Abstract
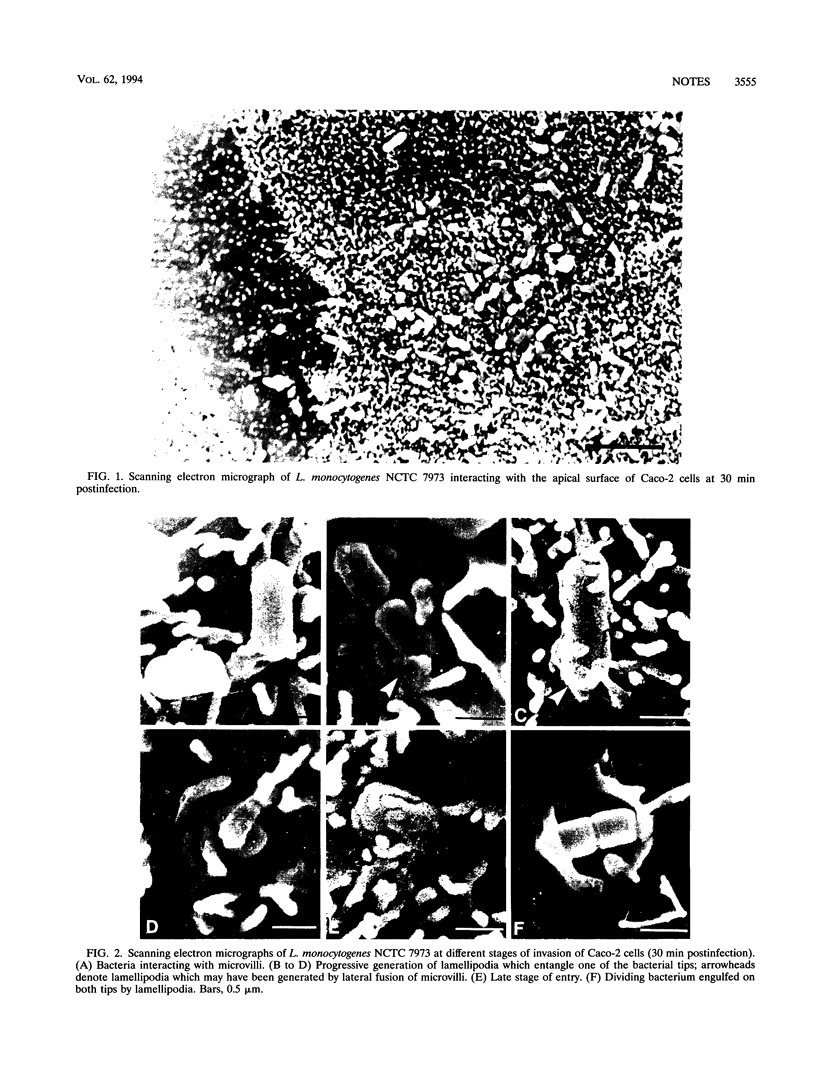
Evidence that Listeria monocytogenes enters Caco-2 cells through the apical surface is presented. Attachment of bacteria to host cells seems to induce modifications of microvilli which are either in direct contact with the bacterial surface or in close vicinity, resulting in the formation of lamellipodia involved in the cellular uptake of the bacteria. Such modifications are not induced by L. monocytogenes SLCC 53, which carries a deletion in the prfA gene, although attachment of this mutant to Caco-2 cells occurs. Listeria innocua does not attach well to Caco-2 cells and also fails to cause structural alterations of the microvilli. Treatment of confluent monolayers of Caco-2 cells with ethylene glycol-bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)- N,N,N1,N1-tetraacetic acid (EGTA), which disrupts intercellular junctions, greatly reduced the uptake of Listeria cells. Attachment and invasion of L. monocytogenes was not accompanied by accumulation of filamentous actin around the entering bacterial cell.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bliska J. B., Galán J. E., Falkow S. Signal transduction in the mammalian cell during bacterial attachment and entry. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):903–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90270-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundage R. A., Fogarty K. E., Tuft R. A., Fay F. S. Calcium gradients underlying polarization and chemotaxis of eosinophils. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):703–706. doi: 10.1126/science.1948048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P. L., Berthon B., Claret M., Sansonetti P. J. Internalization of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells occurs without an increase in cytosolic Ca2+ concentration. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2919–2922. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2919-2922.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M., Peterkin P. I. Listeria monocytogenes, a food-borne pathogen. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):476–511. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.476-511.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Salmonella interactions with polarized human intestinal Caco-2 epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1096–1106. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Gumbiner B., Falkow S. Penetration of Salmonella through a polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cell monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):221–230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karunasagar I., Krohne G., Goebel W. Listeria ivanovii is capable of cell-to-cell spread involving actin polymerization. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):162–169. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.162-169.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Haffner C., Domann E., Goebel W., Chakraborty T. Identification of a gene that positively regulates expression of listeriolysin, the major virulence factor of listeria monocytogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8336–8340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiser J., Molitoris B. A. Disease processes in epithelia: the role of the actin cytoskeleton and altered surface membrane polarity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Nov 25;1225(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(93)90115-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. W., Maxfield F. R. Local and global changes in cytosolic free calcium in neutrophils during chemotaxis and phagocytosis. Cell Calcium. 1990 Feb-Mar;11(2-3):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier J., Vasselon T., Hellio R., Lesourd M., Sansonetti P. J. Shigella flexneri enters human colonic Caco-2 epithelial cells through the basolateral pole. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):237–248. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.237-248.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenshine I., Finlay B. B. Exploitation of host signal transduction pathways and cytoskeletal functions by invasive bacteria. Bioessays. 1993 Jan;15(1):17–24. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruschkowski S., Rosenshine I., Finlay B. B. Salmonella typhimurium induces an inositol phosphate flux in infected epithelial cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Aug 15;74(2-3):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90416-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuchat A., Swaminathan B., Broome C. V. Epidemiology of human listeriosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Apr;4(2):169–183. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolovic Z., Riedel J., Wuenscher M., Goebel W. Surface-associated, PrfA-regulated proteins of Listeria monocytogenes synthesized under stress conditions. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Apr;8(2):219–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young V. B., Falkow S., Schoolnik G. K. The invasin protein of Yersinia enterocolitica: internalization of invasin-bearing bacteria by eukaryotic cells is associated with reorganization of the cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):197–207. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]