Abstract
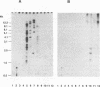
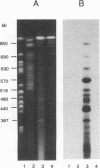
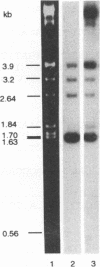
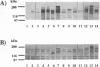
A 13-kb genomic fragment from human Pneumocystis carinii was cloned as repetitive DNA. The fragment contains a cluster of three related genes, each 3 kb in size, and the 5' end of a fourth gene. The predicted polypeptide of the first gene in the cluster comprises 1,030 amino acid residues with a total molecular mass of 116 kDa. The gene's predicted amino acid sequence bears 32% identity to predicted sequences of recently described gene fragments of ferret P. carinii, which encode an immunodominant surface glycoprotein (gpA) (P. J. Haidaris, T. W. Wright, F. Gigliotti, and C. G. Haidaris, J. Infect. Dis. 166:1113-1123, 1992), and 36% identity to the predicted sequence of a rat P. carinii major surface glycoprotein gene (msg) (J. A. Kovacs, F. Powell, J. C. Edman, B. Lundgren, A. Martinez, B. Drew, and C. W. Angus, J. Biol. Chem. 268:6034-6040). DNA hybridization showed that sequences related to the cloned msg genes reside on at least 12 chromosomes of human P. carinii at various degrees of multiplicity and/or homology. Affinity-purified antibodies with specificity to a fusion protein made from the human P. carinii msgI gene recognized two bands on a Western immunoblot containing total human P. carinii protein; they also recognized fusion proteins derived from the other two genes of the cluster. Monoclonal antibodies with reactivity to Msg of human P. carinii recognized fusion proteins produced from two msg genes. Fusion proteins were also recognized by sera from healthy humans and from patients. The msg genes are candidates for the development of immunotherapy and subunit vaccines for the treatment and prevention of P. carinii pneumonia.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall J. A., Mitchell G. F. Identification of a particular antigen from a parasite cDNA library using antibodies affinity purified from selected portions of Western blots. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Feb 12;86(2):217–223. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90456-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P. Molecular genetics of antigenic variation. Immunol Today. 1991 Mar;12(3):A29–A33. doi: 10.1016/S0167-5699(05)80009-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlind T. D., Bartlett M. S., Weinberg G. A., Prah G. N., Smith J. W. The beta-tubulin gene from rat and human isolates of Pneumocystis carinii. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(22):3365–3373. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Williams D. J., Koziel H., Armstrong M. Y., Warner A., Richards F. F., Rose R. M. Uptake of Pneumocystis carinii mediated by the macrophage mannose receptor. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):155–158. doi: 10.1038/351155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher L. D., Berger L. C., Peel S. A., Baric R. S., Tidwell R. R., Dykstra C. C. Isolation and identification of six Pneumocystis carinii genes utilizing codon bias. Gene. 1993 Jul 30;129(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90265-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbe T., Harris D., Vordermeier M., Lathigra R., Ivanyi J., Young D. Expression of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis 19-kilodalton antigen in Mycobacterium smegmatis: immunological analysis and evidence of glycosylation. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):260–267. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.260-267.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbe T., Jones C., Charles I., Dougan G., Young D. Cloning and characterization of the aroA gene from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6774–6782. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6774-6782.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel M. D., Pruitt R. E., Meyerowitz E. M. DNA sequences, gene regulation and modular protein evolution in the Drosophila 68C glue gene cluster. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 25;168(4):765–789. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Ballou L. R., Hughes W. T., Mosley B. D. Purification and initial characterization of a ferret Pneumocystis carinii surface antigen. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):848–854. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F. Host species-specific antigenic variation of a mannosylated surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1992 Feb;165(2):329–336. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Hughes W. T. Passive immunoprophylaxis with specific monoclonal antibody confers partial protection against Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in animal models. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1666–1668. doi: 10.1172/JCI113503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidaris P. J., Wright T. W., Gigliotti F., Haidaris C. G. Expression and characterization of a cDNA clone encoding an immunodominant surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1992 Nov;166(5):1113–1123. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.5.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. T., Steele P. E., Cushion M. T., Walzer P. D., Stringer S. L., Stringer J. R. Pneumocystis carinii karyotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1785–1795. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1785-1795.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iams K. P., Young J. R., Nene V., Desai J., Webster P., ole-MoiYoi O. K., Musoke A. J. Characterisation of the gene encoding a 104-kilodalton microneme-rhoptry protein of Theileria parva. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Feb;39(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Halpern J. L., Lundgren B., Swan J. C., Parrillo J. E., Masur H. Monoclonal antibodies to Pneumocystis carinii: identification of specific antigens and characterization of antigenic differences between rat and human isolates. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jan;159(1):60–70. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Powell F., Edman J. C., Lundgren B., Martinez A., Drew B., Angus C. W. Multiple genes encode the major surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):6034–6040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linke M. J., Cushion M. T., Walzer P. D. Properties of the major antigens of rat and human Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1547–1555. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1547-1555.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Leibowitz M. J. Variation and in vitro splicing of group I introns in rRNA genes of Pneumocystis carinii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2415–2421. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren B., Lebech M., Lind K., Nielsen J. O., Lundgren J. D. Antibody response to a major human Pneumocystis carinii surface antigen in patients without evidence of immunosuppression and in patients with suspected atypical pneumonia. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;12(2):105–109. doi: 10.1007/BF01967583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren B., Lipschik G. Y., Kovacs J. A. Purification and characterization of a major human Pneumocystis carinii surface antigen. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):163–170. doi: 10.1172/JCI114966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Lane H. C., Kovacs J. A., Allegra C. J., Edman J. C. NIH conference. Pneumocystis pneumonia: from bench to clinic. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Nov 15;111(10):813–826. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-111-10-813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen J. H., Tauber I., Leeuwenberg A. D., Beckers P. J., Sieben M. Parasitologic and serologic observations of infection with Pneumocystis in humans. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. F., Mills J. Pulmonary infectious complications of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Part II. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Jun;141(6):1582–1598. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.6.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. J., Spithill T. W. Variants of a Leishmania surface antigen derived from a multigenic family. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24477–24484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peglow S. L., Smulian A. G., Linke M. J., Pogue C. L., Nurre S., Crisler J., Phair J., Gold J. W., Armstrong D., Walzer P. D. Serologic responses to Pneumocystis carinii antigens in health and disease. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):296–306. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Stagno S., Woods D. Pneumocystis carinii infection: evidence for high prevalence in normal and immunosuppressed children. Pediatrics. 1978 Jan;61(1):35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pottratz S. T., Paulsrud J., Smith J. S., Martin W. J., 2nd Pneumocystis carinii attachment to cultured lung cells by pneumocystis gp 120, a fibronectin binding protein. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):403–407. doi: 10.1172/JCI115318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes M. B., Pollevick G. D., Frasch A. C. An unusually small gene encoding a putative mucin-like glycoprotein in Trypanosoma cruzi. Gene. 1994 Mar 11;140(1):139–140. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90745-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinehart F. P., Ritch T. G., Deininger P. L., Schmid C. W. Renaturation rate studies of a single family of interspersed repeated sequences in human deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3003–3010. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roths J. B., Sidman C. L. Single and combined humoral and cell-mediated immunotherapy of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in immunodeficient scid mice. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):1641–1649. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.1641-1649.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair K., Wakefield A. E., Banerji S., Hopkin J. M. Pneumocystis carinii organisms derived from rat and human hosts are genetically distinct. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Mar;45(1):183–184. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smulian A. G., Sullivan D. W., Linke M. J., Halsey N. A., Quinn T. C., MacPhail A. P., Hernandez-Avila M. A., Hong S. T., Walzer P. D. Geographic variation in the humoral response to Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1993 May;167(5):1243–1247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.5.1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer S. L., Garbe T., Sunkin S. M., Stringer J. R. Genes encoding antigenic surface glycoproteins in Pneumocystis from humans. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1993 Nov-Dec;40(6):821–826. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1993.tb04481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
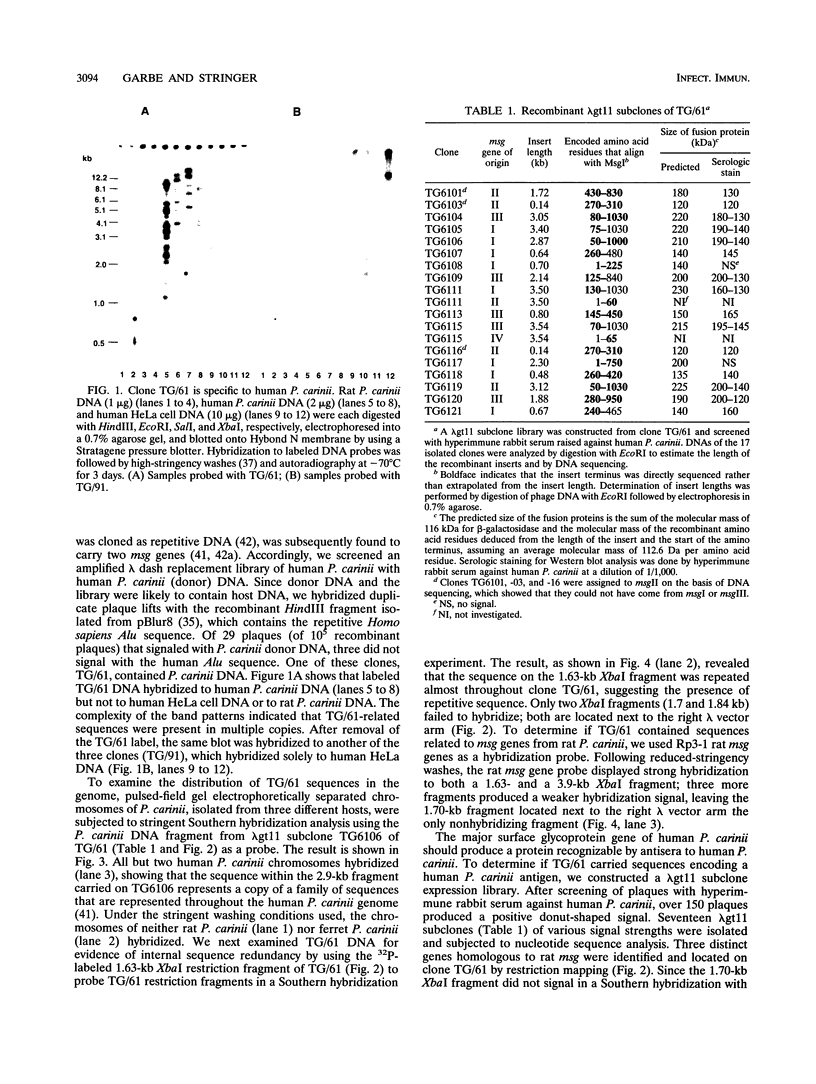
- Stringer S. L., Hong S. T., Giuntoli D., Stringer J. R. Repeated DNA in Pneumocystis carinii. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jun;29(6):1194–1201. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.6.1194-1201.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thole J. E., Schöningh R., Janson A. A., Garbe T., Cornelisse Y. E., Clark-Curtiss J. E., Kolk A. H., Ottenhoff T. H., De Vries R. R., Abou-Zeid C. Molecular and immunological analysis of a fibronectin-binding protein antigen secreted by Mycobacterium leprae. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jan;6(2):153–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada M., Kitada K., Saito M., Egawa K., Nakamura Y. cDNA sequence diversity and genomic clusters of major surface glycoprotein genes of Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1993 Oct;168(4):979–985. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.4.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Linke M. J. A comparison of the antigenic characteristics of rat and human Pneumocystis carinii by immunoblotting. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2257–2265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner C., Higashi G. I., Yates J. A., Rajan T. V. Differential recognition of two cloned Brugia malayi antigens by antibody class. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jul;35(3):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Cushion M. T., Stringer J. R. Molecular characterization of a novel repetitive element from Pneumocystis carinii from rats. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):244–248. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.244-248.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman P. E., Voelker D. R., McCormack F. X., Paulsrud J. R., Martin W. J., 2nd 120-kD surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii is a ligand for surfactant protein A. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):143–149. doi: 10.1172/JCI115554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]