Abstract
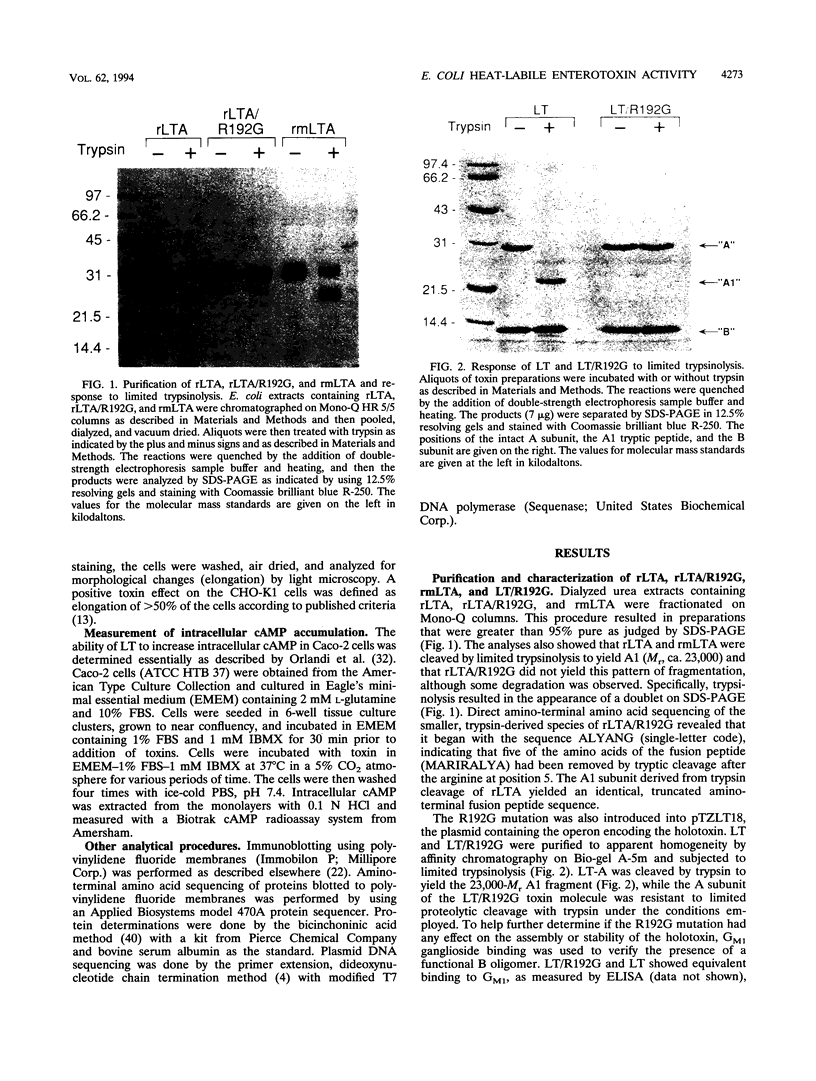
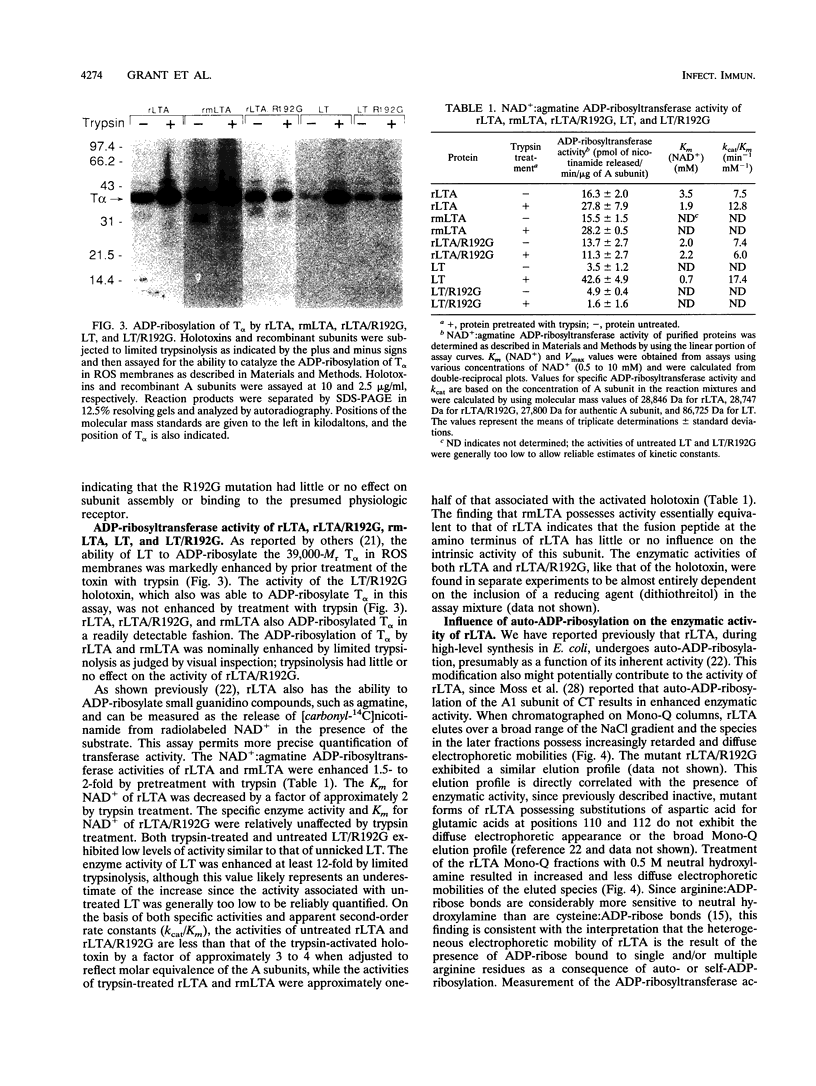
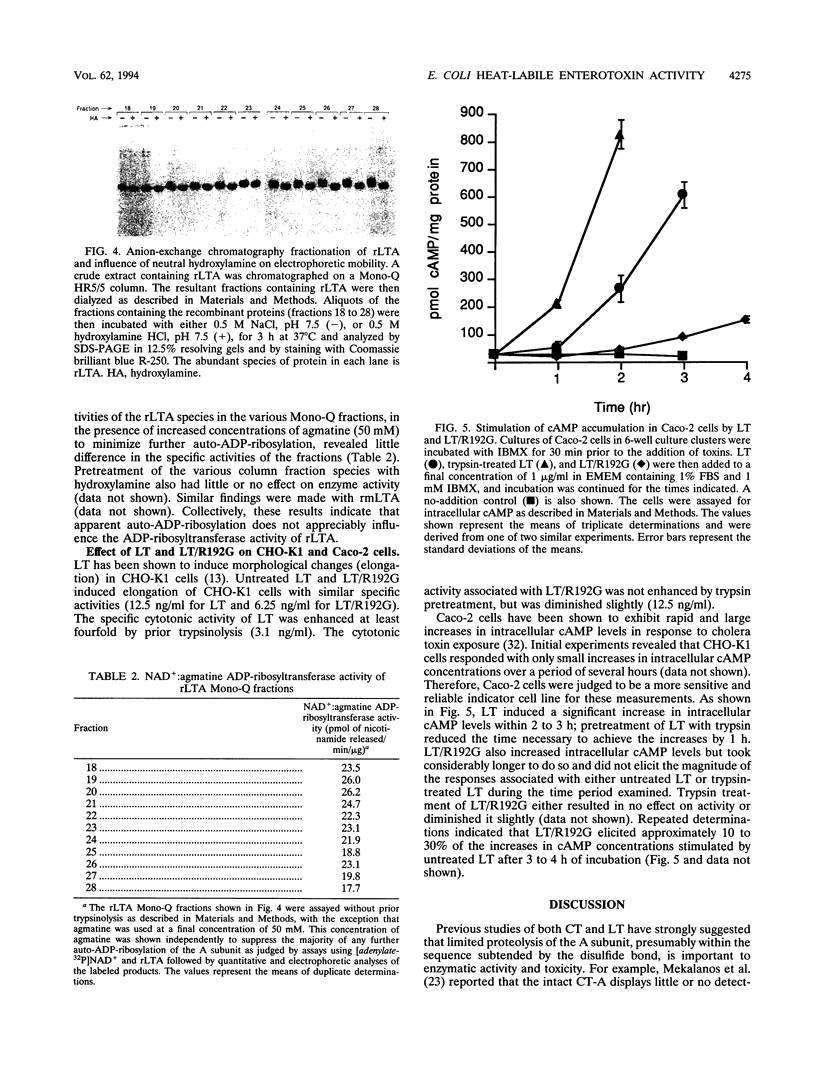
Previous studies of cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin have suggested that proteolytic cleavage plays an important role in the expression of ADP-ribosyltransferase activity and toxicity. Specifically, several studies have implicated a trypsin-like cleavage at arginine 192, which lies within an exposed region subtended by a disulfide bond in the intact A subunit, in toxicity. To investigate the role of this modification in the enzymatic and cytotonic properties of heat-labile enterotoxin, the response of purified, recombinant A subunit to tryptic activation and the effect of substituting arginine 192 with glycine on the activities of the holotoxin were examined. The recombinant A subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin exhibited significant levels of ADP-ribosyltransferase activity that were only nominally increased (approximately twofold) by prior limited trypsinolysis. The enzymatic activity also did not appear to be affected by auto-ADP-ribosylation that occurs during the high-level synthesis of the recombinant A subunit in E. coli. A mutant form of the holotoxin containing the arginine 192-to-glycine substitution exhibited levels of cytotonic activity for CHO cells that were similar to that of the untreated, wild-type holotoxin but exhibited a marked delay in the ability to increase intracellular levels of cyclic AMP in Caco-2 cells. The results indicate that trypsin-like cleavage of the A subunit of E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin at arginine 192 is not requisite to the expression of enzymatic activity by the A subunit and further reveal that this modification, although it enhances the biological and enzymatic activities of the toxin, is not absolutely required for the enterotoxin to elicit cytotonic effects.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baudry B., Fasano A., Ketley J., Kaper J. B. Cloning of a gene (zot) encoding a new toxin produced by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):428–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.428-434.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth B. A., Boesman-Finkelstein M., Finkelstein R. A. Vibrio cholerae hemagglutinin/protease nicks cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):558–560. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.558-560.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N., Mar V. L., Platler B. W., Schlotterbeck J. D., McGinley M. D., Stoney K. S., Rohde M. F., Kaslow H. R. Site-specific mutagenesis of the catalytic subunit of cholera toxin: substituting lysine for arginine 7 causes loss of activity. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4266–4270. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4266-4270.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe J. S., Cooper H. J., Smith M. A., Sims M. J., Parker D., Gewert D. Improved cloning efficiency of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products after proteinase K digestion. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):184–184. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Gill D. M., Falkow S. Cistrons encoding Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):850–858. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.850-858.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Beristain S., Tomicic T. K. Inhibition of heat-labile cholera and Escherichia coli enterotoxins by brefeldin A. Infect Immun. 1993 Aug;61(8):3282–3286. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.8.3282-3286.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower W. J., Miller J. F., Ragsdale C. W. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6127–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryling C., Ogata M., FitzGerald D. Characterization of a cellular protease that cleaves Pseudomonas exotoxin. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):497–502. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.497-502.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Richardson S. H. Adenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of adenylate cyclase catalyzed by heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: comparison with cholera toxin. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jan;141(1):64–70. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon V. M., Leppla S. H. Proteolytic activation of bacterial toxins: role of bacterial and host cell proteases. Infect Immun. 1994 Feb;62(2):333–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.2.333-340.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyningen S Van Cholera toxin: interaction of subunits with ganglioside GM1. Science. 1974 Feb 15;183(4125):656–657. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4125.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst T. R., Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Cellular location of heat-labile enterotoxin in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):637–642. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.637-642.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsia J. A., Tsai S. C., Adamik R., Yost D. A., Hewlett E. L., Moss J. Amino acid-specific ADP-ribosylation. Sensitivity to hydroxylamine of [cysteine(ADP-ribose)]protein and [arginine(ADP-ribose)]protein linkages. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16187–16191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis S., Hagmann J., Fishman P. H., Chang P. P., Moss J. Mechanism of action of cholera toxin on intact cells. Generation of A1 peptide and activation of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12148–12152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Finkelstein R. A., Capra J. D. Subunit structure and N-terminal amino acid sequence of the three chains of cholera enterotoxin. Immunochemistry. 1976 Jul;13(7):605–611. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel K. R., Molloy S. S., Thomas G., Leppla S. H. Anthrax toxin protective antigen is activated by a cell surface protease with the sequence specificity and catalytic properties of furin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10277–10281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Chang P. P., Tsai S. C., Adamik R., Price S. R., Kunz B. C., Moss J., Twiddy E. M., Holmes R. K. Activation of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxins by native and recombinant adenosine diphosphate-ribosylation factors, 20-kD guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. J Clin Invest. 1991 May;87(5):1780–1786. doi: 10.1172/JCI115197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobet Y., Cluff C. W., Cieplak W., Jr Effect of site-directed mutagenic alterations on ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of the A subunit of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2870–2879. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2870-2879.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Collier R. J., Romig W. R. Enzymic activity of cholera toxin. II. Relationships to proteolytic processing, disulfide bond reduction, and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5855–5861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Bacterial toxins: cellular mechanisms of action. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Sep;48(3):199–221. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.3.199-221.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring J. M., Inocencio N. M., Robertson B. J., Moehring T. J. Expression of mouse furin in a Chinese hamster cell resistant to Pseudomonas exotoxin A and viruses complements the genetic lesion. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2590–2594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Richardson S. H. Activation of adenylate cyclase by heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Evidence for ADP-ribosyltransferase activity similar to that of choleragen. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):281–285. doi: 10.1172/JCI109127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Stanley S. J., Lin M. C. NAD glycohydrolase and ADP-ribosyltransferase activities are intrinsic to the A1 peptide of choleragen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):11993–11999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Stanley S. J., Watkins P. A., Vaughan M. ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of mono- and multi-(ADP-ribosylated) choleragen. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7835–7837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Watanabe T., Nakagawa T., Kim W. S., Nagahama M., Hosaka M., Hatsuzawa K., Kondoh-Hashiba K., Murakami K. Consensus sequence for precursor processing at mono-arginyl sites. Evidence for the involvement of a Kex2-like endoprotease in precursor cleavages at both dibasic and mono-arginyl sites. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16335–16340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Chaudhary V. K., Pastan I., FitzGerald D. J. Processing of Pseudomonas exotoxin by a cellular protease results in the generation of a 37,000-Da toxin fragment that is translocated to the cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20678–20685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Okamoto K., Miyama A., Tsuji T., Honda T., Miwatani T. Effect of substitution of glycine for arginine at position 146 of the A1 subunit on biological activity of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2208–2211. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2208-2211.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlandi P. A., Curran P. K., Fishman P. H. Brefeldin A blocks the response of cultured cells to cholera toxin. Implications for intracellular trafficking in toxin action. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):12010–12016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. D., Mekalanos J. J. Molecular cloning of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin genes in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2976–2980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Roberts L. M., Lord J. M. Toxin entry: how reversible is the secretory pathway? Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;2(7):183–185. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90230-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. The retention signal for soluble proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):483–486. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90303-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett C. L., Twiddy E. M., Coker C., Holmes R. K. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and hybridization studies of the type IIb heat-labile enterotoxin gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4945–4952. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4945-4952.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Huda S., Neogi P. K., Daniel R. R., Spira W. M. Microtiter ganglioside enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for vibrio and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxins and antitoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):35–40. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.35-40.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangler B. D. Structure and function of cholera toxin and the related Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Dec;56(4):622–647. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.4.622-647.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepel J. B., Chuang D. M., Neff N. H. Transfer of ADP-ribose from NAD to choleragen: a subunit acts as catalyst and acceptor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5440–5442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuneoka M., Nakayama K., Hatsuzawa K., Komada M., Kitamura N., Mekada E. Evidence for involvement of furin in cleavage and activation of diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26461–26465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dop C., Tsubokawa M., Bourne H. R., Ramachandran J. Amino acid sequence of retinal transducin at the site ADP-ribosylated by cholera toxin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):696–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss O., Holden J., Rulka C., Kahn R. A. Nucleotide binding and cofactor activities of purified bovine brain and bacterially expressed ADP-ribosylation factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21066–21072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Gojobori T., Yokota T. Evolutionary origin of pathogenic determinants in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae O1. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1352–1357. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1352-1357.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]