Abstract
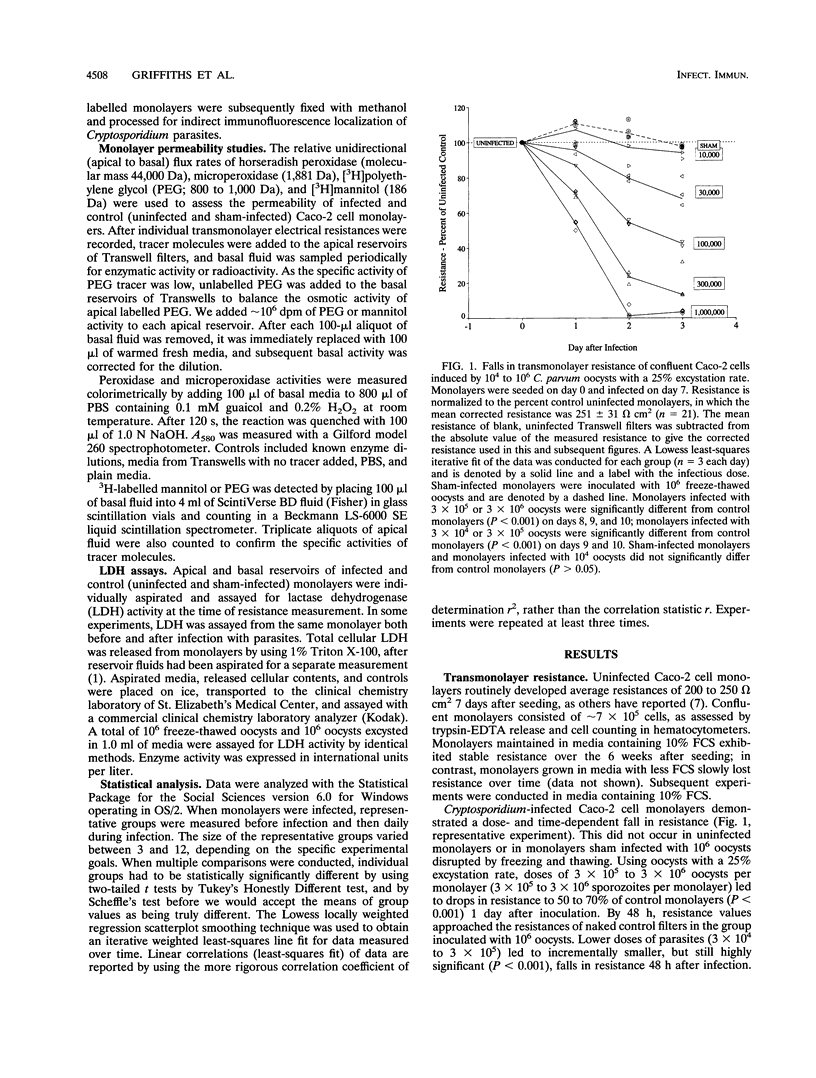
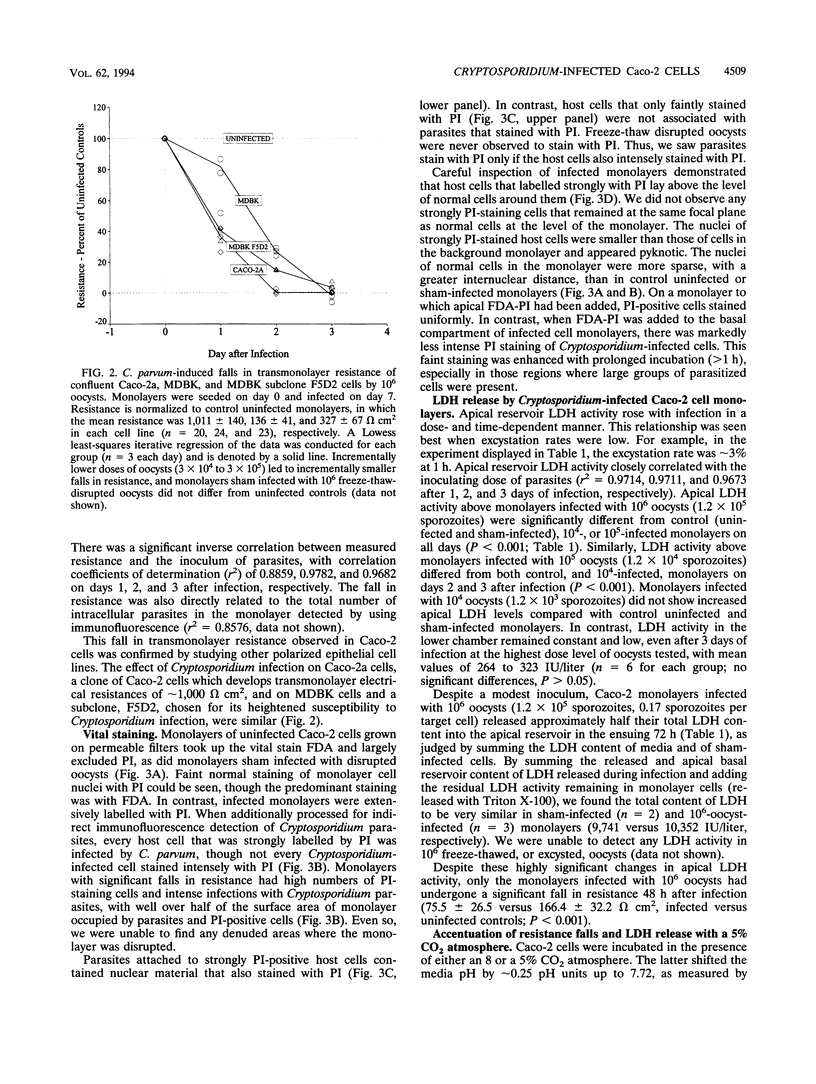
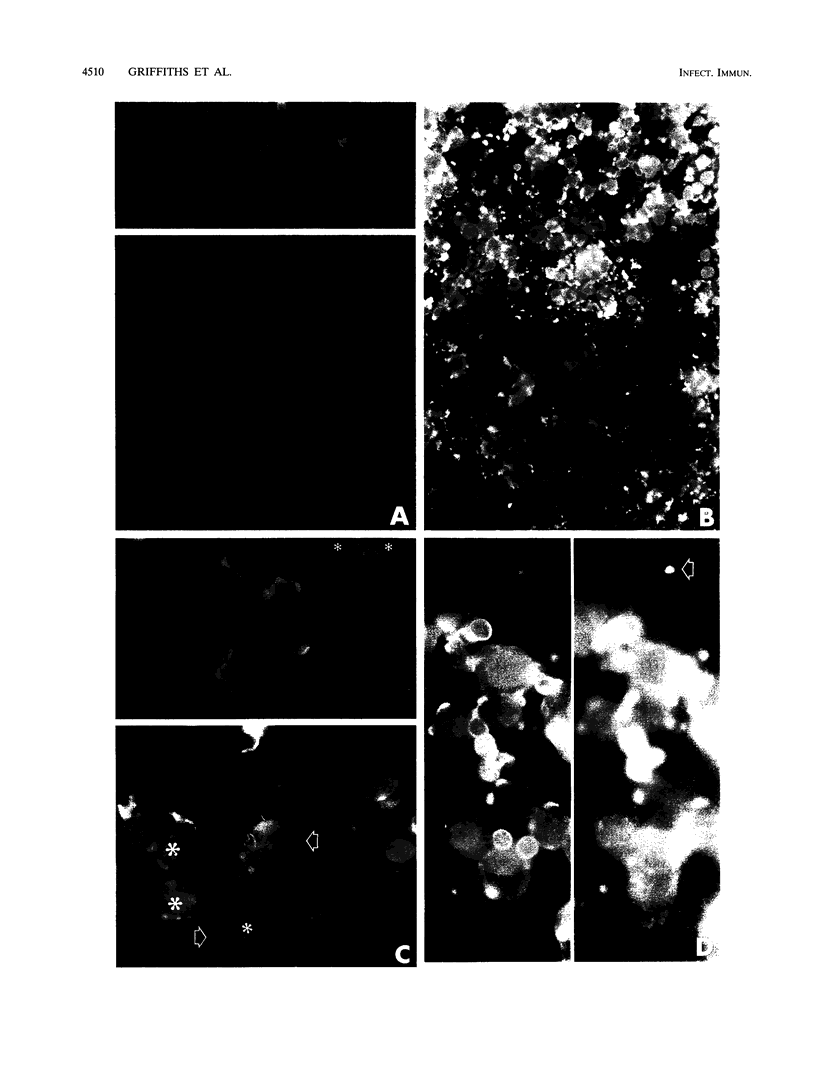
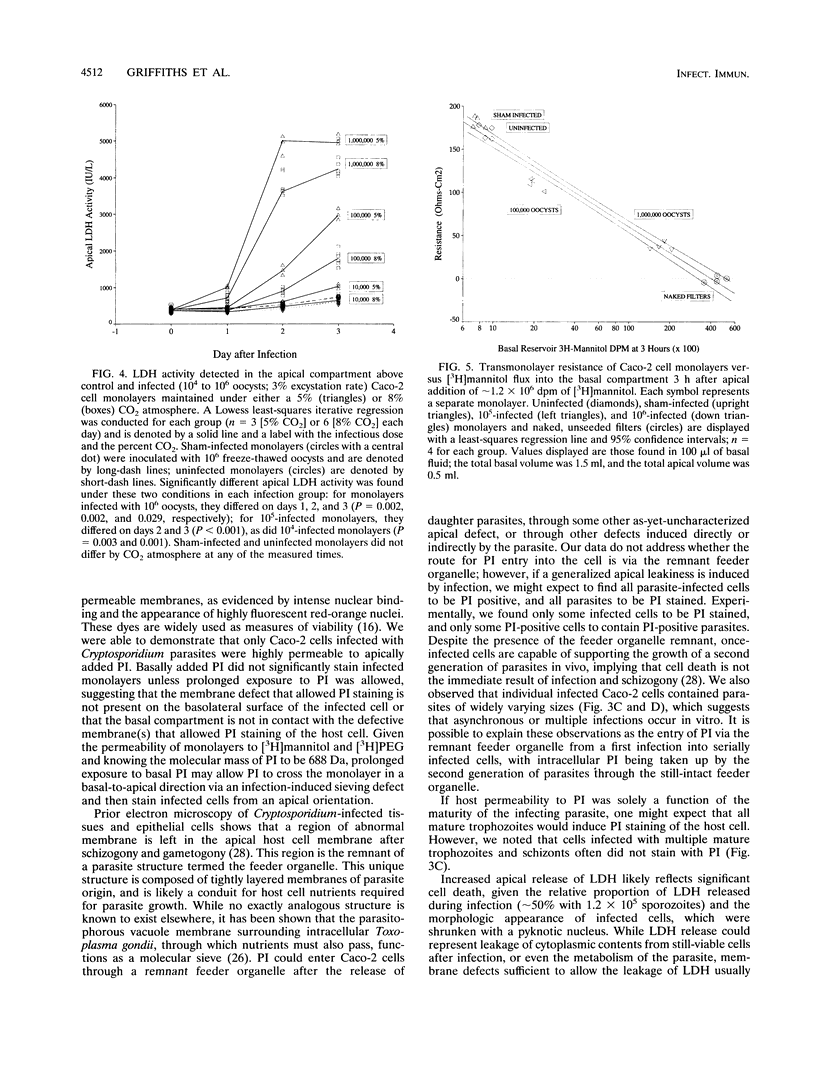
Caco-2 cells were grown on permeable filters and infected with Cryptosporidium parvum. Infection rates exceeded 50% of target cells with a sufficient inoculum dose of parasites. Infection induced a dose- and time-dependent fall in transmonolayer resistance, which was closely related to both the inoculum dose and the number of parasites detected by immunofluorescence. Caco-2a, MDBK, and MDBK subclone F5D2 evidenced similar declines in resistance when grown and infected under similar circumstances. Caco-2 monolayers became permeable to molecules of < or = 1,000 Da but continued to remain impermeable to exogenously added, or endogenously produced, proteins of > or = 1,881 Da. We found that infected monolayers released up to 50% of the total cellular lactase dehydrogenase into apical media, but not basal media, and that the vital dye propidium iodide avidly stained infected cells, and often parasites, when added to the apical reservoir. Cryptosporidium infection of Caco-2 monolayers increases transmonolayer permeability, induces an apical cellular and monolayer defect, and causes cell death.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. B., Guerrant R. L., Zu S., Fang G., Roche J. K. Cryptosporidium parvum infection of intestinal epithelium: morphologic and functional studies in an in vitro model. J Infect Dis. 1994 Jan;169(1):170–177. doi: 10.1093/infdis/169.1.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audus K. L., Bartel R. L., Hidalgo I. J., Borchardt R. T. The use of cultured epithelial and endothelial cells for drug transport and metabolism studies. Pharm Res. 1990 May;7(5):435–451. doi: 10.1023/a:1015800312910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buraud M., Forget E., Favennec L., Bizet J., Gobert J. G., Deluol A. M. Sexual stage development of cryptosporidia in the Caco-2 cell line. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4610–4613. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4610-4613.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canil C., Rosenshine I., Ruschkowski S., Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B., Finlay B. B. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli decreases the transepithelial electrical resistance of polarized epithelial monolayers. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2755–2762. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2755-2762.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Current W. L., Garcia L. S. Cryptosporidiosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jul;4(3):325–358. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Salmonella interactions with polarized human intestinal Caco-2 epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1096–1106. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanigan T. P., Aji T., Marshall R., Soave R., Aikawa M., Kaetzel C. Asexual development of Cryptosporidium parvum within a differentiated human enterocyte cell line. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):234–239. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.234-239.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanigan T. P., Soave R. Cryptosporidiosis. Prog Clin Parasitol. 1993;3:1–20. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-2732-8_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García Velarde E., Chávez Legaspi M., Coello Ramírez P., González J., Aguilar Benavides S. Cryptosporidium sp in 300 children with and without diarrhea. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1991 Jul-Dec;22(3-4):329–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino A., Canani R. B., Pozio E., Terracciano L., Albano F., Mazzeo M. Enterotoxic effect of stool supernatant of Cryptosporidium-infected calves on human jejunum. Gastroenterology. 1994 Jan;106(1):28–34. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(94)94093-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Ward H., Tzipori S., Pereira M. E., Alroy J. P., Keusch G. T. Attachment of Cryptosporidium parvum sporozoites to MDCK cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1994 Jun;62(6):2208–2213. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.6.2208-2213.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J., Pohlenz J. F., Moon H. W., Woode G. N. Enteric lesions and diarrhea in gnotobiotic calves monoinfected with Cryptosporidium species. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):768–775. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Nogueira Araujo G. M. A simple method of reducing the fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(3):349–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. H., Senft J. A. An improved method to determine cell viability by simultaneous staining with fluorescein diacetate-propidium iodide. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Jan;33(1):77–79. doi: 10.1177/33.1.2578146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laxer M. A., Alcantara A. K., Javato-Laxer M., Menorca D. M., Fernando M. T., Ranoa C. P. Immune response to cryptosporidiosis in Philippine children. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Feb;42(2):131–139. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.42.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima A. A., Fang G., Schorling J. B., de Albuquerque L., McAuliffe J. F., Mota S., Leite R., Guerrant R. L. Persistent diarrhea in northeast Brazil: etiologies and interactions with malnutrition. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1992 Sep;381:39–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1992.tb12370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumb R., Smith K., O'Donoghue P. J., Lanser J. A. Ultrastructure of the attachment of Cryptosporidium sporozoites to tissue culture cells. Parasitol Res. 1988;74(6):531–536. doi: 10.1007/BF00531630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L. Maintenance of the macromolecular barrier at cell extrusion sites in intestinal epithelium: physiological rearrangement of tight junctions. J Membr Biol. 1990 Jun;116(2):177–184. doi: 10.1007/BF01868675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcial M. A., Madara J. L. Cryptosporidium: cellular localization, structural analysis of absorptive cell-parasite membrane-membrane interactions in guinea pigs, and suggestion of protozoan transport by M cells. Gastroenterology. 1986 Mar;90(3):583–594. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)91112-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier J., Vasselon T., Hellio R., Lesourd M., Sansonetti P. J. Shigella flexneri enters human colonic Caco-2 epithelial cells through the basolateral pole. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):237–248. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.237-248.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mølbak K., Højlyng N., Gottschau A., Sá J. C., Ingholt L., da Silva A. P., Aaby P. Cryptosporidiosis in infancy and childhood mortality in Guinea Bissau, west Africa. BMJ. 1993 Aug 14;307(6901):417–420. doi: 10.1136/bmj.307.6901.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson L. J., Campbell A. T., Smith H. V. In vitro excystation of Cryptosporidium parvum. Parasitology. 1993 Jan;106(Pt 1):13–19. doi: 10.1017/s003118200007476x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. C., Beckers C. J., Joiner K. A. The parasitophorous vacuole membrane surrounding intracellular Toxoplasma gondii functions as a molecular sieve. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):509–513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears C. L., Guerrant R. L. Cryptosporidiosis: the complexity of intestinal pathophysiology. Gastroenterology. 1994 Jan;106(1):252–254. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(94)95891-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Angus K. W., Campbell I., Clerihew L. W. Diarrhea due to Cryptosporidium infection in artificially reared lambs. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.100-105.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S. Cryptosporidiosis in perspective. Adv Parasitol. 1988;27:63–129. doi: 10.1016/S0065-308X(08)60353-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Rand W., Griffiths J., Widmer G., Crabb J. Evaluation of an animal model system for cryptosporidiosis: therapeutic efficacy of paromomycin and hyperimmune bovine colostrum-immunoglobulin. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1994 Jul;1(4):450–463. doi: 10.1128/cdli.1.4.450-463.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Smith M., Halpin C., Angus K. W., Sherwood D., Campbell I. Experimental cryptosporidiosis in calves: clinical manifestations and pathological findings. Vet Rec. 1983 Feb 5;112(6):116–120. doi: 10.1136/vr.112.6.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]