Abstract
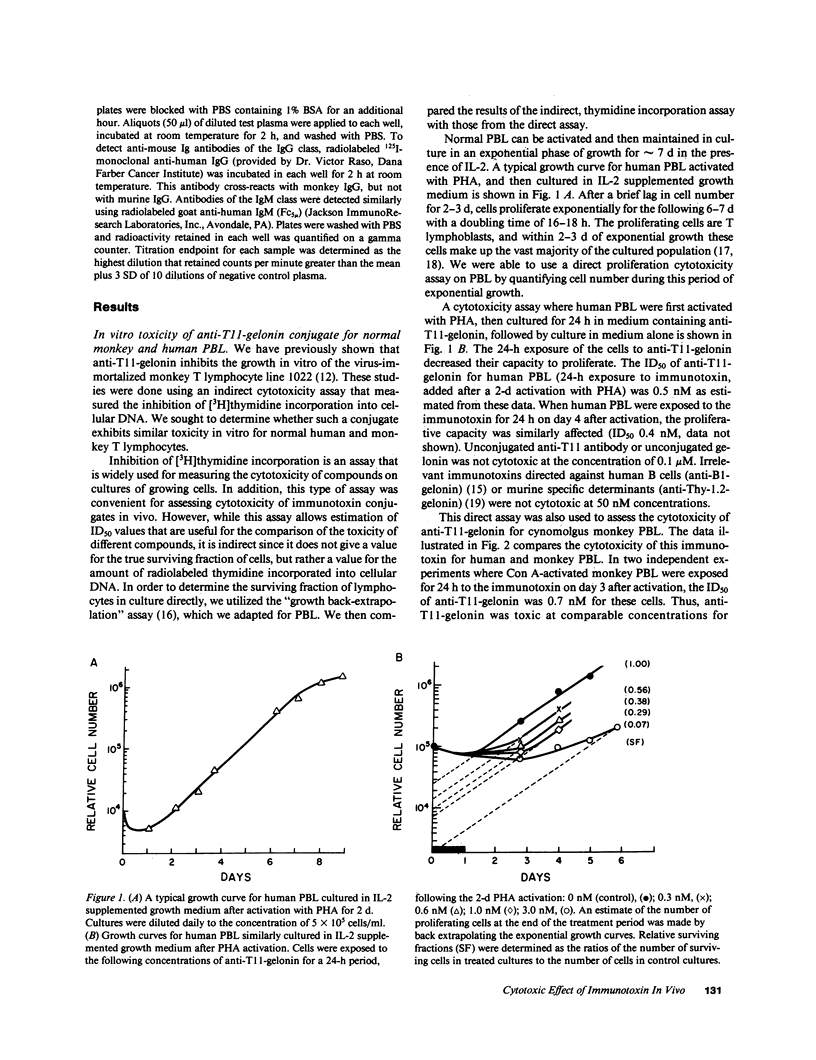
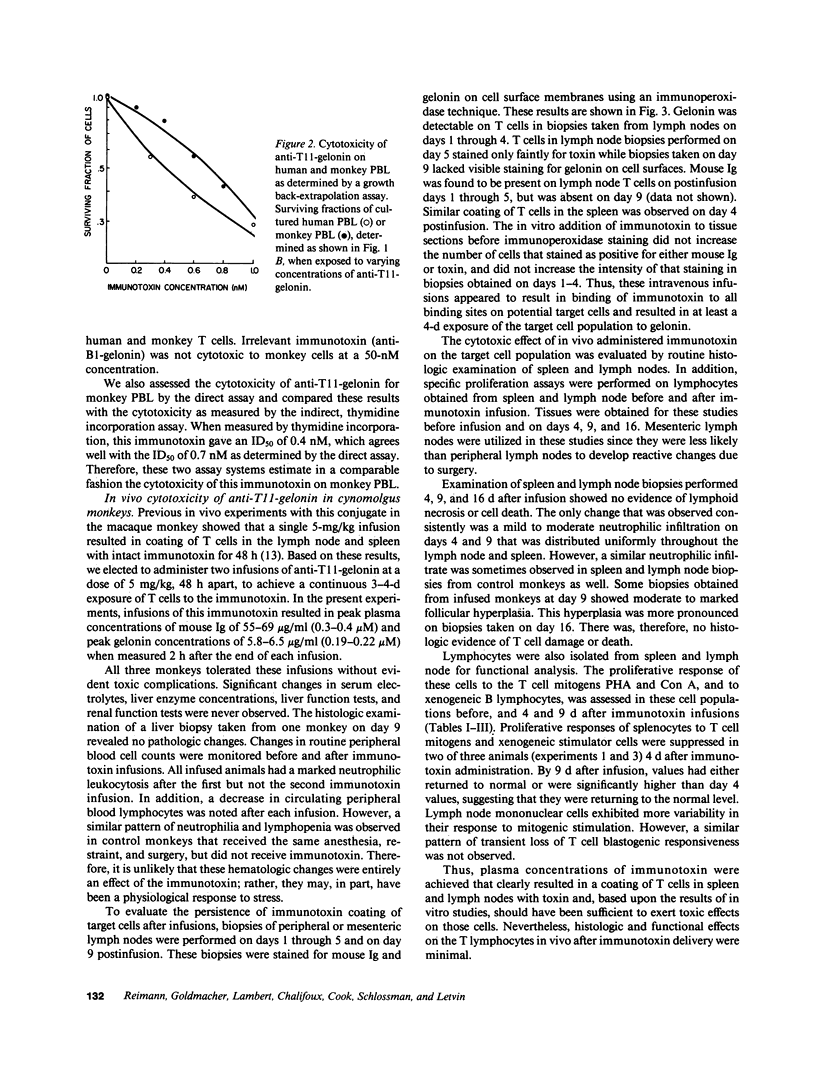
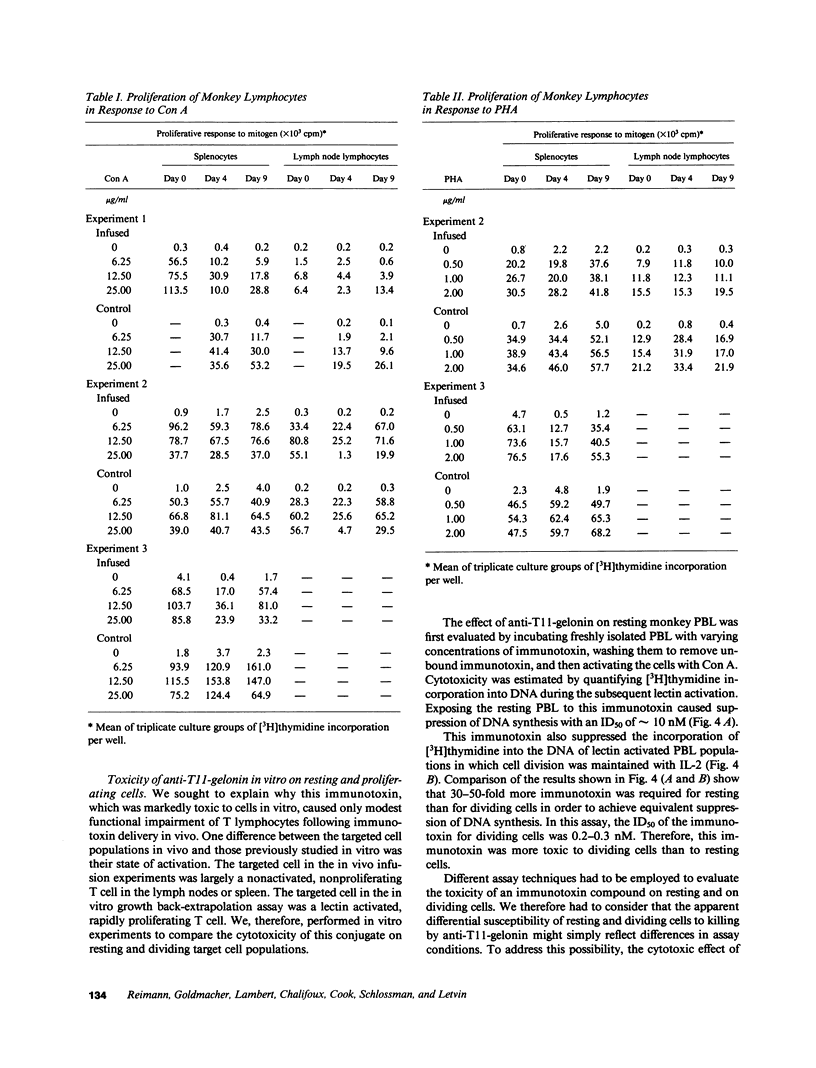
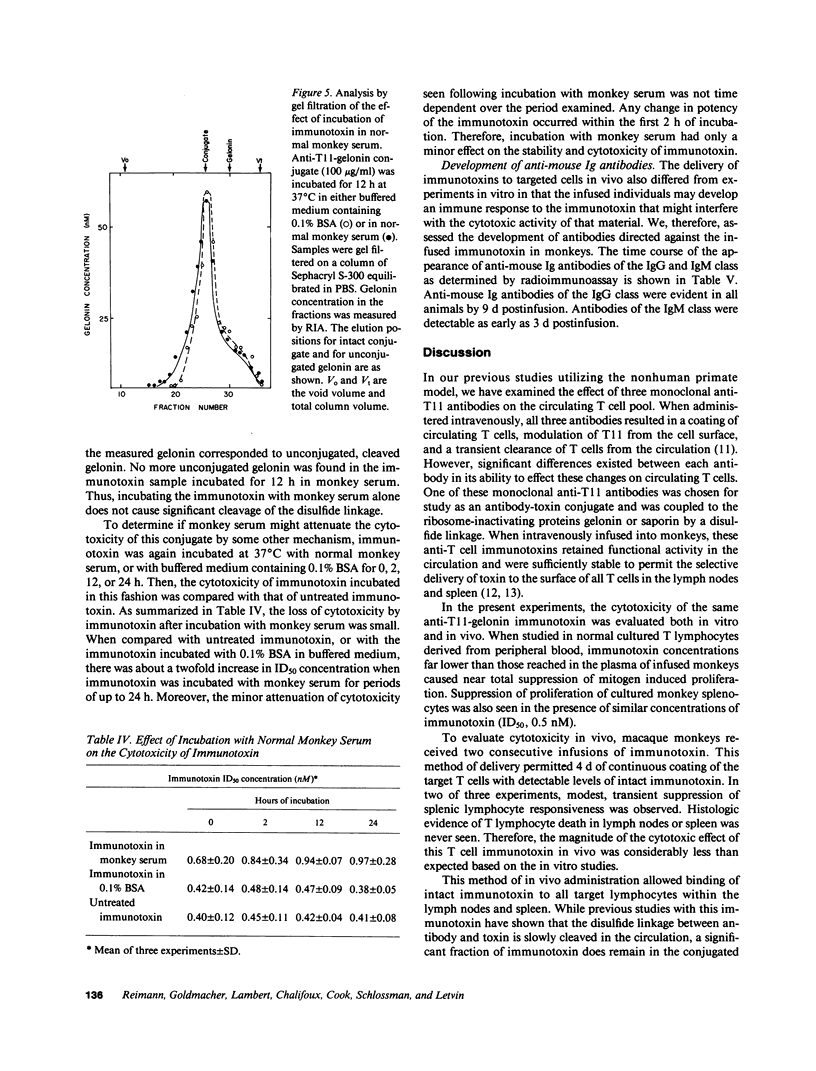
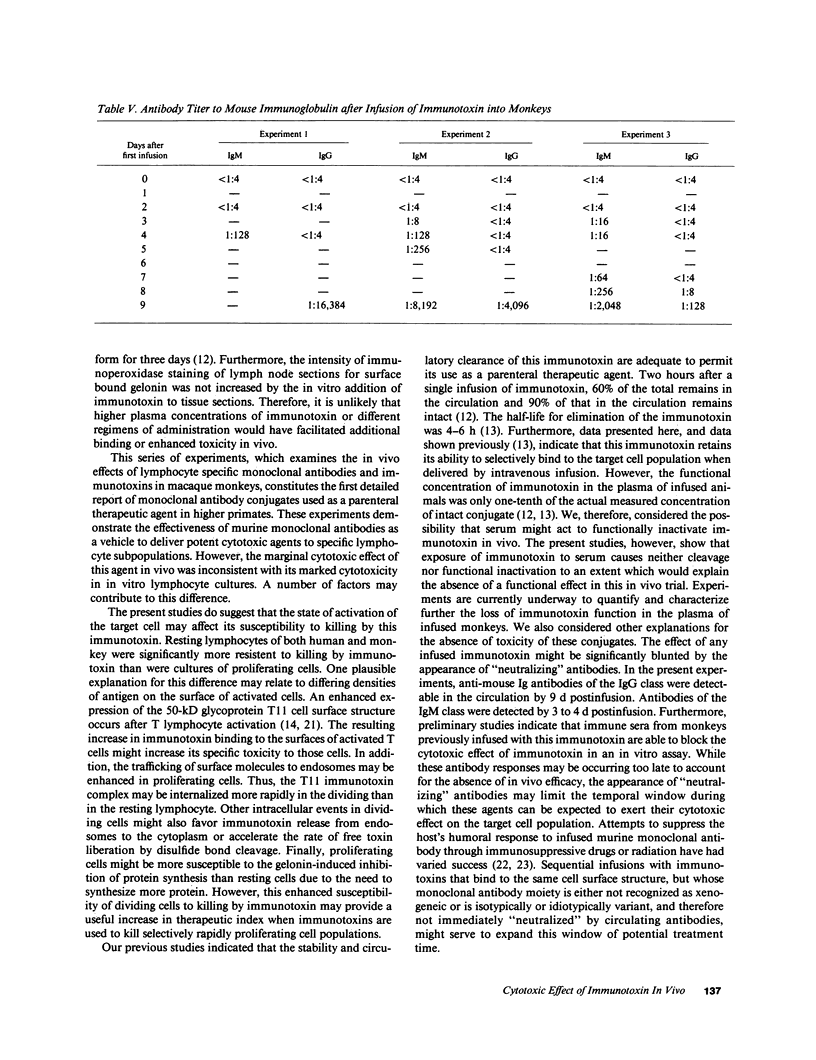
The cytotoxic effect of a lymphocyte-specific immunotoxin formed by disulfide conjugation of an anti-T11 monoclonal antibody with the ribosome-inactivating protein gelonin was assessed in vitro on peripheral blood T cells and in vivo on splenic and lymph node T cells of macaque monkeys. This immunotoxin was cytotoxic to proliferating peripheral blood T cells in vitro as measured by both direct and indirect assays. Two sequential intravenous infusions into macaque monkeys achieved plasma concentrations of immunotoxin far in excess of those shown to be cytotoxic for cultured T cells and coated all T cells in lymph nodes and spleen with intact immunotoxin for four days. However, the cytotoxic effect of the immunotoxin on T cells in vivo was considerably less than that predicted by the in vitro studies. Further experiments suggested that the state of activation of the targeted T cell population in vivo, or the appearance of anti-immunotoxin antibodies, which occurred in all infused monkeys, might attenuate immunotoxin-mediated cell killing in vivo. These studies illustrate the significant differences between the action of immunotoxin conjugates in vitro, and those seen when these conjugates are utilized as therapeutic agents in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernard A., Gelin C., Raynal B., Pham D., Gosse C., Boumsell L. Phenomenon of human T cells rosetting with sheep erythrocytes analyzed with monoclonal antibodies. "Modulation" of a partially hidden epitope determining the conditions of interaction between T cells and erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1317–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. The interleukin-2 T-cell system: a new cell growth model. Science. 1984 Jun 22;224(4655):1312–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.6427923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatenoud L., Baudrihaye M. F., Chkoff N., Kreis H., Goldstein G., Bach J. F. Restriction of the human in vivo immune response against the mouse monoclonal antibody OKT3. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):830–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descotes G., Romano M., Stirpe F., Spreafico F. The immunological activity of plant toxins used in the preparation of immunotoxins--II. The immunodepressive activity of gelonin. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1985;7(4):455–463. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(85)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmacher V. S., Anderson J., Blättler W. A., Lambert J. M., Senter P. D. Antibody-complement-mediated cytotoxicity is enhanced by ribosome-inactivating proteins. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3648–3651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Dowell D. L., Hensley L. L., Gore I., Metzgar R. S. Human T cell antigen expression by primate T cells. Science. 1982 Jan 15;215(4530):298–300. doi: 10.1126/science.6171885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J. M., Senter P. D., Yau-Young A., Blättler W. A., Goldmacher V. S. Purified immunotoxins that are reactive with human lymphoid cells. Monoclonal antibodies conjugated to the ribosome-inactivating proteins gelonin and the pokeweed antiviral proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12035–12041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Aldrich W. R., Thorley-Lawson D. A., Schlossman S. F., Nadler L. M. Surface antigen changes during B-lymphocyte activation in primates. Cell Immunol. 1984 Mar;84(1):163–170. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Chalifoux L. V., Reimann K. A., Ritz J., Schlossman S. F., Lambert J. M. In vivo administration of lymphocyte-specific monoclonal antibodies in nonhuman primates. Delivery of ribosome-inactivating proteins to spleen and lymph node T cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):666–673. doi: 10.1172/JCI112625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Goldmacher V. S., Ritz J., Yetz J. M., Schlossman S. F., Lambert J. M. In vivo administration of lymphocyte-specific monoclonal antibodies in nonhuman primates. In vivo stability of disulfide-linked immunotoxin conjugates. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):977–984. doi: 10.1172/JCI112399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., King N. W., Reinherz E. L., Hunt R. D., Lane H., Schlossman S. F. T lymphocyte surface antigens in primates. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Apr;13(4):345–347. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Ritz J., Guida L. J., Yetz J. M., Lambert J. M., Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. In vivo administration of lymphocyte-specific monoclonal antibodies in nonhuman primates: I. Effects of anti-T11 antibodies on the circulating T cell pool. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):961–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Todd R. F., 3rd, Palley L. S., Schlossman S. F., Griffin J. D. Conservation of myeloid surface antigens on primate granulocytes. Blood. 1983 Feb;61(2):408–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowder J. N., Miller R. A., Hoppe R., Levy R. Suppression of anti-mouse immunoglobulin antibodies in subhuman primates receiving murine monoclonal antibodies against T cell antigens. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):401–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Fabbi M., Fox D., Acuto O., Fitzgerald K. A., Hodgdon J. C., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. An alternative pathway of T-cell activation: a functional role for the 50 kd T11 sheep erythrocyte receptor protein. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):897–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Pihl A. Chimeric toxins. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;15(3):355–381. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palley L. S., Schlossman S. F., Letvin N. L. Common tree shrews and primates share leukocyte membrane antigens. J Med Primatol. 1984;13(2):67–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Willingham M. C., FitzGerald D. J. Immunotoxins. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):641–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90506-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti F. W., Morgan D. A., Gallo R. C. Functional and morphologic characterization of human T cells continuously grown in vitro. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):131–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. F., Jr, Goldmacher V. S., Lambert J. M., Chari R. V., Bolender S., Gauthier M. N., Blättler W. A. The antileukemic efficacy of an immunotoxin composed of a monoclonal anti-Thy-1 antibody disulfide linked to the ribosome-inactivating protein gelonin. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1987;25(1):31–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00199298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Krolick K. A., Miyama-Inaba M., Cushley W., Uhr J. W. Immunotoxins: a new approach to cancer therapy. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):644–650. doi: 10.1126/science.6218613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Uhr J. W. Immunotoxins: redirecting nature's poisons. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):653–654. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]