Abstract
The HLA class I molecules identified serologically as HLA-B27 are highly associated with ankylosing spondylitis and related human disorders. All known HLA-B27 amino acid sequences contain a cysteine residue at position 67; no other published HLA class I sequence contains a cysteine within the hypervariable region of the alpha 1 domain, which extends from amino acid residues 63-84. To investigate the role of this cysteine residue in the antigenic structure of HLA-B27, we isolated a genomic clone encoding a molecule of the HLA-B27.1 subtype and performed oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis to convert the cysteine at position 67 to a tyrosine. When transfected into mouse L cells, both the wild-type and Cys67----Tyr67 mutant B27 genes directed the synthesis and surface expression of molecules reactive with the monomorphic anti-HLA class I antibody W6/32. However, only the L cells transfected with the wild-type B27 gene reacted with the anti-B27 antibody ME1; L cells transfected with the mutant B27 were completely unreactive with this antibody. Experiments with hybrid exons created from the HLA-B27 and HLA-A2 genes yielded results consistent with the mapping of the ME1 epitope to the B27 alpha 1 domain. A second anti-B27 antibody, GS145.2, also showed markedly reduced binding to the Cys67----Tyr67 mutant. These studies document the importance of the unique Cys67 residue in the antigenic structure of HLA-B27.
Full text
PDF

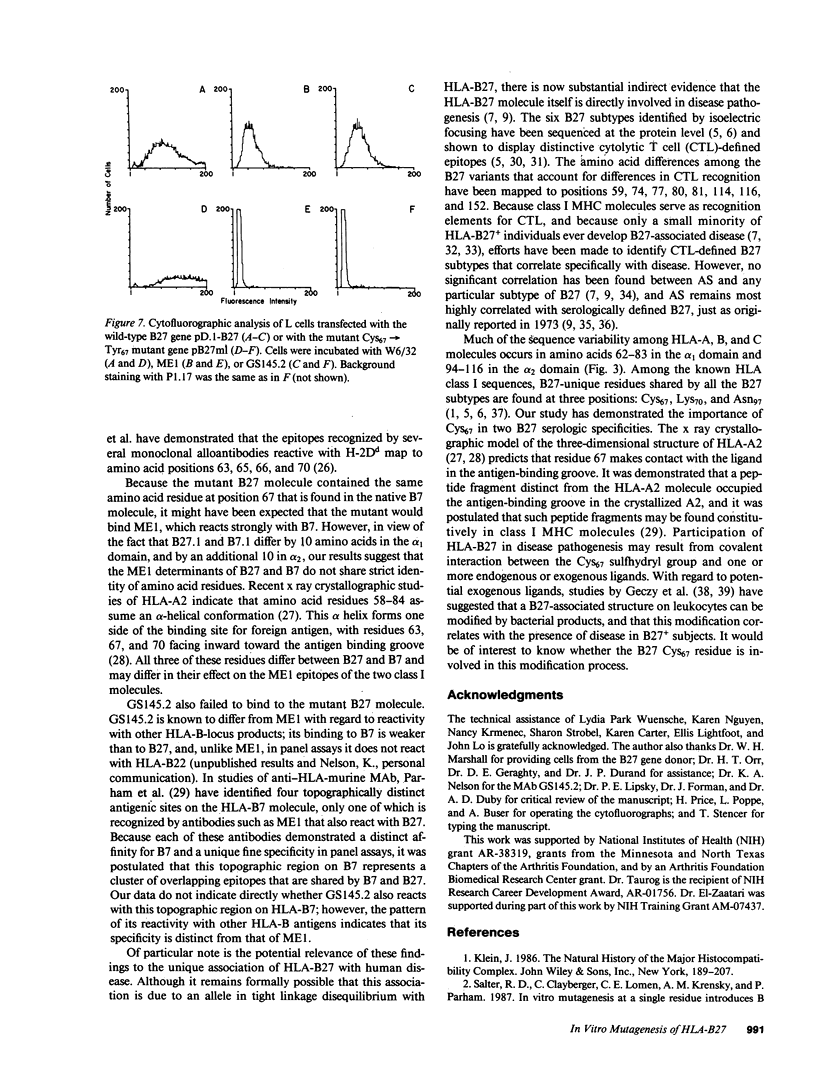

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aparicio P., Rojo S., Jaraquemada D., López de Castro J. A. Fine specificity of HLA-B27 cellular allorecognition. HLA-B27f is a functional variant distinguishable by cytolytic T cell clones. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):837–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio P., Vega M. A., López de Castro J. A. One allogeneic cytolytic T lymphocyte clone distinguishes three different HLA-B27 subtypes: identification of amino acid residues influencing the specificity and avidity of recognition. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3074–3081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):506–512. doi: 10.1038/329506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):512–518. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breur-Vriesendorp B. S., Dekker-Saeys A. J., Ivanyi P. Distribution of HLA-B27 subtypes in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: the disease is associated with a common determinant of the various B27 molecules. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 May;46(5):353–356. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.5.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
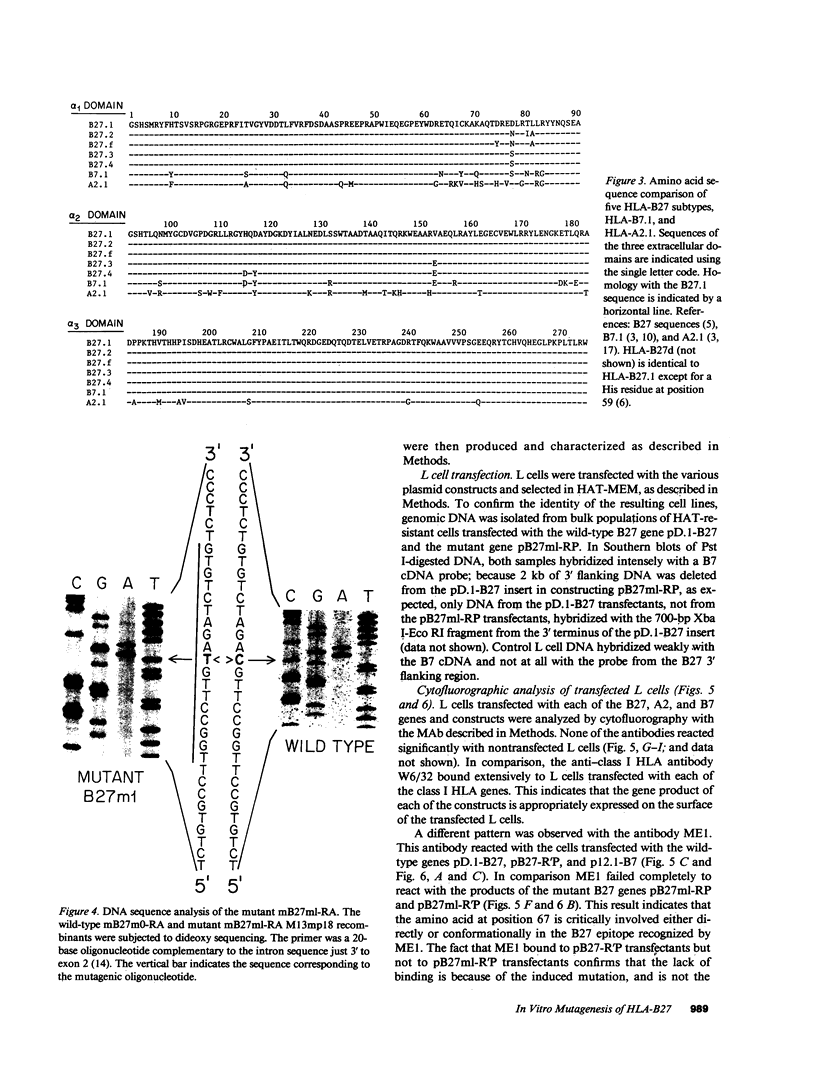
- Brewerton D. A., Hart F. D., Nicholls A., Caffrey M., James D. C., Sturrock R. D. Ankylosing spondylitis and HL-A 27. Lancet. 1973 Apr 28;1(7809):904–907. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen F. T., Hawkins B. R., Dawkins R. L., Owen E. T., Potter R. M. The prevalence of ankylosing spondylitis among B27 positive normal individuals--a reassessment. J Rheumatol. 1979 Nov-Dec;6(6):713–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan E. P., Jelachich M. L., Biddison W. E., Coligan J. E. DNA sequence of HLA-A11: remarkable homology with HLA-A3 allows identification of residues involved in epitopes recognized by antibodies and T cells. Immunogenetics. 1987;25(4):241–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00404694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan E. P., Jordan B. R., Coligan J. E. Molecular cloning and DNA sequence analysis of genes encoding cytotoxic T lymphocyte-defined HLA-A3 subtypes: the E1 subtype. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2835–2841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis S. A., Taylor C., McMichael A. Recognition of HLA-B27 and related antigen by a monoclonal antibody. Hum Immunol. 1982 Aug;5(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(82)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumaki Y., Collins F., Kole R., Stoeckert C. J., Jr, Jagadeeswaran P., Duncan C. H., Weissman S. M., Jagadeeswaran P., Pan J., Forget B. G. Sequences of human repetitive DNA, non-alpha-globin genes, and major histocompatibility locus genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1079–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geczy A. F., McGuigan L. E., Sullivan J. S., Edmonds J. P. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes against disease-associated determinant(s) in ankylosing spondylitis. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):932–937. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geczy A. F., van Leeuwen A., van Rood J. J., Ivanyi P., Breur B. S., Cats A. Blind confirmation in Leiden of Geczy factor on the cells of Dutch patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Hum Immunol. 1986 Nov;17(3):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90275-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güssow D., Rein R. S., Meijer I., de Hoog W., Seemann G. H., Hochstenbach F. M., Ploegh H. L. Isolation, expression, and the primary structure of HLA-Cw1 and HLA-Cw2 genes: evolutionary aspects. Immunogenetics. 1987;25(5):313–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00404424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeller D., Lieberman R., Miyazaki J., Appella E., Ozato K., Mann D. W., Forman J. Introduction of H-2Dd determinants into the H-2Ld antigen by site-directed mutagenesis. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):744–760. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Orr H. T. Cloning and complete sequence of an HLA-A2 gene: analysis of two HLA-A alleles at the nucleotide level. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2727–2733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Sidwell B., DeMars R., Orr H. T. Isolation of HLA locus-specific DNA probes from the 3'-untranslated region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5175–5178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layet C., Kahn-Perles B., Pontarotti P., Ferrier P., Sire J., Lemonnier F. A. Creation of an HLA-A2/HLA-Aw69 alloantigenic determinant on an HLA-A3 molecule by site-directed mutagenesis. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2197–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Look A. T., Peiper S. C., Rebentisch M. B., Ashmun R. A., Roussel M. F., Rettenmier C. W., Sherr C. J. Transfer and expression of the gene encoding a human myeloid membrane antigen (gp150). J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):569–579. doi: 10.1172/JCI111733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyachi Y., Wee S. L., Chen L. K., Grumet F. C., Bowman R. J., Taurog J. D. A cytolytic human T lymphocyte clone differentially recognizing HLA-B27 subtypes. Hum Immunol. 1984 Aug;10(4):237–249. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(84)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Androlewicz M. J., Brodsky F. M., Holmes N. J., Ways J. P. Monoclonal antibodies: purification, fragmentation and application to structural and functional studies of class I MHC antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Sep 17;53(2):133–173. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Antonelli P., Herzenberg L. A., Kipps T. J., Fuller A., Ward F. E. Further studies on the epitopes of HLA-B7 defined by murine monoclonal antibodies. Hum Immunol. 1986 Jan;15(1):44–67. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90316-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo S., Aparicio P., Choo S. Y., Hansen J. A., López de Castro J. A. Structural analysis of an HLA-B27 population variant, B27f. Multiple patterns of amino acid changes within a single polypeptide segment generate polymorphism in HLA-B27. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):831–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo S., Aparicio P., Hansen J. A., Choo S. Y., López de Castro J. A. Structural analysis of an HLA-B27 functional variant, B27d, detected in American blacks. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3396–3401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter R. D., Clayberger C., Lomen C. E., Krensky A. M., Parham P. In vitro mutagenesis at a single residue introduces B and T cell epitopes into a class I HLA molecule. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):283–288. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlosstein L., Terasaki P. I., Bluestone R., Pearson C. M. High association of an HL-A antigen, W27, with ankylosing spondylitis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Apr 5;288(14):704–706. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197304052881403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann G. H., Rein R. S., Brown C. S., Ploegh H. L. Gene conversion-like mechanisms may generate polymorphism in human class I genes. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):547–552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04245.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodoyer R., Kahn-Perles B., Strachan T., Sire J., Santoni M. J., Layet C., Ferrier P., Jordan B. R., Lemonnier F. A. Transfection of murine LMTK- cells with purified HLA class I genes. VII. Association of allele- and locus-specific serological reactivities with respectively the first and second domains of the HLA-B7 molecule. Immunogenetics. 1986;23(4):246–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00373019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere K., Sidwell B., Leach R., Ward F. E., Taurog J. D., Orr H. T. Use of DNA probes from the 5' flanking region of the HLA-B gene to examine polymorphism at the HLA-B locus. Hum Immunol. 1986 Jun;16(2):137–147. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Kuon W., Dörner C., Lang M., Riethmüller G. Organization, sequence and expression of the HLA-B27 gene: a molecular approach to analyze HLA and disease associations. Immunobiology. 1985 Dec;170(5):367–380. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(85)80061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):479–488. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Linden S. M., Valkenburg H. A., de Jongh B. M., Cats A. The risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis in HLA-B27 positive individuals. A comparison of relatives of spondylitis patients with the general population. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Mar;27(3):241–249. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]