Abstract
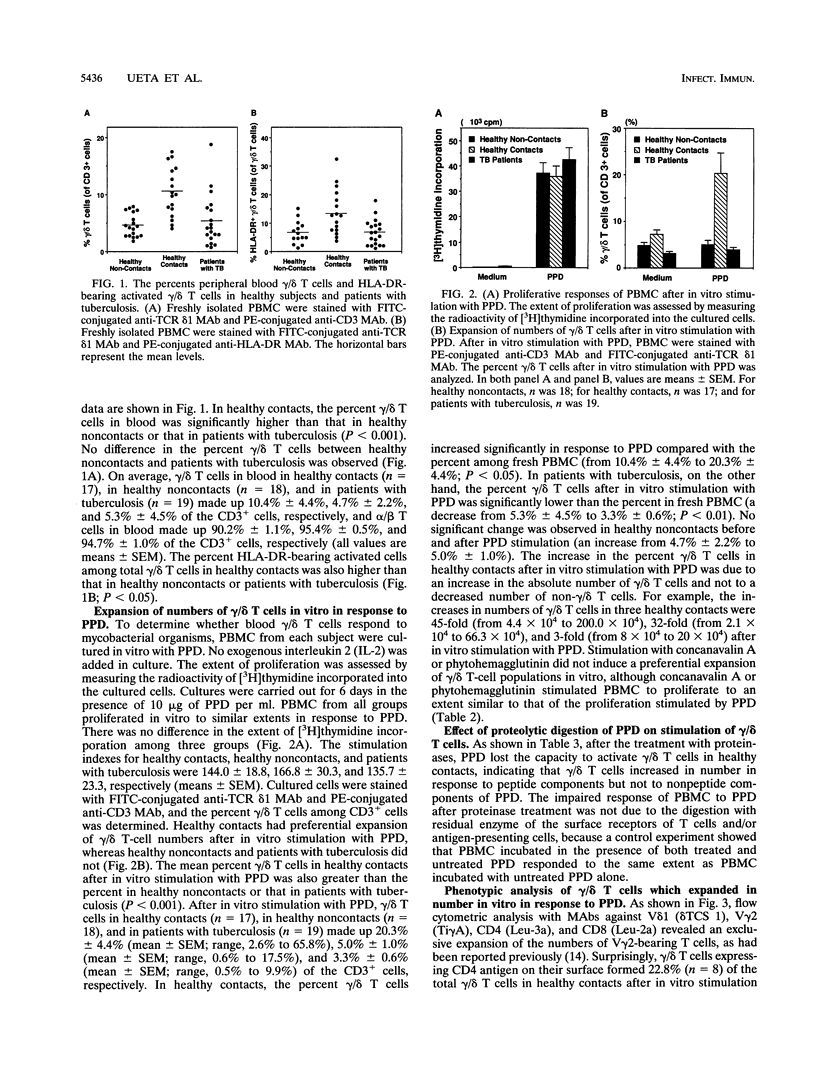
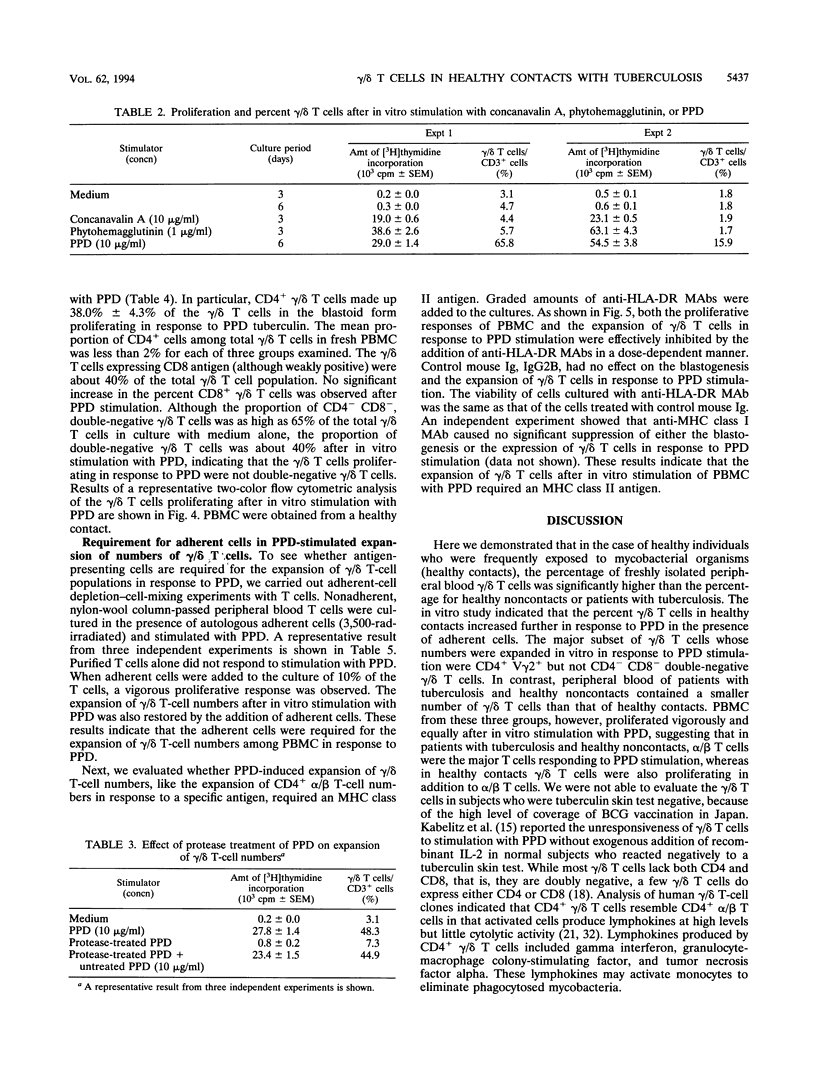
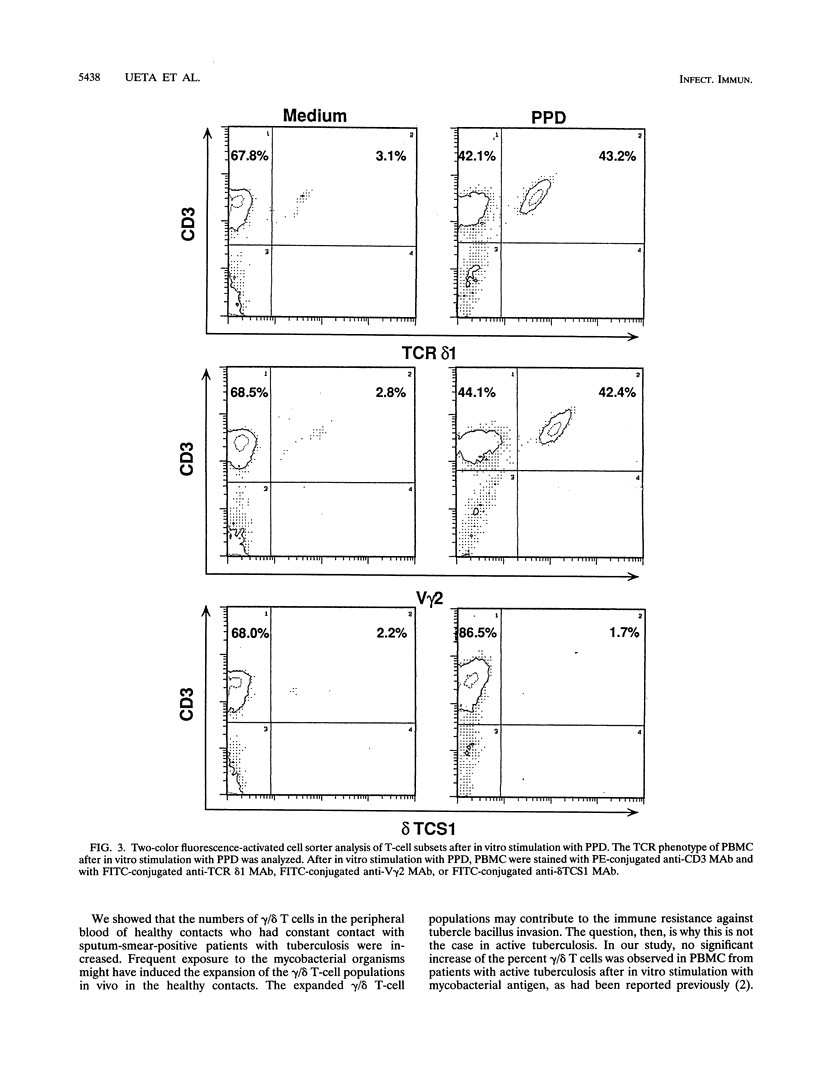
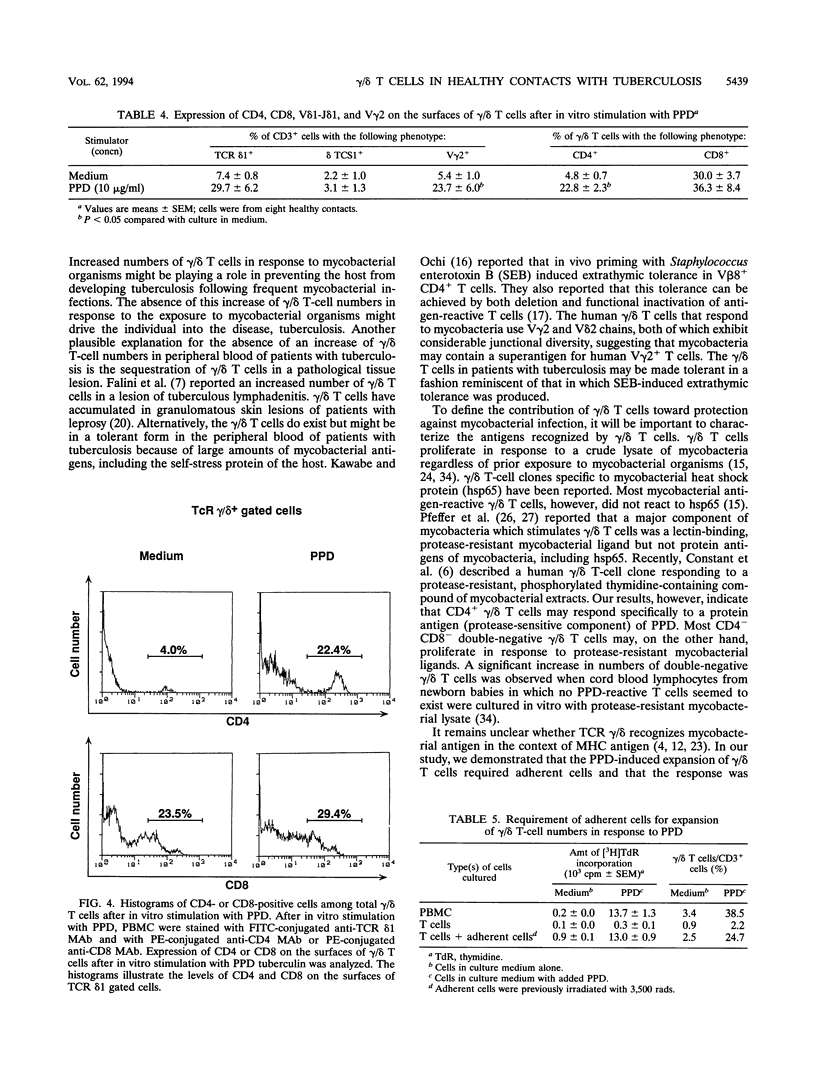
gamma/delta T cells are likely to participate in the immune response to tuberculous infection in humans. In this study, we carried out an investigation to characterize the responsiveness of gamma/delta T cells from tuberculous patients and healthy individuals to mycobacterial stimulation in vitro. Healthy subjects were assigned to the following two groups: those who had been exposed to tuberculosis (contacts) and those who had not been exposed (noncontacts). The percent gamma/delta T cells in fresh peripheral blood obtained from health care workers who were tuberculin skin test positive and who had constant contact with patients with active tuberculosis (healthy contacts) was significantly higher, whereas healthy noncontacts showed the normal range of gamma/delta T cells. Patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis also had low levels of gamma/delta T cells. HLA-DR antigen-bearing activated gamma/delta T cells were observed in higher percentages among healthy contacts than among healthy noncontacts or patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. In healthy contacts, gamma/delta T cells increased as a percentage of peripheral blood mononuclear cells after in vitro stimulation with purified protein derivative (PPD) tuberculin compared with the percentage of fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells that they made up, whereas no such increase was observed in patients with tuberculosis or in healthy noncontacts. Phenotypic analysis of the gamma/delta T cells in healthy contacts, which increased in number in vitro in response to PPD, revealed the preferential outgrowth of CD4+ V gamma 2+ gamma/delta T cells. This expansion of gamma/delta T cells by PPD required accessory cells, and it was inhibited by the addition of an antibody against HLA-DR in culture. Proteolytic digestion of PPD showed that gamma/delta T cells increased in number in response to peptide, but not nonpeptide, components of PPD. These findings suggest that gamma/delta T cells, especially CD4+ V gamma 2+ gamma/delta T cells, may participate in the immune surveillance of tuberculous infections in humans.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augustin A., Kubo R. T., Sim G. K. Resident pulmonary lymphocytes expressing the gamma/delta T-cell receptor. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):239–241. doi: 10.1038/340239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. F., Grisso C. L., Abrams J. S., Band H., Rea T. H., Modlin R. L. Gamma delta T lymphocytes in human tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;165(3):506–512. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.3.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Murray C. J. Tuberculosis: commentary on a reemergent killer. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1055–1064. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born W., Hall L., Dallas A., Boymel J., Shinnick T., Young D., Brennan P., O'Brien R. Recognition of a peptide antigen by heat shock--reactive gamma delta T lymphocytes. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.1695022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M. B., McLean J., Dialynas D. P., Strominger J. L., Smith J. A., Owen F. L., Seidman J. G., Ip S., Rosen F., Krangel M. S. Identification of a putative second T-cell receptor. Nature. 1986 Jul 10;322(6075):145–149. doi: 10.1038/322145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constant P., Davodeau F., Peyrat M. A., Poquet Y., Puzo G., Bonneville M., Fournié J. J. Stimulation of human gamma delta T cells by nonpeptidic mycobacterial ligands. Science. 1994 Apr 8;264(5156):267–270. doi: 10.1126/science.8146660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falini B., Flenghi L., Pileri S., Pelicci P., Fagioli M., Martelli M. F., Moretta L., Ciccone E. Distribution of T cells bearing different forms of the T cell receptor gamma/delta in normal and pathological human tissues. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2480–2488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiseler P. J., Nelson K. E., Crispen R. G., Moses V. K. Tuberculosis in physicians: a continuing problem. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 May;133(5):773–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haregewoin A., Soman G., Hom R. C., Finberg R. W. Human gamma delta+ T cells respond to mycobacterial heat-shock protein. Nature. 1989 Jul 27;340(6231):309–312. doi: 10.1038/340309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromatsu K., Yoshikai Y., Matsuzaki G., Ohga S., Muramori K., Matsumoto K., Bluestone J. A., Nomoto K. A protective role of gamma/delta T cells in primary infection with Listeria monocytogenes in mice. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):49–56. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Koning F., Coligan J. E., De Bruyn J., Strober S. Isolation of CD4- CD8- mycobacteria-reactive T lymphocyte clones from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):226–229. doi: 10.1038/339226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Vila L. M., Keroack B. J., McKinley D. R., Bayne N. K. Dual antigenic recognition by cloned human gamma delta T cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):308–314. doi: 10.1172/JCI115577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janis E. M., Kaufmann S. H., Schwartz R. H., Pardoll D. M. Activation of gamma delta T cells in the primary immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):713–716. doi: 10.1126/science.2524098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabelitz D., Bender A., Prospero T., Wesselborg S., Janssen O., Pechhold K. The primary response of human gamma/delta + T cells to Mycobacterium tuberculosis is restricted to V gamma 9-bearing cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1331–1338. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabelitz D., Bender A., Schondelmaier S., Schoel B., Kaufmann S. H. A large fraction of human peripheral blood gamma/delta + T cells is activated by Mycobacterium tuberculosis but not by its 65-kD heat shock protein. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):667–679. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe Y., Ochi A. Programmed cell death and extrathymic reduction of Vbeta8+ CD4+ T cells in mice tolerant to Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):245–248. doi: 10.1038/349245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe Y., Ochi A. Selective anergy of V beta 8+,CD4+ T cells in Staphylococcus enterotoxin B-primed mice. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1065–1070. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Federspiel N. A., Ruitenberg J. J., Phillips J. H., Allison J. P., Littman D., Weiss A. The T cell antigen receptor complex expressed on normal peripheral blood CD4-, CD8- T lymphocytes. A CD3-associated disulfide-linked gamma chain heterodimer. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):1076–1094. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liippo K. K., Kulmala K., Tala E. O. Focusing tuberculosis contact tracing by smear grading of index cases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Jul;148(1):235–236. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.1.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Pirmez C., Hofman F. M., Torigian V., Uyemura K., Rea T. H., Bloom B. R., Brenner M. B. Lymphocytes bearing antigen-specific gamma delta T-cell receptors accumulate in human infectious disease lesions. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):544–548. doi: 10.1038/339544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita C. T., Verma S., Aparicio P., Martinez C., Spits H., Brenner M. B. Functionally distinct subsets of human gamma/delta T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Dec;21(12):2999–3007. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardell E., McInnis B., Thomas B., Weidhaas S. Exogenous reinfection with tuberculosis in a shelter for the homeless. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 18;315(25):1570–1575. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612183152502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. L., Happ M. P., Dallas A., Palmer E., Kubo R., Born W. K. Stimulation of a major subset of lymphocytes expressing T cell receptor gamma delta by an antigen derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmen J. D., Barnes P. F., Uyemura K., Lu S. Z., Grisso C. L., Modlin R. L. The T cell receptors of human gamma delta T cells reactive to Mycobacterium tuberculosis are encoded by specific V genes but diverse V-J junctions. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 15;147(10):3353–3359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pechhold K., Wesch D., Schondelmaier S., Kabelitz D. Primary activation of V gamma 9-expressing gamma delta T cells by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Requirement for Th1-type CD4 T cell help and inhibition by IL-10. J Immunol. 1994 May 15;152(10):4984–4992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer K., Schoel B., Gulle H., Kaufmann S. H., Wagner H. Primary responses of human T cells to mycobacteria: a frequent set of gamma/delta T cells are stimulated by protease-resistant ligands. Eur J Immunol. 1990 May;20(5):1175–1179. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer K., Schoel B., Plesnila N., Lipford G. B., Kromer S., Deusch K., Wagner H. A lectin-binding, protease-resistant mycobacterial ligand specifically activates V gamma 9+ human gamma delta T cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):575–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh J. W., Wichelhausen R. H., Rado T. A., Bates J. H. Evidence for infection by two distinct strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in pulmonary tuberculosis: report of 9 cases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Oct;112(4):497–503. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.112.4.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raziuddin S., Telmasani A. W., el-Hag el-Awad M., al-Amari O., al-Janadi M. Gamma delta T cells and the immune response in visceral leishmaniasis. Eur J Immunol. 1992 May;22(5):1143–1148. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeyn J. A. Exogenous reinfection in tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 Jun;101(6):923–927. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.101.6.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small P. M., Shafer R. W., Hopewell P. C., Singh S. P., Murphy M. J., Desmond E., Sierra M. F., Schoolnik G. K. Exogenous reinfection with multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in patients with advanced HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 1993 Apr 22;328(16):1137–1144. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199304223281601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., Paliard X., Vandekerckhove Y., van Vlasselaer P., de Vries J. E. Functional and phenotypic differences between CD4+ and CD4- T cell receptor-gamma delta clones from peripheral blood. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1180–1188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuyuguchi I., Kawasumi H., Takashima T., Tsuyuguchi T., Kishimoto S. Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellular complex-induced suppression of T-cell proliferation in vitro by regulation of monocyte accessory cell activity. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1369–1378. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1369-1378.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuyuguchi I., Kawasumi H., Ueta C., Yano I., Kishimoto S. Increase of T-cell receptor gamma/delta-bearing T cells in cord blood of newborn babies obtained by in vitro stimulation with mycobacterial cord factor. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3053–3059. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3053-3059.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


