Abstract
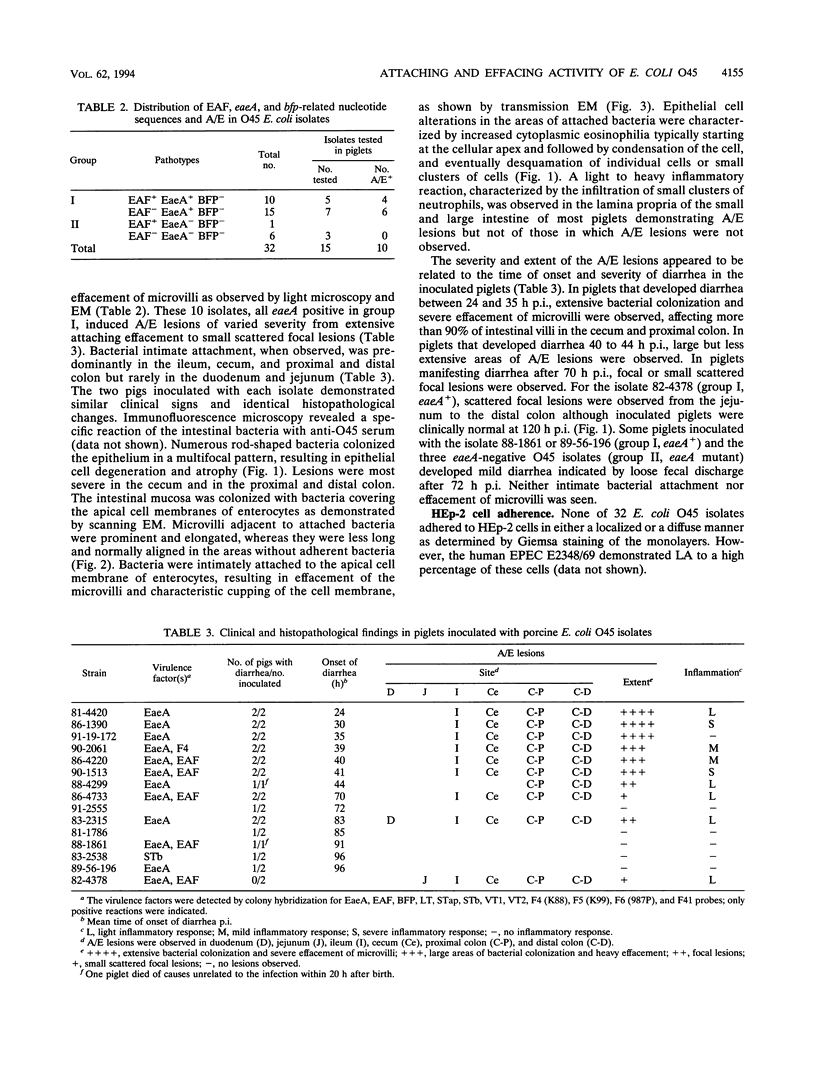
Escherichia coli O45 isolates associated with swine postweaning diarrhea in Québec were characterized with respect to virulence determinants genetically and investigated for their attaching and effacing (A/E) activities by experimental inoculation of gnotobiotic piglets and by the HEp-2 cell adherence assay. All of 32 isolates tested were negative for enterotoxigenic and verotoxigenic E. coli virulence determinants, heat-labile enterotoxin (LT), heat-stable enterotoxins (STap, STb), verotoxins (VT1, VT2), and F4 (K88), F5 (K99), F6 (987P), and F41, except one STb-positive and two F4-positive isolates. A total of 25 isolates hybridized with an EaeA probe, and 11 hybridized with an enteropathogenic E. coli adherence factor (EAF) probe. None of 32 isolates hybridized with a bundle-forming pilus (BFP) probe. The EAF, EaeA, and BFP factors have been associated with human enteropathogenic E. coli strains. A total of 10 of 12 eaeA-positive porcine O45 isolates induced A/E lesions characterized by intimate adherence of bacteria to the intestinal epithelial cell membrane with effacement of the microvilli, similar to those of human attaching-effacing E. coli. However, A/E lesions were not observed in the piglets inoculated with any one of three eaeA-negative O45 isolates. All E. coli O45 isolates were non-adherent to HEp-2 cells. Thus, we have demonstrated the production of typical A/E lesions by nonenterotoxigenic E. coli O45 isolates from swine postweaning diarrhea. The results indicate the significance of the eaeA gene in A/E activities of these isolates and suggest that EAF and BFP are not involved in O45 E. coli infection of weaning piglets.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin T. J., Brooks S. F., Knutton S., Manjarrez Hernandez H. A., Aitken A., Williams P. H. Protein phosphorylation by protein kinase C in HEp-2 cells infected with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):761–765. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.761-765.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. J., Ward W., Aitken A., Knutton S., Williams P. H. Elevation of intracellular free calcium levels in HEp-2 cells infected with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1599–1604. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1599-1604.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebakhee G., Louie M., De Azavedo J., Brunton J. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the eae gene homologue from enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli serotype O157:H7. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Feb 1;70(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90563-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broes A., Drolet R., Jacques M., Fairbrother J. M., Johnson W. M. Natural infection with an attaching and effacing Escherichia coli in a diarrheic puppy. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Apr;52(2):280–282. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broes A., Fairbrother J. M., Larivière S., Jacques M., Johnson W. M. Virulence properties of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli O8: KX105 strains isolated from diarrheic piglets. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):241–246. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.241-246.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broes A., Fairbrother J. M., Mainil J., Harel J., Lariviere S. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli serotype O8:KX105 and O8:K"2829" strains isolated from piglets with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2402–2409. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2402-2409.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., Blake R. K. Diarrhea due to Escherichia coli in the rabbit: a novel mechanism. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):454–462. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Calderwood S. B., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Kaper J. B. Construction and analysis of TnphoA mutants of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli unable to invade HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1565–1571. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1565-1571.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. Construction of an eae deletion mutant of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by using a positive-selection suicide vector. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4310–4317. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4310-4317.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):3953–3961. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.3953-3961.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Tzipori S., McKee M. L., O'Brien A. D., Alroy J., Kaper J. B. The role of the eae gene of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli in intimate attachment in vitro and in a porcine model. J Clin Invest. 1993 Sep;92(3):1418–1424. doi: 10.1172/JCI116718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Yu J., Kaper J. B. A second chromosomal gene necessary for intimate attachment of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to epithelial cells. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(15):4670–4680. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.15.4670-4680.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbrother J. M., Larivière S., Lallier R. New fimbrial antigen F165 from Escherichia coli serogroup O115 strains isolated from piglets with diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):10–15. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.10-15.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. H., Collins J. E., Duimstra J. R. Infection of gnotobiotic pigs with an Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain associated with an outbreak of hemorrhagic colitis. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):953–956. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.953-956.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon V. P., Gyles C. L., Friendship R. W. Characteristics of verotoxigenic Escherichia coli from pigs. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;52(3):331–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girón J. A., Donnenberg M. S., Martin W. C., Jarvis K. G., Kaper J. B. Distribution of the bundle-forming pilus structural gene (bfpA) among enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1993 Oct;168(4):1037–1041. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.4.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girón J. A., Ho A. S., Schoolnik G. K. An inducible bundle-forming pilus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):710–713. doi: 10.1126/science.1683004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. J., Rowe B. Escherichia coli diarrhoea. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Dec;95(3):531–550. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel J., Lapointe H., Fallara A., Lortie L. A., Bigras-Poulin M., Larivière S., Fairbrother J. M. Detection of genes for fimbrial antigens and enterotoxins associated with Escherichia coli serogroups isolated from pigs with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):745–752. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.745-752.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helie P., Morin M., Jacques M., Fairbrother J. M. Experimental infection of newborn pigs with an attaching and effacing Escherichia coli O45:K"E65" strain. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):814–821. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.814-821.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques M., Foiry B. Electron microscopic visualization of capsular material of Pasteurella multocida types A and D labeled with polycationic ferritin. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3470–3472. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3470-3472.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janke B. H., Francis D. H., Collins J. E., Libal M. C., Zeman D. H., Johnson D. D. Attaching and effacing Escherichia coli infections in calves, pigs, lambs, and dogs. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1989 Jan;1(1):6–11. doi: 10.1177/104063878900100104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Gicquelais K. G., Kaper J. B. Plasmid and chromosomal elements involved in the pathogenesis of attaching and effacing Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3869–3875. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3869-3875.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Kaper J. B. The eae gene of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli encodes a 94-kilodalton membrane protein, the expression of which is influenced by the EAF plasmid. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4302–4309. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4302-4309.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Yu J., Tall B. D., Kaper J. B. A genetic locus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli necessary for the production of attaching and effacing lesions on tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7839–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., McNeish A. S. Adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to human intestinal enterocytes and cultured human intestinal mucosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):69–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.69-77.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Edelman R. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of classic serotypes associated with infant diarrhea: epidemiology and pathogenesis. Epidemiol Rev. 1984;6:31–51. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nataro J. P., Karch H., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L., O'Brien A. D. The diarrheal response of humans to some classic serotypes of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is dependent on a plasmid encoding an enteroadhesiveness factor. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):550–559. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Prado V., Robins-Browne R., Lior H., Kaper J. B., Moseley S. L., Gicquelais K., Nataro J. P., Vial P., Tall B. Use of DNA probes and HEp-2 cell adherence assay to detect diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):224–228. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lortie L. A., Dubreuil J. D., Harel J. Characterization of Escherichia coli strains producing heat-stable enterotoxin b (STb) isolated from humans with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):656–659. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.656-659.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Argenzio R. A., Levine M. M., Giannella R. A. Attaching and effacing activities of rabbit and human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1340–1351. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1340-1351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxley R. A., Francis D. H. Natural and experimental infection with an attaching and effacing strain of Escherichia coli in calves. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):339–346. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.339-346.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B., Casey T. A., Moon H. W. Phenotype and genotype of Escherichia coli isolated from pigs with postweaning diarrhea in Hungary. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):651–653. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.651-653.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa M., Sugimoto C., Isayama Y., Kashiwazaki M. Virulence factors in Escherichia coli isolated from piglets with neonatal and post-weaning diarrhea in Japan. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Apr;13(4):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nataro J. P., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Bravo N., Levine M. M. Detection of an adherence factor of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with a DNA probe. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):560–565. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngeleka M., Jacques M., Martineau-Doizé B., Daigle F., Harel J., Fairbrother J. M. Pathogenicity of an Escherichia coli O115:K"V165" mutant negative for F165(1) fimbriae in septicemia of gnotobiotic pigs. Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):836–843. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.836-843.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I. Escherichia coli serotyping and disease in man and animals. Can J Microbiol. 1992 Jul;38(7):699–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters J. E., Pohl P., Okerman L., Devriese L. A. Pathogenic properties of Escherichia coli strains isolated from diarrheic commercial rabbits. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):34–39. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.34-39.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M. Traditional enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of infantile diarrhea. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):28–53. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenshine I., Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B., Finlay B. B. Signal transduction between enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) and epithelial cells: EPEC induces tyrosine phosphorylation of host cell proteins to initiate cytoskeletal rearrangement and bacterial uptake. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3551–3560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salajka E., Salajkova Z., Alexa P., Hornich M. Colonization factor different from K88, K99, F41 and 987P in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from postweaning diarrhoea in pigs. Vet Microbiol. 1992 Sep;32(2):163–175. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(92)90103-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaletsky I. C., Silva M. L., Trabulsi L. R. Distinctive patterns of adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):534–536. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.534-536.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer D. B., Falkow S. Attaching and effacing locus of a Citrobacter freundii biotype that causes transmissible murine colonic hyperplasia. Infect Immun. 1993 Jun;61(6):2486–2492. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.6.2486-2492.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., McCarthy B. J. Nucleotide sequence of the bacterial transposon Tn1681 encoding a heat-stable (ST) toxin and its identification in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4011–4015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Gibson R., Montanaro J. Nature and distribution of mucosal lesions associated with enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli in piglets and the role of plasmid-mediated factors. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1142–1150. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1142-1150.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Robins-Browne R. M., Gonis G., Hayes J., Withers M., McCartney E. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli enteritis: evaluation of the gnotobiotic piglet as a model of human infection. Gut. 1985 Jun;26(6):570–578. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.6.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Wachsmuth I. K., Chapman C., Birden R., Brittingham J., Jackson C., Hogg J. The pathogenesis of hemorrhagic colitis caused by Escherichia coli O157:H7 in gnotobiotic piglets. J Infect Dis. 1986 Oct;154(4):712–716. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.4.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulshen M. H., Rollo J. L. Pathogenesis of escherichia coli gastroenteritis in man--another mechanism. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 10;302(2):99–101. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001103020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M. K., Andrews G. P., Fritz D. L., Sjogren R. W., Jr, Boedeker E. C. Characterization of the plasmid from Escherichia coli RDEC-1 that mediates expression of adhesin AF/R1 and evidence that AF/R1 pili promote but are not essential for enteropathogenic disease. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1846–1857. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1846-1857.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M. K., Boedeker E. C. Cloning of the genes for AF/R1 pili from rabbit enteroadherent Escherichia coli RDEC-1 and DNA sequence of the major structural subunit. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1124–1128. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1124-1128.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. J., Carroll P. J., Wray C. Detection of entero- and verocyto-toxin genes in Escherichia coli from diarrhoeal disease in animals using the polymerase chain reaction. Vet Microbiol. 1992 Jun 1;31(2-3):251–261. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(92)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





