Abstract
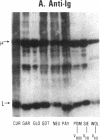
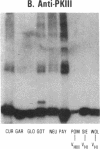
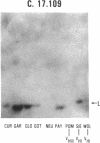
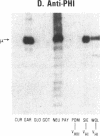
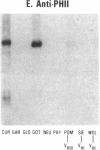
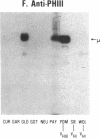
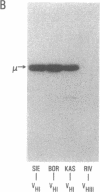
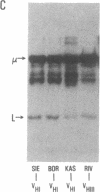
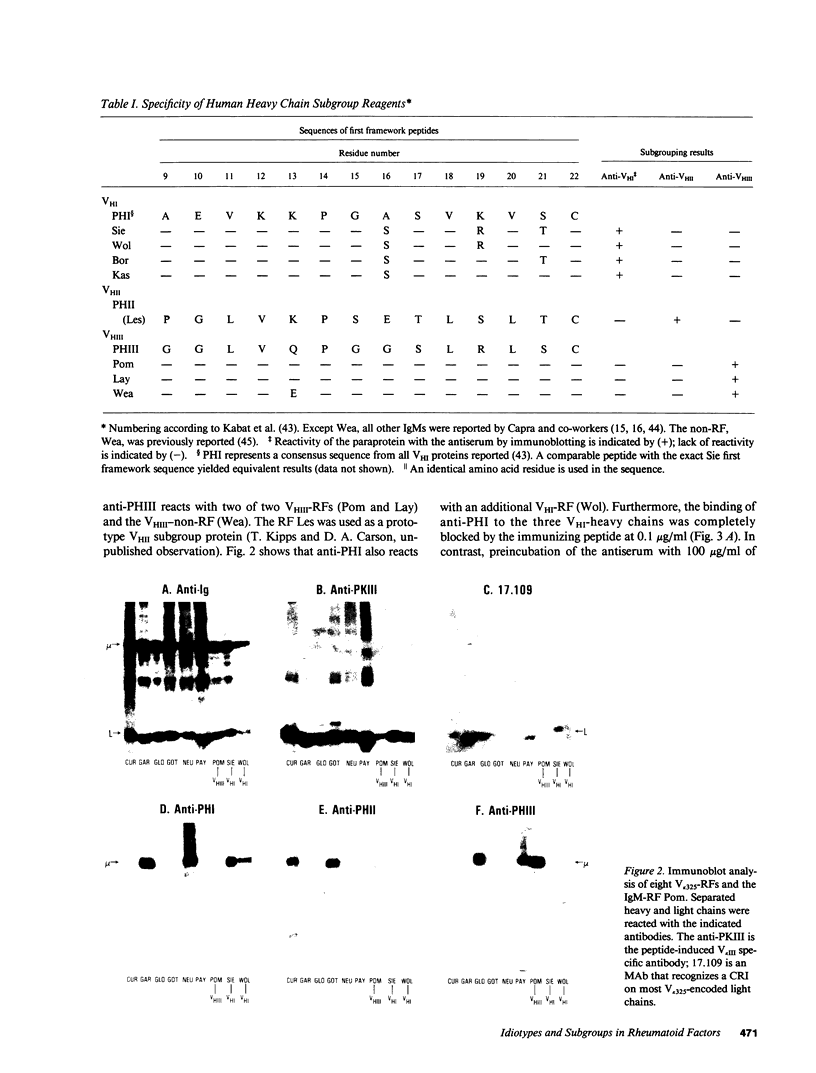
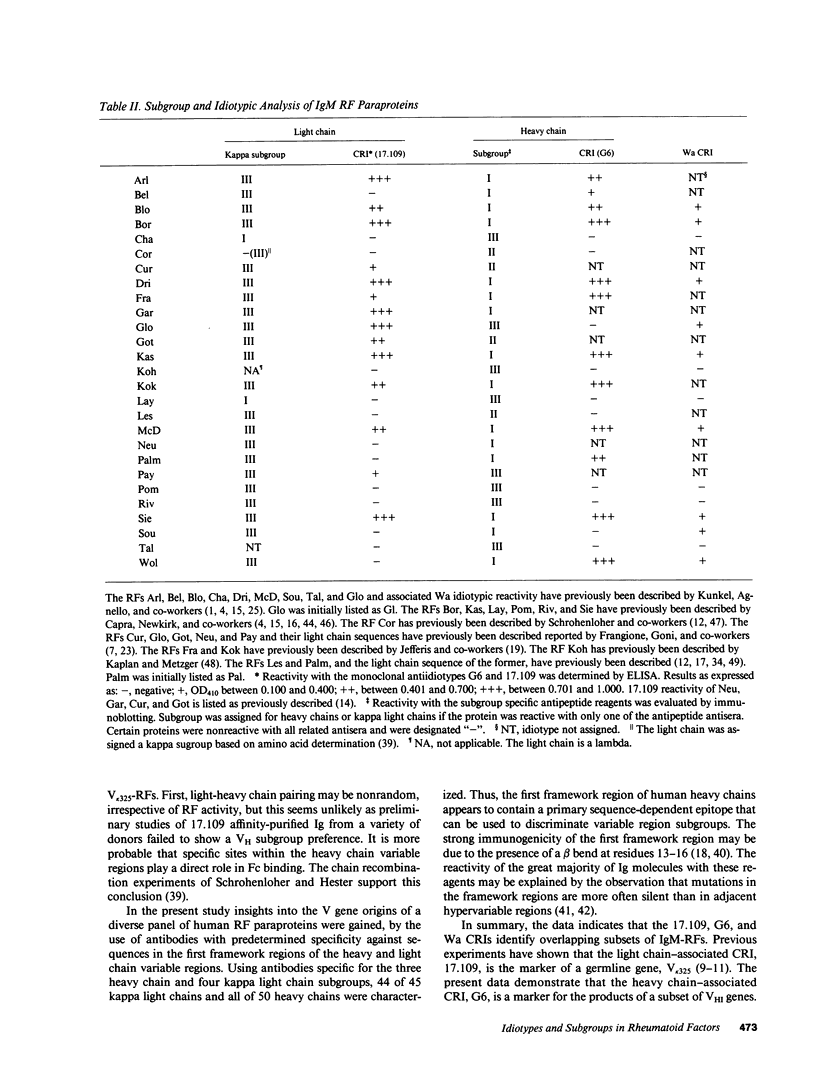
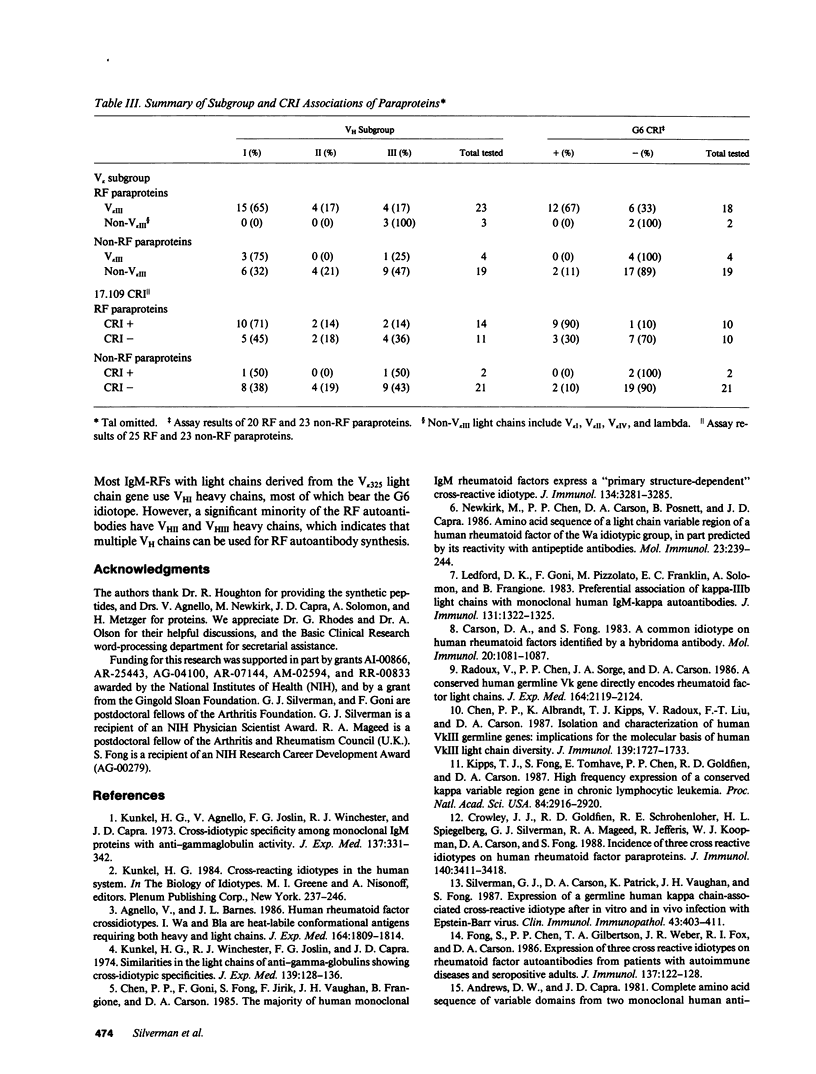
Rheumatoid factors (RFs) in humans have been studied intensively because of their association with autoimmune and lymphoproliferative diseases. Many human IgM-RFs express cross-reactive idiotypes (CRIs) and have homologous light chains, some of which are encoded by a single V kappa gene, termed V kappa 325. However, although antibody activity generally requires the interaction between heavy and light chain variable regions, much less is known about structural relationships among RF heavy chains. To delineate further the structural and genetic basis of RF autoantibody synthesis, we generated "sequence-dependent" reagents specific for the human heavy and kappa light chain subgroups, and used them to analyze a panel of 27 monoclonal RFs. In addition, these proteins were tested for the expression of a heavy chain-associated CRI (G6), and a light chain-associated CRI (17.109). The results showed that most 17.109-reactive RFs contain heavy chains of the VHI subgroup, which bear the G6 idiotypic marker. However, among the 14 17.109-reactive RFs, two have heavy chains of the VHII subgroup, and another two contain heavy chains of the VHIII subgroup. Previously, we have shown that 17.109 is a phenotypic marker of the human V kappa 325 gene. Accordingly, these results demonstrate that the same human V kappa gene can combine with several VH genes from different VH gene subgroups to generate RF activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnello V., Barnes J. L. Human rheumatoid factor crossidiotypes. I. WA and BLA are heat-labile conformational antigens requiring both heavy and light chains. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1809–1814. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agnello V., Goñi F., Barnes J. L., de la Vega M. T., Frangione B. Human rheumatoid factor crossidiotypes. II. Primary structure-dependent crossreactive idiotype, PSL2-CRI, present on Wa monoclonal rheumatoid factors is present on Bla and other IgM kappa monoclonal autoantibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):263–267. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews D. W., Capra J. D. Complete amino acid sequence of variable domains from two monoclonal human anti-gamma globulins of the Wa cross-idiotypic group: suggestion that the J segments are involved in the structural correlate of the idiotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3799–3803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Chen P. P., Fox R. I., Kipps T. J., Jirik F., Goldfien R. D., Silverman G., Radoux V., Fong S. Rheumatoid factor and immune networks. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:109–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Fong S. A common idiotope on human rheumatoid factors identified by a hybridoma antibody. Mol Immunol. 1983 Oct;20(10):1081–1087. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90116-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Albrandt K., Kipps T. J., Radoux V., Liu F. T., Carson D. A. Isolation and characterization of human VkIII germ-line genes. Implications for the molecular basis of human VkIII light chain diversity. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1727–1733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Albrandt K., Orida N. K., Radoux V., Chen E. Y., Schrantz R., Liu F. T., Carson D. A. Genetic basis for the cross-reactive idiotypes on the light chains of human IgM anti-IgG autoantibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8318–8322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Goñi F., Fong S., Jirik F., Vaughan J. H., Frangione B., Carson D. A. The majority of human monoclonal IgM rheumatoid factors express a "primary structure-dependent" cross-reactive idiotype. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3281–3285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Gõni F., Houghten R. A., Fong S., Goldfien R., Vaughan J. H., Frangione B., Carson D. A. Characterization of human rheumatoid factors with seven antiidiotypes induced by synthetic hypervariable region peptides. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):487–500. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Houghten R. A., Fong S., Rhodes G. H., Gilbertson T. A., Vaughan J. H., Lerner R. A., Carson D. A. Anti-hypervariable region antibody induced by a defined peptide: an approach for studying the structural correlates of idiotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1784–1788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Robbins D. L., Jirik F. R., Kipps T. J., Carson D. A. Isolation and characterization of a light chain variable region gene for human rheumatoid factors. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1900–1905. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. H., Huppi K., Ruezinsky D., Staudt L., Gerhard W., Weigert M. Inter- and intraclonal diversity in the antibody response to influenza hemagglutinin. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):687–704. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulie P., Van Snick J. Rheumatoid factors and secondary immune responses in the mouse. II. Incidence, kinetics and induction mechanisms. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Nov;13(11):895–899. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830131107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley J. J., Goldfien R. D., Schrohenloher R. E., Spiegelberg H. L., Silverman G. J., Mageed R. A., Jefferis R., Koopman W. J., Carson D. A., Fong S. Incidence of three cross-reactive idiotypes on human rheumatoid factor paraproteins. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3411–3418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong S., Chen P. P., Gilbertson T. A., Weber J. R., Fox R. I., Carson D. A. Expression of three cross-reactive idiotypes on rheumatoid factor autoantibodies from patients with autoimmune diseases and seropositive adults. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):122–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goñi F., Chen P. P., Pons-Estel B., Carson D. A., Frangione B. Sequence similarities and cross-idiotypic specificity of L chains among human monoclonal IgM kappa with anti-gamma-globulin activity. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4073–4079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goñi F., Frangione B. Amino acid sequence of the Fv region of a human monoclonal IgM (protein WEA) with antibody activity against 3,4-pyruvylated galactose in Klebsiella polysaccharides K30 and K33. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4837–4841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirik F. R., Sorge J., Fong S., Heitzmann J. G., Curd J. G., Chen P. P., Goldfien R., Carson D. A. Cloning and sequence determination of a human rheumatoid factor light-chain gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2195–2199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Metzger H. Partial sequences of six macroglobulin light chains. Absence of sequence correlates to functional activity. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):3944–3951. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipps T. J., Fong S., Tomhave E., Chen P. P., Goldfien R. D., Carson D. A. High-frequency expression of a conserved kappa light-chain variable-region gene in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2916–2920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Capra J. D. The amino acid sequence of the variable regions of the light chains from two idiotypically cross reactive IgM anti-gamma globulins. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1976 Jun-Jul;127(3-4):261–271. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodaira M., Kinashi T., Umemura I., Matsuda F., Noma T., Ono Y., Honjo T. Organization and evolution of variable region genes of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 20;190(4):529–541. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90239-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Agnello V., Joslin F. G., Winchester R. J., Capra J. D. Cross-idiotypic specificity among monoclonal IgM proteins with anti- -globulin activity. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):331–342. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Winchester R. J., Joslin F. G., Capra J. D. Similarities in the light chains of anti-gamma-globulins showing cross-idiotypic specificities. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):128–136. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledford D. K., Goñi F., Pizzolato M., Franklin E. C., Solomon A., Frangione B. Preferential association of kappa IIIb light chains with monoclonal human IgM kappa autoantibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1322–1325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Zinnecker M., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. New procedures for preparation and isolation of conjugates of proteins and a synthetic copolymer of D-amino acids and immunochemical characterization of such conjugates. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):690–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mageed R. A., Dearlove M., Goodall D. M., Jefferis R. Immunogenic and antigenic epitopes of immunoglobulins. XVII--Monoclonal antibodies reactive with common and restricted idiotopes to the heavy chain of human rheumatoid factors. Rheumatol Int. 1986;6(4):179–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00541285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemazee D. A., Sato V. L. Induction of rheumatoid antibodies in the mouse. Regulated production of autoantibody in the secondary humoral response. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):529–545. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newkirk M. M., Mageed R. A., Jefferis R., Chen P. P., Capra J. D. Complete amino acid sequences of variable regions of two human IgM rheumatoid factors, BOR and KAS of the Wa idiotypic family, reveal restricted use of heavy and light chain variable and joining region gene segments. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):550–564. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newkirk M., Capra J. D. Cross-idiotypic specificity among human rheumatoid factors. Monogr Allergy. 1987;22:1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newkirk M., Chen P. P., Carson D., Posnett D., Capra J. D. Amino acid sequence of a light chain variable region of a human rheumatoid factor of the Wa idiotypic group, in part predicted by its reactivity with antipeptide antibodies. Mol Immunol. 1986 Mar;23(3):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotný J., Handschumacher M., Haber E. Location of antigenic epitopes on antibody molecules. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jun 20;189(4):715–721. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90502-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons-Estel B., Goñi F., Solomon A., Frangione B. Sequence similarities among kappa IIIb chains of monoclonal human IgM kappa autoantibodies. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):893–904. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell R., Agnello V. Characterization of complement-fixing activity and cross-idiotypes of rheumatoid factors in idiopathic mixed cryoglobulinemia. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Oct;29(1):146–151. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radoux V., Chen P. P., Sorge J. A., Carson D. A. A conserved human germline V kappa gene directly encodes rheumatoid factor light chains. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):2119–2124. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.2119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrohenloher R. E., Hester R. B. Reassembly of immunoglobulin M heavy and light chains in vitro. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(6-7):637–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M. J., Marshak-Rothstein A., Wolfowicz C. B., Rothstein T. L., Weigert M. G. The role of clonal selection and somatic mutation in autoimmunity. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):805–811. doi: 10.1038/328805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M., Nemazee D., van Snick J., Weigert M. Variable region sequences of murine IgM anti-IgG monoclonal autoantibodies (rheumatoid factors). II. Comparison of hybridomas derived by lipopolysaccharide stimulation and secondary protein immunization. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):970–987. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman G. J., Carson D. A., Patrick K., Vaughan J. H., Fong S. Expression of a germline human kappa chain-associated cross-reactive idiotype after in vitro and in vivo infection with Epstein-Barr virus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Jun;43(3):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman G. J., Carson D. A., Solomon A., Fong S. Human kappa light chain subgroup analysis with synthetic peptide-induced antisera. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 24;95(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. L., Coulie P. Monoclonal anti-IgG autoantibodies derived from lipopolysaccharide-activated spleen cells of 129/Sv mice. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):219–230. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J., Coulie P. Rheumatoid factors and secondary immune responses in the mouse. I. Frequent occurrence of hybridomas secreting IgM anti-IgG1 autoantibodies after immunization with protein antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Nov;13(11):890–894. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830131106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch M. J., Fong S., Vaughan J., Carson D. Increased frequency of rheumatoid factor precursor B lymphocytes after immunization of normal adults with tetanus toxoid. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Feb;51(2):299–304. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]