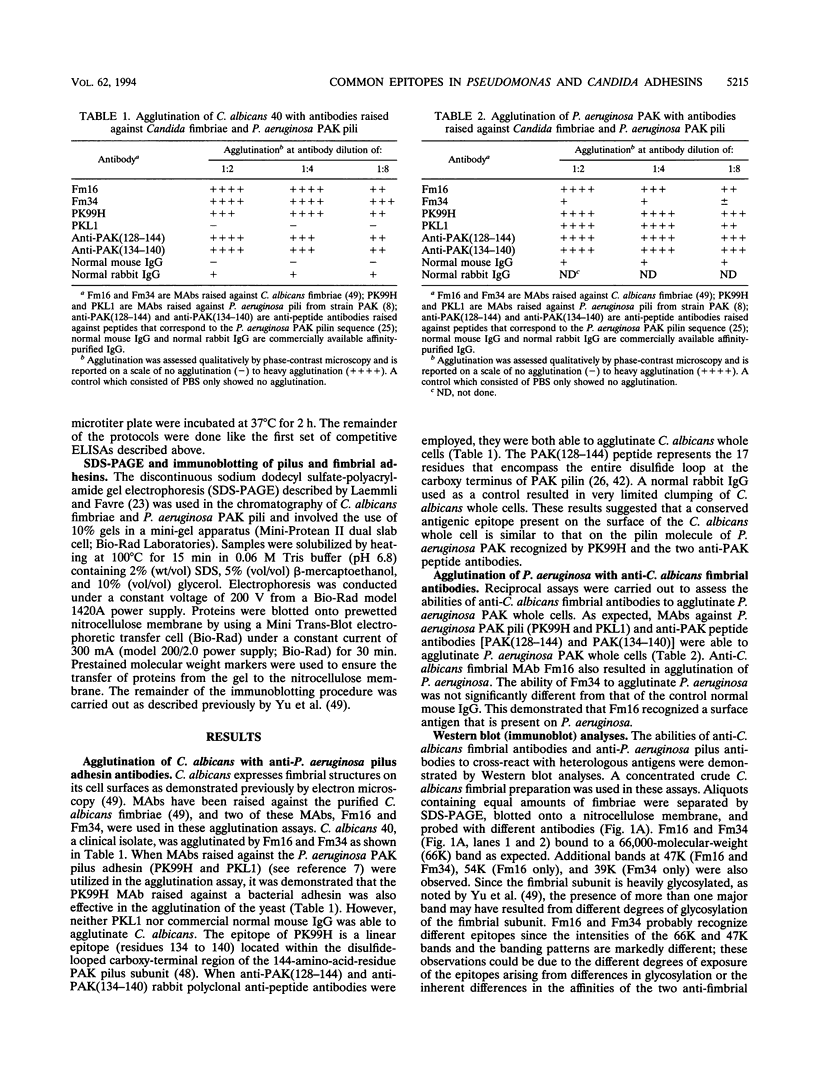
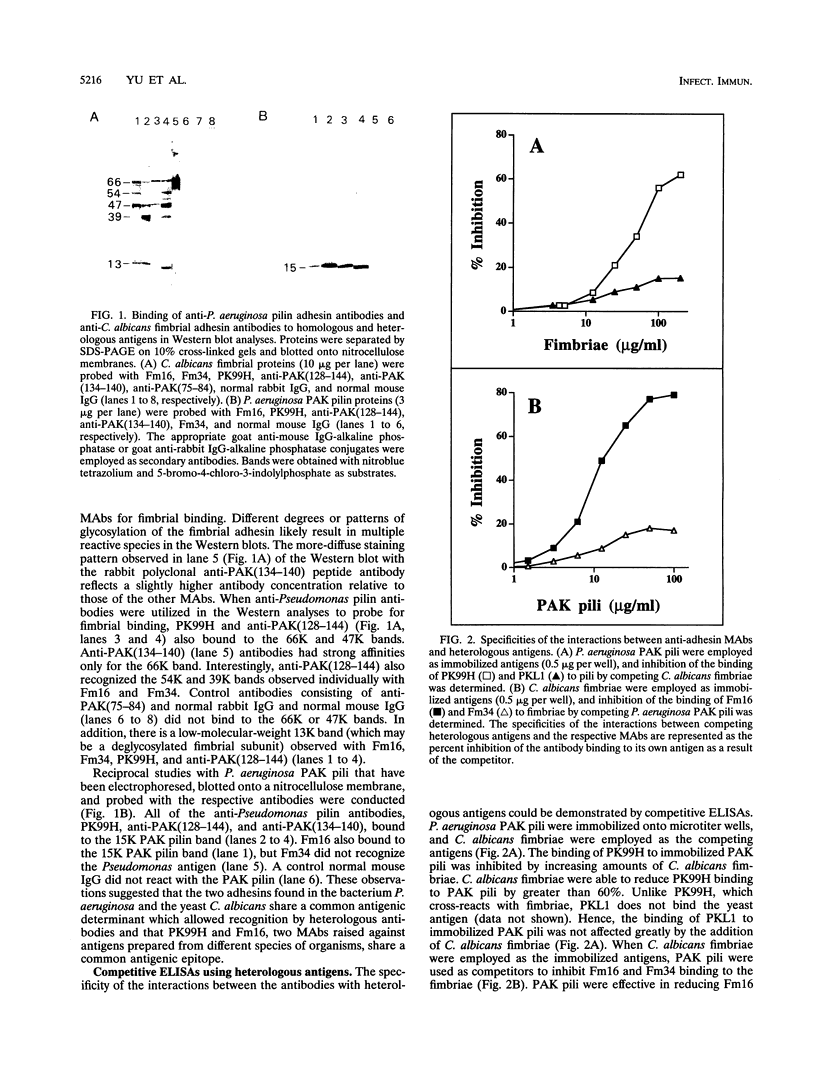
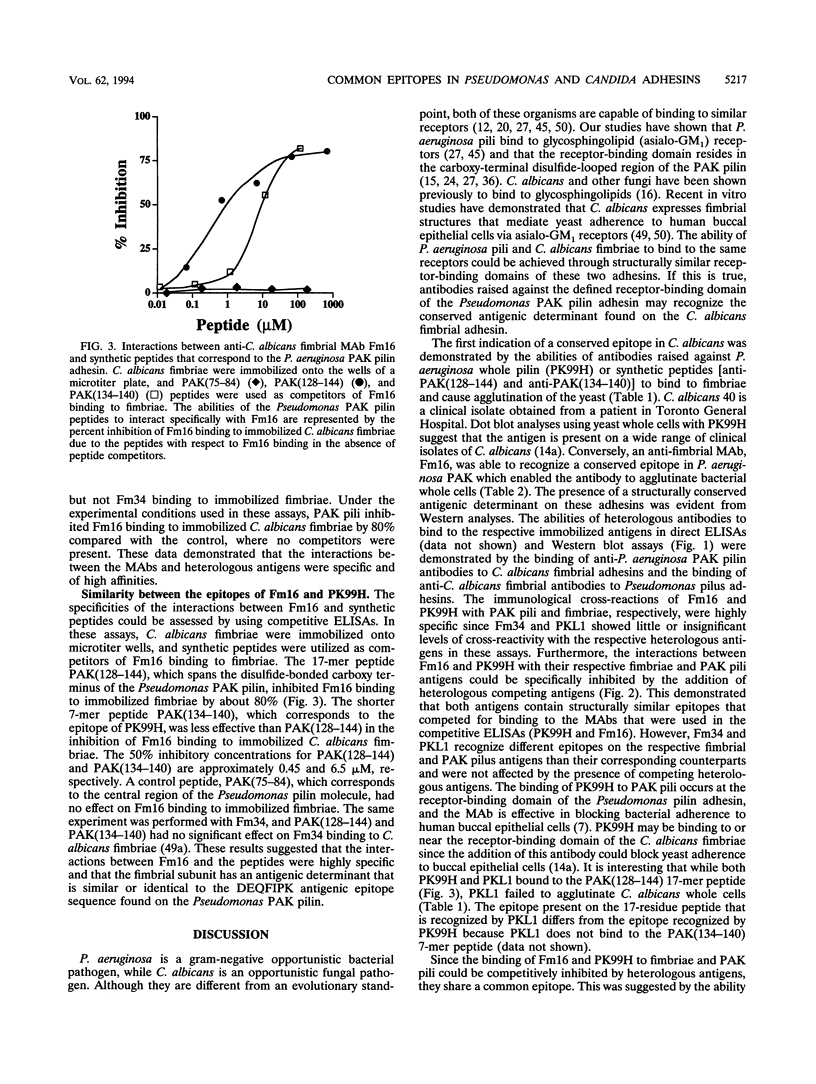
Abstract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a gram-negative bacterium, and Candida albicans, a dimorphic yeast, are evolutionarily distant microorganisms which can utilize filamentous structures termed pili and fimbriae, respectively, to mediate adherence to glycosphingolipids (asialoganglioside-GM1) receptors. The mechanism of adherence to glycosphingolipid receptors was investigated in these studies. By using monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) against purified pili of P. aeruginosa PAK (PK99H) and monospecific anti-peptide antibodies against the PAK pilin peptides [anti-PAK(128-144) and anti-PAK(134-140)], we demonstrated that these antibodies agglutinated C. albicans whole cells and cross-reacted with C. albicans fimbriae in immunoblots. A control MAb, PKL1, and anti-PAK(75-84) peptide antibodies failed to agglutinate C. albicans whole cells or cross-react with the fimbrial proteins. Conversely, the anti-C. albicans fimbrial MAb Fm16, but not Fm34, agglutinated P. aeruginosa PAK whole cells and Western blots (immunoblots). The interactions between PK99H and Fm16 and their respective homologous antigens were competitively inhibited by heterologous antigens; this demonstrated that the interactions between the antibodies and the heterologous antigens, i.e., PK99H with C. albicans fimbriae and Fm16 with P. aeruginosa pili, were highly specific and suggested that both adhesins share a common antigenic determinant. The immunological cross-reactivity between Fm16 and P. aeruginosa PAK pilin is localized onto the PAK(134-140) region as shown by a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The PAK(134-140) region of PAK pilin contains the epitope recognized by PK99H and also constitutes part of the receptor-binding domain of the pilus adhesin. Thus, the results from these studies suggest that common cell surface receptors are recognized by the P. aeruginosa and C. albicans adhesins because of a conserved receptor-binding domain on the adhesins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker N. R., Minor V., Deal C., Shahrabadi M. S., Simpson D. A., Woods D. E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S is an adhesion. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2859–2863. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2859-2863.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker N., Hansson G. C., Leffler H., Riise G., Svanborg-Edén C. Glycosphingolipid receptors for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2361–2366. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2361-2366.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendel C. M., Hostetter M. K. Distinct mechanisms of epithelial adhesion for Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis. Identification of the participating ligands and development of inhibitory peptides. J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):1840–1849. doi: 10.1172/JCI116775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R. A., Braun P. C. Adherence and receptor relationships of Candida albicans. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):1–20. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.1-20.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova M., Lopez-Ribot J. L., Monteagudo C., Llombart-Bosch A., Sentandreu R., Martinez J. P. Identification of a 58-kilodalton cell surface fibrinogen-binding mannoprotein from Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4221–4229. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4221-4229.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E. Putative virulence factors of Candida albicans. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:187–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig P., Sastry P. A., Hodges R. S., Lee K. K., Paranchych W., Irvin R. T. Inhibition of pilus-mediated adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to human buccal epithelial cells by monoclonal antibodies directed against pili. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):124–130. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.124-130.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig P., Smith N. R., Todd T., Irvin R. T. Characterization of the binding of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate to human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1517–1522. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1517-1522.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghannoum M. A., Burns G. R., Elteen K. A., Radwan S. S. Experimental evidence for the role of lipids in adherence of Candida spp. to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):189–193. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.189-193.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore B. J., Retsinas E. M., Lorenz J. S., Hostetter M. K. An iC3b receptor on Candida albicans: structure, function, and correlates for pathogenicity. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):38–46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlett L. D., Masinick S., Barrett R., Rosol K. Evidence for asialo GM1 as a corneal glycolipid receptor for Pseudomonas aeruginosa adhesion. Infect Immun. 1993 Dec;61(12):5164–5173. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.12.5164-5173.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter M. K. Adhesins and ligands involved in the interaction of Candida spp. with epithelial and endothelial surfaces. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1994 Jan;7(1):29–42. doi: 10.1128/cmr.7.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter M. K., Lorenz J. S., Preus L., Kendrick K. E. The iC3b receptor on Candida albicans: subcellular localization and modulation of receptor expression by glucose. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):761–768. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvin R. T., Doig P., Lee K. K., Sastry P. A., Paranchych W., Todd T., Hodges R. S. Characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa pilus adhesin: confirmation that the pilin structural protein subunit contains a human epithelial cell-binding domain. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3720–3726. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3720-3726.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez-Lucho V., Ginsburg V., Krivan H. C. Cryptococcus neoformans, Candida albicans, and other fungi bind specifically to the glycosphingolipid lactosylceramide (Gal beta 1-4Glc beta 1-1Cer), a possible adhesion receptor for yeasts. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2085–2090. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2085-2090.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanbe T., Han Y., Redgrave B., Riesselman M. H., Cutler J. E. Evidence that mannans of Candida albicans are responsible for adherence of yeast forms to spleen and lymph node tissue. Infect Immun. 1993 Jun;61(6):2578–2584. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.6.2578-2584.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K. A. Animal glycosphingolipids as membrane attachment sites for bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:309–350. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.001521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivan H. C., Ginsburg V., Roberts D. D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas cepacia isolated from cystic fibrosis patients bind specifically to gangliotetraosylceramide (asialo GM1) and gangliotriaosylceramide (asialo GM2). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jan;260(1):493–496. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivan H. C., Nilsson B., Lingwood C. A., Ryu H. Chlamydia trachomatis and Chlamydia pneumoniae bind specifically to phosphatidylethanolamine in HeLa cells and to GalNAc beta 1-4Gal beta 1-4GLC sequences-found in asialo-GM1 and asial-GM2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 29;175(3):1082–1089. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivan H. C., Roberts D. D., Ginsburg V. Many pulmonary pathogenic bacteria bind specifically to the carbohydrate sequence GalNAc beta 1-4Gal found in some glycolipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6157–6161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. K., Doig P., Irvin R. T., Paranchych W., Hodges R. S. Mapping the surface regions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK pilin: the importance of the C-terminal region for adherence to human buccal epithelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1493–1499. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. K., Paranchych W., Hodges R. S. Cross-reactive and strain-specific antipeptide antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK and PAO pili. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2727–2732. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2727-2732.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. K., Sastry P. A., Paranchych W., Hodges R. S. Immunological studies of the disulfide bridge region of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK and PAO pilins, using anti-PAK pilus and antipeptide antibodies. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):520–526. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.520-526.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. K., Sheth H. B., Wong W. Y., Sherburne R., Paranchych W., Hodges R. S., Lingwood C. A., Krivan H., Irvin R. T. The binding of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pili to glycosphingolipids is a tip-associated event involving the C-terminal region of the structural pilin subunit. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Feb;11(4):705–713. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood C. A., Cheng M., Krivan H. C., Woods D. Glycolipid receptor binding specificity of exoenzyme S from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 29;175(3):1076–1081. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91675-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer C. L., Filler S. G., Edwards J. E., Jr Candida albicans adherence to endothelial cells. Microvasc Res. 1992 Mar;43(2):218–226. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(92)90018-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEachran D. W., Irvin R. T. Adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to human buccal epithelial cells: evidence for two classes of receptors. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Jun;31(6):563–569. doi: 10.1139/m85-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa Y., Kuribayashi T., Kagaya K., Suzuki M., Nakase T., Fukazawa Y. Role of specific determinants in mannan of Candida albicans serotype A in adherence to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2493–2499. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2493-2499.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollert M. W., Wadsworth E., Calderone R. A. Reduced expression of the functionally active complement receptor for iC3b but not for C3d on an avirulent mutant of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):909–913. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.909-913.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paranchych W., Sastry P. A., Frost L. S., Carpenter M., Armstrong G. D., Watts T. H. Biochemical studies on pili isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Oct;25(10):1175–1181. doi: 10.1139/m79-182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paranchych W., Sastry P. A., Volpel K., Loh B. A., Speert D. P. Fimbriae (pili): molecular basis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa adherence. Clin Invest Med. 1986;9(2):113–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. Adhesins and receptors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with infection of the respiratory tract. Microb Pathog. 1992 Oct;13(4):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90035-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Pier G. B. Role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid exopolysaccharide in adherence to tracheal cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.1-4.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Sadoff J. C., Pyle M., Silipigni J. D. Role of pili in the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to injured tracheal epithelium. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):38–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.38-40.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiman L., Ishimoto K., Lory S., Prince A. The effect of piliation and exoproduct expression on the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to respiratory epithelial monolayers. J Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;161(3):541–548. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.3.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry P. A., Finlay B. B., Pasloske B. L., Paranchych W., Pearlstone J. R., Smillie L. B. Comparative studies of the amino acid and nucleotide sequences of pilin derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK and PAO. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):571–577. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.571-577.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Okinaga K. Role of pili in the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to mouse epidermal cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1774–1778. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1774-1778.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Savage D. C. Adhesion of Candida albicans to mouse intestinal mucosa in vitro: development of the assay and test of inhibitors. J Med Vet Mycol. 1986 Dec;24(6):477–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheth H. B., Lee K. K., Wong W. Y., Srivastava G., Hindsgaul O., Hodges R. S., Paranchych W., Irvin R. T. The pili of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains PAK and PAO bind specifically to the carbohydrate sequence beta GalNAc(1-4)beta Gal found in glycosphingolipids asialo-GM1 and asialo-GM2. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Feb;11(4):715–723. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Okawa Y., Hashimoto K., Suzuki S., Suzuki M. Protecting effect of chitin and chitosan on experimentally induced murine candidiasis. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(8):903–912. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosh F. D., Douglas L. J. Characterization of a fucoside-binding adhesin of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4734–4739. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4734-4739.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong W. Y., Irvin R. T., Paranchych W., Hodges R. S. Antigen-antibody interactions: elucidation of the epitope and strain-specificity of a monoclonal antibody directed against the pilin protein adherence binding domain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain K. Protein Sci. 1992 Oct;1(10):1308–1318. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560011010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L., Lee K. K., Ens K., Doig P. C., Carpenter M. R., Staddon W., Hodges R. S., Paranchych W., Irvin R. T. Partial characterization of a Candida albicans fimbrial adhesin. Infect Immun. 1994 Jul;62(7):2834–2842. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.7.2834-2842.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L., Lee K. K., Sheth H. B., Lane-Bell P., Srivastava G., Hindsgaul O., Paranchych W., Hodges R. S., Irvin R. T. Fimbria-mediated adherence of Candida albicans to glycosphingolipid receptors on human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1994 Jul;62(7):2843–2848. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.7.2843-2848.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



