Abstract
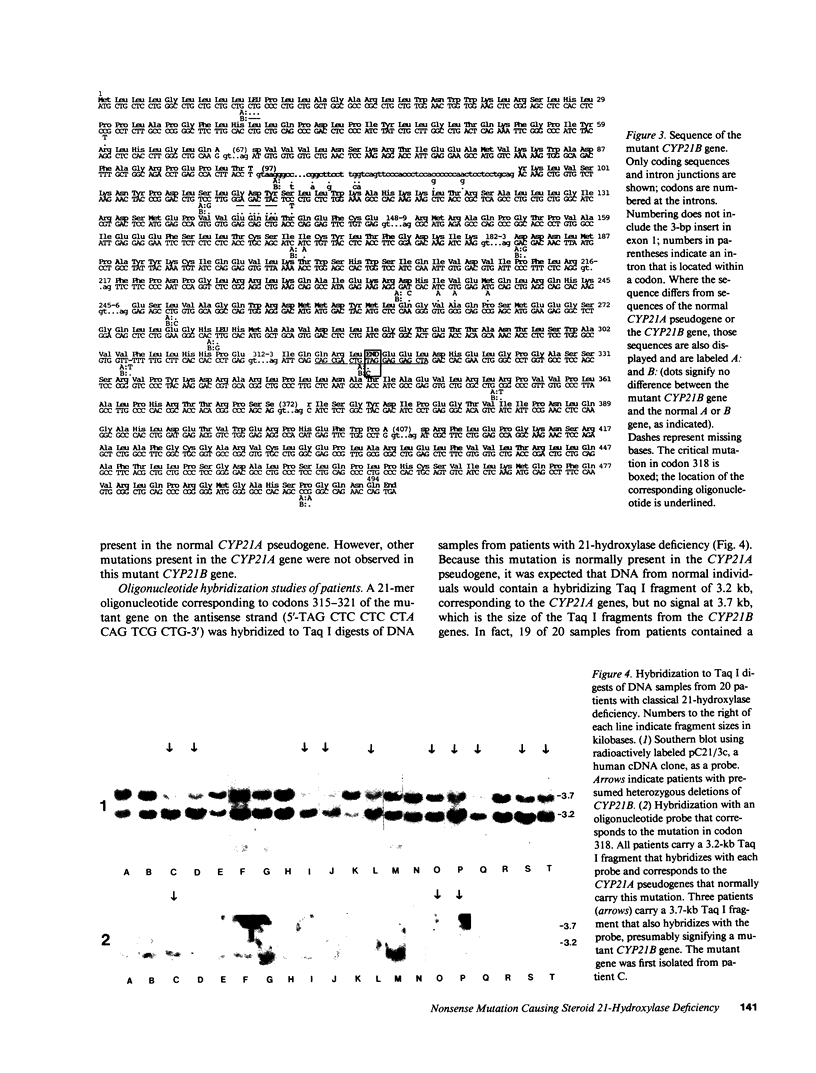
We determined the sequence of a mutant CYP21B gene isolated from a patient with the severe, "salt-wasting" form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Codon 318 in this gene is changed from CAG, encoding glutamine, to TAG, a nonsense codon. This is predicted to result in a completely nonfunctional enzyme due to premature termination of translation. In addition, when the cloned mutant gene was transfected into mouse Y1 adrenal cells, the resulting mRNA levels were decreased compared with transfected normal CYP21B genes. This mutation was carried by 3 of 20 unrelated patients with 21-hydroxylase deficiency alleles as determined by hybridization with a specific oligonucleotide probe. This mutation is also seen in the normal CYP21A pseudogene, so that its presence in the abnormal CYP21B gene may be the result of a gene conversion event.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amor M., Parker K. L., Globerman H., New M. I., White P. C. Mutation in the CYP21B gene (Ile-172----Asn) causes steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1600–1604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M., Adesnik M. Gene conversion in a cytochrome P-450 gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2300–2304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Campbell R. D., Porter R. R. Mapping of steroid 21-hydroxylase genes adjacent to complement component C4 genes in HLA, the major histocompatibility complex in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):521–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. C., Kan Y. W. beta 0 thalassemia, a nonsense mutation in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2886–2889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin D. D., Galbraith L. J., Seidman J. G., White P. C., Parker K. L. Nucleotide sequence analysis of murine 21-hydroxylase genes: mutations affecting gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9601–9605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Miller W. L. Cloning and characterization of the bovine gene for steroid 21-hydroxylase (P-450c21). DNA. 1985 Jun;4(3):211–219. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Marvit J., Lidsky A. S., Güttler F., Woo S. L. Tight linkage between a splicing mutation and a specific DNA haplotype in phenylketonuria. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):799–803. doi: 10.1038/322799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. I., Chrousos G. P., Mann D. W., Larsen J. W., Jr, Green I., McCluskey J., Loriaux D. L., Fletcher J. C., Koons G., Overpeck J. Pharmacologic suppression of the fetal adrenal gland in utero. Attempted prevention of abnormal external genital masculinization in suspected congenital adrenal hyperplasia. JAMA. 1985 Feb 15;253(7):1015–1020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Yoshioka H., Yamane M., Gotoh O., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes tandemly arranged in human chromosome: a pseudogene and a genuine gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2841–2845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd V. J., Wallace R. B., Itakura K., Woo S. L. alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency detection by direct analysis of the mutation in the gene. Nature. 1983 Jul 21;304(5923):230–234. doi: 10.1038/304230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. In vitro RNA synthesis with SP6 RNA polymerase. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:397–415. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet E., Boue J., Raux-Demay M., Couillin P., Oury J. F., Dumez Y., Dausset J., Cohen D., Boué A. First trimester prenatal diagnosis of 21-hydroxylase deficiency by linkage analysis to HLA-DNA probes and by 17-hydroxyprogesterone determination. Hum Genet. 1986 Aug;73(4):358–364. doi: 10.1007/BF00279101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang S., Pollack M. S., Loo M., Green O., Nussbaum R., Clayton G., Dupont B., New M. I. Pitfalls of prenatal diagnosis of 21-hydroxylase deficiency congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Jul;61(1):89–97. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. L., Chaplin D. D., Wong M., Seidman J. G., Smith J. A., Schimmer B. P. Expression of murine 21-hydroxylase in mouse adrenal glands and in transfected Y1 adrenocortical tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7860–7864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues N. R., Dunham I., Yu C. Y., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R., Campbell R. D. Molecular characterization of the HLA-linked steroid 21-hydroxylase B gene from an individual with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1653–1661. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02414.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumsby G., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R., Grant D. B., Hjelm M. Deletion of the steroid 21-hydroxylase and complement C4 genes in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Med Genet. 1986 Jun;23(3):204–209. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.3.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner E., Dimartino-Nardi J., Kuhnle U., Levine L. S., Oberfield S. E., New M. I. Is salt-wasting in congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to the same gene as the fasciculata defect? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1986 Jan;24(1):9–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1986.tb03249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werkmeister J. W., New M. I., Dupont B., White P. C. Frequent deletion and duplication of the steroid 21-hydroxylase genes. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;39(4):461–469. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Chaplin D. D., Weis J. H., Dupont B., New M. I., Seidman J. G. Two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes are located in the murine S region. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):465–467. doi: 10.1038/312465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Grossberger D., Onufer B. J., Chaplin D. D., New M. I., Dupont B., Strominger J. L. Two genes encoding steroid 21-hydroxylase are located near the genes encoding the fourth component of complement in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (2). N Engl J Med. 1987 Jun 18;316(25):1580–1586. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198706183162506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. HLA-linked congenital adrenal hyperplasia results from a defective gene encoding a cytochrome P-450 specific for steroid 21-hydroxylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7505–7509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. Structure of human steroid 21-hydroxylase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5111–5115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., White R. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6754–6758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka H., Morohashi K., Sogawa K., Yamane M., Kominami S., Takemori S., Okada Y., Omura T., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Structural analysis of cloned cDNA for mRNA of microsomal cytochrome P-450(C21) which catalyzes steroid 21-hydroxylation in bovine adrenal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4106–4109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]