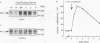Abstract
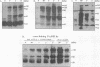
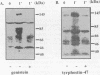
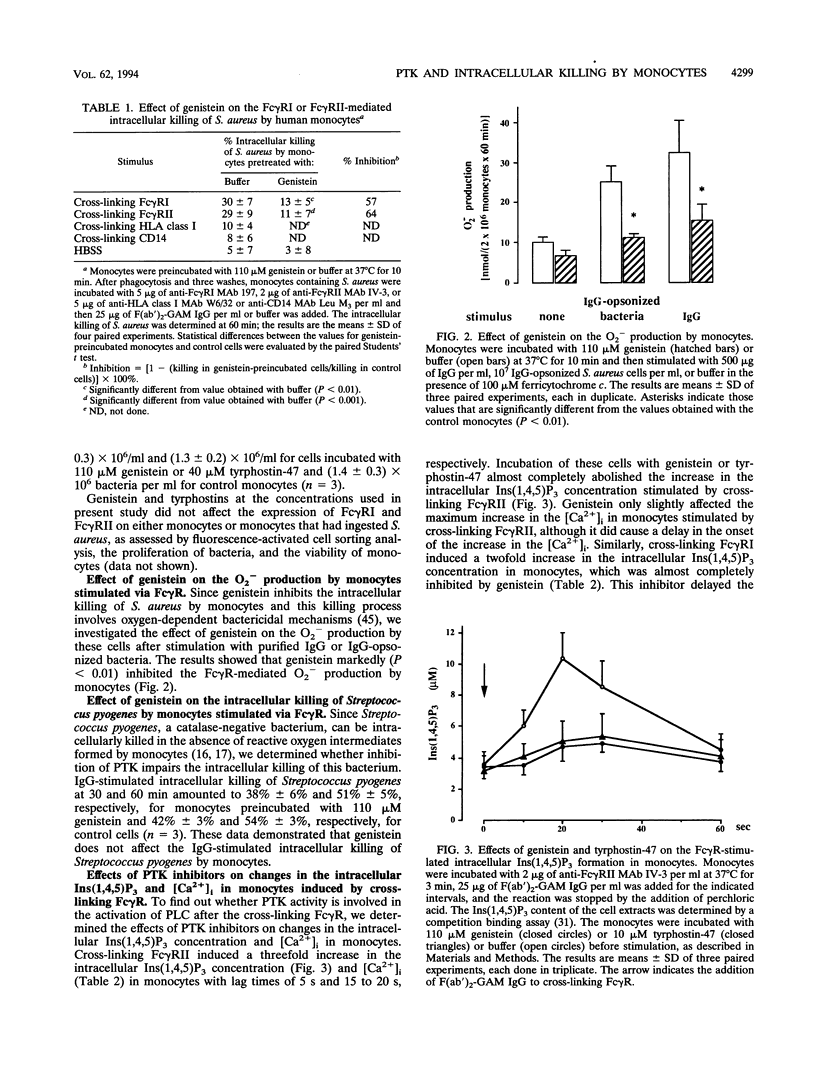
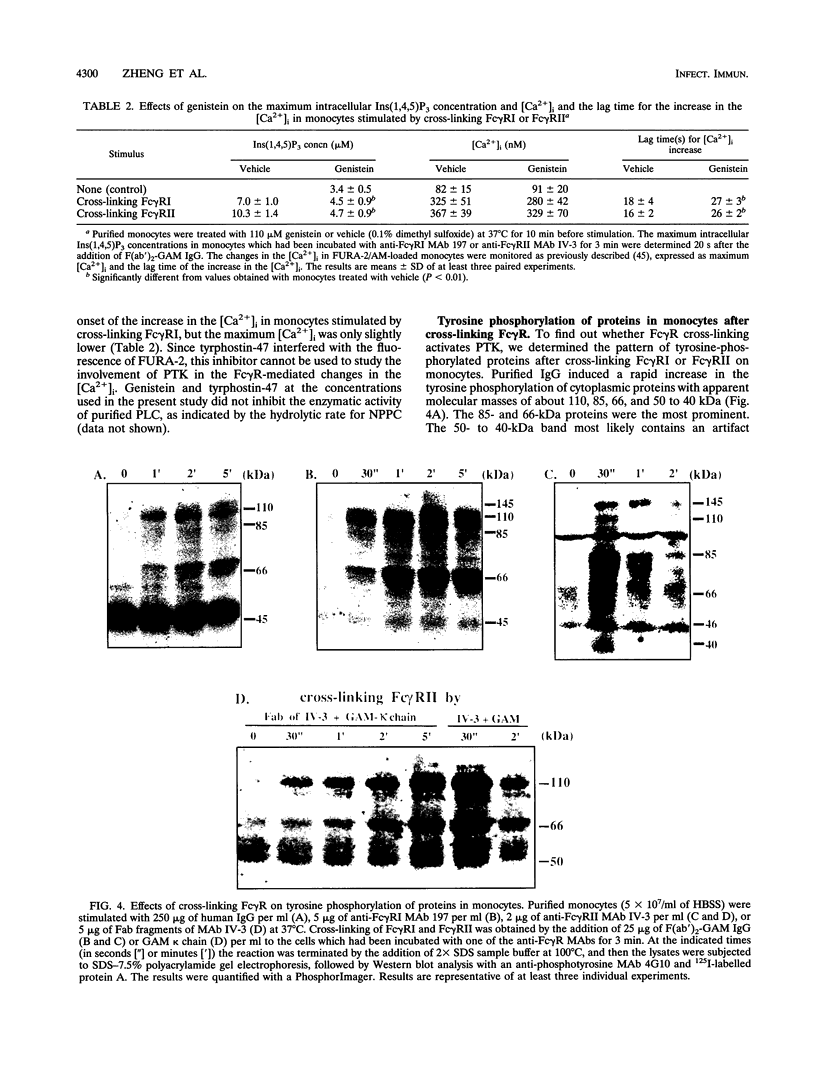
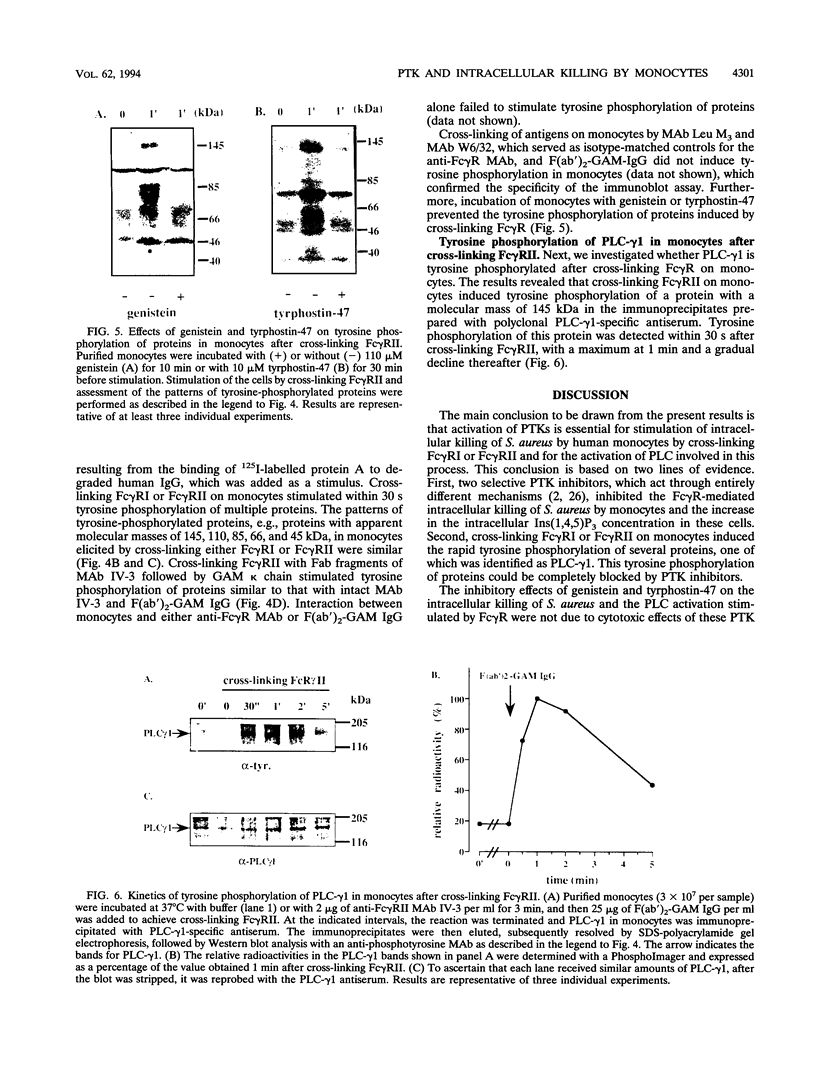
Our previous study revealed that the intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus by human monocytes after cross-linking Fc gamma receptor I (Fc gamma RI) or Fc gamma RII is a phospholipase C (PLC)-dependent process. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) activity plays a role in the Fc gamma R-mediated intracellular killing of bacteria and activation of PLC in these cells. The results showed that phagocytosis of bacteria by monocytes was not affected by the PTK inhibitors genistein and tyrphostin-47. The intracellular killing of S. aureus by monocytes after cross-linking Fc gamma RII or Fc gamma RII with anti-Fc gamma R monoclonal antibody and a bridging antibody or with human immunoglobulin G (IgG) was inhibited by these compounds in a dose-dependent fashion. The production of O2- by monocytes after stimulation with IgG or IgG-opsonized S. aureus was almost completely blocked by the PTK inhibitor. These results indicate that inhibition of PTK impairs the oxygen-dependent bactericidal mechanisms of monocytes. Genistein and tyrphostin-47, which do not affect the enzymatic activity of purified PLC, prevented activation of PLC after cross-linking Fc gamma RI or Fc gamma RII, measured as an increase in the intracellular inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate concentration. Cross-linking Fc gamma RI or Fc gamma RII induced rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of several proteins in monocytes, one of which was identified as PLC-gamma 1, and the phosphorylation could be completely blocked by PTK inhibitors, leading to the conclusion that activation of PLC after cross-linking Fc gamma R in monocytes is regulated by PTK activity. Together, these results demonstrate that PTK activity is essential for the activation of PLC which is involved in the Fc gamma R-mediated intracellular killing of S. aureus by human monocytes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal A., Salem P., Robbins K. C. Involvement of p72syk, a protein-tyrosine kinase, in Fc gamma receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15900–15905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama T., Ishida J., Nakagawa S., Ogawara H., Watanabe S., Itoh N., Shibuya M., Fukami Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5592–5595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Seed B. Isolation and expression of functional high-affinity Fc receptor complementary DNAs. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):378–381. doi: 10.1126/science.2911749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson G. P., Anderson C. L. Signal transduction by the platelet Fc receptor. Blood. 1990 Sep 15;76(6):1165–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven M. A., Metzger H. Signal transduction by Fc receptors: the Fc epsilon RI case. Immunol Today. 1993 May;14(5):222–226. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90167-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliska J. B., Guan K. L., Dixon J. E., Falkow S. Tyrosine phosphate hydrolysis of host proteins by an essential Yersinia virulence determinant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1187–1191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmüller-Rouiller Y., Mauël J. Macrophage activation for intracellular killing as induced by calcium ionophore. Correlation with biologic and biochemical events. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):217–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of leucocytes from human blood. A two-phase system for removal of red cells with methylcellulose as erythrocyte-aggregating agent. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:9–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly P. A., Farrell C. A., Merenda J. M., Conklyn M. J., Showell H. J. Tyrosine phosphorylation is an early signaling event common to Fc receptor crosslinking in human neutrophils and rat basophilic leukemia cells (RBL-2H3). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 31;177(1):192–201. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91967-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debets J. M., Van de Winkel J. G., Ceuppens J. L., Dieteren I. E., Buurman W. A. Cross-linking of both Fc gamma RI and Fc gamma RII induces secretion of tumor necrosis factor by human monocytes, requiring high affinity Fc-Fc gamma R interactions. Functional activation of Fc gamma RII by treatment with proteases or neuraminidase. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1304–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst L. K., Duchemin A. M., Anderson C. L. Association of the high-affinity receptor for IgG (Fc gamma RI) with the gamma subunit of the IgE receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6023–6027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feister A. J., Browder B., Willis H. E., Mohanakumar T., Ruddy S. Pertussis toxin inhibits human neutrophil responses mediated by the 42-kilodalton IgG Fc receptor. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):228–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel T. H., Pabst M. J., Suzuki H., Guthrie L. A., Forehand J. R., Phillips W. A., Johnston R. B., Jr Priming of neutrophils and macrophages for enhanced release of superoxide anion by the calcium ionophore ionomycin. Implications for regulation of the respiratory burst. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12589–12596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geertsma M. F., Broos H. R., van den Barselaar M. T., Nibbering P. H., van Furth R. Lung surfactant suppresses oxygen-dependent bactericidal functions of human blood monocytes by inhibiting the assembly of the NADPH oxidase. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2391–2400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazizadeh S., Fleit H. B. Tyrosine phosphorylation provides an obligatory early signal for Fc gamma RII-mediated endocytosis in the monocytic cell line THP-1. J Immunol. 1994 Jan 1;152(1):30–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano R. F., Fanger M. W. Fc gamma RI and Fc gamma RII on monocytes and granulocytes are cytotoxic trigger molecules for tumor cells. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3536–3541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S., Chang P., Silverstein S. C. Tyrosine phosphorylation is required for Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis in mouse macrophages. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):529–534. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity of an essential virulence determinant in Yersinia. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2166336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurioka S., Matsuda M. Phospholipase C assay using p-nitrophenylphosphoryl-choline together with sorbitol and its application to studying the metal and detergent requirement of the enzyme. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusunoki T., Higashi H., Hosoi S., Hata D., Sugie K., Mayumi M., Mikawa H. Tyrosine phosphorylation and its possible role in superoxide production by human neutrophils stimulated with FMLP and IgG. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 16;183(2):789–796. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90552-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., van Zwet T. L., Daha M. R., van Furth R. Requirement of extracellular complement and immunoglobulin for intracellular killing of micro-organisms by human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):772–784. doi: 10.1172/JCI109362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A. Tyrphostins: tyrosine kinase blockers as novel antiproliferative agents and dissectors of signal transduction. FASEB J. 1992 Nov;6(14):3275–3282. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.14.1426765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao F., Shin H. S., Rhee S. G. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 induced by cross-linking of the high-affinity or low-affinity Fc receptor for IgG in U937 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda M., Roos D. Association of all three types of Fc gamma R (CD64, CD32, and CD16) with a gamma-chain homodimer in cultured human monocytes. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):7188–7195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda M., Verhoeven A. J., Roos D. Tyrosine phosphorylation of a gamma-chain homodimer associated with Fc gamma RIII (CD16) in cultured human monocytes. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 1;151(11):6382–6388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. A., McPhail L. C., Snyderman R. Redistribution of protein kinase C activity in human monocytes: correlation with activation of the respiratory burst. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3411–3416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nibbering P. H., Zomerdijk T. P., van Haastert P. J., van Furth R. A competition binding assay for determination of the inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate content of human leucocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 31;170(2):755–762. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92155-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odin J. A., Edberg J. C., Painter C. J., Kimberly R. P., Unkeless J. C. Regulation of phagocytosis and [Ca2+]i flux by distinct regions of an Fc receptor. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1785–1788. doi: 10.1126/science.1837175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D. J., Min H. K., Rhee S. G. IgE-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 in rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24237–24240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn L. C., Fanger M. W. Cross-linking of the high affinity Fc receptor for human immunoglobulin G1 triggers transient activation of NADPH oxidase activity. Continuous oxidase activation requires continuous de novo receptor cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14112–14120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin B. M., Yocum S. A., Mittler R. S., Kiener P. A. Stimulation of tyrosine phosphorylation and calcium mobilization by Fc gamma receptor cross-linking. Regulation by the phosphotyrosine phosphatase CD45. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):605–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales C., Jones S. L., McCourt D., Brown E. J. Bromophenacyl bromide binding to the actin-bundling protein l-plastin inhibits inositol trisphosphate-independent increase in Ca2+ in human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3534–3538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenshine I., Duronio V., Finlay B. B. Tyrosine protein kinase inhibitors block invasin-promoted bacterial uptake by epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2211–2217. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2211-2217.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholl P. R., Ahern D., Geha R. S. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation induced via the IgG receptors Fc gamma Ri and Fc gamma RII in the human monocytic cell line THP-1. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 1;149(5):1751–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart S. G., Simister N. E., Clarkson S. B., Kacinski B. M., Shapiro M., Mellman I. Human IgG Fc receptor (hFcRII; CD32) exists as multiple isoforms in macrophages, lymphocytes and IgG-transporting placental epithelium. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3657–3666. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Chae H. Z., Rhee S. G., Exton J. H. Activation of the beta 1 isozyme of phospholipase C by alpha subunits of the Gq class of G proteins. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):516–518. doi: 10.1038/350516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting A. T., Karnitz L. M., Schoon R. A., Abraham R. T., Leibson P. J. Fc gamma receptor activation induces the tyrosine phosphorylation of both phospholipase C (PLC)-gamma 1 and PLC-gamma 2 in natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1751–1755. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres M., Hall F. L., O'Neill K. Stimulation of human neutrophils with formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine induces tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of two distinct mitogen-activated protein-kinases. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 15;150(4):1563–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirthmueller U., Kurosaki T., Murakami M. S., Ravetch J. V. Signal transduction by Fc gamma RIII (CD16) is mediated through the gamma chain. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1381–1390. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng L., Nibbering P. H., van Furth R. Cytosolic free calcium is essential for immunoglobulin G-stimulated intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus by human monocytes. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3092–3097. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3092-3097.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng L., Nibbering P. H., van Furth R. Stimulation of the intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus by human monocytes mediated by Fc gamma receptors I and II. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Nov;23(11):2826–2833. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Winkel J. G., Anderson C. L. Biology of human immunoglobulin G Fc receptors. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 May;49(5):511–524. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.5.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]