Abstract
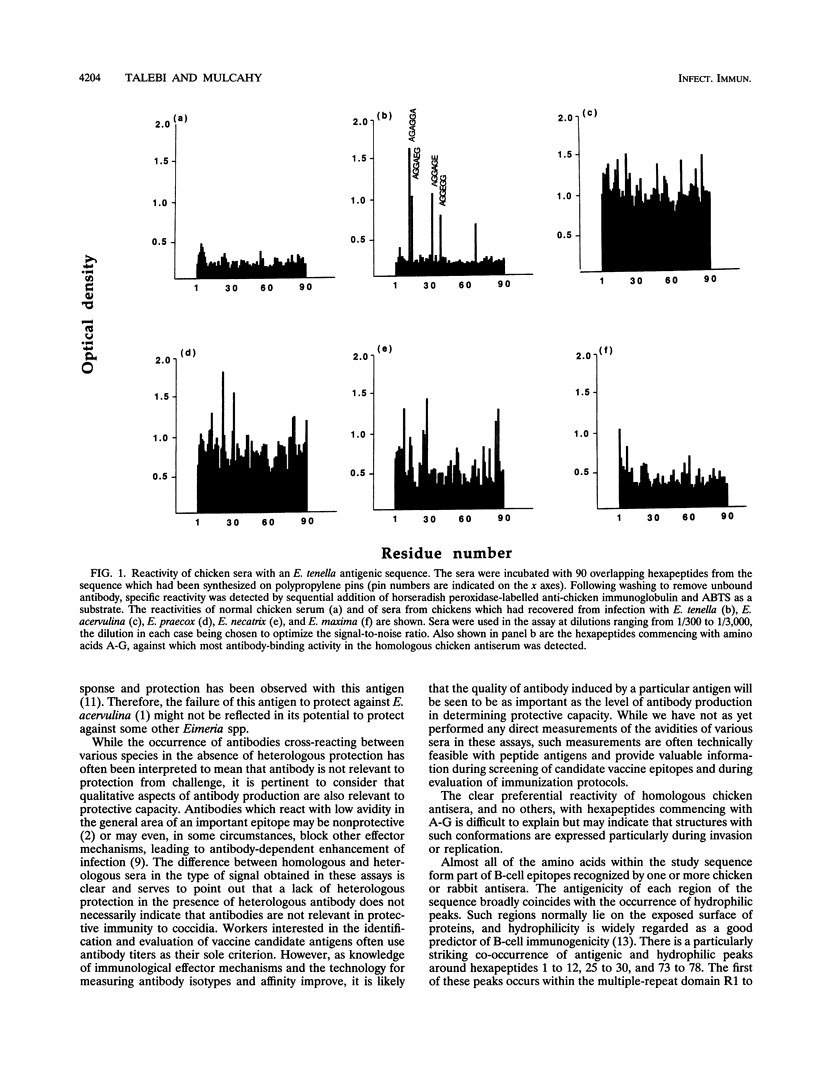
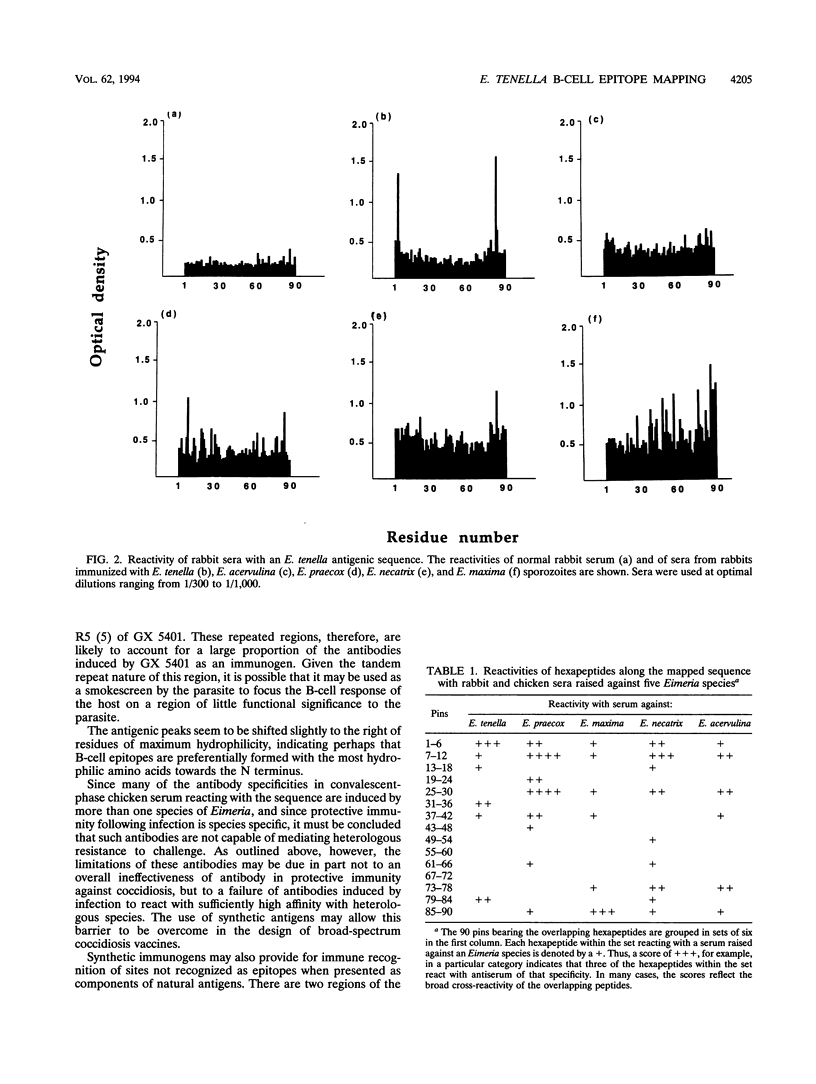
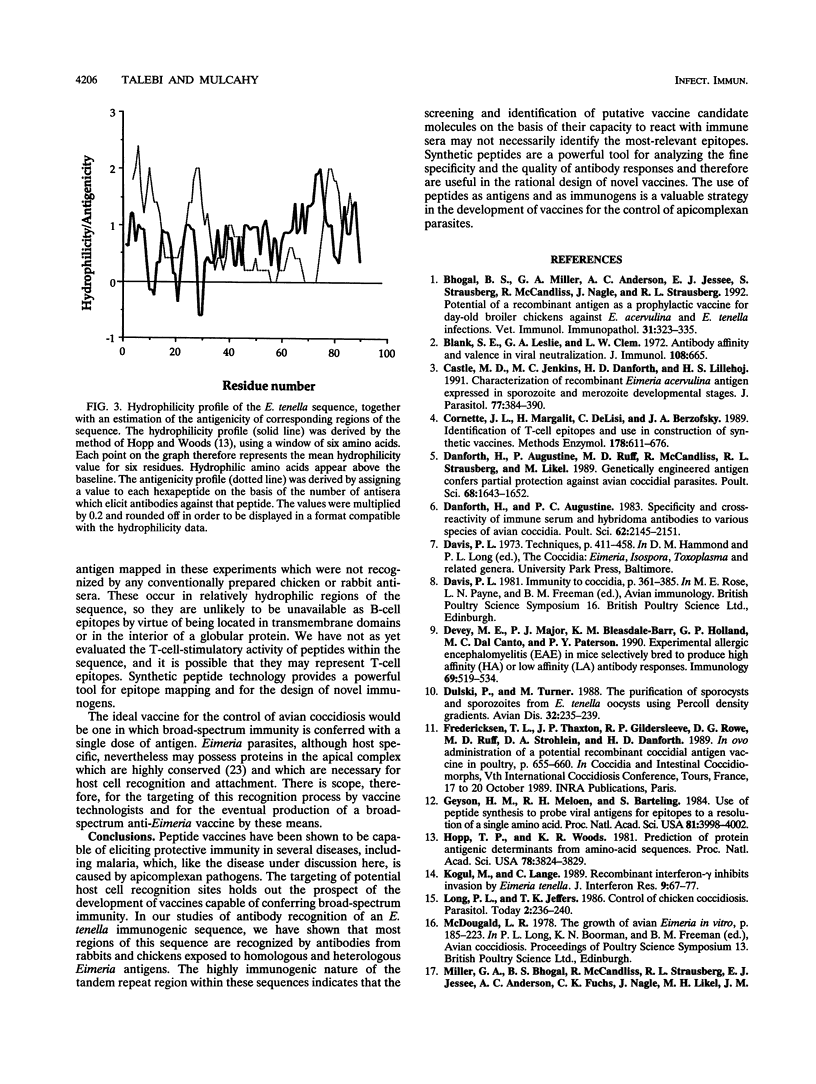
Overlapping hexapeptides representing part of an Eimeria tenella antigenic sequence, shown to induce partial immunity to homologous challenge in chickens, were synthesized on polypropylene pins (Pepskan technique; Cambridge Research Biochemicals, Cambridge, United Kingdom). The binding to these hexapeptides of antibodies from chickens infected and rabbits immunized with five species of Eimeria was studied, using the coated pins as the solid phase of an enzyme-linked immunoassay. Antibody binding to most regions of the sequence was demonstrated, with peak areas of antigenicity correlating with the most hydrophilic regions. A particularly hydrophilic and antigenic area towards the N terminus of the sequence consists of a peptide motif repeated five times in the native antigen. Homologous antisera (chicken and rabbit anti-E. tenella antisera) differed in their pattern of reactivity from heterologous sera raised against other Eimeria species. While the former bound to fewer of the hexapeptides than the latter, they did so very strongly, indicating affinity maturation of the antibody response to E. tenella-specific sequences. No antibody reactivity to two regions of the sequence was detected. These regions occur in relatively hydrophilic areas and so are unlikely to be situated in transmembrane domains or in the interior of globular proteins. Synthetic peptides, as used in these experiments, make possible analysis of the fine specificity of immune responses and thus have a role to play in the development of novel vaccines for the control of coccidiosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhogal B. S., Miller G. A., Anderson A. C., Jessee E. J., Strausberg S., McCandliss R., Nagle J., Strausberg R. L. Potential of a recombinant antigen as a prophylactic vaccine for day-old broiler chickens against Eimeria acervulina and Eimeria tenella infections. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Mar;31(3-4):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(92)90019-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank S. E., Leslie G. A., Clem L. W. Antibody affinity and valence in viral neutralization. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):665–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle M. D., Jenkins M. C., Danforth H. D., Lillehoj H. S. Characterization of a recombinant Eimeria acervulina antigen expressed in sporozoite and merozoite developmental stages. J Parasitol. 1991 Jun;77(3):384–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornette J. L., Margalit H., DeLisi C., Berzofsky J. A. Identification of T-cell epitopes and use in construction of synthetic vaccines. Methods Enzymol. 1989;178:611–634. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)78042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danforth H. D., Augustine P. C., Ruff M. D., McCandliss R., Strausberg R. L., Likel M. Genetically engineered antigen confers partial protection against avian coccidial parasites. Poult Sci. 1989 Dec;68(12):1643–1652. doi: 10.3382/ps.0681643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danforth H. D., Augustine P. C. Specificity and crossreactivity of immune serum and hybridoma antibodies to various species of avian coccidia. Poult Sci. 1983 Nov;62(11):2145–2151. doi: 10.3382/ps.0622145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devey M. E., Major P. J., Bleasdale-Barr K. M., Holland G. P., Dal Canto M. C., Paterson P. Y. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice selectively bred to produce high affinity (HA) or low affinity (LA) antibody responses. Immunology. 1990 Apr;69(4):519–524. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulski P., Turner M. The purification of sporocysts and sporozoites from Eimeria tenella oocysts using Percoll density gradients. Avian Dis. 1988 Apr-Jun;32(2):235–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Meloen R. H., Barteling S. J. Use of peptide synthesis to probe viral antigens for epitopes to a resolution of a single amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogut M. H., Lange C. Recombinant interferon-gamma inhibits cell invasion by Eimeria tenella. J Interferon Res. 1989 Feb;9(1):67–77. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long P. L., Jeffers T. K. Control of chicken coccidiosis. Parasitol Today. 1986 Sep;2(9):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(86)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. A., Bhogal B. S., McCandliss R., Strausberg R. L., Jessee E. J., Anderson A. C., Fuchs C. K., Nagle J., Likel M. H., Strasser J. M. Characterization and vaccine potential of a novel recombinant coccidial antigen. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2014–2020. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2014-2020.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patarroyo M. E., Amador R., Clavijo P., Moreno A., Guzman F., Romero P., Tascon R., Franco A., Murillo L. A., Ponton G. A synthetic vaccine protects humans against challenge with asexual blood stages of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):158–161. doi: 10.1038/332158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. K., 2nd, Strout R. G. Eimeria tenella: accumulation and retention of anticoccidial ionophores by extracellular sporozoites. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Dec;48(3):325–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90115-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton C. A., Shirley M. W., Wisher M. H. Characterization of coccidial proteins by two-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Parasitology. 1989 Oct;99(Pt 2):175–187. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000058613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. W., Evans C. B., Aley S. B., Barta J. R., Danforth H. D. Identification of an apically-located antigen that is conserved in sporozoan parasites. J Protozool. 1990 Nov-Dec;37(6):540–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1990.tb01262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach M., Halabi A., Pillemer G., Sar-Shalom O., Mencher D., Gilad M., Bendheim U., Danforth H. D., Augustine P. C. Maternal immunization with gametocyte antigens as a means of providing protective immunity against Eimeria maxima in chickens. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):2036–2039. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.2036-2039.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


