Abstract
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a unique bacterium in that it shares a common place with a number of chemical compounds which are used commercially to control insects important to agriculture and public health. Although other bacteria, including B. popilliae and B. sphaericus, are used as microbial insecticides, their spectrum of insecticidal activity is quite limited compared to Bt. Importantly, Bt is safe for humans and is the most widely used environmentally compatible biopesticide worldwide. Furthermore, insecticidal Bt genes have been incorporated into several major crops, rendering them insect resistant, and thus providing a model for genetic engineering in agriculture.
This review highlights what the authors consider the most relevant issues and topics pertaining to the genomics and proteomics of Bt. At least one of the authors (L.A.B.) has spent most of his professional life studying different aspects of this bacterium with the goal in mind of determining the mechanism(s) by which it kills insects. The other authors have a much shorter experience with Bt but their intellect and personal insight have greatly enriched our understanding of what makes Bt distinctive in the microbial world. Obviously, there is personal interest and bias reflected in this article notwithstanding oversight of a number of published studies. This review contains some material not published elsewhere although several ideas and concepts were developed from a broad base of scientific literature up to 2010.
Key words: Bacillus thuringiensis, cadherin receptors, cry toxins, parasporal crystals, sporulation, toxin-receptor interaction
Background and History
The concept and practice of utilizing microorganisms to control insect pests is not new.1,2 Pest control strategies in prehistoric times are mentioned in the writings of ancient Egyptian and Chinese scholars. One story relates the practice by gardeners of several Egyptian pharaohs of maintaining bacterial collections for use against insects that attacked and ravaged the gardens surrounding their houses and tomb chapels. Later, in the third century, maladies of insects, most likely occasioned by bacteria, viruses and fungi, were observed. Indeed, Aristotle3 described in his writings insect diseases such as foulbrood of the honey bee (Apis millifera). Louis Pasteur studied silkworm diseases and differentiated pebrine and flacherie diseases of the silkworm Bombyx mori. Also, Kirby4 and Bassi5 made significant contributions to the area of insect pathology, and they, along with Pasteur are considered among the pioneers of infectious disease and pathogenic microbiology.
The era of Bt had its beginning when, in 1901, a Japanese scientist named Shigetane Ishiwata isolated a bacterium from dead silkworm larvae while he was investigating the cause of the socalled “sotto disease” (sudden-collapse disease). The disease was responsible for the loss of large numbers of silkworms in Japan and the surrounding region. Ishiwata named the bacterium Bacillus sotto.6 A few years thereafter, in 1911, a German scientist Ernst Berliner isolated a related strain from dead Mediterranean flour moth larvae he found in a flour mill in the German state of Thuringia. He appropriately named the organism Bacillus thuringiensis. Berliner studied the bacterium and found inclusion bodies or “Restkorper” alongside the endospore.7,8 The year was 1915. Mattes9 in 1927 again observed the same inclusion bodies in Bt but it was not until much later (25 years) that insecticidal activity was attributed to these highly refractile bodies now referred to as “parasporal crystals,” a phrase coined by Christopher Hannay in 1953.10 Once the significance of the parasporal crystals was realized by Thomas Angus, he promptly demonstrated in the same year the insecticidal activity of the inclusion bodies.11 And, together with Philip Fitz-James, Hannay in 1955 discovered that the toxic parasporal crystals are composed of protein.12
The first commercial insecticide based on Bt, Sporine, was produced in France in 1938 and used primarily to control flour moths. In the United States, Bt was first manufactured commercially in 1958 and, by 1961, Bt-based bioinsecticides were being registered by the US Environmental Protection Agency. Since 1996, insect-resistant transgenic crops, known as Bt crops, have expanded around the globe and are proving to be quite efficient and helpful in reducing the use of chemical insecticides.13,14 Latest estimates indicate that more than 50% of the cotton and 40% of the corn planted in the US are genetically engineered to produce Bt insecticidal toxins. The current global market for pesticides (herbicides, insecticides, fungicides, nematicides and fumigants) is valued at $25.3 billion. Biopesticides represent only 2.5% of this market but their share is expected to increase to about 4.2%, or more than $1 billion, in 2010.
Interestingly, some strains of Bt produce non-insecticidal proteins that crystallize into irregular-shaped parasporal inclusions.15 Inclusions of one isolate treated with protease were toxic to human cancer cells, including leukemic T (MOLT-4) and cervical cancer cells (HeLa).16 Cytotoxicity was dose-dependent. Another non-insecticidal protein, parasporin, also showed strong cytotoxic activity against MOLT-4 and HeLa cells.17
Life Cycle of Bacillus thuringiensis
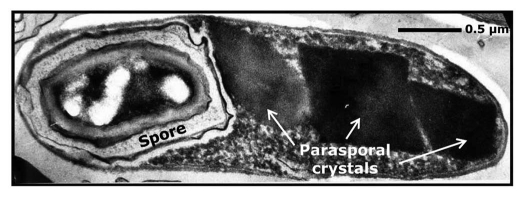
The life cycle of Bt is characterized by two phases which include vegetative cell division and spore development, otherwise referred to as the sporulation cycle.18 The vegetative cell is rod-shaped (2–5 µm long and about 1.0 µm wide) and divides into two uniform daughter cells by formation of a division septum initiated midway along the plasma membrane. Sporulation, on the other hand, involves asymmetric cell division and is characterized by seven stages19 which include (stage I) axial filament formation, (stage II) forespore septum formation, (stage III) engulfment, first appearance of parasporal crystals and formation of a forespore, (stages IV to VI) formation of exosporium, primordial cell wall, cortex and spore coats accompanied by transformation of the spore nucleoid and (stage VII) spore maturation and sporangial lysis. Figure 1 portrays a fully sporulated cell of Bt in which there are several parasporal crystals lying along side the endospore. The production of crystal proteins by Bt during sporulation is a unique genetically regulated biological phenomenon that, probably, relieves stress physically by offsetting water loss during spore formation and affords an additional survival advantage by exerting lethal action against host insects. In turn, the toxic action provides sufficient host nutrients to allow germination of the dormant bacterial spore and its return to vegetative growth.
Classification and Taxonomy of Bacillus thuringiensis
As indicated above, vegetative cells of Bt are characterized as large stout rods that are straight or slightly curved with rounded ends. They usually occur in pairs or short chains. Bt is Grampositive, non-capsulated and motile with peritrichous flagella. Classification of Bt strains has been accomplished by H serotyping, the immunological reaction to the bacterial flagellar antigen.20 The hag gene encodes flagellin, which is responsible for eliciting the immunological reaction in H serotyping. Specific flagellin amino acid sequences have been correlated to specific Bt H serotypes and at least 69 H serotypes and 82 serological varieties (serovars) of Bt have been characterized.21 H serotyping, however, is limited in its capability to distinguish strains from the same H serotype or from the same serovar.22 Due to its economic importance, it has become necessary to develop alternative tools for classification and grouping of Bt strains and isolates. Accordingly, several screening programs have been established to isolate novel Bt strains with unique insecticidal properties. As a result, numerous Bt strains with activity against lepidopteran, dipteran and coleopteran insects have been isolated. Additionally, Bt strains active against insects belonging to the orders Hymenoptera, Homoptera, Orthoptera and Mallophaga as well as nematodes, mites and protozoa have been isolated.
The placement of Bt as a separate species within the genus Bacillus has been controversial since the publication of The Genus Bacillus in 1973,23 and Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in 1974.24 The genus Bacillus is one of the most diverse genera in the class Bacilli and includes aerobic and facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped, Gram-positive spore-forming bacteria with G + C contents ranging from 32–69%.25 Based on phylogenetic heterogeneity, eight genera in the class Bacilli have been proposed: Bacillus, Alicyclobacillus, Paenibacillus, Brevibacillus, Aneurinibacillus, Virgibacillus, Salibacillus and Gracilibacillus.26–30 Many species of these genera are of practical importance because they produce antibiotics and peptides with anti-microbial, anti-viral and anti-tumor activities. They also synthesize thermostable enzymes and molecules that can suppress soil-borne phytopathogenic organisms.31–35
In the monograph The Genus Bacillus, Gordon et al.23 considered Bt a variety of B. cereus (Bc) along with B. anthracis (Ba) and B. mycoides (Bm). Certainly, Bt, Ba and Bc share many common phenotypic and genotypic properties to the extent that the three species have been placed under one group called the Bacillus cereus (BC) group. Ba is the causative agent of anthrax, an acute and often lethal disease in humans and animals. Bc is an opportunistic human pathogen and may cause food poisoning, eye infections and periodontal disease, among other ailments. Bt possesses a variety of special features including its (1) ability to live in the environment free and independent from other Gram-positive spore-forming bacilli, (2) production of entomocidal parasporal crystal proteins and (3) survival in a unique environmental niche in the midgut and hemocoel of insects. In addition to Ba, Bc, Bt and Bm, there are two other highly related species B. pseudomycoides (Bpm) and B. weihenstephanensi (Bw) in the BC group.
Curiously, Bt has been alleged to be an opportunistic pathogen in animals and human.36–38 Two Bt strains, Bt 97-27 (subsp. konkukian) and Bt Al Hakam (isolated in Iraq by a United Nations Special Commission), were initially designated as human pathogens. Bt 97-27 was first isolated from necrotic tissue in a twenty-eight year old male hospital patient.36 The designation of strain 97-27 as Bt was based on biochemical tests and the appearance of inclusion bodies.36 However, a second isolate from the same patient lacked inclusion bodies. Sequence analysis showed no insecticidal (cry) genes present on the 97-27 chromosome or a lone single plasmid pBT9727.37 Sequence analysis of the Al Hakam genome also revealed no chromosome-encoded or plasmid-encoded ORFs with significant similarity to any insecticidal genes. Interestingly, pBT9727 of strain 97-27 and the pXO2 plasmid of Ba have almost identical replication proteins and a highly conserved origin of replication. However, the pXO2 region encoding a poly-c-D-glutamic acid capsule was replaced on pBT9727 with genetic mobile elements, suggesting that pBT9727 may have evolved from pXO2 to perform other functions in strain 97-27. Phylogenetic lineage placement using amplified fragment length polymorphism analysis (AFLP)39 and comparative sequence analysis40 indicate that strain 97-27 is more related to Bc and Ba than to Bt. To the authors' knowledge, no other studies have been reported that characterize Bt as an opportunistic pathogen of humans or warm-blooded animals.
Genome sequences of a number of strains in the BC group have been completed: Bc (ATCC 14579 and 10987 and strain E33L), Bw-KBAB4, Ba-Ames, Ba-Ames Ancestor and Ba-Sterne. Sequencing and annotation of the genome of Bt subsp. kurstaki is near completion in the Bulla laboratory. Comparison of all the genome sequences, including that of subspecies kurstaki, reveals enormous similarity in terms of nucleotide sequence identity and gene and operon organization, a combination not observed heretofore among different bacterial species. The primary distinguishing features of Bt are its virulence and pathogenicity factors, represented by the insecticidal genes located on the chromosome and several plasmids. Those of Ba are its tripartite toxin and capsule encoded by plasmids only.41
Analysis of 16S and 23S rDNA nucleotide sequences, a powerful technology for bacterial identification, likewise indicates that species belonging to the BC group have almost identical sequence similarity.42 Molecular techniques such as multi-locus enzyme electrophoresis,43,44 AFLP analysis45 and multi-locus sequence typing46 have helped resolve some of the issues related to BC group classification. Analysis of various Bc and Bt strains reveal very high diversity in multi-locus genotypes, indicating that Bc and Bt exhibit a low degree of clonality and that exchange of genetic material can occur frequently in their natural environments.43 It has been suggested that Ba, Bc and Bt should be classified as one species,43 or that Ba be considered in the lineage of Bc.44 Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and dendrographic analysis corroborate the latter idea44 by showing that Ba isolates fall into the same cluster but are distinct from Bc and Bt.47 Additionally, the use of the gene gyrB (a house-keeping gene encoding the B subunit of DNA gyrase, topoisomerase type I) has proven very useful to distinguish members of the BC group.48–51
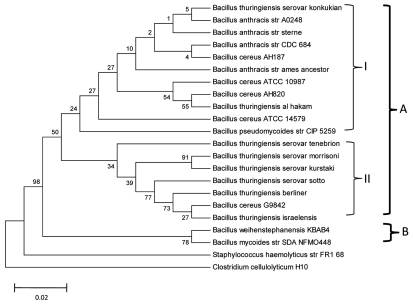
We have constructed a phylogenetic tree, based on sequence alignment of the 16S rRNA of 20 strains in the BC group using the Bootstrapped neighbor-joining method (Fig. 2). Bootstrap volumes are reported on the branches. The tree displays division of the 20 strains into two major groups. Group A includes all Ba, Bc and Bpm strains and Group B includes Bw strain KBAB4 and Bm strain SDANFMO448. There are two clusters in Group A, each marked with a Roman numeral. Cluster I includes Ba strains Sterne CDC684 and Ames Ancestor A0248; Bc strains AH187 and AH 820 and ATCC 10987 and 14579; Bpm strain CIP 5259; and Bt serovar konkukian and Bt Al-Hakm. Bc AH820 and serovar konkukian in Cluster 1, both alleged human pathogens, are more closely related whereas Bpm strain CIP 5259 and Bc ATCC 14579, neither of which are pathogenic, are the most divergent in the cluster. Cluster II includes Bt serovars tenebrionis, morrisoni, kurstaki, sotto, israelensis and berliner and Bc G9842. We infer from the dendogram that both Bt serovar konkukian and the Al-Hakm strain group rather well with the Ba and Bc strains, but not with the Bt serovars, as previously suggested.39,40
Figure 2.
Bootstrapped neighbor-joining tree of 20 strains belonging to different species of the BC group. The tree was generated based on nucleotide sequence alignment of 16S rRNA. Bootstrap volumes are reported on the branches. The 20 strains are divided into two main groups. Group A includes all Ba, Bc and Bpm strains and Group B includes Bw strain KBAB4 and Bm strain SDANFMO448. There are two clusters within Group A, each marked with Roman numerals I and II. Cluster I includes Ba strains Sterne CDC684 and Ames Ancestor A0248; Bc strains AH187 and AH 820 and ATCC 10987 and 14579; Bpm strain CIP 5259; and Bt serovar konkukian and Bt Al-Hakm. Bpm strain CIP 5259 and Bc ATCC 14579 are the most divergent in this cluster. Cluster II includes Bt serovars tenebrionis, morrisoni, kurstaki, sotto, israelensis and berliner and Bc G9842. The horizontal bar represents 0.02% differences in nucleotide similarities.
Expression and Regulation of Insecticidal Genes
One of the most dramatic aspects of Bt sporulation is the formation of parasporal crystals. The insecticidal toxins (Cry toxins) of Bt, oftentimes referred to as δ-endotoxins after Heimpel,52 are somewhat specific to certain insects. The family of genes coding for these toxins is the cry gene family.53,54 A common characteristic of cry genes is that they are expressed during the stationary phase of growth. Cry proteins, the end-products of cry gene expression, constitute 20–30% of the cell dry weight and generally accumulate in the mother cell, beginning in stage III of sporulation and continuing through stage VII.18
The term δ-endotoxin, relative to Bt Cry toxin, is a mis nomer. Heimpel52 named the parasporal crystalline protein of Bt as such because it forms inside the cell and because it is fourth in the order of other toxic components discovered in the bacterium. However, endotoxins are associated with the lipo-polysaccharide moiety of the complete “O” somatic antigen complex found in the outer membrane of various Gram-negative bacteria and are an important factor in their ability to cause disease.55 Based on its mode of action, a Cry toxin is a “simple” toxin, which is defined as a monomer or oligomer of a toxic simple protein.56 A Cry toxin exists as a toxic monomer capable of oligomerization. The parasporal crystals of Bt are oligomers composed of polypeptide protoxin subunits. The protoxin is the immediate atoxic precursor of a Cry toxin, i.e., upon activation of the protoxin, an insecticidal Cry toxin is generated.57,58 Interestingly, the processing of protoxin to toxin is different among the respective toxin groups, depending on host specificity, i.e., toxins that kill moths, beetles or mosquitoes. For example, Cry1A and Cry4 toxins (∼65 kDA) that primarily kill moths and mosquitoes, respectively, are the products of protoxins in the molecular weight range of 125–135 kDa whereas Cry3 toxins (∼68 kDa) that kill beetles are conversion products of 72-kDa protoxins. The mechanism of Cry toxin action is discussed later in this review.
The high level of Cry protein synthesis appears to be co ordinately controlled by a variety of mechanisms occurring at the transcriptional, posttranscriptional and posttranslational levels. Typically, initiation of the sporulation process in Bt is controlled by successive activation of sigma factors that bind the core RNA polymerase and direct transcription utilizing sporulation-specific promoters.59 There are five sporulation-specific transcription factors, σH, σF, σE, σG and σK, which are tightly regulated and appear in fixed order during sporulation. The σH factor is active in the pre-divisional cell; σE and σK are active in the mother cell; and σF and σG are active in the forespore. Several cry gene promoters have been identified and their sequences determined.60–64 The cry1Aa gene, for example, is expressed via two overlapping promoters (BtI and BtII).65 Transcription from the downstream promoter, BtI, is active between stages II and VI of sporulation and employs σE. Later transcription is facilitated by the upstream promoter, BtII, which is active from stage VI through the end of sporulation, and employs σK. The sequential use of the two promoters most likely ensures synthesis of the protoxin throughout the sporulation cycle. Some cry genes, however, appear to be expressed independently of sporulation. For instance, cry3A gene expression is enhanced and prolonged in mutant strains unable to initiate sporulation.66 Also, De Souze et al.67 and Malvar et al.68 reported that the cry3A gene is expressed during vegetative growth. The cry3A promoter, recognized by σA, the sigma factor of vegetative cells, is activated at the end of exponential vegetative growth and remains active through stage III of sporulation.
An additional regulatory mechanism for expression of some cry genes at the transcriptional level involves a regulatory protein that binds with different affinities within an inverted repeat and a potential bend region lying 200–300 base pairs upstream of different cry1 promoters.69 This regulatory protein was identified as the E2 subunit of pyruvate dehydrogenase. A chimera consisting of a mutated upstream region and the coding sequence of β-galactosidase resulted in decreased binding of the E2 subunit and reduction in β-galactosidase synthesis. Apparently, involvement of the E2 subunit of pyruvate dehydrogenase in cry gene regulation implicates a connection between catabolic activity and Cry toxin synthesis.69
Regulation of cry gene expression at the posttranscriptional level may depend on mRNA stability. The half-life of cry mRNA is approximately ten minutes, which is at least five-fold greater than the half-life of an average bacterial mRNA.70 The presence of putative transcriptional terminators—acting as positive retroregulators—at the 3′-end of many cry genes could contribute to mRNA stability.71 In other words, the transcriptional terminator could increase cry mRNA stability by protecting it from exonuclease degradation, beginning at the 3′-end. Certainly, the processing activities of 3′-5′ exoribonucleases are impaired by 3′ stem-loop structures.
Agaisse and Lereclus72 identified a perfect Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence (GAAAGGAGG) in Bt required for stabilization of cry3A mRNAs. The sequence mapped at a position between −125 and −117 in the 5′ untranslated region and the authors called the sequence the stabilizing Shine-Dalgarno (STAB-SD) motif. It is quite possible that stability of the mRNA resulted from interaction of the 3′-end of 16S rRNA of the 30S ribosomal subunit and STAB-SD. The binding of a 30S ribosomal subunit to this sequence probably protects the mRNA from 5′–3′ ribonuclease activity, resulting in stable transcripts. Potential STAB-SD sequences also have been identified in similar positions upstream of the cry3Ba and cry7Aa genes73,74 and upstream of cry1Ic in the intergenic region between the cry1Ac and cry1Ic genes.75
It may be that formation of stable parasporal crystals, comprised of Cry proteins, represents a posttranslational regulatory mechanism that protects the toxins from premature proteolytic degradation. The presence of a cysteine-rich region in the C-terminal half of the protoxin also may contribute to a stable crystal structure through formation of disulfide bonds. Those toxins that lack the cysteine-rich C-terminal region, e.g., truncated Cry toxins, may circumvent adversity by forming intermolecular salt bridges and hydrophobic interactions that can stabilize crystal structure. Several investigators have reported that certain parasporal crystals require additional proteins to stabilize and crystallize the cognate Cry toxins.76–78 These accessory proteins may act as chaperons to stabilize nascent protoxin molecules, facilitating crystallization.
One interesting feature of cry genes is their high degree of plasticity. This particular characteristic may contribute to the versatility of Cry toxins as it relates to their insect host range. The most likely explanation for such genetic plasticity is the presence of numerous transposons and insertion elements that flank the cry genes. Indeed, these transposable elements may facilitate gene multiplication and evolution of new toxins.79 Furthermore, the fact that cry genes are carried on transmissible plasmids increases the likelihood of horizontal gene transfer among different Bt strains, which leads to the creation of new strains with different sets of Cry toxins.80,81
The organization and clustering of cry genes in operons has been demonstrated in numerous Bt strains.82 Specifically, cry1Ac, cry1F, cry1I, cry2Aa, cry2Ac, cry9Ca and cry11Aa are constituents of operons. Some of the operons include at least another upstream reading frame such as orf1 or p19. A second orf (orf2 or p20) resides in cry2 and cry11 operons. Why are the different cry genes organized in operons? One explanation is that such organization facilitates differential gene expression, rendering parasporal crystals containing different Cry toxins, or different crystals, each of which contains a specific individual toxin. The nature of and the molar concentration of toxins produced by a given subspecies of Bt reflect not only specificity to a target insect(s) but also the structural design of individual parasporal crystals. A consequence of this scenario could be synergism among the various Cry toxins.75,83
Another plausible explanation for the arrangement of cry genes in operons is enhancement of genetic recombination that might generate new toxins or combinations thereof, which, in turn, would impart novel host specificities. Also, conservation in the usage of sigma factors could be a potential outcome. Sharing polymerases with multiple copies of cry genes most likely would bring about competition for the appropriate transcription factors, ultimately affecting structural and physiological properties not only of the parasporal crystals but of the endospore itself. Aronson et al.84 reported that a plasmid-cured acrystalliferous strain of Bt had normal spore coats whereas the parental strain was deficient in spore coat protein. The deficiency in spore coat protein most likely was due to a limited capacity of the organism to transcribe σK- and σE-dependent spore-coat genes.
Significantly, most of the cry genes organized in operons, e.g., cry1Ic1, cry2Aa, cry2Ac and cry11A, code for truncated toxins which lack the cysteine-rich C-terminal region necessary for proper folding and crystallization. In some cases, protoxins may act as molecular chaperons for the truncated toxins just as the P19 and P20 proteins presumably do for Cry2A and Cry11, respectively.75–77
Biochemistry and Functional Proteomics of Cry Toxins
Once a mature spore is formed, both the spore and parasporal crystal are released from the mother cell into the environment where they are readily available for larval consumption. The Cry toxin contained in the crystal is the virulence factor that truly distinguishes Bt from its genetic cousins Ba and Bc. And, it is the Cry toxin that establishes safe harbor for the bacterium in an insect carcass. Different parasporal crystals are made either of single or multiple Cry proteins. For example, the parasporal crystal of Bt subsp. kurstaki HD-73 contains Cry1Ac protein only, whereas the parasporal crystal of HD1 strain, which belongs to the same subspecies, is comprised of five different Cry toxins—Cry1Aa, Cry1Ab, Cry1Ac, Cry2Aa and Cry2Ab. Another feature of Cry toxins is that their precursor protoxins co-crystallize in various forms and shapes as evidenced by electron microscopy (see Fig. 1). Cry toxins are encoded by cry genes found mainly on large plasmids. However, the genes may be integrated into the chromosome. Since the cloning and sequencing of the first cry genes,85,86 nucleotide sequences have been reported for more than 300 cry genes. Höfte and Whiteley87 and Carlton88 proposed a universal nomenclature and classification scheme for Cry proteins and their genes based on host range. Later, another nomenclature format, based on amino acid sequence similarity, was proposed.54 In the classification proposed by Crickmore et al.54 the cry genes are divided into 51 groups and subgroups and the Cry toxins are separated into six major classes according to their insect host specificities and include: Group 1—lepidopteran (Cry1, Cry9 and Cry15); group 2—lepidopteran and dipteran (Cry2); group 3—coleopteran (Cry3, Cry7 and Cry8); group 4—dipteran (Cry4, Cry10, Cry11, Cry16, Cry17, Cry19 and Cry20); group 5—lepidopteran and coleopteran (Cry1I); and group 6—nematodes (Cry6). The Cry1I, Cry2, Cry3, Cry10 and Cry11 toxins (73–82 kDa) are unique because they appear to be natural truncations of the larger Cry1 and Cry4 proteins (130–140 kDa).
Figure 1.
Transmission electron micrograph of a sporulated cell of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. morrisoni strain C18 (× 44,000). Strain C18 was isolated from dead cotton bollworm larvae. The strain is unique in that it harbors 15 cry genes. The host range of C18 includes three major insect orders: Lepidoptera, Diptera and Coleoptera as well as nematodes. The parasporal crystals of C18 vary in shape and size (arrows), and represent ∼50% of the cell dry weight.
The three-dimensional structures of a number of Cry toxins have been published: Cry3Aa,89 Cry1Aa,90 Cry1Ac,91 Cry2Aa,92 Cry3Bb,93 Cry4Ba,94 Cry4Aa95 and Cry8Ea1.96 All Cry toxins contain three structural domains and share a high degree of topological similarity. Domain I is composed of a bundle of seven α-helices connected by loops. The α-helical bundle has a central amphipathic α helix that is well conserved among all the toxins described. Various mutations in Domain I appear to abolish toxicity but not binding to cellular receptors. Whether these mutations affect overall conformation of the toxin molecule, compromising toxicity, is not known. Domain II consists of three sets of antiparallel β-sheets, each terminating with a loop. The beta sheets are packed around a central hydrophobic core forming a so-called beta-prism structure. Domain III is a sandwich of two antiparallel β-sheets that form a “jelly-roll” topology. Results of site-directed mutagenesis and truncation analysis provide strong evidence for the involvement of Domains II and III in receptor binding and insecticidal activity.
Domain I purportedly functions to form ion channels in the cell membrane,53 and the hydrophobic motifs within this domain are what effect toxicity. Upon contact with the cell membrane, the domain undergoes refolding to facilitate insertion of the toxin into the membrane as with other bacterial toxins.97,98 Several articles have reported that hydrophobic α-4 and α-5 helices insert into the membrane and that this orientation is responsible for toxicity.99,100 However, there is no in situ or in vivo evidence to support these claims. What function the other helices have is not clear although alanine substitutions of four highly conserved aromatic residues, Trp243, Phe246, Tyr249 and Phe264, in α helix 7 of the mosquitocidal Cry4B toxin resulted in a dramatic decrease in toxicity against the mosquito Stegomyia aegypti.101 In addition, a nearly complete loss in toxicity was found for Phe264Ala/Tyr249Ala double mutants. Further mutagenic analysis of the double mutants showed that upon replacement with other aromatic residues, particularly at Tyr249 and Phe264, insecticidal activity was regained.101 In other work,102 deletion of 42 amino acid residues immediately upstream of α-helix 1 followed by replacement of Lys residues (Lys63 and Lys64) by alanine and proline, respectively, enhanced the potency of Cry2A toxin. An explanation afforded by the authors is that removal of the 42-amino acid fragment exposes a formerly occluded region of the toxin which corresponds to the receptor-binding region of the Cry2 toxin.
Domain II is the most divergent domain among the Cry toxins and its replacement or switching with domains II and III of other toxins can affect host specificity.103,104 The loops connecting strands of the antiparallel β-sheets are exposed at the apex of the domain and represent the least conserved regions amongst the Cry toxins. Interestingly, the apical loops of Cry1A, Cry2A, Cry3A, Cry4A and Cry5A toxins are highly variable in length. Cry5Aa toxin has the longest loop whereas Cry3Aa has the shortest one.105 What impact loop length has on domain structure and function is not known. Certainly, the span of the loops contributes to the configuration of Domain II and, most likely, influences the interactions of all three domains as well as the binding of individual toxins to their cognate receptors. Boonserm et al.94 have suggested that shorter loops are more likely to disturb the structure of the core β-sheets of Domain II and, consequently, interrupt the interaction of Domains I and II. Whatever their structural or functional roles, the loops appear to be key elements in receptor recognition, binding and specificity.
The contribution of the surface-exposed loops in Domain II to insect toxicity has been examined in a number of site-directed mutagenesis studies.106–108 The involvement of loop 2 (specifically Arg368-Ile375) in toxicity of Cry1Ab toxin to the tobacco hornworm was indicated by single amino acid deletion or alanine substitution for Phe371 and Gly374.109 The relevance of Arg368 and Arg369 also was shown using the same approach. Alanine substitutions of loop 3 residues, Ser438-Ser443, in the Cry1Ab toxin showed reduced toxicity and binding in both the tobacco hornworm and tobacco budworm.110 Likewise, deletion of residues Ala440-Ala443 in loop 3 of Cry1Aa resulted in reduction in toxicity to the silkworm as well as to the tobacco hornworm. Other experiments with Cry3A toxin implicated loops 1 and 3 of Domain II in receptor binding whereas loop 2 double mutations had no effect on binding or toxicity.111
Domain II loops in the mosquitocidal toxins Cry4A, Cry4B, Cry11A and Cry11B are very important not only in receptor binding but in specificity as well. When loop 3 of Cry4B was made to mimic that of Cry4A by site-directed mutagenesis, Cry4B became toxic to Culex pipiens whereas the wild-type toxin was not.112 Curiously, mutations in loops 1 and 2 of Cry4B eliminated toxicity to Aedes and Anopheles larvae but not to Culex.112 In vitro competition binding assays with Cry11A toxin indicated that loops 2 and 3 were important for binding to Aedes aegypti brush-border membrane vesicles.113 Peptides corresponding to loops α8, 1 and 3, but not loop 2, of the Cry11B toxin competed with toxin binding in Aedes midgut membranes and mutagenesis data suggested that loops α8, 1 and 3 are involved in toxicity.114 Taken together, all of these results provide strong evidence that loop 3 is important to the toxin-receptor interaction.
Domain III has been correlated with receptor binding115–117 and channel formation in the cell membrane.118,119 It has been linked to toxicity as well. Aronson and co-workers84 reported that single alanine substitutions of two serine residues at positions 503 and 504 in the Cry1Ac toxin significantly decreased binding affinity of the toxin and reduced toxicity to the tobacco hornworm. In vitro Domain III swapping in certain Cry1 toxins, has resulted in alterations in insect specificity.120,121 Examples of toxins that may have undergone domain swapping naturally are toxins with dual specificity, especially to moths and beetles, such as Cry1I.75 Domain III swapping has been suggested as an evolutionary scheme79,122 and that such activity may be responsible for the emergence of toxins with varying specificities. In any event, Domain III most assuredly is involved in both receptor binding and insecticidal action.
A significant number of studies on the functionality of the different domains and regions within the framework of Cry toxins point to the involvement of Domains II and III in receptor binding and toxin action. Numerous site-directed mutagenesis experiments indicate participation of the three surface-exposed loops (loops 1, 2 and 3) of domain II.123–126 Putative binding sites also have been estimated by testing whether synthetic peptides can disrupt the toxin-receptor interaction.107,127 Conclusions drawn from these studies were that loop α8 and loop 2 (Domain II) of Cry1Ab and loops 2 and 3 (Domain II) of Cry1Aa are the sites that participate in receptor binding.107,128 Domain III also was linked to toxin action because mutations in this domain affected both toxicity and receptor binding.84 Other reports show the dependence on specific sequences in Domains II and III for insecticidal activity.129–131
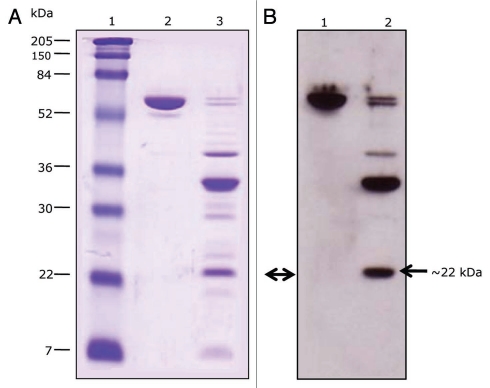
To circumvent complications inherent in site-directed mutagenesis, Natalya Griko and Mohamed Ibrahim (Bulla laboratory) utilized truncation analysis in an attempt to localize the receptor-binding region in the Cry1Ab toxin. The toxin was subjected to proteinase K and the resulting proteolytic fragments were exposed to the soluble toxin-binding region (TBR) of BT-R1.132 Immuno-ligand blot analysis revealed several fragments that bound the TBR (Fig. 3). The minimal binding fragment was ∼22 kDa. The N-terminal amino acid sequence of this fragment is “NSSVSIIRAPMFSWIHR,” which corresponds to amino acid residues 442–458 in loop 3 of Domain II (Fig. 4). Apparently then, loop 3 of Domain II and the N-terminal portion of Domain III are determinants in binding Cry1Ab to its corresponding receptor BT-R1.
Figure 3.
Cadherin receptor and Cry1Ab toxin binding analysis. (A) SDS-PAGE. Lane 1, molecular markers; lane 2, Cry1Ab toxin; lane 3, proteinase K-digested Cry1Ab. (B) Immunoligand blot. Cry1Ab toxin and its proteinase K proteolytic fragments were trans-blotted to a PVDF membrane and tested for their ability to bind the soluble toxin-binding region of BT-R1 (TBR). Lane 1, Cry1AB toxin; lane 2, proteinase K digested Cry1Ab. The smallest binding fragment of Cry1Ab (∼22 kDa, double arrow) was subjected to N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis. The N-terminal amino acid sequence is 442NSSVSIIRAPMFSWIHR458.
Figure 4.
Proposed secondary structure and three-dimensional model for the putative receptor-binding regions of Cry1Ab, Cry3A and Cry4B. (A) Multiple sequence alignments and secondary structure prediction of the amino acid residues spanning β10, loop 3, β11–β16 (end of Domain II and beginning of Domain III) of Cry1Ab (residues 422–498); Cry3A (residues 466–537) and Cry4B (residues 437–506), using Pfam181 and SAS182 databases. The sequence in red represents solvent-exposed residues. Underlined, bold residues in the three Cry toxins constitute loop 3. The symbols (*), (:) and (.) beneath the alignments denote identical, similar and less similar amino acid residues, respectively. (B) Three-dimensional structure in ribbon format for the putative receptor-binding regions on Cry1Ab, Cry3A and Cry4B. The Cry3A and Cry4B structures are from crystal structures (PDB codes 1DLC and 1W99, respectively). The Cry1Ab structure was generated as a model by the SWISS-MODEL protein modeling server173 using the crystal structure of the Cry1Aa toxin (88% sequence identity; PDB code 1CIY) as a template. Blue, red and golden shaded areas highlight predicted β-strands and loops.
The relevance of Domain III for binding Cry1Ab toxin was demonstrated a number of years ago by de Maagd et al.,133 who constructed special hybrids of Cry1Ab and Cry1C and examined their binding capabilities both in vivo and in vitro. Only one hybrid containing Domains I and II of Cry1C and Domain III of Cry1Ab bound to a 200-kDa protein in brush border membrane vesicles prepared from the beet armyworm. Hybrids devoid of Domain III showed no ability to bind the protein, establishing the relevance of Domain III of Cry1Ab in receptor binding. Similar kinds of hybrids derived from Cry1C and Cry1E120 showed Domain III to be a major determinant of toxicity. Likewise, Domain II of several Cry toxins have been documented as necessary, but not sufficient, for toxin activity.134 Thus, the receptor-binding region of Cry toxins can be narrowed to a region that includes loop 3 in Domain II and part of Domain III.
Domain I is the most conserved among Cry toxins. Domain II and the beginning of Domain III are the least-conserved. As mentioned above, the putative receptor-binding region in Cry1Ab is localized in loop 3 of Domain II and the immediate N-terminal region of Domain III. Based on immunoligand blot analysis (Fig. 3) and the mutation analysis of loop 3 of Domain II described above, the putative receptor-binding region most likely includes β10, loop 3 and β11–β16 (Fig. 4). Based on motif structural analysis of this region, two putative solvent-exposed regions (residues 432–449 and 480–493) were identified (shown in red in Fig. 4). Multiple sequence alignment of the putative receptor binding regions of Cry1Ab, Cry3Aa and Cry4Ba revealed that β10, loop 3 and β11 are the most divergent (Fig. 4A), supporting the assumption that this region has a major role in determining specificity.
Three-dimensional structure prediction of this particular region is represented in ribbon format in Figure 4B. Structurally, Cry1Ab, Cry3A and Cry4B have very similar topologies, except that Cry3A and Cry4B have more extended β10 strands and shorter loops 3. Interestingly, multiple sequence alignment of the putative receptor-binding regions of Cry1Aa and Cry1Ab (very closely related toxins) revealed that loop 3 is the least conserved, whereas β10 and β11–β16 are the most conserved (data not shown).
Cadherins as Cognate Receptors for Cry Toxins
The receptor molecules that serve as targets for Cry toxins are cadherins and are localized in the midgut of insects. Cadherins belong to a large family of calcium-dependent transmembrane glycoproteins which are highly diverse and multi-functional. Several key functions include cell-cell adhesion, cell migration, regulation of tissue organization and morphogenesis.135,136 Cadherins also are involved in signal transduction pathways and interact with other cell adhesion molecules through their ectodomain and with specific cytoplasmic proteins via their cytoplasmic domain.136–139 During embryonic morphogenesis, the expression of multiple members of the cadherin family is spatio-temporally regulated and correlates with a variety of morphogenetic events that involve cell aggregation or disaggregation. The functional relevance of midgut-specific cadherins in insect larvae is manifested in their involvement in controlling cell growth, cell division and cell death through various signaling pathways.140 Significantly, the concentration of the cadherin BT-R1 in the midgut of the tobacco hornworm increases dramatically, along with accumulation of its mRNA, during larval growth and development of the insect.141 The increasing number of cadherin molecules in developing larvae emphasizes their importance in maintaining epithelial organization and correlates directly to the susceptibility of the tobacco hornworm to Cry1Ab toxin.142 BT-R1 serves as a receptor for the Cry1Ab toxin of Bt and is coupled to programmed oncotic-like cell death,143,144 which is triggered by binding of the toxin to a highly conserved structural motif in the receptor.132 Apparently, the Cry1Ab toxin, like other Cry toxins, takes advantage of a natural phenomenon involving inborn death ligands that act to destroy the midgut epithelium and clear larvae of excessive tissue before entry to the pupal stage.
Cadherins serve as Cry toxin receptors on midgut epithelial cells in a variety of insects, including the tobacco hornworm,145,146 tobacco budworm,147,148 silkworm,149,150 cotton bollworm,151 pink bollworm,152 European corn borer,153 western corn rootworm,154 yellow mealworm beetle155 and mosquito.156 Recently, Mohamed Ibrahim and Natalya Griko (Bulla laboratory) characterized a cadherin molecule (BT-R3) in Anopheles gambiae, the primary mosquito vector of malaria, and demonstrated that, once bound to the Cry4Ba toxin, death ensues in insect cells transfected with the BT-R3 cDNA (Ibrahim M and Griko N, unpublished data).
Obviously, there is ample evidence to implicate cadherins as primary targets of Cry toxins within the insect gut. Gahan et al.147 reported that resistance to the Cry1Ac toxin by the tobacco budworm is linked to a cadherin gene. Similarly, Morin et al.152 showed that the pink bollworm has three different cadherin alleles, all linked to the emergence of a resistance phenotype in transgenic cotton expressing the Cry1Ac toxin. Mutations in genes encoding cadherin proteins also are tightly linked to resistance to the Cry1A toxin by the cotton bollworm.157 Fabrick et al.155 showed that knocking down TmCad1, a Cry3A-binding cadherin in the yellow mealworm, by injecting the insect with Tmcad1-specific double stranded RNA resulted in resistance to the toxin.
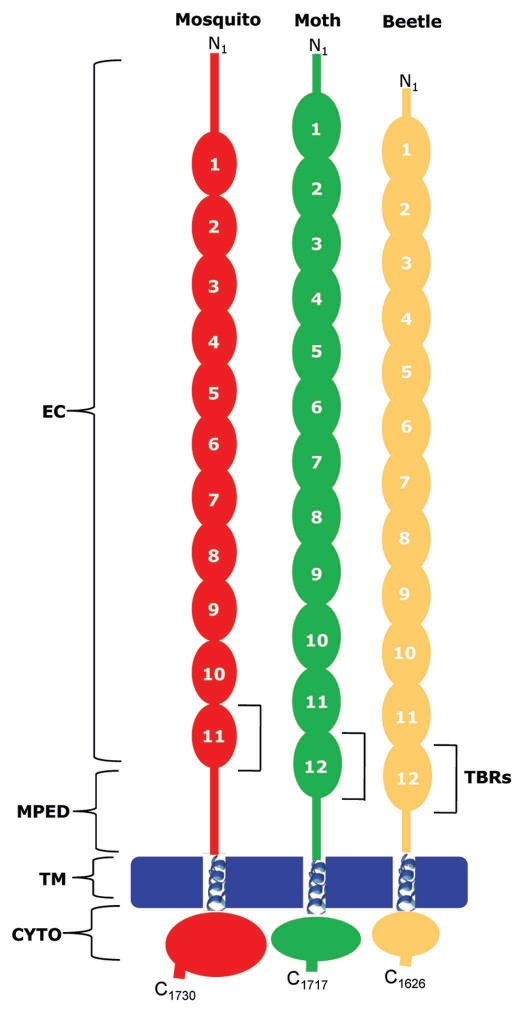
Cadherins are comprised of repeating calcium-binding cadherin repeats of approximately 110 amino acids in length. The ectodomain of cadherins can range from five cadherin repeats in classical cadherins136,137 to as many as thirty-four.158 Cry toxin-binding cadherins from different insect orders, share a structure composed of four domains: ectodomain (EC), membrane proximal extracellular domain (MPED), transmembrane domain (TM), and cytoplasmic domain (CYTO) (Fig. 5). The EC consists of 11–12 ectodomain modules, each of which is composed mainly of β-strands organized in β-barrel cadherin repeats connected one to another by interdomain linkers. The EC modules adjacent to the MPED contain the Cry toxin-binding region.155,156,159,160 Toxinbinding regions (TBRs) have been identified for cadherins representative of three major insect orders: Lepidoptera (moths, skippers and butterflies),132,149 Coleoptera (beetles)155 and Diptera (mosquitoes and black flies, among others).156 All of the TBRs are located within those EC modules positioned at or near the MPED, suggesting that this particular area of the cadherin molecule is critical not only for toxin binding but for mediating toxin action as well (Fig. 5).
Figure 5.
Domain structure and putative Cry toxin-binding regions in cadherin-like proteins from mosquito (red), moth (green) and beetle (golden). EC, ectodomain; MPED, membrane proximal extracellular domain; TM, transmembrane domain; CYTO, cytoplasmic domain, TBR, toxin binding region.
Comparative sequence analysis of the toxin-binding motifs in the BT-Rs of moth (BT-R1), mosquito (BT-R3) and beetle (BT-R4), combined with their secondary structures and three-dimensional folding predictions, reveal highly conserved structural features in all three molecules (Fig. 6). For consistency, we ascribe BT-R4 to the cadherin of the yellow mealworm beetle, which was called Tmcad1 in the published article by Fabrick et al.155 BT-R2 is the Cry toxin receptor in the pink bollworm161 but is not included for comparison in Figure 6. Inspection of the three BT-R sequences discloses two highly conserved stretches of amino acid residues within the N- and C-termini that flank EC11 of BT-R3 and EC12 of BT-R1 and BT-R4. These sequences are highlighted in the black boxes (Fig. 6A) and represent signatures that mark the toxin-binding function in all three BT-Rs. Griko et al.132 observed the same high level of conservation of these signature sequences in a number of lepidopteran insects.
Figure 6.
Predicted secondary structure and three-dimensional models of EC modules containing the TBRs for moth, mosquito and beetle. (A) Multiple sequence alignments and secondary structure prediction of the amino acid residues spanning the TBRs of BT-R1 (residues 1349–1460), BT-R3 (residues 1339–1451) and BT-R4 (residues 1292–1405). The structures were generated using the Pfam181 and SAS182 databases. The two black boxes contain the conserved residues in the upstream and downstream regions of the Cry toxin-binding motifs. The designations beneath the alignments are as described in the legend to Fig. 4. (B) Three-dimensional models of the TBRs of BT-R1, BT-R3 and BT-R4 generated from crystal structures of homologous cadherin domains from a mouse E-cadherin (PDB code ledh), a mouse N-cadherin (PDB code 1ncj), and a frog C-cadherin (PDB code 1l3w). The three TBRs were templated onto the superimposed crystal structures by sequence alignment using the DeepView (Swiss-PdbViewer) computer program.183 The alignment was guided by secondary structure prediction by the JPred 3 server184 to match predicted β-strands in the receptor sequences to β-strands in the cadherin crystal structures. The templated models were then refined on the SWISS-MODEL protein modeling server.173 Golden arrows and gray lines highlight predicted β-strands and loops, respectively. Blue arrows and blue lines represent sequences that flank the TBRs and are required for binding.
The toxin-binding motifs of BT-R1, BT-R3 and BT-R4 are displayed in three-dimensional models (Fig. 6B) based on the known crystal structure of Domain 2 of the classical mouse E-cadherin (PDB code 113w), an N-cadherin (PDB code 1ncj) and a C-cadherin (PDB code 113w).162–164 All three BT-R models are very similar topologically in that there are two essential sequences for toxin binding located at the N- and C-termini of either EC11 or EC-12. The two signature sequences (Fig. 6A) form two adjacent β strands and a loop within the β-barrel fold of either EC11 or EC12 (Fig. 6B), providing an interface for toxin binding. The structural features of the TBRs on all three BT-Rs most likely are critical to the specificity, selectivity and affinity of their cognate toxins. And, apparently, the signaling events that lead to cell death depend on binding of Cry toxin to the conserved motifs in EC11 or EC12.
Mechanism of Cry Toxin Action
Just as the classification and taxonomy of Bt remains somewhat controversial, so does the explanation of how Cry toxins destroy insects. There are several models reviewed in the literature that seek to explain how Cry toxins exert their killing capacity.165 For sake of brevity, we have chosen to describe only two mechanisms. The first one postulates that Cry toxin binds to midgut receptor(s), oligomerizes and inserts into the membrane to form lytic pores.166 The notion that Cry toxins assemble lytic pores in the plasma membrane by forming oligomers is based on detection of ion fluxing in brush border membrane vesicles and synthetic lipid bilayers treated with Cry toxins.90,166 However, no direct evidence has been provided for such a mechanism in either living cells or an insect. In fact, it has been shown that toxin oligomers incorporated into the plasma membrane of living cells do not form lytic pores and are not toxic.143 Furthermore, studies of mutated Cry toxins demonstrate that neither toxin oligomers nor commensurate changes in membrane vesicle permeability correlate directly with toxicity.167–169
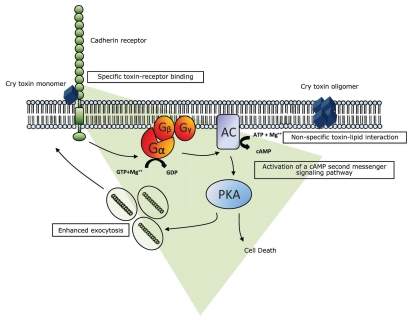
The second model (Fig. 7) advanced by Zhang et al.143,144 challenges the notion that Cry toxin kills cells exclusively by osmotic lysis.166 Instead, toxin monomer binds to the cadherin receptor BT-R1 and activates a Mg2+-dependent signal-transduction pathway leading to cell death. The model demonstrates that, in living cells, Cry1Ab oligomers, integrated into the cell membrane does not correlate with cytotoxicity (Fig. 7). Actually, toxin action is much more complicated than the proposed toxin-induced osmotic lysis. Cry toxin action is a complex, dynamic process that involves univalent binding of toxin to the highly conserved structural motif (described above) in the cadherin receptor BT-R1.132 In turn, a cascade of events is triggered that leads to a form of programmed cell death referred to as oncosis.143 Binding of Cry1Ab toxin to the BT-R1 receptor educes a molecular signal that stimulates heterotrimeric G protein and adenylyl cyclase with an accompanying dramatic increase in production of cAMP. The cAMP activates protein kinase A, bringing about an array of cellular alterations, which includes cytoskeletal rearrangement and ion fluxing. Acceleration of this second messenger pathway alters the chemistry of the cell and brings about cell death.143,144 Furthermore, the killing mechanism involves promotion by the toxin of exocytotic translocation of BT-R1 from intracellular membrane vesicles to the cell membrane.170 Movement of the receptor is mediated by toxin-induced signal-transduction, and amplification of this signaling is correlated directly to the execution of cell death.
Figure 7.
Proposed model for Cry toxin action. The univalent binding of Cry toxin monomer to BT-R initiates the progression of cell death by transmitting a death signal into the cell. A signal transduction pathway, involving G protein (Gα) adenylyl cyclase (AC) and protein kinase A (PKA), is activated. Activation of the signaling pathway mediates exocytosis of the BT-R receptor from intracellular vesicles to the cell membrane. The resulting enhanced display of BT-R on the cell surface facilitates recruitment of additional toxin molecules which, in turn, amplifies the original signal in a cascade-like fashion. The signaling kinase PKA modifies downstream molecules that promote the biochemical activities that destroy the cell. Toxin oligomers incorporated into the plasma membrane of living cells do not form lytic pores and are not toxic.
Phenotypic changes associated with the progression of Cry1Ab toxin-induced cell death are the hallmarks of the killing process. Figure 8 summarizes the cytological changes in High Five cells transfected with BT-R1 cDNA143 and BT-R3 cDNA. (Ibrahim M and Griko N, unpublished results). The BT-R1-transfected cells (Fig. 8, lower) respond to the Cry1Ab toxin by undergoing a series of biochemical events, including activation of a signaling pathway, which leads to discrete morphological changes, modified cell membrane permeability and complete cellular lysis. Importantly, Cry4Ba toxin also induces similar biochemical and cytological changes in High Five cells transfected with BT-R3 cDNA (Fig. 8, upper). This particular result corroborates the effects of Cry toxin on living cells and establishes a pattern of cell death events brought about by cellular machinery intrinsic to the cell (Fig. 7).
Figure 8.
Morphological changes associated with BT-R-transfected High-Five cells treated with mosquito and moth toxins. High-Five cells transfected with BT-R3 cDNA (M5 cells, upper photos) and BT-R1 cDNA (S5 cells, lower photos) were treated with Cry4Ba and Cry1Ab, respectively. The sequence of cytological changes during the course of toxin-induced cell death was captured by phase contrast microscopy. The long arrow beneath the photographs indicates the stages of cell death: toxin binding, membrane blebbing and cellular swelling. Cytotoxicity is Mg2+-dependent and involves exocytosis of the cadherin receptors (BT-R).
It is particularly noteworthy that toxin action can be inhibited by blocking the binding of the toxin to BT-R1 either in an insect126,159 or in cultured insect cells.143,171 Recently, Liu et al.172 reported that Cry1Ac cytotoxicity in the cotton bollworm can be reduced by a soluble toxin-binding cadherin fragment. All of these results demonstrate that the primary determinant of toxicity involves specific toxin-receptor interaction.
Determining the chemistry of the toxin-receptor structure-function relationship would provide a significant step toward better understanding Cry toxin action. In this regard, we have constructed and described a structural model for the toxinbinding cadherin domain of the BT-R1 receptor generated from X-ray crystal structures of homologous cadherin domains.132 The structure includes residues 1349–1460 that comprise EC12 (Fig. 6). A structural model for the Cry1Ab toxin also was generated by the SWISS-MODEL protein modeling server173 using the crystal structure of the Cry1Aa toxin (protein data bank code 1CIY) as a template. The Cry1Ab and Cry1Aa amino acid sequences are 88.3% identical, ensuring a reliable model.
A cropped view of the modeled toxin-receptor complex (see ribbon structure in Fig. 9A) shows residues within the sequence 422–498 in Cry1Ab that most likely are required for BT-R1 binding, suggesting that this sequence contains the receptor-binding site. In the model, this sequence spans the end of Domain II (blue) and the beginning of Domain III (gold) and contributes to two distinct regions (red) on the toxin surface. Also as seen in Figure 9, the two regions are oriented such that they can interact with the signature sequences of BT-R1 depicted in Figure 6. Close inspection of the interface between the Cry1Ab toxin and the TBR of BT-R1 reveals potential hydrophobic interactions involving surface-exposed Phe440 in Cry1Ab and Leu1358, Tyr1453 and Val1455 in the TBR of BT-R1. Furthermore, potential electrostatic interaction between the positively charged Arg437 in Cry1Ab and the negatively charged Glu1357 in the TBR is probable. Importantly, both Arg437 and Phe440 have been shown to be essential to receptor binding and insecticidal activity.110 It is noteworthy that Glu1357, Leu1358 Tyr1453 and Val1455 lie either within or immediately adjacent to the signature sequences in the TBR of BT-R1 (Fig. 6 and blue arrows). Figure 9B shows a potential docking arrangement in a ribbon structure, with residues forming the two surface regions in the toxin highlighted in red (residues 432–449 and 480–493) and residues in the signature sequences of BT-R1 highlighted in purple (residues 1349–1354 and 1451–1460). Figure 9C is a space-filling representation of the proposed docking. This docking arrangement maximizes the surface contact between the predicted binding residues on both proteins.
Figure 9.
A proposed model showing docking of the Cry1Ab toxin to BT-R1. (A) Ribbon structures showing docking of the putative receptor-binding sequence of the Cry1Ab toxin (residues 422–498) to the TBR (residues 1349–1460) in BT-R1. The structure for the TBR was generated from the X-ray crystal structures of homologous cadherin domains as described in the legend to Figure 6. Note that in the interface between the Cry1Ab toxin and the TBR of BT-R1 there are potential hydrophobic interactions involving surface-exposed Phe440 in Cry1Ab and Leu1358, Tyr1453 and Val1455 in the TBR of BT-R1. Also, there is probable electrostatic interaction between the positively charged Arg437 in Cry1Ab and the negatively charged Glu1357 in the TBR. Glu1357, Leu1358, Tyr1453 and Val1455 lie either within or immediately adjacent to the signature sequences in the TBR of BT-R1 (Fig. 6 and blue arrows). Ribbon (B) and space-filling (C) representations showing docking of Cry1Ab toxin to TBR. Domains I, II and III of the toxin are colored green, blue and gold, respectively. The TBR is colored pink. Surface-exposed residues 432–449 and 480–493 in Cry1Ab are colored red, and residues 1349–1354 and 1451–1460 (signature sequences) in the TBR are colored purple.
Insect Resistance to Cry Toxins
For the past 50–60 years, commercial formulations of Bt have been utilized to control economically important insect pests worldwide. Today, a number of agricultural crops carry cry genes that render them resistant to insect infestation. Because the bacterium has co-existed and co-evolved with insects for millions of years, it was assumed that insects would not develop resistance to Bt or its insecticidal toxins. Furthermore, it has been taken for granted that Bt can adapt to an insect's defense system simply by altering the toxins produced to fit the situation or by generating several different toxins with varying specific activities. Although co-evolution and adaptability are relevant factors, interference with nature by questionable management practices involving widespread and intensive use of Bt and its cry genes has increased the likelihood of insects developing resistance to Bt-based bioinsecticides and transgenic plants. In other words, strong evolutionary pressure on insects by Bt will promote development of defense mechanisms that can circumvent bacterial and toxin attack. In fact, a number of different Bt-resistant insect species have been generated in the laboratory through special selection techniques or have been discovered naturally in the field.174–176
The insecticidal activity of Cry toxins involves a number of sequential events, including dissociation of the parasporal crystals into protoxins, activation of the protoxins to toxins by gut proteases, interaction of the toxins with midgut epithelium and binding to specific receptors. Toxin-receptor interactions trigger a cAMP-dependent signaling pathway, which leads to disruption of the structure and functionality of the midgut epithelium (Fig. 7).143,144 When in continual touch with Bt, insects exhibit physiological changes and enhanced immune response. The upshot is resistance to the insecticidal activity of Bt. Three possible scenarios that describe the loss of sensitivity to Bt toxins are summarized in Figure 10. A heightened immune response primarily involves changes in the activity of the mucosal surface, causing increased secretion of proteases and pro-coagulants (Fig. 10A). For example, a 75-kDa pro-coagulant protein from the gut juice of the spruce budworm, which exhibits elastase-like activity, has been shown to bring about precipitation of the protoxin of Bt subsp. sotto.177 Precipitation leads to sequestering of the toxin and limiting its accessibility to its target receptor.
Figure 10.
Possible mechanisms of insect resistance to Bt. Once Bt parasporal crystals are ingested by an insect larva, the crystals are dissociated, followed by proteolytic activation of protoxin and conversion to toxin. The activated toxin binds to the receptor, effecting a cascade of signal transduction events that lead to eventual larval death. There are three ways by which the insect larva could become resistant: (A) an enhanced immune response that inhibits dissociation and accessibility of protoxin; (B) erroneous protease production or defective protease activity that interferes with protoxin/toxin activation; (C) reduced number of binding sites or mutated receptors that retard or prevent appropriate toxin-receptor interaction.
The profile of gut juice proteases involved in protoxin activation changes with larval age. During larval growth and development, there is an observable increase in the concentration of proteases in the alimentary canal. This boost in the amount of gut proteases may account for the reduced sensitivity to Cry toxins (Fig. 10B). In the case of a resistant strain of the Colorado potato beetle (CPB), function-based activity profiling using zymographic gels containing gelatin as a substrate showed specific proteolytic bands present in midgut extracts and brush border membrane vesicles of the resistant strain not apparent in the sensitive strain. Furthermore, the aminopeptidase activity associated with the membrane vesicles was higher in the resistant strain than the sensitive one.176 Increased levels of aminopeptidase also were seen in a resistant colony of Indian meal moth.178 Unlike the CPB, proteolytic activation of Bt subsp. kurstaki protoxins was significantly reduced in a resistant strain of the Egyptian cotton leafworm compared to a sensitive strain (Ibrahim M, unpublished data), indicating that impaired proteolytic processing of toxins in insect guts is an essential mechanism for resistance. Similarly, in the Indian meal moth, a chymotrypsin-like enzyme was significantly reduced in the resistant moth.178 Whether this proteolytic enzyme is essential for toxin activation is not known.
Decreased toxin binding due to reduction in the number of toxin-binding sites or to mutations that render the receptor incapable of binding to the Cry toxin has been implicated also in resistance (Fig. 10C).147,176 Saturation-binding assays revealed that brush border membrane vesicles from the resistant CPB strain bound ∼60% less Cry3A toxin than membrane vesicles from the sensitive strain. Homologous competition inhibition of 125I-Cry3A binding to membrane vesicles also revealed differences in binding affinity between the sensitive and resistant strains.176 Apparently, resistance in the CPB correlates with specific alterations in protease activity in the midgut as well as decreased toxin binding.
Future Considerations
What's next for Bt? Although scientific and technical knowledge about Bt has advanced during the last few decades, detailed studies involving global gene expression and regulation of physiological responses in addition to phenotypic differences and comparative analyses with related bacteria, particularly Ba and Bc, have been limited due to lack of functional genomics and proteomics information. Because Bt typically establishes a pathogenic relationship with its host, but also can exist symbiotically with some invertebrate animals, the bacterium provides an exceptional model to address questions related to microbe-host interactions and to those factors that influence pathogenic and symbiotic relationships. As already discussed, the pathogenicity of Bt involves targeting specific cadherin receptors within susceptible hosts, indicating that attacking cell adhesion molecules is evolutionarily significant for Bt and many other pathogens that disrupt and penetrate epithelial barriers in their hosts.159,179 Therefore, deciphering the genome and proteome of Bt can help answer various questions related to bacterial disease processes as exemplified in insect systems. Likewise, understanding more about insect host immune response to Bt would help explain some of the features and characteristics of the immune system in invertebrates in general. Also, fathoming insect immunity a la Bt infections would enlighten us about vertebrate immunity as well because insects are similar in a number of ways to vertebrates in their ability to ward off disease.
A most promising area of investigation is the discovery, identification and validation of molecular targets for development of new insecticides. There are extensive databases for genome sequences of insects and other organisms which afford valuable information for identification of new targets. Recently, a web-based computational pipeline platform was developed for automated large-scale gene mining and insecticide target identification.180 The platform utilizes bioinformatics, genomics and proteomics for high-throughput gene and protein target identifi- cation (Fig. 11). It brings together genome- and proteome-based target identification and target-directed screening for validating the action of engineered Bt toxins in cell-based assays. All targets selected for consideration can then be analyzed in silico by docking calculations, molecular dynamics simulations and other techniques to characterize appropriate target interactions with chemically or genetically altered Cry toxins. Such an approach should facilitate protein design for the creation of Cry protein and peptide mimics that might be more effective than the natural toxins themselves and less able to induce insect host resistance.
Figure 11.
A genomics/proteomics platform for new insecticide discovery. There are three pathways to discovery, identification and validation of insecticide targets. (A) Bioinformatics pipeline to identify target proteins and to design specific primers or probes for cDNA screening. The process of target selection starts with data mining of a list of protein sequences from available genomic databases. The proteins are selected and categorized based on their potential to mediate insecticidal action. (B) Construction of cDNA libraries from tissue or cell samples, cloning and transfection of selected genes in insect cells and formatting of transfected cells for gene expression. (C) Construction of engineered toxins and target screening for evaluation and validation.
Acknowledgements
We are deeply grateful for the expert technical assistance of Shweta Biliya and Gayathri Raghupathy in preparing this manuscript.
Abbreviations
- AC
adenylyl cyclase
- AFLP
amplified fragment length polymorphism
- BC
Bacillus cereus group
- Bt
Bacillus thuringiensis
- ORF
open reading frame
- PKA
protein kinase A
- TBR
toxin-binding region
Footnotes
Previously published online: www.landesbioscience.com/journals/bioengineeredbugs/article/10519
References
- 1.Bulla LA, Rhodes RA, St Julian G. Bacteria as insect pathogens. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:163–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Candas M, Bulla LA. Microbial insecticides. In: Bitton G, editor. Encyclopedia of Environmental Microbiology. NY: John Wiley and Sons; 2002. pp. 1709–1717. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Smith JA, Ross WD, editors. The Works of Aristotle. Vol. 4. Oxford: Clarendon; 1910. Aristotle. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kirby W, Spence W. An Introduction to Entomology: Or Elements of the Natural History of Insects. London: Longman; 1826. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bassi A. Opere di Agostino Bassi. Pavia, Italy: Tipografia Cooperativa di Pavia; 1925. pp. 87–152. (Ita). [Google Scholar]
- 6.Aoki K, Chegâsaki Y. Âoeber die pathogenitât der sog. sotto Bacillen (Ishiwata) bei seidenrauven. Mitt Med Fak Kais. 1915;13:419. (Ita). [Google Scholar]
- 7.Berliner E. Âœber die schlafsucht der mehlmottenraupe. Z Gesamte Getreidewes. 1911;3:63. (Ita). [Google Scholar]
- 8.Berliner E. Uber die Schlafsucht der Mehlmottenraupe (Ephestia kuhniella Zell.) und ihren Erreger Bacillus thuringiensis, n.sp. Z angew Ent. 1915;2:29. (Ger). [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mattes O. Parasitare krankheiten der mehimottenlarven und versuche uber ihre verwendbarkeit als biologisches bekamfungsmittel. Ges Naturw Marburg Schrift. 1927:381. (Ita). [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hannay CL. Crystalline inclusions in aerobic sporeforming bacteria. Nature. 1953;172:1004. doi: 10.1038/1721004a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Angus TA. Progress Report. Vol. 9. Forest Biology Division, Canada Department of Science Service; 1953. Studies of Bacillus spp. pathogenic for silkworm; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hannay CL, Fitz-James P. The protein crystals of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner. Can J Microbiol. 1955;1:694–710. doi: 10.1139/m55-083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Qaim M, Zilberman D. Yield effects of genetically modified crops in developing countries. Science. 2003;299:900–902. doi: 10.1126/science.1080609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kleter GA, Bhula R, Bodnaruk K, Carazo E, Felsot AS, Harris CA, et al. Altered pesticide use on transgenic crops and the associated general impact from an environmental perspective. Pest Manag Sci. 2007;63:1107–1115. doi: 10.1002/ps.1448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mizuki E, Ohba M, Akao T, Yamashita S, Saitoh H, Park YS. Unique activity associated with non-insecticidal Bacillus thuringiensis parasporal inclusions: in vitro cell-killing action on human cancer cells. J Appl Microbiol. 1999;86:477–486. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.1999.00692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lee DW, Akao T, Yamashita S, Katayama H, Maeda M, Saitoh H, et al. Noninsecticidal parasporal proteins of a Bacillus thuringiensis serovar shandongiensis isolate exhibit a preferential cytotoxicity against human leukemic T cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;272:218–223. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.2765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mizuki E, Park YS, Saitoh H, Yamashita S, Akao T, Higuchi K, Ohba M. Parasporin, a human leukemic cell-recognizing parasporal protein of Bacillus thuringiensis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2000;7:625–634. doi: 10.1128/cdli.7.4.625-634.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bulla LA, Bechtel DB, Kramer KJ, Shethna YI, Aronson AI, Fitz-James PC. Ultrastructure, physiology and biochemistry of Bacillus thuringiensis. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1980;8:147–204. doi: 10.3109/10408418009081124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bechtel DB, Bulla LA. Ultrastructural analysis of membrane development during Bacillus thuringiensis sporulation. J Ultrastruct Res. 1982;79:121–132. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(82)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.de Barjac H, Bonnefoi A. Essai de classification biochimique se sérologique de 24 souches de Bacillus du type B. thuringiensis. Entomophaga. 1962;7:5–31. (Ita). [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lecadet MM, Frachon E, Dumanoir VC, Ripouteau H, Hamon S, Laurent P, Thiery I. Updating the H-antigen classification of Bacillus thuringiensis. J Appl Microbiol. 1999;86:660–672. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.1999.00710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Soufiane B, Cote JC. Discrimination among Bacillus thuringiensis H serotypes, serovars and strains based on 16S rRNA, gyrB and aroE gene sequence analyses. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2009;95:33–45. doi: 10.1007/s10482-008-9285-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gordon RL, Haynes WC, Pang CHN. Agricultural Handbook. 427 Washington DC: Agricultural research service, US Department of Agriculture; 1973. The Genus Bacillus. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Buchanan RE, Gibbons NE. Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology. Vol. 7. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins Co; 1974. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Garbeva P, van Veen JA, van Elsas JD. Predominant Bacillus spp. in agricultural soil under different management regimes detected via PCR-DGGE. Microb Ecol. 2003;45:302–316. doi: 10.1007/s00248-002-2034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ash C, Farrow JAE, Wallbanks S, Collins MD. Phylogenetic heterogeneity of the genus Bacillus revealed by comparative analysis of small subunit ribosomal RNA sequences. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1991;13:202–206. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Heyndrickx M, Vandemeulebroecke K, Scheldeman P, Kersters K, de Vos P, Logan NA, et al. A polyphasic reassessment of the genus Paenibacillus, reclassification of Bacillus lautus (Nakamura 1984) as Paenibacillus lautus comb. nov. and of Bacillus peoriae (Montefusco et al. 1993) as Paenibacillus peoriae comb. nov., and emended descriptions of Paenibacillus lautus and of Paenibacillus peoriae. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1996;46:988–1003. doi: 10.1099/00207713-46-4-988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Heyndrickx M, Lebbe L, Kersters K, De Vos P, Forsyth G, Logan N. Virgibacillus: a new genus to accommodate Bacillus pantothenticus (Proom and Knight 1950). Emended description of Virgibacillus pantothenticus. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1998;48:99–106. doi: 10.1099/00207713-49-3-1083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nazina TN, Tourova TP, Poltaraus AB, Novikova EV, Grigoryan AA, Ivanova AE, et al. Taxonomic study of aerobic thermophilic bacilli: descriptions of Geobacillus subterraneus gen. nov., sp. nov. and Geobacillus uzenensis sp. nov. from petroleum reservoirs and transfer of Bacillus stearothermophilus, Bacillus thermocatenulatus, Bacillus thermoleovorans, Bacillus kaustophilus, Bacillus thermodenitrificans to Geobacillus as the new combinations G. stearothermophilus, G. th. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001;51:433–446. doi: 10.1099/00207713-51-2-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nakamura LK, Shida O, Takagi H, Komagata K. Bacillus pycnus sp. nov. and Bacillus neidei sp. nov., round-spored bacteria from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2002;52:501–505. doi: 10.1099/00207713-52-2-501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bergquist PL, Morgan HW. The molecular genetics and biotechnological application of enzymes from extremely thermophilic eubacteria. In: Herbert RA, Sharp RJ, editors. Molecular Biology and Biotechnology of Extremophiles. New York: Chapman & Hall; 1922. pp. 44–75. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pleban S, Sörensen J. Multi-target and medium-independent fungal antagonism by hydrolytic enzymes in Paenibacillus polymyxa and Bacillus pumilus strains from barley rhizosphere. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 1996;22:183–192. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Spharga BM, Lyon GD. Bacillus subtilis BS107 as an antagonist of potato blackleg and soft rot bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1998;44:777–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Emmert EA, Handelsman J. Biocontrol of plant disease: a (Gram-) positive perspective. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999;171:1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Giacomodonato MN, Pettinari MJ, Guadalupe IS, Beatriz SM, Lopez NI. A PCR-based method for the screening of bacterial strains with antifungal activity in suppressive soybean rhizosphere. World J Microbiol Biotechno. 2001;17:51–55. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hernandez E, Ramisse F, Ducoureau JP, Cruel T, Cavallo JD. Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. konkukian (serotype H34) superinfection: case report and experimental evidence of pathogenicity in immunosuppressed mice. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:2138–2139. doi: 10.1128/jcm.36.7.2138-2139.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hernandez E, Ramisse F, Cruel T, le VR, Cavallo JD. Bacillus thuringiensis serotype H34 isolated from human and insecticidal strains serotypes 3a3b and H14 can lead to death of immunocompetent mice after pulmonary infection. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1999;24:43–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.1999.tb01263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hernandez E, Ramisse F, Gros P, Cavallo J. Superinfection by Bacillus thuringiensis H34 or 3a3b can lead to death in mice infected with the influenza A virus. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2000;29:177–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2000.tb01520.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hill KK, Ticknor LO, Okinaka RT, Asay M, Blair H, Bliss KA, et al. Fluorescent amplified fragment length polymorphism analysis of Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004;70:1068–1080. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.2.1068-1080.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Han CS, Xie G, Challacombe JF, Altherr MR, Bhotika SS, Brown N, et al. Pathogenomic sequence analysis of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis isolates closely related to Bacillus anthracis. J Bacteriol. 2006;188:3382–3390. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.9.3382-3390.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mock M, Fouet A. Anthrax. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2001;55:647–671. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ash C, Collins MD. Comparative analysis of 23S ribosomal RNA gene sequences of Bacillus anthracis and emetic Bacillus cereus determined by PCR-direct sequencing. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992;73:75–80. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90586-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Helgason E, Caugant DA, Lecadet MM, Chen Y, Mahillon J, Lovgren A, et al. Genetic diversity of Bacillus cereus/Bacillus thuringiensis isolates from natural sources. Curr Microbiol. 1998;37:80–87. doi: 10.1007/s002849900343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Helgason E, Caugant DA, Olsen I, Kolsto AB. Genetic structure of population of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis isolates associated with periodontitis and other human infections. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:1615–1622. doi: 10.1128/jcm.38.4.1615-1622.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ticknor LO, Kolsto AB, Hill KK, Keim P, Laker MT, Tonks M, Jackson PJ. Fluorescent amplified fragment length polymorphism analysis of Norwegian Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis soil isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001;67:4863–4873. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.10.4863-4873.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Helgason E, Tourasse NJ, Meisal R, Caugant DA, Kolsto AB. Multilocus sequence typing scheme for bacteria of the Bacillus cereus group. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004;70:191–201. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.1.191-201.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zhong W, Shou Y, Yoshida TM, Marrone BL. Differentiation of Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus cereus, and Bacillus thuringiensis by using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73:3446–3449. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02478-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bavykin SG, Lysov YP, Zakhariev V, Kelly JJ, Jackman J, Stahl DA, Cherni A. Use of 16S rRNA, 23S rRNA and gyrB gene sequence analysis to determine phylogenetic relationships of Bacillus cereus group microorganisms. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:3711–3730. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.8.3711-3730.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ko KS, Kim JW, Kim JM, Kim W, Chung SI, Kim IJ, et al. Population structure of the Bacillus cereus group as determined by sequence analysis of six housekeeping genes and the plcR Gene. Infect Immun. 2004;72:5253–5261. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5253-5261.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.La Duc MT, Satomi M, Agata N, Venkateswaran K. gyrB as a phylogenetic discriminator for members of the Bacillus anthracis-cereus-thuringiensis group. J Microbiol Methods. 2004;56:383–394. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2003.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Park SH, Kim HJ, Kim JH, Kim TW, Kim HY. Simultaneous detection and identification of Bacillus cereus group bacteria using multiplex PCR. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007;17:1177–1182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Heimpel AM. A critical review of Bacillus thuringiensis var. thuringiensis Berliner and other crystalliferous bacteria. Annu Rev Entomol. 1967;12:287–322. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.12.010167.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Schnepf E, Crickmore N, Van RJ, Lereclus D, Baum J, Feitelson J, et al. Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1998;62:775–806. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.62.3.775-806.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Crickmore N, Zeigler DR, Feitelson J, Schnepf E, Van Rie J, Lereclus D, et al. Revision of the nomenclature for the Bacillus thuringiensis pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1998;62:807–813. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.62.3.807-813.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Tzeng YL, Datta A, Kolli VK, Carlson RW, Stephens DS. Endotoxin of Neisseria meningitidis composed only of intact lipid A: inactivation of the meningococcal 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid transferase. J Bacteriol. 2002;184:2379–2388. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.9.2379-2388.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lamanna C, Sakaguchi G. Botulinal toxins and the problem of nomenclature of simple toxins. Bacteriol Rev. 1971;35:242–249. doi: 10.1128/br.35.3.242-249.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Bulla LA, Davidson LI, Kramer KJ, Jones BL. Purification of the insecticidal toxin from the parasporal crystal of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979;91:1123–1130. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91997-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Bulla LA, Kramer KJ, Cox DJ, Jones BL, Davidson LI, Lookhart GL. Purification and characterization of the entomocidal protoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. J Biol Chem. 1981;256:3000–3004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Moran CP. RNA polymerase and transcription factors. In: Sonenshein AL, Hoch JA, Losick R, editors. Bacillus subtilis and other Gram-positive bacteria. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology; 1993. pp. 653–667. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Bizzard BL, Schnepf HE, Kronstad W. Expression of the cry1B crystal protein gene of Bacillus thuringiensis. Mol Gen Genet. 1991;231:59–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00293822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Brown KL. Transcriptional regulation of the Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. thompsoni crystal protein gene operons. J Bacteriol. 1993;1175:7951–7957. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.24.7951-7957.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yoshisue H, Nishimoto T, Sakai H, Komano T. Identification of a promoter for the crystal protein-encoding gene cryIVB from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Gene. 1993;137:247–251. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90015-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Yoshisue H, Fukada T, Yoshida K, Sen K, Kurosawa S, Sakai H, et al. Transcriptional regulation of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis mosquito larvicidal crystal protein gene cryIVA. J Bacteriol. 1993;175:2750–2753. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2750-2753.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Dervyn E, Poncet S, Klier A, Rapoport G. Transcriptional regulation of the cryIVD gene operon from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. J Bacteriol. 1995;177:2283–2291. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.9.2283-2291.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Wong HC, Schnepf HE, Whiteley HR. Transcriptional and translational start sites for the Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein gene. J Biol Chem. 1983;258:1960–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Lereclus D, Agaisse H, Gominet M, Chaufaux J. Overproduction of encapsulated insecticidal crystal proteins in a Bacillus thuringiensis spo0A mutant. Biotechnology (NY) 1995;13:67–71. doi: 10.1038/nbt0195-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.De Souza MT, Lecadet MM, Lereclus D. Full expression of the cryIIIA toxin gene of Bacillus thuringiensis requires a distant upstream DNA sequence affecting transcription. J Bacteriol. 1993;175:2952–2960. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.10.2952-2960.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Malvar T, Gawron-Burke C, Baum JA. Overexpression of Bacillus thuringiensis HknA, a histidine protein kinase homology, bypasses early spo mutations that result in CryIIIA overproduction. J Bacteriol. 1994;176:4742–4749. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.15.4742-4749.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Walter T, Aronson A. Specific binding of the E2 subunit of pyruvate dehydrogenase to the upstream region of Bacillus thuringiensis protoxin genes. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:7901–7906. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.12.7901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Glatron MF, Rapoport G. Biosynthesis of the parasporal inclusion of Bacillus thuringiensis: half-life of its corresponding messenger RNA. Biochimie. 1972;54:1291–1301. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(72)80070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Wong HC, Chang S. Identification of a positive retroregulator that stabilizes mRNAs in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1986;83:3233–3237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Agaisse H, Lereclus D. STAB-SD: a Shine-Dalgarno sequence in the 5′ untranslated region is a determinant of mRNA stability. Mol Microbiol. 1996;20:633–643. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1996.5401046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Donovan WP, Johnson TB, Burke N, Gawron MC, Malvar T, Slaney AC, et al. Characterization of two genes encoding Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal protein toxic to Coleoptera species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992;158:3921–3927. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.12.3921-3927.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Lambert B, Theunis W, Aguda R, Van Audenhove K, Decock C, Jansens S, et al. Nucleotide sequence of gene cryIIID encoding a novel coleopteran-active crystal protein from strain BTI109P of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki. Gene. 1992;110:131–132. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90457-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Ibrahim MA. Cloning, organization and enhancement of activity of two insecticidal crystal protein genes. Univeristy of Wyoming; 1999. PhD Dissertation. [Google Scholar]
- 76.Crickmore N, Ellar DJ. Involvement of a possible chaperonin in the efficient expression of a cloned cryIIA delta-endotoxin gene in Bacillus thuringiensis. Mol Microbiol. 1992;6:1533–1537. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Adams LF, Visick JE, Whiteley HR. A 20-kilodalton protein is required for efficient production of the Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis 27-kilodalton crystal protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989;171:521–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.521-530.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Baum JA, Malvar T. Regulation of insecticidal crystal protein production in Bacillus thuringiensis. Mol Microbiol. 1995;18:1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.mmi_18010001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.de Maagd RA, Bravo A, Crickmore N. How Bacillus thuringiensis has evolved specific toxins to colonize the insect world. Trends Genet. 2001;17:193–199. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(01)02237-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Thomas DJ, Morgan JA, Whipps JM, Saunders JR. Plasmid transfer between the Bacillus thuringiensis subspecies kurstaki and tenebrionis in laboratory culture and soil and in lepidopteran and coleopteran larvae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000;66:118–124. doi: 10.1128/aem.66.1.118-124.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Thomas DJ, Morgan JA, Whipps JM, Saunders JR. Plasmid transfer between Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis strains in laboratory culture, river water and dipteran larvae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001;67:330–338. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.1.330-338.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Widner WR, Whiteley HR. Two highly related insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki possess different host range specificities. J Bacteriol. 1989;171:965–974. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.965-974.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Sedlak M, Walter T, Aronson A. Regulation by overlapping promoters of the rate of synthesis and deposition into crystalline inclusions of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins. J Bacteriol. 2000;182:734–741. doi: 10.1128/jb.182.3.734-741.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Aronson AI, Wu D, Zhang C. Mutagenesis of specificity and toxicity regions of a Bacillus thuringiensis protoxin gene. J Bacteriol. 1995;177:4059–4065. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.14.4059-4065.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Held GA, Bulla LA, Ferrari E, Hoch J, Aronson AI, Minnich SA. Cloning and localization of the lepidopteran protoxin gene of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1982;79:6065–6069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Schnepf HE, Whiteley HR. Cloning and expression of the Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein gene in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1981;78:2893–2897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Hofte H, Whiteley HR. Insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Microbiol Rev. 1989;53:242–255. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.242-255.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Carlton BC, Gawron-Burke C. Genetic improvement of Bacillus thuringiensis for bioinsecticide development. In: Kim L, editor. Advanced engineered pesticides. New York: Marcel Dekker inc; 1993. pp. 43–71. [Google Scholar]
- 89.Li J, Carroll J, Ellar DJ. Crystal structure of insecticidal delta-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis at 2.5 Å resolution. Nature. 1991;353:815–821. doi: 10.1038/353815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Grochulski P, Masson L, Borisova S, Pusztai-Carey M, Schwartz JL, Brousseau R, et al. Bacillus thuringiensis CryIA(a) insecticidal toxin: crystal structure and channel formation. J Mol Biol. 1995;254:447–464. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Derbyshire DJ, Ellar DJ, Li J. Crystallization of the Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1Ac and its complex with the receptor ligand N-acetyl-D-galactosamine. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2001;57:1938–1944. doi: 10.1107/s090744490101040x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Morse RJ, Yamamoto T, Stroud RM. Structure of Cry2Aa suggests an unexpected receptor binding epitope. Structure. 2001;9:409–417. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00601-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Galitsky N, Cody V, Wojtczak A, Ghosh D, Luft JR, Pangborn W, et al. Structure of the insecticidal bacterial delta-endotoxin Cry3Bb1 of Bacillus thuringiensis. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2001;57:1101–1109. doi: 10.1107/s0907444901008186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Boonserm P, Davis P, Ellar DJ, Li J. Crystal structure of the mosquito-larvicidal toxin Cry4Ba and its biological implications. J Mol Biol. 2005;348:363–382. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Boonserm P, Mo M, Angsuthanasombat C, Lescar J. Structure of the functional form of the mosquito larvicidal Cry4Aa toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis at a 2.8-angstrom resolution. J Bacteriol. 2006;188:3391–3401. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.9.3391-3401.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Guo S, Ye S, Liu Y, Wei L, Xue J, Wu H, et al. Crystal structure of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry8Ea1: An insecticidal toxin toxic to underground pests, the larvae of Holotrichia parallela. J Struct Biol. 2009;168:259–266. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2009.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Cabiaux V, Wolff C, Ruysschaert JM. Interaction with a lipid membrane: a key step in bacterial toxins virulence. Int J Biol Macromol. 1997;21:285–298. doi: 10.1016/s0141-8130(97)00078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Falnes PO, Sandvig K. Penetration of protein toxins into cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000;12:407–413. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Gazit E, La RP, Sansom MS, Shai Y. The structure and organization within the membrane of the helices composing the pore-forming domain of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin are consistent with an “umbrella-like” structure of the pore. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:12289–12294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Kanintronkul Y, Sramala I, Katzenmeier G, Panyim S, Angsuthanasombat C. Specific mutations within the alpha4-alpha5 loop of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4B toxin reveal a crucial role for Asn-166 and Tyr-170. Mol Biotechnol. 2003;24:11–20. doi: 10.1385/MB:24:1:11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Tiewsiri K, Angsuthanasombat C. Structurally conserved aromaticity of Tyr249 and Phe264 in helix 7 is important for toxicity of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2007;40:163–171. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2007.40.2.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Mandal CC, Gayen S, Basu A, Ghosh KS, Dasgupta S, Maiti MK, Sen SK. Prediction-based protein engineering of domain I of Cry2A entomocidal toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis for the enhancement of toxicity against lepidopteran insects. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2007;20:599–606. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzm058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.de Maagd RA, Bakker PL, Masson L, Adang MJ, Sangadala S, Stiekema W, Bosch D. Domain III of the Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin Cry1Ac is involved in binding to Manduca sexta brush border membranes and to its purified aminopeptidase N. Mol Microbiol. 1999;31:463–471. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Gomez I, Miranda-Rios J, Rudino-Pinera E, Oltean DI, Gill SS, Bravo A, Soberon M. Hydropathic complementarity determines interaction of epitope (869) HITDTNNK(876) in Manduca sexta Bt-R(1) receptor with loop 2 of domain II of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1A toxins. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:30137–30143. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M203121200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Xin-Min Z, Li-Qiu X, Xue-Zhi D, Fa-Xiang W. The theoretical three-dimensional structure of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry5Aa and its biological implications. Protein J. 2009;28:104–110. doi: 10.1007/s10930-009-9169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Lee MK, You TH, Curtiss A, Dean DH. Involvement of two amino acid residues in the loop region of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab toxin in toxicity and binding to Lymantria dispar. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;229:139–146. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.1770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Gomez I, Dean DH, Bravo A, Soberon M. Molecular basis for Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab toxin specificity: two structural determinants in the Manduca sexta Bt-R1 receptor interact with loops alpha-8 and 2 in domain II of Cy1Ab toxin. Biochemistry. 2003;42:10482–10489. doi: 10.1021/bi034440p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Tuntitippawan T, Boonserm P, Katzenmeier G, Angsuthanasombat C. Targeted mutagenesis of loop residues in the receptor-binding domain of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin affects larvicidal activity. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005;242:325–332. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2004.11.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Rajamohan F, Alcantara E, Lee MK, Chen XJ, Curtiss A, Dean DH. Single amino acid changes in domain II of Bacillus thuringiensis CryIAb delta-endotoxin affect irreversible binding to Manduca sexta midgut membrane vesicles. J Bacteriol. 1995;177:2276–2282. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.9.2276-2282.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Abdul-Rauf M, Ellar DJ. Mutations of loop 2 and loop 3 residues in domain II of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1C δ-endotoxin affect insecticidal specificity and initial binding to Spodoptera littoralis and Aedes aegypti midgut membranes. Curr Microbiol. 1999;39:94–98. doi: 10.1007/s002849900425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Wu SJ, Dean DH. Functional significance of loops in the receptor binding domain of Bacillus thuringiensis CryIIIA delta-endotoxin. J Mol Biol. 1996;255:628–640. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Abdullah MA, Alzate O, Mohammad M, McNall RJ, Adang MJ, Dean DH. Introduction of Culex toxicity into Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba by protein engineering. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003;69:5343–5353. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.9.5343-5353.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Fernandez LE, Perez C, Segovia L, Rodriguez MH, Gill SS, Bravo A, Soberon M. Cry11Aa toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis binds its receptor in Aedes aegypti mosquito larvae through loop alpha-8 of domain II. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:3508–3514. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.05.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Likitvivatanavong S, Aimanova KG, Gill SS. Loop residues of the receptor binding domain of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry11Ba toxin are important for mosquitocidal activity. FEBS Lett. 2009;583:2021–2030. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.05.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Burton SL, Ellar DJ, Li J, Derbyshire DJ. N-acetylgalactosamine on the putative insect receptor aminopeptidase N is recognised by a site on the domain III lectin-like fold of a Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal toxin. J Mol Biol. 1999;287:1011–1022. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.2649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Jenkins JL, Lee MK, Valaitis AP, Curtiss A, Dean DH. Bivalent sequential binding model of a Bacillus thuringiensis toxin to Gypsy moth aminopeptidase N receptor. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:14423–14431. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.19.14423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Lee MK, You TH, Gould FL, Dean DH. Identification of residues in domain III of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin that affect binding and toxicity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999;65:4513–4520. doi: 10.1128/aem.65.10.4513-4520.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Wolfersberger MG, Chen XJ, Dean DH. Site-directed mutations in the third domain of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin CryIAa affect its ability to increase the permeability of Bombyx mori midgut brush border membrane vesicles. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1996;62:279–282. doi: 10.1128/aem.62.1.279-282.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Schwartz JL, Lu YJ, Sohnlein P, Brousseau R, Laprade R, Masson L, et al. Ion channels formed in planar lipid bilayers by Bacillus thuringiensis toxins in the presence of Manduca sexta midgut receptors. FEBS Lett. 1997;412:270–276. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(97)00801-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Bosch D, Schipper B, van der Kleij H, de Maagd RA, Stiekema WJ. Recombinant Bacillus thuringiensis crystal proteins with new properties: possibilities for resistance management. Biotechnology (NY) 1994;12:915–918. doi: 10.1038/nbt0994-915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.de Maagd RA, Weemen-Hendriks M, Stiekema W, Bosch D. Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin Cry1C domain III can function as a specificity determinant for Spodoptera exigua in different, but not all, Cry1-Cry1C hybrids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000;66:1559–1563. doi: 10.1128/aem.66.4.1559-1563.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Bravo A. Phylogenetic relationships of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin family proteins and their functional domains. J Bacteriol. 1997;179:2793–2801. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.9.2793-2801.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Ge AZ, Shivarova NI, Dean DH. Location of the Bombyx mori specificity domain on a Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86:4037–4041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Lee MK, Milne RE, Ge AZ, Dean DH. Location of a Bombyx mori receptor binding region on a Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:3115–3121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Liang Y, Dean DH. Location of a lepidopteran specificity region in insecticidal crystal protein CryIIA from Bacillus thuringiensis. Mol Microbiol. 1994;13:569–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Masson L, Mazza A, Gringorten L, Baines D, Aneliunas V, Brousseau R. Specificity domain localization of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal toxins is highly dependent on the bioassay system. Mol Microbiol. 1994;14:851–860. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Xie R, Zhuang M, Ross LS, Gomez I, Oltean DI, Bravo A, et al. Single amino acid mutations in the cadherin receptor from Heliothis virescens affect its toxin binding ability to Cry1A toxins. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:8416–8425. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408403200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Gomez I, Arenas I, Benitez I, Miranda-Rios J, Becerril B, Grande R, et al. Specific epitopes of domains II and III of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab toxin involved in the sequential interaction with cadherin and aminopeptidase-N receptors in Manduca sexta. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:34032–34039. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M604721200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Schnepf HE, Tomczak K, Ortega JP, Whiteley HR. Specificity-determining regions of a lepidopteran-specific insecticidal protein produced by Bacillus thuringiensis. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:20923–20930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Ge AZ, Rivers D, Milne R, Dean DH. Functional domains of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal proteins. Refinement of Heliothis virescens and Trichoplusia ni specificity domains on CryIA(c) J Biol Chem. 1991;266:17954–17958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Honee G, Convents D, Van RJ, Jansens S, Peferoen M, Visser B. The C-terminal domain of the toxic fragment of a Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein determines receptor binding. Mol Microbiol. 1991;5:2799–2806. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Griko NB, Rose-Young L, Zhang X, Carpenter L, Candas M, Ibrahim MA, et al. Univalent binding of the Cry1Ab toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis to a conserved structural motif in the cadherin receptor BT-R1. Biochemistry. 2007;46:10001–10007. doi: 10.1021/bi700769s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.de Maagd RA, van der KH, Bakker PL, Stiekema WJ, Bosch D. Different domains of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins can bind to insect midgut membrane proteins on ligand blots. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1996;62:2753–2757. doi: 10.1128/aem.62.8.2753-2757.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Rang C, Vachon V, de Maagd RA, Villalon M, Schwartz JL, Bosch D, et al. Interaction between functional domains of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal proteins. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999;65:2918–2925. doi: 10.1128/aem.65.7.2918-2925.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Gumbiner BM. Cell adhesion: the molecular basis of tissue architecture and morphogenesis. Cell. 1996;84:345–357. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81279-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Angst BD, Marcozzi C, Magee AI. The cadherin superfamily: diversity in form and function. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:629–641. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.4.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Nollet F, Kools P, Van RF. Phylogenetic analysis of the cadherin superfamily allows identification of six major subfamilies besides several solitary members. J Mol Biol. 2000;299:551–572. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Takeichi M. Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator. Science. 1991;251:1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.2006419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Ruoslahti E, Obrink B. Common principles in cell adhesion. Exp Cell Res. 1996;227:1–11. doi: 10.1006/excr.1996.0243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Lecuit T, Lenne PF. Cell surface mechanics and the control of cell shape, tissue patterns and morphogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:633–644. doi: 10.1038/nrm2222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Midboe EG, Candas M, Bulla LA. Expression of a midgut-specific cadherin BT-R1 during the development of Manduca sexta larva. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2003;135:125–137. doi: 10.1016/s1096-4959(03)00054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Griko N, Zhang X, Ibrahim M, Midboe EG, Bulla LA. Susceptibility of Manduca sexta to Cry1Ab toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis correlates directly to developmental expression of the cadherin receptor BT-R(1) Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2008;151:59–63. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2008.05.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Zhang X, Candas M, Griko NB, Rose-Young L, Bulla LA. Cytotoxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab toxin depends on specific binding of the toxin to the cadherin receptor BT-R1 expressed in insect cells. Cell Death Differ. 2005;12:1407–1416. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Zhang X, Candas M, Griko NB, Taussig R, Bulla LA. A mechanism of cell death involving an adenylyl cyclase/PKA signaling pathway is induced by the Cry1Ab toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:9897–9902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604017103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Vadlamudi RK, Ji TH, Bulla LA. A specific binding protein from Manduca sexta for the insecticidal toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. berliner. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:12334–12340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Vadlamudi RK, Weber E, Ji I, Ji TH, Bulla LA. Cloning and expression of a receptor for an insecticidal toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:5490–5494. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.10.5490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Gahan LJ, Gould F, Heckel DG. Identification of a gene associated with Bacillus thuringiensis resistance in Heliothis virescens. Science. 2001;293:857–860. doi: 10.1126/science.1060949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Jurat-Fuentes JL, Adang MJ. The Heliothis virescens cadherin protein expressed in Drosophila S2 cells functions as a receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1A but not Cry1Fa toxins. Biochemistry. 2006;45:9688–9695. doi: 10.1021/bi0606703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Nagamatsu Y, Toda S, Koike T, Miyoshi Y, Shigematsu S, Kogure M. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the Bombyx mori receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal CryIA(a) toxin. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1998;62:727–734. doi: 10.1271/bbb.62.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Nagamatsu Y, Toda S, Yamaguchi F, Ogo M, Kogure M, Nakamura M, et al. Identification of Bombyx mori midgut receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal CryIA(a) toxin. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1998;62:718–726. doi: 10.1271/bbb.62.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Wang G, Wu K, Liang G, Guo Y. Gene cloning and expression of cadherin in midgut of Helicoverpa armigera and its Cry1A binding region. Sci China C Life Sci. 2005;48:346–356. doi: 10.1360/03yc0273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Morin S, Biggs RW, Sisterson MS, Shriver L, Ellers-Kirk C, Higginson D, et al. Three cadherin alleles associated with resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis in pink bollworm. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:5004–5009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0831036100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Flannagan RD, Yu CG, Mathis JP, Meyer TE, Shi X, Siqueira HA, et al. Identification, cloning and expression of a Cry1Ab cadherin receptor from European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2005;35:33–40. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2004.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Sayed A, Nekl ER, Siqueira HA, Wang HC, Ffrench-Constant RH, Bagley M, et al. A novel cadherin-like gene from western corn rootworm, Diabrotica virgifera virgifera (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), larval midgut tissue. Insect Mol Biol. 2007;16:591–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2007.00755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Fabrick J, Oppert C, Lorenzen MD, Morris K, Oppert B, Jurat-Fuentes JL. A Novel Tenebrio molitor cadherin is a functional receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis Cry3Aa toxin. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:18401–18410. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.001651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Hua G, Zhang R, Abdullah MA, Adang MJ. Anopheles gambiae cadherin AgCad1 binds the Cry4Ba toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis and a fragment of AgCad1 synergizes toxicity. Biochemistry. 2008;47:5101–5110. doi: 10.1021/bi7023578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Xu X, Yu L, Wu Y. Disruption of a cadherin gene associated with resistance to Cry1Ac (delta)-endotoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis in Helicoverpa armigera. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005;71:948–954. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.2.948-954.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Dunne J, Hanby AM, Poulsom R, Jones TA, Sheer D, Chin WG, et al. Molecular cloning and tissue expression of FAT, the human homologue of the Drosophila fat gene that is located on chromosome 4q34-q35 and encodes a putative adhesion molecule. Genomics. 1995;30:207–223. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.9884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Dorsch JA, Candas M, Griko NB, Maaty WS, Midboe EG, Vadlamudi RK, et al. Cry1A toxins of Bacillus thuringiensis bind specifically to a region adjacent to the membrane-proximal extracellular domain of BT-R(1) in Manduca sexta: involvement of a cadherin in the entomopathogenicity of Bacillus thuringiensis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2002;32:1025–1036. doi: 10.1016/s0965-1748(02)00040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Fabrick JA, Tabashnik BE. Binding of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1Ac to multiple sites of cadherin in pink bollworm. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2007;37:97–106. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2006.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Bulla LA, Candas M. Pectinophora gossypiella (pink bollworm) Bt toxin receptor BT-R2. US Patent 6 660, 497 B1 2004
- 162.Boggon TJ, Murray J, Chappuis-Flament S, Wong E, Gumbiner BM, Shapiro L. C-cadherin ectodomain structure and implications for cell adhesion mechanisms. Science. 2002;296:1308–1313. doi: 10.1126/science.1071559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Nagar B, Overduin M, Ikura M, Rini JM. Structural basis of calcium-induced E-cadherin rigidification and dimerization. Nature. 1996;380:360–364. doi: 10.1038/380360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Tamura K, Shan WS, Hendrickson WA, Colman DR, Shapiro L. Structure-function analysis of cell adhesion by neural (N-) cadherin. Neuron. 1998;20:1153–1163. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80496-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Pigott CR, Ellar DJ. Role of receptors in Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxin activity. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007;71:255–281. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00034-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Bravo A, Gomez I, Conde J, Munoz-Garay C, Sanchez J, Miranda R, et al. Oligomerization triggers binding of a Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab poreforming toxin to aminopeptidase N receptor leading to insertion into membrane microdomains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1667:38–46. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Kumar AS, Aronson AI. Analysis of mutations in the pore-forming region essential for insecticidal activity of a Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1999;181:6103–6107. doi: 10.1128/jb.181.19.6103-6107.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Luo K, Banks D, Adang MJ. Toxicity, binding and permeability analyses of four Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1 delta-endotoxins using brush border membrane vesicles of Spodoptera exigua and Spodoptera frugiperda. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999;65:457–464. doi: 10.1128/aem.65.2.457-464.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Vachon V, Prefontaine G, Rang C, Coux F, Juteau M, Schwartz JL, et al. Helix 4 mutants of the Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal toxin Cry1Aa display altered pore-forming abilities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004;70:6123–6130. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.10.6123-6130.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Zhang X, Griko NB, Corona SK, Bulla LA. Enhanced exocytosis of the receptor BT-R(1) induced by the Cry1Ab toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis directly correlates to the execution of cell death. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2008;149:581–588. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2007.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Tsuda Y, Nakatani F, Hashimoto K, Ikawa S, Matsuura C, Fukada T, et al. Cytotoxic activity of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry proteins on mammalian cells transfected with cadherin-like Cry receptor gene of Bombyx mori (silkworm) Biochem J. 2003;369:697–703. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Liu C, Wu K, Wu Y, Gao Y, Ning C, Oppert B. Reduction of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxicity against Helicoverpa armigera by a soluble toxinbinding cadherin fragment. J Insect Physiol. 2009;55:686–693. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2009.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Bordoli L, Kiefer F, Arnold K, Benkert P, Battey J, Schwede T. Protein structure homology modeling using SWISS-MODEL workspace. Nat Protoc. 2009;4:1–13. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Ferre J, Real MD, Van Rie J, Jansens S, Peferoen M. Resistance to the Bacillus thuringiensis bioinsecticide in a field population of Plutella xylostella is due to a change in a midgut membrane receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991;88:5119–5123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Tabashnik BE, Finson N, Johnson MW, Heckel DG. Cross-resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin CryIF in the diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella) Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994;60:4627–4629. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.12.4627-4629.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Loseva O, Ibrahim M, Candas M, Koller CN, Bauer LS, Bulla LA. Changes in protease activity and Cry3Aa toxin binding in the Colorado potato beetle: implications for insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxins. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2002;32:567–577. doi: 10.1016/s0965-1748(01)00137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Milne R, Wright T, Kaplan H, Dean D. Spruce budworm elastase precipitates Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin by specifically recognizing the C-terminal region. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1998;28:1013–1023. doi: 10.1016/s0965-1748(98)00090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Candas M, Loseva O, Oppert B, Kosaraju P, Bulla LA. Insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis: alterations in the Indianmeal moth larval gut proteome. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2003;2:19–28. doi: 10.1074/mcp.m200069-mcp200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Loeb MJ, Hakim RS, Martin P, Narang N, Goto S, Takeda M. Apoptosis in cultured midgut cells from Heliothis virescens larvae exposed to various conditions. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2000;45:12–23. doi: 10.1002/1520-6327(200009)45:1<12::AID-ARCH2>3.0.CO;2-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Sun J, Griko N, Ibrahim M, Zhang X, Bulla LA. Genome-bases technology for discovery, identification and validation of insecticide and drug targets. Trends Comp Biochem & Physiol. 2008;13:1–10. [Google Scholar]
- 181.Finn RD, Mistry J, Schuster-Bockler B, Griffiths-Jones S, Hollich V, Lassmann T, et al. Pfam: clans, web tools and services. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:247–251. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Milburn D, Laskowski RA, Thornton JM. Sequences annotated by structure: a tool to facilitate the use of structural information in sequence analysis. Protein Eng. 1998;11:855–859. doi: 10.1093/protein/11.10.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Guex N, Peitsch MC. SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis. 1997;18:2714–2723. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150181505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Cole C, Barber JD, Barton GJ. The Jpred 3 secondary structure prediction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:197–201. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]