Abstract
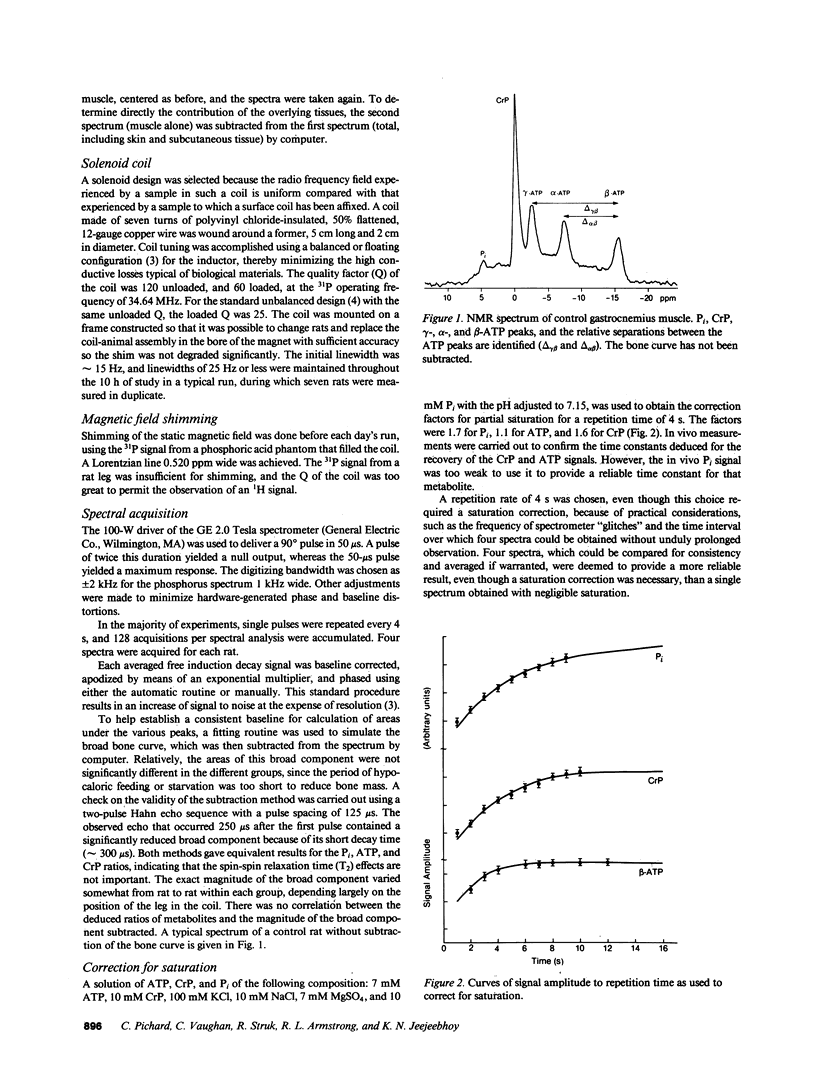
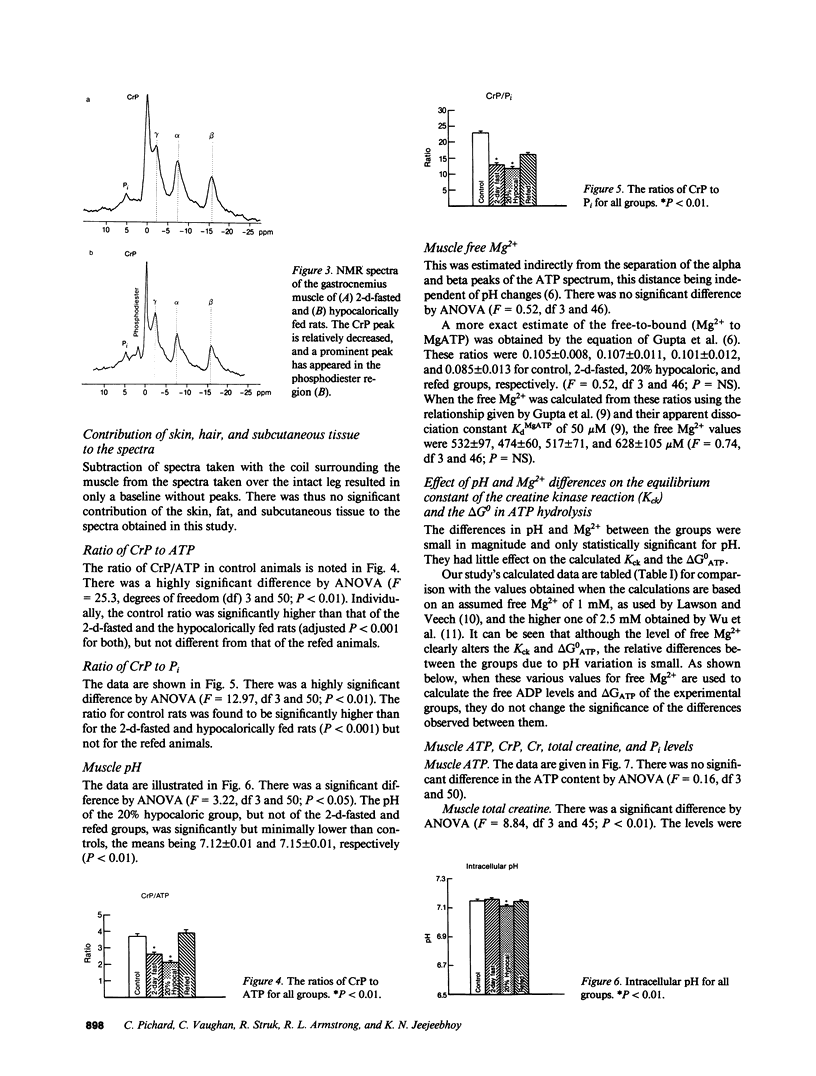
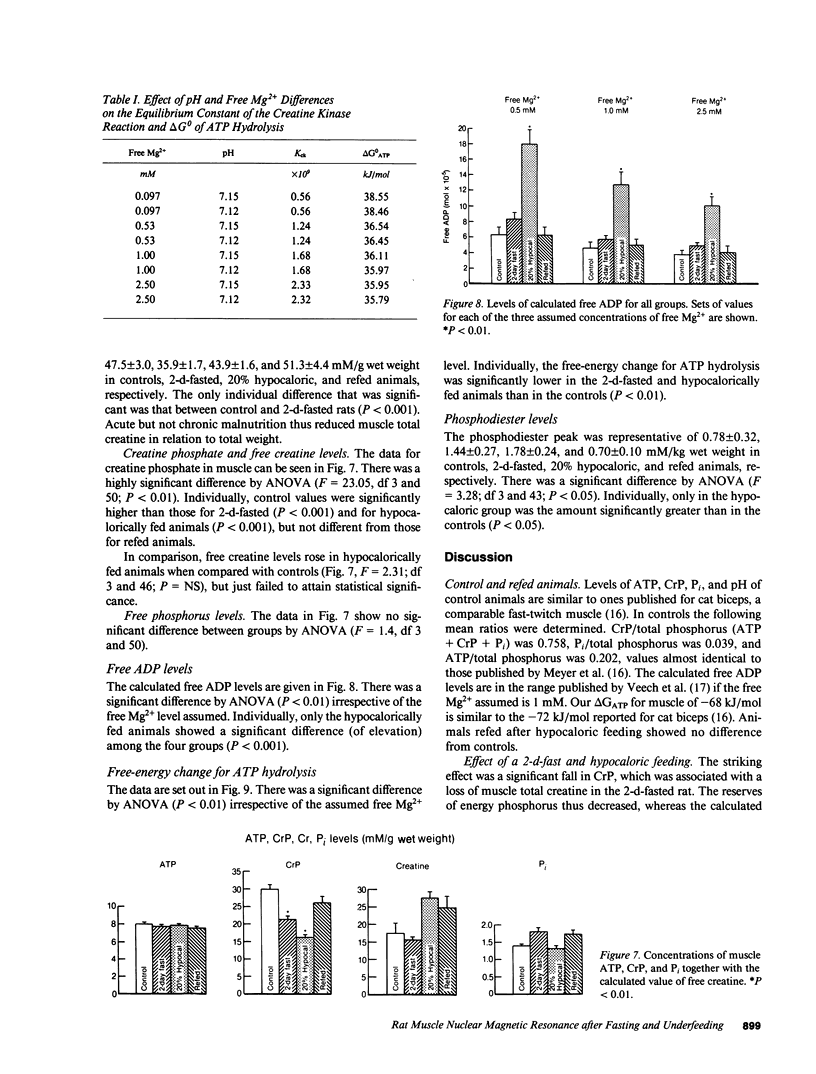
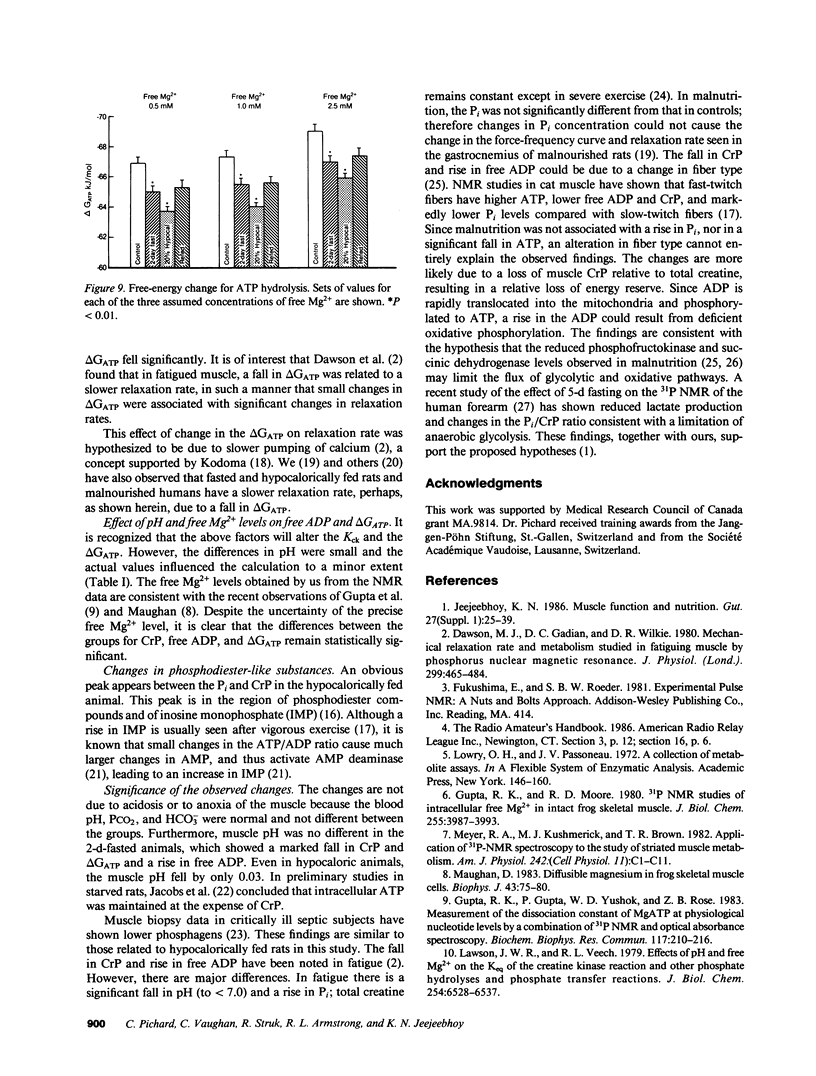
31P nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in vivo and fluorometry were used to measure muscle ATP, total creatine, pH, and Mg2+ in vivo; and to calculate creatine phosphate (CrP), the ratios of CrP/inorganic phosphate (Pi), CrP/ATP, free ADP levels, and the free-energy change in ATP hydrolysis so nutritional effects could be ascertained. These parameters were determined in vivo in resting control, 2-d-fasted, and hypocalorically fed rats and in animals similarly hypocalorically fed and then refed. The ATP, Pi, and intracellular Mg2+ levels were comparable in the four groups. When the fasted and underfed animals were compared with the control and refed animals, there were falls in the ratios of CrP/Pi and CrP/ATP, in the calculated CrP, and the free-energy change of ATP hydrolysis, but a rise in the calculated free ADP. In the hypocaloric group, intracellular pH fell significantly and a large peak was noted in the phosphodiester region. The data are consistent with the hypothesis that ATP levels are maintained at the cost of CrP, suggesting that ATP production is disturbed by aerobic and anaerobic mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan S. T., McLaughlin S. J., Ponting G. A., Biglin J., Dudley H. A. Muscle power after glucose-potassium loading in undernourished patients. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Oct 25;293(6554):1055–1056. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6554.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church J. M., Choong B. Y., Hill G. L. Abnormal muscle fructose bisphosphatase activity in malnourished cancer patients. Cancer. 1986 Dec 1;58(11):2448–2452. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19861201)58:11<2448::aid-cncr2820581116>3.0.co;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson M. J., Gadian D. G., Wilkie D. R. Mechanical relaxation rate and metabolism studied in fatiguing muscle by phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:465–484. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. K., Gupta P., Yushok W. D., Rose Z. B. Measurement of the dissociation constant of MgATP at physiological nucleotide levels by a combination of 31P NMR and optical absorbance spectroscopy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 30;117(1):210–216. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91562-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. K., Moore R. D. 31P NMR studies of intracellular free Mg2+ in intact frog skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3987–3993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeejeebhoy K. N. Muscle function and nutrition. Gut. 1986 Nov;27 (Suppl 1):25–39. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.suppl_1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T. Thermodynamic analysis of muscle ATPase mechanisms. Physiol Rev. 1985 Apr;65(2):467–551. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1985.65.2.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson J. W., Veech R. L. Effects of pH and free Mg2+ on the Keq of the creatine kinase reaction and other phosphate hydrolyses and phosphate transfer reactions. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6528–6537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liaw K. Y., Askanazi J., Michelson C. B., Kantrowitz L. R., Fürst P., Kinney J. M. Effect of injury and sepsis on high-energy phosphates in muscle and red cells. J Trauma. 1980 Sep;20(9):755–759. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198009000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunt J. A., Allen P. S., Brauer M., Swinamer D., Treiber E. O., Belcastro A., Eccles R., King E. G. An evaluation of the effect of fasting on the exercise-induced changes in pH and Pi/PCr from skeletal muscle. Magn Reson Med. 1986 Dec;3(6):946–952. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910030616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maughan D. Diffusible magnesium in frog skeletal muscle cells. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84325-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. A., Brown T. R., Kushmerick M. J. Phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance of fast- and slow-twitch muscle. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):C279–C287. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.3.C279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. M., Atwood H. L., Whittaker J. S., Itakura T., Walker P. M., Mickle D. A., Jeejeebhoy K. N. The effect of fasting and hypocaloric diets on the functional and metabolic characteristics of rat gastrocnemius muscle. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 Aug;67(2):185–194. doi: 10.1042/cs0670185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. M., Walker P. M., Leiter L. A., Sima A. A., Tanner W. K., Mickle D. A., Whitwell J., Marliss E. B., Jeejeebhoy K. N. Metabolic and structural changes in skeletal muscle during hypocaloric dieting. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984 Apr;39(4):503–513. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/39.4.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahlin K., Palmskog G., Hultman E. Adenine nucleotide and IMP contents of the quadriceps muscle in man after exercise. Pflugers Arch. 1978 May 18;374(2):193–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00581301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoubridge E. A., Bland J. L., Radda G. K. Regulation of creatine kinase during steady-state isometric twitch contraction in rat skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 14;805(1):72–78. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veech R. L., Lawson J. W., Cornell N. W., Krebs H. A. Cytosolic phosphorylation potential. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6538–6547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. R., Gadian D. G. Tissue metabolism studied in vivo by nuclear magnetic resonance. Q J Exp Physiol. 1986 Jul;71(3):335–360. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1986.sp002994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. T., Pieper G. M., Salhany J. M., Eliot R. S. Measurement of free magnesium in perfused and ischemic arrested heart muscle. A quantitative phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance and multiequilibria analysis. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 22;20(26):7399–7403. doi: 10.1021/bi00529a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


