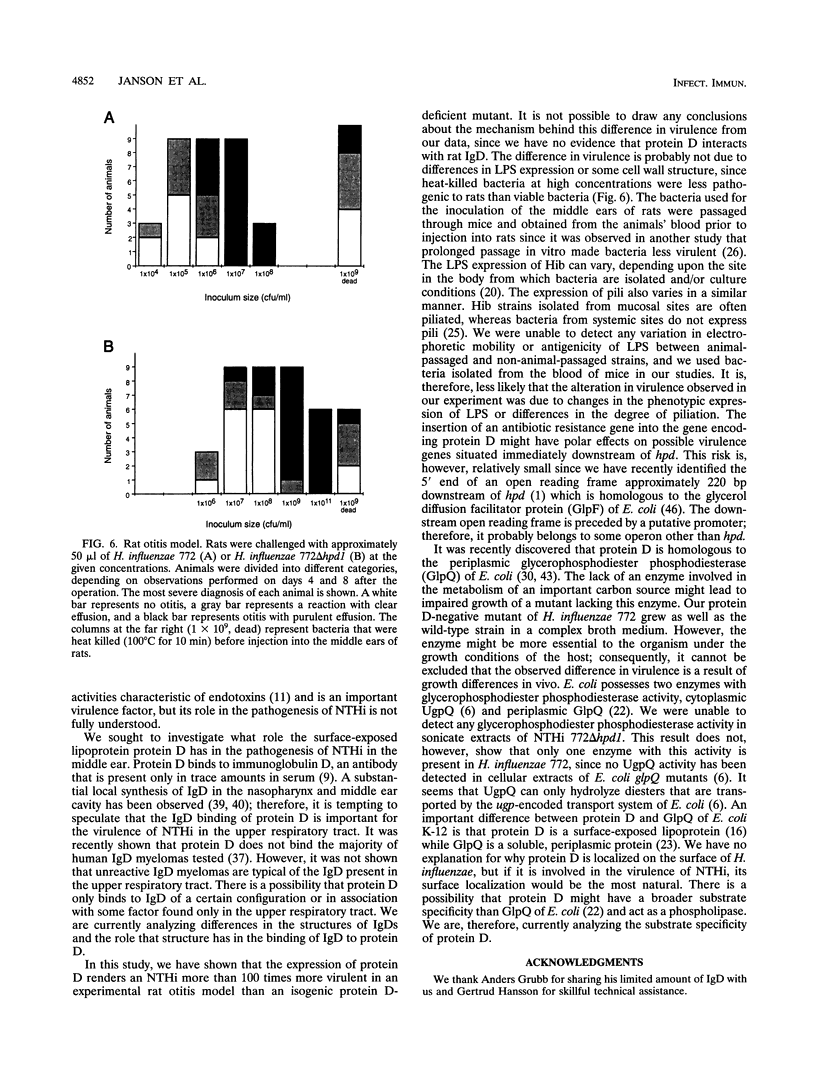
Abstract
A mutant lacking the ability to express the surface-exposed lipoprotein protein D was constructed by linker insertion and deletion mutagenesis of a cloned DNA insert containing the protein D structural gene from a nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae strain (NTHi). An isogenic NTHi mutant was isolated after transformation of genetically competent bacteria. The transformant was unreactive to a protein D-specific monoclonal antibody in a colony immunoassay. In addition, the mutant lacked the ability to synthesize detectable levels of protein D by protein staining, immunoblot methods, glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase activity, and binding studies of radiolabelled immunoglobulin D. The isogenic protein D-deficient mutant was compared with its parental strain for its ability to induce experimental otitis media in rats challenged with bacteria. An approximately 100-times-higher concentration of the mutant compared with that of the wild-type strain was required in order to cause otitis among all rats challenged with that given dose. The protein D mutant exhibited a generation time that was equal to that of the wild-type strain in complex broth medium. No difference in lipopolysaccharide expression was found between the mutant and the parental strain. These results suggest that protein D may influence the pathogenesis of NTHi in the upper respiratory tract.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akkoyunlu M., Ruan M., Forsgren A. Distribution of protein D, an immunoglobulin D-binding protein, in Haemophilus strains. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1231–1238. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1231-1238.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P. W., Pichichero M. E., Connor E. M. Enhanced nasopharyngeal colonization of rats by piliated Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):565–568. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.565-568.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNHART B. J., HERRIOTT R. M. PENETRATION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID INTO HEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 17;76:25–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Outer membrane protein and biotype analysis of pathogenic nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):535–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.535-540.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzoska P., Boos W. Characteristics of a ugp-encoded and phoB-dependent glycerophosphoryl diester phosphodiesterase which is physically dependent on the ugp transport system of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4125–4135. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4125-4135.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanyangam M., Smith A. L., Moseley S. L., Kuehn M., Jenny P. Contribution of a 28-kilodalton membrane protein to the virulence of Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):600–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.600-608.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnette S. L., Gleich G. J., Miller R. D., Kyle R. A. Measurement of IgD by a double antibody radioimmunoassay: demonstration of an apparent trimodal distribution of IgD levels in normal human sera. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1727–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel J. R. Simple and efficient system for synthesis of non-radioactive nucleic acid hybridization probes using PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2790–2790. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesher A. R., Insel R. A. Characterization of lipopolysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1978 Dec;138(6):719–730. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.6.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Shand G. H., Freudenberg M. A., Galanos C., Conrad R. S., Kronborg G., Høiby N. Antibodies from chronically infected cystic fibrosis patients react with lipopolysaccharides extracted by new micromethods from all serotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. APMIS. 1993 Feb;101(2):101–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1993.tb00088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Grubb A. O. Many bacterial species bind human IgD. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1468–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODGAL S. H., HERRIOTT R. M. Studies on transformations of Hemophilus influenzae. I. Competence. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Jul;44:1201–1227. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.6.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermansson A., Emgård P., Prellner K., Hellström S. A rat model for pneumococcal otitis media. Am J Otolaryngol. 1988 May-Jun;9(3):97–101. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0709(88)80013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janson H., Hedén L. O., Forsgren A. Protein D, the immunoglobulin D-binding protein of Haemophilus influenzae, is a lipoprotein. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1336–1342. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1336-1342.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janson H., Hedén L. O., Grubb A., Ruan M. R., Forsgren A. Protein D, an immunoglobulin D-binding protein of Haemophilus influenzae: cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):119–125. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.119-125.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janson H., Ruan M., Forsgren A. Limited diversity of the protein D gene (hpd) among encapsulated and nonencapsulated Haemophilus influenzae strains. Infect Immun. 1993 Nov;61(11):4546–4552. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.11.4546-4552.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kar S., To S. C., Brinton C. C., Jr Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of LKP pilus genes from a nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae strain. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):903–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.903-908.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Hansen E. J. Antigenic and phenotypic variations of Haemophilus influenzae type b lipopolysaccharide and their relationship to virulence. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):69–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.69-79.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Patrick C. C., Miller E. E., Cope L. D., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. Haemophilus influenzae type b lipooligosaccharide: stability of expression and association with virulence. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1979–1986. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1979-1986.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson T. J., Ehrmann M., Boos W. Periplasmic glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase of Escherichia coli, a new enzyme of the glp regulon. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5428–5432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson T. J., van Loo-Bhattacharya A. T. Purification and characterization of glpQ-encoded glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase from Escherichia coli K-12. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Feb 1;260(2):577–584. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90484-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason E. O., Jr, Kaplan S. L., Wiedermann B. L., Norrod E. P., Stenback W. A. Frequency and properties of naturally occurring adherent piliated strains of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):98–103. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.98-103.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melhus A., Hermansson A., Prellner K. Nontypeable and encapsulated Haemophilus influenzae yield different clinical courses of experimental otitis media. Acta Otolaryngol. 1994 May;114(3):289–294. doi: 10.3109/00016489409126058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation and preservation of competent bacterial cells by freezing. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:326–331. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Vaughn K. A. The type b capsular polysaccharide as a virulence determinant of Haemophilus influenzae: studies using clinical isolates and laboratory transformants. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):517–524. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Sasaki K. Protein D, a putative immunoglobulin D-binding protein produced by Haemophilus influenzae, is glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4569–4571. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4569-4571.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: a review of clinical aspects, surface antigens, and the human immune response to infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. A subtyping system for nontypable Haemophilus influenzae based on outer-membrane proteins. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):838–846. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. Identification of a specific epitope of Haemophilus influenzae on a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1300–1307. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Kubitschek K. R., Crennan J., Baughn R. E. Pneumonia and acute febrile tracheobronchitis due to haemophilus influenzae. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Oct;99(4):444–450. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-4-444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G. Microbial IgA proteases. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 29;298(26):1459–1463. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806292982608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruan M. R., Akkoyunlu M., Grubb A., Forsgren A. Protein D of Haemophilus influenzae. A novel bacterial surface protein with affinity for human IgD. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3379–3384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Munson R. S., Jr Protein D of Haemophilus influenzae is not a universal immunoglobulin D-binding protein. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):3026–3031. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.3026-3031.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Geme J. W., 3rd, Falkow S., Barenkamp S. J. High-molecular-weight proteins of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae mediate attachment to human epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2875–2879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swancutt M. A., Riley B. S., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Molecular characterization of the pathogen-specific, 34-kilodalton membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3314–3323. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3314-3323.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald E. R., Milmoe G. J., Bowen A., Ledesma-Medina J., Salamon N., Bluestone C. D. Acute maxillary sinusitis in children. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 26;304(13):749–754. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103263041302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Harris K., Lohrke S., Forney L., Smith A. L. Inability to express fimbriae results in impaired ability of Haemophilus influenzae b to colonize the nasopharynx. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4724–4728. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4724-4728.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenborn D. L., Wittekindt N., Larson T. J. Structure and regulation of the glpFK operon encoding glycerol diffusion facilitator and glycerol kinase of Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6122–6131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P. F., Smith A. L., Anderson P., Smith D. H. The role of encapsulation and host age in the clearance of Haemophilus influenzae bacteremia. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jan;135(1):34–41. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.1.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwahlen A., Rubin L. G., Moxon E. R. Contribution of lipopolysaccharide to pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae: comparative virulence of genetically-related strains in rats. Microb Pathog. 1986 Oct;1(5):465–473. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





