Abstract
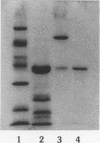
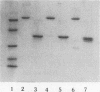
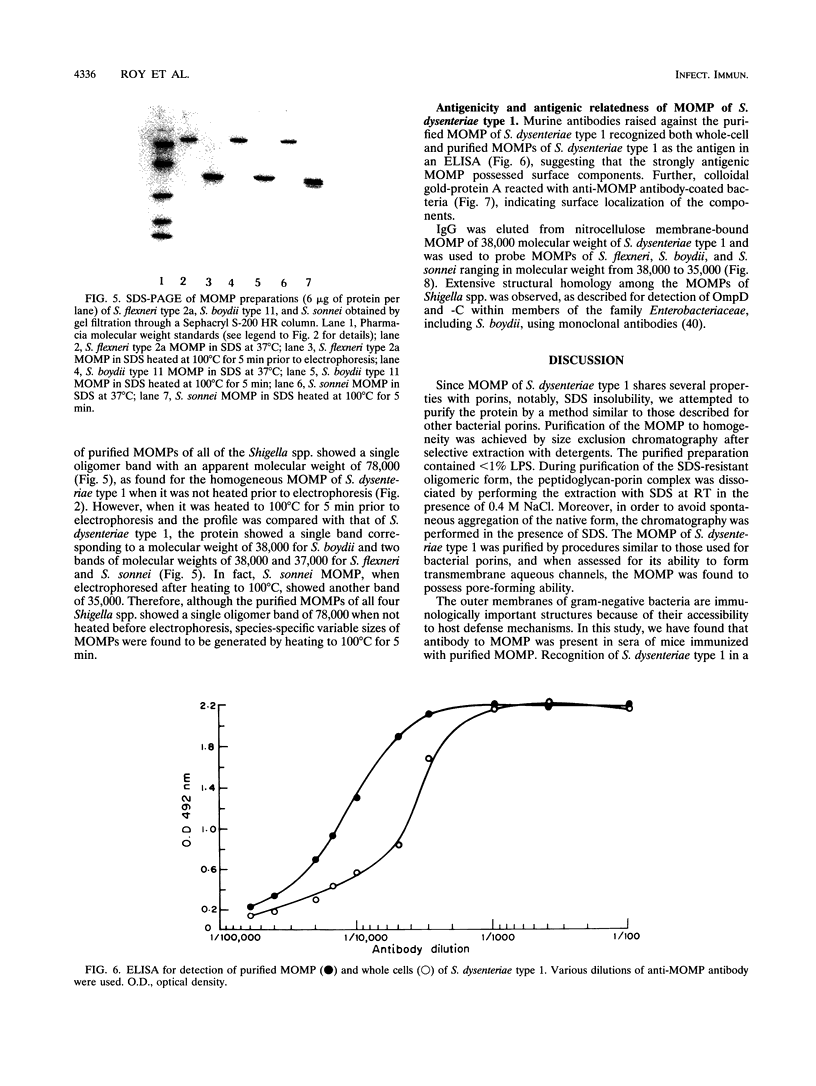
The major outer membrane protein (MOMP), the most abundant outer membrane protein, was purified to homogeneity from Shigella dysenteriae type 1. The purification method involved selective extraction of MOMP with sodium dodecyl sulfate in the presence of 0.4 M sodium chloride followed by size exclusion chromatography with Sephacryl S-200 HR. MOMP was found to form hydrophilic diffusion pores by incorporation into artificial liposome vesicles composed of egg yolk phosphatidylcholine and dicetylphosphate, indicating that MOMP of S. dysenteriae type 1 exhibited significant porin activity. However, the liposomes containing heat-denatured MOMP were barely active. The molecular weight of MOMP found by size exclusion chromatography was 130,000, and in sodium dodecyl sulfate-10% polyacrylamide gel it moved as an oligomer of 78,000 molecular weight. Upon boiling, fully dissociated monomers of 38,000 molecular weight were seen for S. dysenteriae type 1. However, among the four Shigella spp., the monomeric MOMP generated upon boiling ranged from 38,000 to 35,000 in molecular weight. Antibody raised in BALB/c mice immunized with MOMP of S. dysenteriae type 1 reacted strongly with purified MOMP of S. dysenteriae type 1 in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The antibody reacted with whole-cell preparations of S. dysenteriae type 1 in an ELISA, suggesting that MOMP possessed surface components. Moreover, MOMP could be visualized on the bacterial surface by immunoelectron microscopy with anti-MOMP antibody. S. dysenteriae type 1 MOMP-specific immunoglobulin eluted from MOMP bound to a nitrocellulose membrane was found to cross-react with MOMP preparations of S. flexneri, S. boydii, and S. sonnei, indicating that MOMPs were antigenically related among Shigella species. The strong immunogenicity, surface exposure, and antigenic relatedness make MOMP of Shigella species an immunologically significant macromolecule for study.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamus G., Mulczyk M., Witkowska D., Romanowska E. Protection against keratoconjunctivitis shigellosa induced by immunization with outer membrane proteins of Shigella spp. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):321–324. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.321-324.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Schmid A., Hancock R. E. Ion selectivity of gram-negative bacterial porins. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):722–727. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.722-727.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R. Structure and function of porins from gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:359–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini M. L., Mounier J., d'Hauteville H., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Identification of icsA, a plasmid locus of Shigella flexneri that governs bacterial intra- and intercellular spread through interaction with F-actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3867–3871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini M. L., Sanna M. G., Fontaine A., Sansonetti P. J. OmpC is involved in invasion of epithelial cells by Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3625–3635. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3625-3635.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P. L., Ryter A., Mounier J., Sansonetti P. J. Plasmid-mediated early killing of eucaryotic cells by Shigella flexneri as studied by infection of J774 macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):521–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.521-527.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan S. W., Schirmer T., Rummel G., Steiert M., Ghosh R., Pauptit R. A., Jansonius J. N., Rosenbusch J. P. Crystal structures explain functional properties of two E. coli porins. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):727–733. doi: 10.1038/358727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filip C., Fletcher G., Wulff J. L., Earhart C. F. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by the ionic detergent sodium-lauryl sarcosinate. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):717–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.717-722.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galdiero F., Tufano M. A., Galdiero M., Masiello S., Di Rosa M. Inflammatory effects of Salmonella typhimurium porins. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3183–3186. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3183-3186.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galdiero F., de L'ero G. C., Benedetto N., Galdiero M., Tufano M. A. Release of cytokines induced by Salmonella typhimurium porins. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):155–161. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.155-161.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Parker M. G., Matthews J. M., Berg R. D. Use of a purified outer membrane protein F (porin) preparation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a protective vaccine in mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):49–54. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.49-54.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L. Genetic basis of virulence in Shigella species. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jun;55(2):206–224. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.2.206-224.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Oaks E. V., Formal S. B. Identification and antigenic characterization of virulence-associated, plasmid-coded proteins of Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):620–629. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.620-629.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. Role of porins in outer membrane permeability. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):929–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.929-933.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoenger A., Pagès J. M., Fourel D., Engel A. The orientation of porin OmpF in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1993 Oct 5;233(3):400–413. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstra H., Dankert J. Porin from the outer membrane of Escherichia coli: immunological characterization of native and heat-dissociated forms. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Aug;125(2):285–292. doi: 10.1099/00221287-125-2-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isibasi A., Ortiz-Navarrete V., Paniagua J., Pelayo R., González C. R., García J. A., Kumate J. Active protection of mice against Salmonella typhi by immunization with strain-specific porins. Vaccine. 1992;10(12):811–813. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90041-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebba P. E., Benson S. A., Bala S., Abdullah T., Reid J., Singh S. P., Nikaido H. Determinants of OmpF porin antigenicity and structure. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6800–6810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Pál T. Strategies for development of potential candidate Shigella vaccines. Vaccine. 1993;11(2):168–179. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(93)90014-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupi N., Bourgois A., Bernadac A., Laboucarié S., Pagès J. M. Immunological analysis of porin polymorphism in Escherichia coli B and K-12. Mol Immunol. 1989 Nov;26(11):1027–1036. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller F. W., Twitty S. A., Biswas T., Plotz P. H. Origin and regulation of a disease-specific autoantibody response. Antigenic epitopes, spectrotype stability, and isotype restriction of anti-Jo-1 autoantibodies. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):468–475. doi: 10.1172/JCI114461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Proteins forming large channels from bacterial and mitochondrial outer membranes: porins and phage lambda receptor protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;97:85–100. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)97122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Rosenberg E. Y. Porin channels in Escherichia coli: studies with liposomes reconstituted from purified proteins. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):241–252. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.241-252.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Saier M. H., Jr Transport proteins in bacteria: common themes in their design. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):936–942. doi: 10.1126/science.1279804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks E. V., Hale T. L., Formal S. B. Serum immune response to Shigella protein antigens in rhesus monkeys and humans infected with Shigella spp. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.57-63.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P. Characterization of the major envelope protein from Escherichia coli. Regular arrangement on the peptidoglycan and unusual dodecyl sulfate binding. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):8019–8029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Das A. B., Biswas T. Antigenicity and antigenic relatedness of the outer membrane proteins of Shigella species. Microbios. 1994;79(318):55–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental keratoconjunctivitis shigellosa. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1957;4(4):367–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Ryter A., Clerc P., Maurelli A. T., Mounier J. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri within HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):461–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.461-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahid N. S., Rahaman M. M., Haider K., Banu H., Rahman N. Changing pattern of resistant Shiga bacillus (Shigella dysenteriae type 1) and Shigella flexneri in Bangladesh. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1114–1119. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh S. P., Upshaw Y., Abdullah T., Singh S. R., Klebba P. E. Structural relatedness of enteric bacterial porins assessed with monoclonal antibodies to Salmonella typhimurium OmpD and OmpC. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1965–1973. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1965-1973.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada H., Ogawa T., Yoshimura F., Otsuka K., Kokeguchi S., Kato K., Umemoto T., Kotani S. Immunobiological activities of a porin fraction isolated from Fusobacterium nucleatum ATCC 10953. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):855–863. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.855-863.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga H., Tokunaga M., Nakae T. Characterization of porins from the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. 1. Chemical analysis. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):433–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. B., Ribi E., Wheat R. W. Enhancement of macrophage-mediated tumor cell killing by bacterial outer membrane proteins (porins). Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):219–223. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.219-223.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. S., Kreusch A., Schiltz E., Nestel U., Welte W., Weckesser J., Schulz G. E. The structure of porin from Rhodobacter capsulatus at 1.8 A resolution. FEBS Lett. 1991 Mar 25;280(2):379–382. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Oshima N., Mizuno T., Matsui H., Kai Y., Noguchi H., Mizushima S. Use of a series of ompF-ompC chimeric proteins for locating antigenic determinants recognized by monoclonal antibodies against the ompC and ompF proteins of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. J Biochem. 1987 Sep;102(3):455–464. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gier J., Mandersloot J. G., van Deenen L. L. Lipid composition and permeability of liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 11;150(4):666–675. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90056-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ley P., Struyvé M., Tommassen J. Topology of outer membrane pore protein PhoE of Escherichia coli. Identification of cell surface-exposed amino acids with the aid of monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12222–12225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]