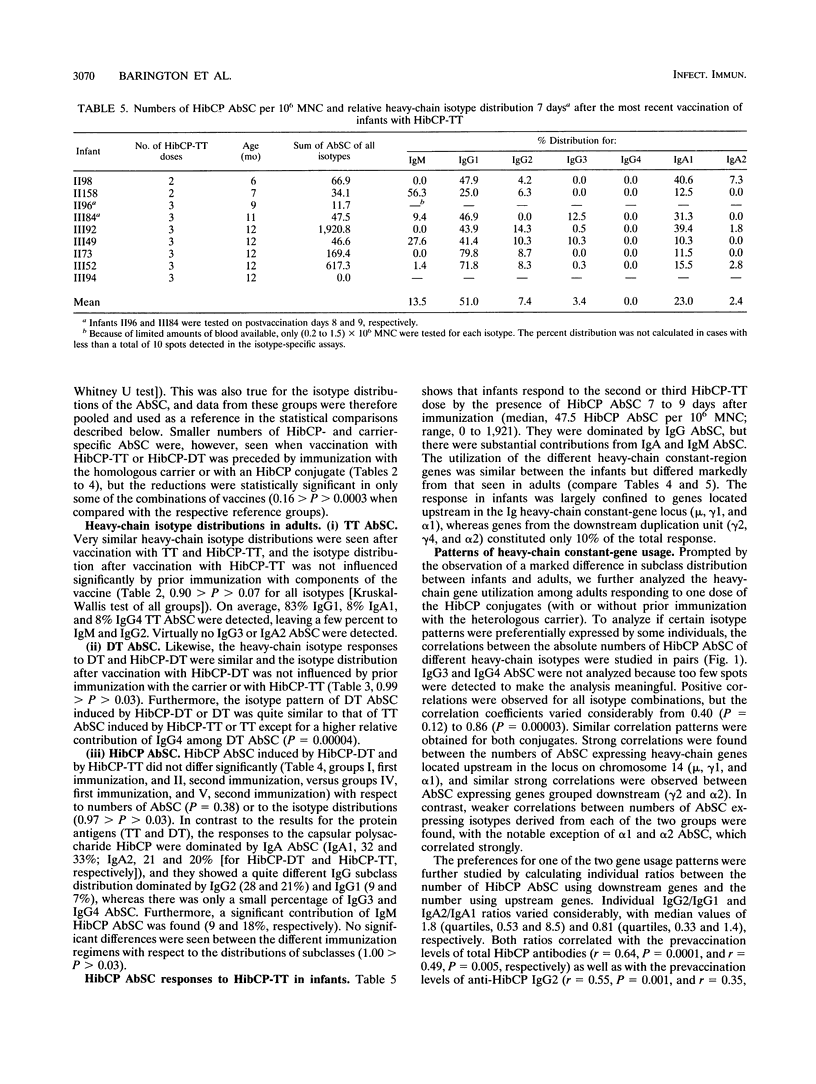
Abstract
The influence of preexisting immunity on the heavy-chain isotypes of circulating antibody-secreting cells (AbSC) induced by vaccination with Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) capsular polysaccharide (HibCP) coupled to tetanus toxoid (TT) or diphtheria toxoid (DT) and by vaccination with TT or DT alone in 51 healthy adults and 9 infants was studied. In adults, the isotypes of TT and DT AbSC were dominated by immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) followed by IgG4 and IgA1. HibCP AbSC were dominated by the isotype IgA1 followed by (in decreasing order) IgG2, IgA2, IgM, and IgG1. The isotype distributions of TT and DT AbSC were independent of whether the toxoids were coupled to HibCP, and the isotypes of HibCP AbSC were not influenced by the nature of the carrier (TT or DT). Furthermore, the isotype distributions were unaffected by recent immunization with components of the conjugates, although this reduced the numbers of AbSC. The heavy-chain gene usage of HibCP AbSC in adults differed clearly from that in infants, which was restricted largely to the genes mu, gamma 1, and alpha 1, all lying upstream in the heavy-chain constant-region gene locus, while the usage in adults also, to different extents, involved the downstream genes gamma 2 and alpha 2. The ratio between the numbers of HibCP AbSC using heavy-chain genes from the downstream duplication unit (gamma 2, gamma 4, and alpha 2) and those using genes from the upstream duplication unit (gamma 3, gamma 1, and alpha 1) correlated with the preimmunization level of natural HibCP antibodies (r = 0.59; P = 0.00002). A possible role of natural exposure for Hib or cross-reactive bacteria on the mucosal surfaces in the shaping of the isotype response to HibCP conjugate vaccines is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amir J., Scott M. G., Nahm M. H., Granoff D. M. Bactericidal and opsonic activity of IgG1 and IgG2 anticapsular antibodies to Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):163–171. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Pichichero M., Edwards K., Porch C. R., Insel R. Priming and induction of Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular antibodies in early infancy by Dpo20, an oligosaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine. J Pediatr. 1987 Nov;111(5):644–650. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80237-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barington T., Gyhrs A., Kristensen K., Heilmann C. Opposite effects of actively and passively acquired immunity to the carrier on responses of human infants to a Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine. Infect Immun. 1994 Jan;62(1):9–14. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.1.9-14.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barington T., Heilmann C., Andersen V. Quantitation of antibody-secreting cells in the blood after vaccination with Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Apr;31(4):515–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barington T., Kristensen K., Henrichsen J., Heilmann C. Influence of prevaccination immunity on the human B-lymphocyte response to a Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1057–1064. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1057-1064.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barington T., Skettrup M., Juul L., Heilmann C. Non-epitope-specific suppression of the antibody response to Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccines by preimmunization with vaccine components. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):432–438. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.432-438.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barington T., Sparholt S., Juul L., Heilmann C. A simplification of the enzyme-linked immunospot technique. Increased sensitivity for cells secreting IgG antibodies to Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Dec 8;156(2):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90025-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerke K., Brandtzaeg P. Terminally differentiated human intestinal B cells. IgA and IgG subclass-producing immunocytes in the distal ileum, including Peyer's patches, compared with lymph nodes and palatine tonsils. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Aug;32(2):61–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson B. A., Schneerson R., Robbins J. B., Johansson J., Lagergard T., Taranger J., Bryla D., Levi L., Cramton T., Trollfors B. Protective levels of serum antibodies stimulated in infants by two injections of Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugate. J Pediatr. 1989 Jan;114(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(89)80611-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson B. A., Trollfors B., Lagergard T., Taranger J., Bryla D., Otterman G., Cramton T., Yang Y., Reimer C. B., Robbins J. B. Clinical and immunologic responses to the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b alone or conjugated to tetanus toxoid in 18- to 23-month-old children. J Pediatr. 1988 May;112(5):695–702. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80684-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C. C., Nilsson L. A., Nygren H., Ouchterlony O., Tarkowski A. A solid-phase enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay for enumeration of specific antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn M. S., Weinberg G. A., Anderson E. L., Granoff P. D., Granoff D. M. Immunogenicity in infants of Haemophilus influenzae type B polysaccharide in a conjugate vaccine with Neisseria meningitidis outer-membrane protein. Lancet. 1986 Aug 9;2(8502):299–302. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eskola J., Käyhty H., Peltola H., Karanko V., Mäkelä P. H., Samuelson J., Gordon L. K. Antibody levels achieved in infants by course of Haemophilus influenzae type B polysaccharide/diphtheria toxoid conjugate vaccine. Lancet. 1985 May 25;1(8439):1184–1186. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92863-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Rabbitts T. H. Arrangement of human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes implies evolutionary duplication of a segment containing gamma, epsilon and alpha genes. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):709–713. doi: 10.1038/300709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Rathore M. H., Holmes S. J., Granoff P. D., Lucas A. H. Effect of immunity to the carrier protein on antibody responses to Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccines. Vaccine. 1993;11 (Suppl 1):S46–S51. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(93)90160-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Weinberg G. A., Shackelford P. G. IgG subclass response to immunization with Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-outer membrane protein conjugate vaccine. Pediatr Res. 1988 Aug;24(2):180–185. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198808000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray B. M. ELISA methodology for polysaccharide antigens: protein coupling of polysaccharides for adsorption to plastic tubes. J Immunol Methods. 1979;28(1-2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90340-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. G., Morrison S. L. Epitope mapping of human immunoglobulin-specific murine monoclonal antibodies with domain-switched, deleted and point-mutated chimeric antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Jan 14;158(1):107–122. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., Mellstedt H., Persson M. A., Smith C. I., Ahre A. IgA subclass distribution in paraproteinemias: suggestion of an IgG-IgA subclass switch pattern. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1984 Aug;92(4):207–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb00076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., Persson M. A., Smith C. I. Subclass distribution of human anti-Staphylococcus aureus alpha toxin antibodies: suggestion of an IgG1, IgA1, IgG4 switch pattern. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Sep;20(3):247–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handzel Z. T., Argaman M., Parke J. C., Jr, Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. Heteroimmunization to the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b induced by enteric cross-reacting bacteria. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1045–1052. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1045-1052.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmann C., Barington T., Sigsgaard T. Subclass of individual IgA-secreting human lymphocytes. Investigation of in vivo pneumococcal polysaccharide-induced and in vitro mitogen-induced blood B cells by monolayer plaque-forming cell assays. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1496–1499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmann C., Henrichsen J., Pedersen F. K. Vaccination-induced circulation of human B cells secreting type-specific antibodies against pneumococcal polysaccharides. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Jan;25(1):61–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb01047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann D. J., Hamilton R. G., Barington T., Frasch C. E., Arakere G., Mäkelä O., Mitchell L. A., Nagel J., Rijkers G. T., Zegers B. Quantitation of human IgG subclass antibodies to Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide. Results of an international collaborative study using enzyme immunoassay methodology. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Apr 8;148(1-2):101–114. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90163-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel R. A., Anderson P. W. IgG subclass distribution of antibody induced by immunization with the isolated and protein-conjugated polysaccharide of H. influenzae b and G2m(n) distribution of serum IgG2 in man. Monogr Allergy. 1988;23:128–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasato T., Arakawa H., Shimizu A., Honjo T., Yamagishi H. Biased distribution of recombination sites within S regions upon immunoglobulin class switch recombination induced by transforming growth factor beta and lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1992 Jun 1;175(6):1539–1546. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.6.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis G. A., Griffiss J. M. Human IgA1 blockade of IgG-initiated lysis of Neisseria meningitidis is a function of antigen-binding fragment binding to the polysaccharide capsule. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1962–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Mestecky J., Russell M. W. Defense mechanisms involving Fc-dependent functions of immunoglobulin A and their subversion by bacterial immunoglobulin A proteases. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):296–303. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.296-303.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagergård T., Thiringer K., Wassén L., Schneerson R., Trollfors B. Isotype composition of antibodies to streptococcus group B type III polysaccharide and to tetanus toxoid in maternal, cord blood sera and in breast milk. Eur J Pediatr. 1992 Feb;151(2):98–102. doi: 10.1007/BF01958951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebman D. A., Coffman R. L. Interleukin 4 causes isotype switching to IgE in T cell-stimulated clonal B cell cultures. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):853–862. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J. The common mucosal immune system and current strategies for induction of immune responses in external secretions. J Clin Immunol. 1987 Jul;7(4):265–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00915547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills F. C., Thyphronitis G., Finkelman F. D., Max E. E. Ig mu-epsilon isotype switch in IL-4-treated human B lymphoblastoid cells. Evidence for a sequential switch. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 1;149(3):1075–1085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rautonen N., Pelkonen J., Sipinen S., Käyhty H., Mäkelä O. Isotype concentrations of human antibodies to group A meningococcal polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2670–2675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Barrera O., Sutton A., Robbins J. B. Preparation, characterization, and immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-protein conjugates. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):361–376. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. Induction of serum Haemophilus influenzae type B capsular antibodies in adult volunteers fed cross-reacting Escherichia coli 075:K100:H5. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 22;292(21):1093–1096. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505222922103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber J. R., Barrus V., Cates K. L., Siber G. R. Functional characterization of human IgG, IgM, and IgA antibody directed to the capsule of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):8–16. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick J. D., Holt P. G. A solid-phase immunoenzymatic technique for the enumeration of specific antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Feb 25;57(1-3):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford P. G., Granoff D. M., Nelson S. J., Scott M. G., Smith D. S., Nahm M. H. Subclass distribution of human antibodies to Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):587–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Vercelli D., Jabara H. H., Fu S. M., Geha R. S. Molecular analysis of the induction of immunoglobulin E synthesis in human B cells by interleukin 4 and engagement of CD40 antigen. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):289–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sideras P., Nilsson L., Islam K. B., Quintana I. Z., Freihof L., Rosén A., Juliusson G., Hammarström L., Smith C. I. Transcription of unrearranged Ig H chain genes in human B cell malignancies. Biased expression of genes encoded within the first duplication unit of the Ig H chain locus. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 1;149(1):244–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. H., Macy E., Morrow C., Saxon A. Characterization of a circulating subpopulation of spontaneous antitetanus toxoid antibody producing B cells following in vivo booster immunization. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2498–2504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strober W. Regulation of IgA B-cell development in the mucosal immune system. J Clin Immunol. 1990 Nov;10(6 Suppl):56S–63S. doi: 10.1007/BF00918692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkowski A., Lue C., Moldoveanu Z., Kiyono H., McGhee J. R., Mestecky J. Immunization of humans with polysaccharide vaccines induces systemic, predominantly polymeric IgA2-subclass antibody responses. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):3770–3778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu L., Gorham B., Li S. C., Bottaro A., Alt F. W., Rothman P. Replacement of germ-line epsilon promoter by gene targeting alters control of immunoglobulin heavy chain class switching. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3705–3709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Vlasselaer P., Punnonen J., de Vries J. E. Transforming growth factor-beta directs IgA switching in human B cells. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2062–2067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


