Abstract
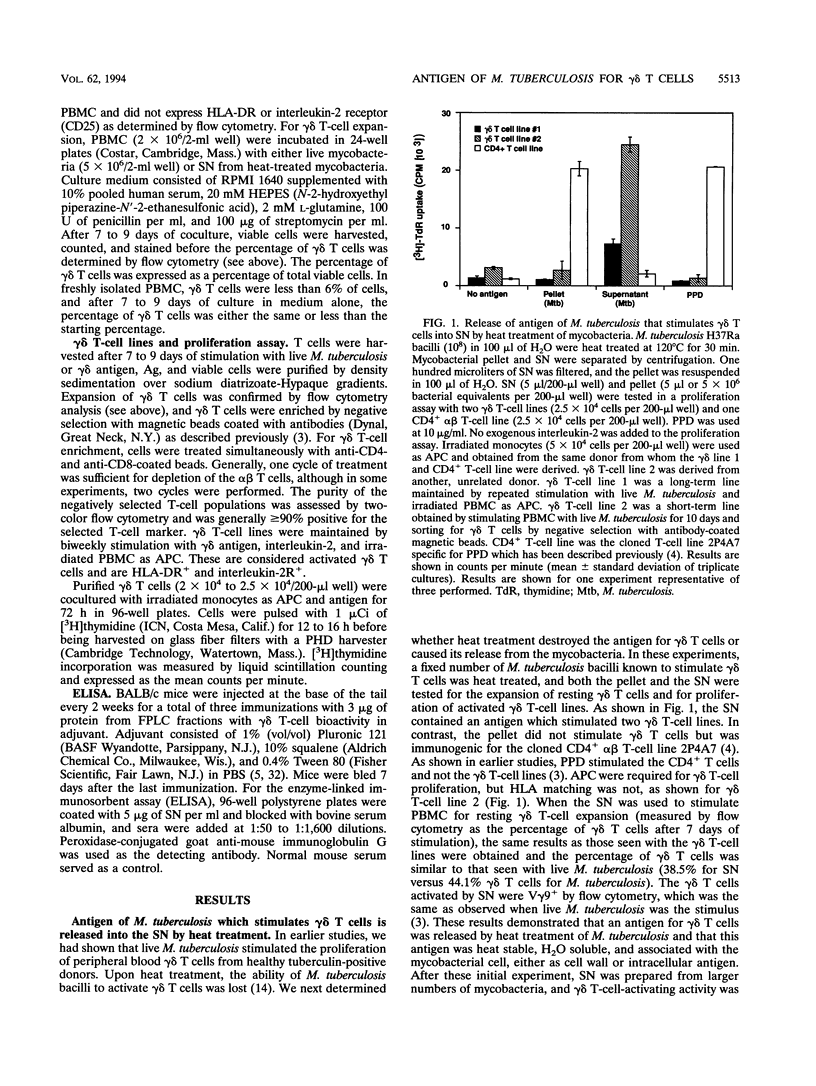
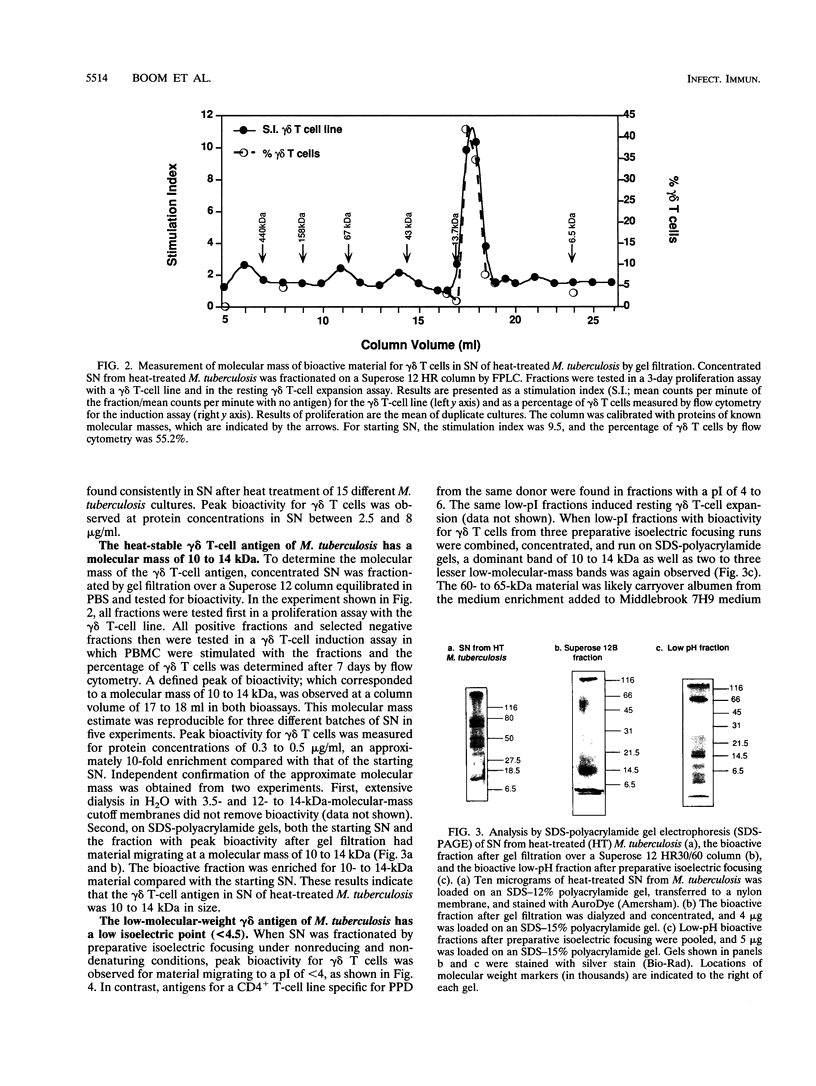
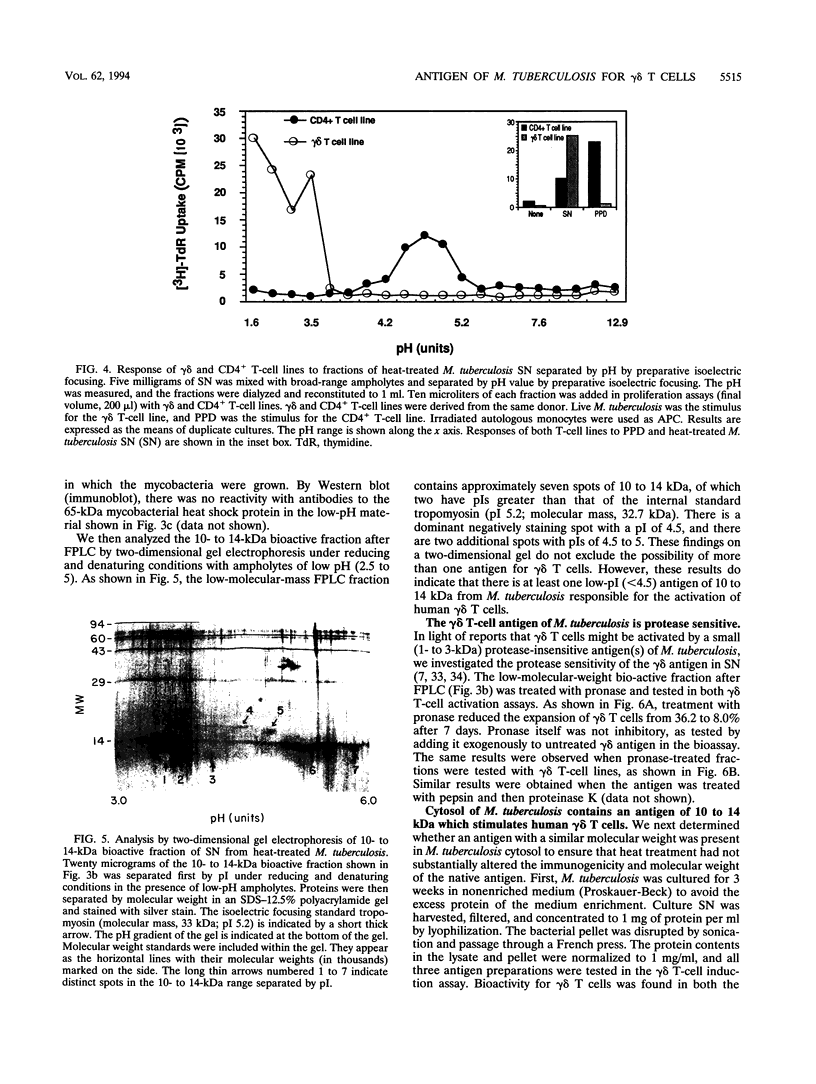
gamma delta T-cell receptor-bearing T cells (gamma delta T cells) are readily activated by intracellular bacterial pathogens such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacterial antigens responsible for gamma delta T-cell activation remain poorly characterized. We have found that heat treatment of live M. tuberculosis bacilli released into the supernatant an antigen which stimulated human gamma delta T cells. gamma delta T-cell activation was measured by determining the increase in percentage of gamma delta T cells by flow cytometry in peripheral blood mononuclear cells stimulated with antigen and by proliferation of gamma delta T-cell lines with monocytes as antigen-presenting cells. Supernatant from heat-treated M. tuberculosis was fractionated by fast-performance liquid chromatography (FPLC) on a Superose 12 column. Maximal gamma delta T-cell activation was measured for a fraction of 10 to 14 kDa. Separation of the supernatant by preparative isoelectric focusing demonstrated peak activity at a pI of < 4.0. On two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, the 10- to 14-kDa FPLC fraction contained at least seven distinct molecules, of which two had a pI of < 4.5. Protease treatment reduced the bioactivity of the 10- to 14-kDa FPLC fraction for both resting and activated gamma delta T cells. Murine antibodies raised to the 10- to 14-kDa fraction reacted by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with antigens of 10 to 14 kDa in lysate of M. tuberculosis. In addition, gamma delta T cells proliferated in response to an antigen of 10 to 14 kDa present in M. tuberculosis lysate. gamma delta T-cell-stimulating antigen was not found in culture filtrate of M. tuberculosis but was associated with the bacterial pellet and lysate of M. tuberculosis. These results provide a preliminary characterization of a 10- to 14-kDa, cell-associated, heat-stable, low-pI protein antigen of M. tuberculosis which is a major stimulus for human gamma delta T cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augustin A., Kubo R. T., Sim G. K. Resident pulmonary lymphocytes expressing the gamma/delta T-cell receptor. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):239–241. doi: 10.1038/340239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autran B., Triebel F., Katlama C., Rozenbaum W., Hercend T., Debre P. T cell receptor gamma/delta+ lymphocyte subsets during HIV infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Feb;75(2):206–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom W. H., Chervenak K. A., Mincek M. A., Ellner J. J. Role of the mononuclear phagocyte as an antigen-presenting cell for human gamma delta T cells activated by live Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3480–3488. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3480-3488.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom W. H., Wallis R. S., Chervenak K. A. Human Mycobacterium tuberculosis-reactive CD4+ T-cell clones: heterogeneity in antigen recognition, cytokine production, and cytotoxicity for mononuclear phagocytes. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2737–2743. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2737-2743.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byars N. E., Allison A. C. Adjuvant formulation for use in vaccines to elicit both cell-mediated and humoral immunity. Vaccine. 1987 Sep;5(3):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(87)90105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carding S. R., Allan W., Kyes S., Hayday A., Bottomly K., Doherty P. C. Late dominance of the inflammatory process in murine influenza by gamma/delta + T cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1225–1231. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constant P., Davodeau F., Peyrat M. A., Poquet Y., Puzo G., Bonneville M., Fournié J. J. Stimulation of human gamma delta T cells by nonpeptidic mycobacterial ligands. Science. 1994 Apr 8;264(5156):267–270. doi: 10.1126/science.8146660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Libero G., Casorati G., Giachino C., Carbonara C., Migone N., Matzinger P., Lanzavecchia A. Selection by two powerful antigens may account for the presence of the major population of human peripheral gamma/delta T cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1311–1322. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Paoli P., Gennari D., Martelli P., Basaglia G., Crovatto M., Battistin S., Santini G. A subset of gamma delta lymphocytes is increased during HIV-1 infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Feb;83(2):187–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Paoli P., Gennari D., Martelli P., Cavarzerani V., Comoretto R., Santini G. Gamma delta T cell receptor-bearing lymphocytes during Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):1013–1016. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emoto M., Danbara H., Yoshikai Y. Induction of gamma/delta T cells in murine salmonellosis by an avirulent but not by a virulent strain of Salmonella choleraesuis. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):363–372. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodier M., Krause-Jauer M., Langhorne J. Quantitative analysis of the response of human T cell receptor V gamma 9+ cells to Plasmodium falciparum. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Oct;22(10):2757–2760. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas W., Pereira P., Tonegawa S. Gamma/delta cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:637–685. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havlir D. V., Ellner J. J., Chervenak K. A., Boom W. H. Selective expansion of human gamma delta T cells by monocytes infected with live Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):729–733. doi: 10.1172/JCI115053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M., Webster H. K., Tongtawe P., Pattanapanyasat K., Weidanz W. P. Increased gamma delta T cells in acute Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Immunol Lett. 1990 Aug;25(1-3):139–141. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(90)90105-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Vila L. M., Keroack B. J., McKinley D. R., Bayne N. K. Dual antigenic recognition by cloned human gamma delta T cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):308–314. doi: 10.1172/JCI115577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Yoshikai Y., Matsuzaki G., Nomoto K. Early appearing gamma/delta-bearing T cells during infection with Calmétte Guérin bacillus. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2754–2762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M., Lancki D. W., Sperling A. I., Dick R. F., Spear P. G., Fitch F. W., Bluestone J. A. A murine CD4-, CD8- T cell receptor-gamma delta T lymphocyte clone specific for herpes simplex virus glycoprotein I. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 15;148(4):983–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabelitz D., Bender A., Prospero T., Wesselborg S., Janssen O., Pechhold K. The primary response of human gamma/delta + T cells to Mycobacterium tuberculosis is restricted to V gamma 9-bearing cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1331–1338. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabelitz D., Bender A., Schondelmaier S., Schoel B., Kaufmann S. H. A large fraction of human peripheral blood gamma/delta + T cells is activated by Mycobacterium tuberculosis but not by its 65-kD heat shock protein. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):667–679. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolick J. B., Scott E. R., Odaka N., Saah A. J. Flow cytometric analysis of gamma delta T cells and natural killer cells in HIV-1 infection. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Jan;58(1):126–138. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Pirmez C., Hofman F. M., Torigian V., Uyemura K., Rea T. H., Bloom B. R., Brenner M. B. Lymphocytes bearing antigen-specific gamma delta T-cell receptors accumulate in human infectious disease lesions. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):544–548. doi: 10.1038/339544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mombaerts P., Arnoldi J., Russ F., Tonegawa S., Kaufmann S. H. Different roles of alpha beta and gamma delta T cells in immunity against an intracellular bacterial pathogen. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):53–56. doi: 10.1038/365053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munk M. E., Gatrill A. J., Kaufmann S. H. Target cell lysis and IL-2 secretion by gamma/delta T lymphocytes after activation with bacteria. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2434–2439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. L., Happ M. P., Dallas A., Palmer E., Kubo R., Born W. K. Stimulation of a major subset of lymphocytes expressing T cell receptor gamma delta by an antigen derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohga S., Yoshikai Y., Takeda Y., Hiromatsu K., Nomoto K. Sequential appearance of gamma/delta- and alpha/beta-bearing T cells in the peritoneal cavity during an i.p. infection with Listeria monocytogenes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Mar;20(3):533–538. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmen J. D., Barnes P. F., Uyemura K., Lu S. Z., Grisso C. L., Modlin R. L. The T cell receptors of human gamma delta T cells reactive to Mycobacterium tuberculosis are encoded by specific V genes but diverse V-J junctions. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 15;147(10):3353–3359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Andersen P., Boom W. H. T cell response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1481–1497. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panchamoorthy G., McLean J., Modlin R. L., Morita C. T., Ishikawa S., Brenner M. B., Band H. A predominance of the T cell receptor V gamma 2/V delta 2 subset in human mycobacteria-responsive T cells suggests germline gene encoded recognition. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 15;147(10):3360–3369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S. S., Wacholtz M. C., Duby A. D., Thiele D. L., Lipsky P. E. Analysis of the functional capabilities of CD3+CD4-CD8- and CD3+CD4+CD8+ human T cell clones. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1108–1117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman E., Kazura J. W., Hazlett F. E., Jr, Boom W. H. Modulation of murine cytokine responses to mycobacterial antigens by helminth-induced T helper 2 cell responses. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 1;151(9):4857–4864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer K., Schoel B., Gulle H., Kaufmann S. H., Wagner H. Primary responses of human T cells to mycobacteria: a frequent set of gamma/delta T cells are stimulated by protease-resistant ligands. Eur J Immunol. 1990 May;20(5):1175–1179. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer K., Schoel B., Plesnila N., Lipford G. B., Kromer S., Deusch K., Wagner H. A lectin-binding, protease-resistant mycobacterial ligand specifically activates V gamma 9+ human gamma delta T cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):575–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambukkana A., Das P. K., Chand A., Baas J. G., Groothuis D. G., Kolk A. H. Subcellular distribution of monoclonal antibody defined epitopes on immunodominant Mycobacterium tuberculosis proteins in the 30-kDa region: identification and localization of 29/33-kDa doublet proteins on mycobacterial cell wall. Scand J Immunol. 1991 Jun;33(6):763–775. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1991.tb02551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H. The structure, function, and molecular genetics of the gamma/delta T cell receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:175–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raziuddin S., Telmasani A. W., el-Hag el-Awad M., al-Amari O., al-Janadi M. Gamma delta T cells and the immune response in visceral leishmaniasis. Eur J Immunol. 1992 May;22(5):1143–1148. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivas A., Koide J., Cleary M. L., Engleman E. G. Evidence for involvement of the gamma, delta T cell antigen receptor in cytotoxicity mediated by human alloantigen-specific T cell clones. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):1840–1846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. D., Ordway D. J., Orme I. M. Listeria monocytogenes infection in beta 2 microglobulin-deficient mice. Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):1113–1116. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.1113-1116.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo D. M., Armitage R. J., Barral-Netto M., Barral A., Grabstein K. H., Reed S. G. Antigen-reactive gamma delta T cells in human leishmaniasis. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 1;151(7):3712–3718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoel B., Gulle H., Kaufmann S. H. Heterogeneity of the repertoire of T cells of tuberculosis patients and healthy contacts to Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens separated by high-resolution techniques. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1717–1720. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1717-1720.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeen M. J., Ziegler H. K. Induction of murine peritoneal gamma/delta T cells and their role in resistance to bacterial infection. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):971–984. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuyuguchi I., Kawasumi H., Ueta C., Yano I., Kishimoto S. Increase of T-cell receptor gamma/delta-bearing T cells in cord blood of newborn babies obtained by in vitro stimulation with mycobacterial cord factor. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3053–3059. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3053-3059.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]