Abstract
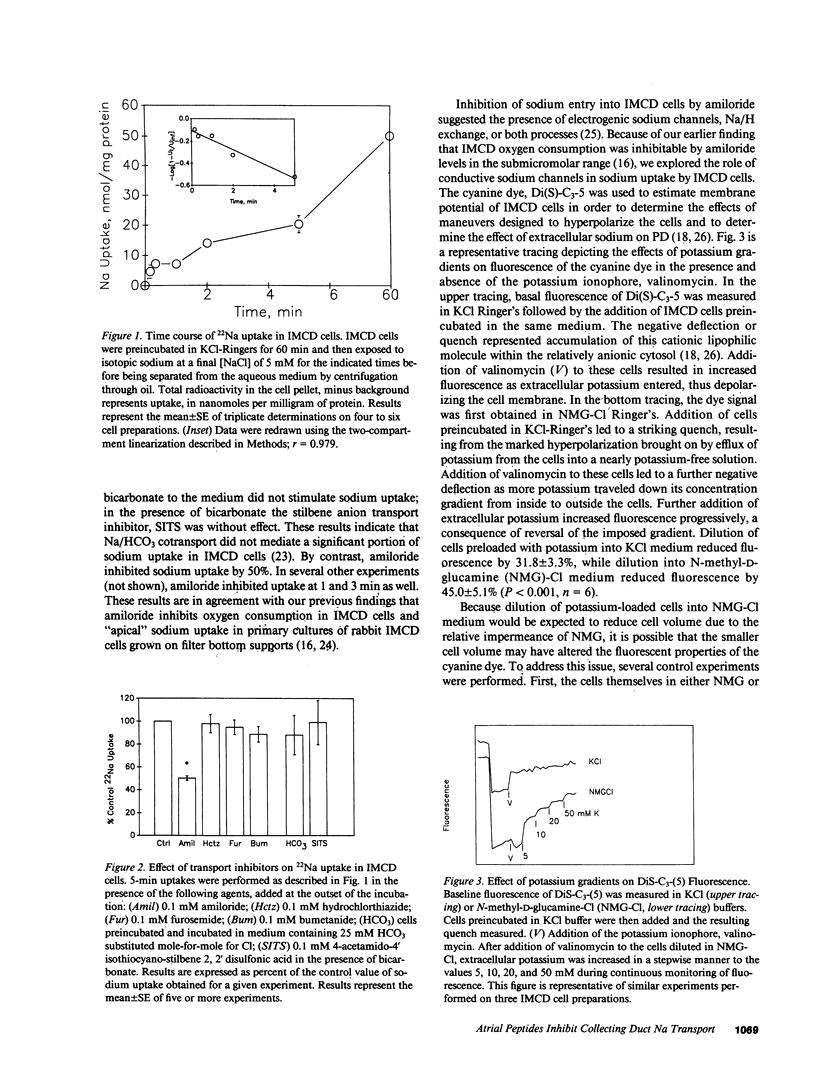
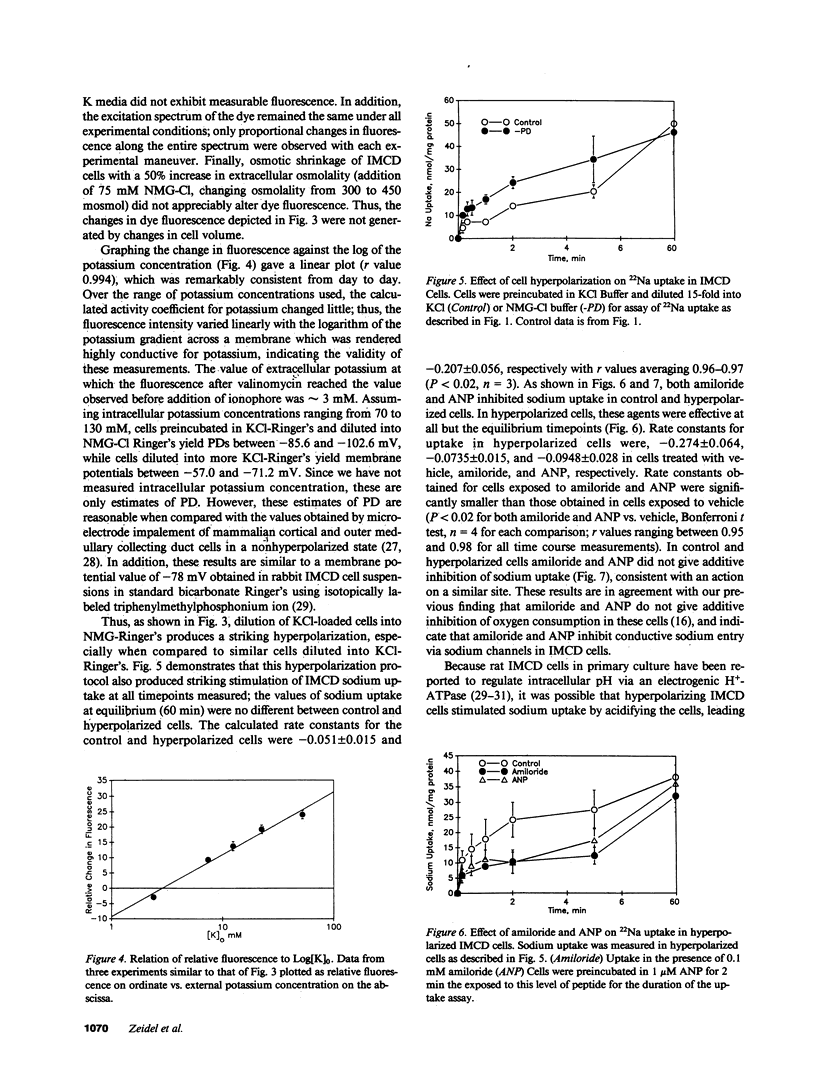
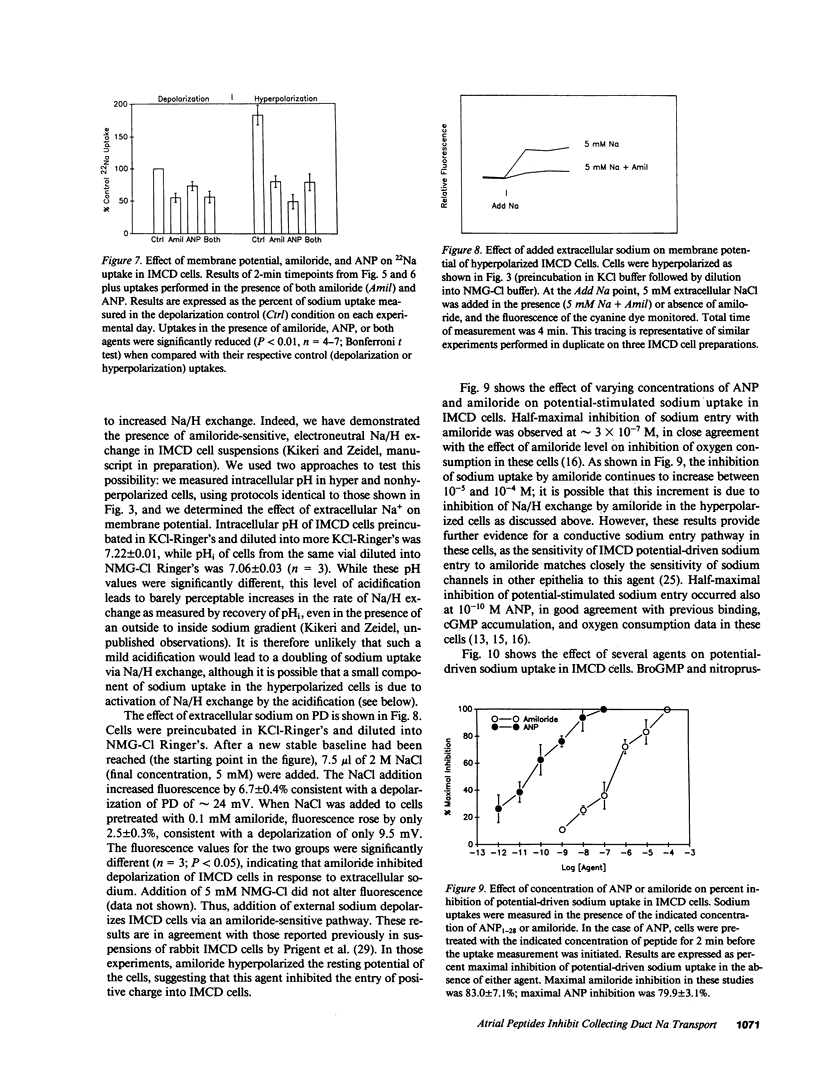
The inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD) effects net sodium reabsorption under the control of volume regulatory hormones, including atrial natriuretic peptides (ANP). These studies examined the mechanisms of sodium transport and its regulation by ANP in fresh suspensions of IMCD cells. Sodium uptake was inhibited by amiloride but insensitive to furosemide, bu-metanide, and hydrochlorthiazide. These results are consistent with uptake mediated by a sodium channel or Na+/H+ exchange. To determine the role of sodium channels, cells were hyperpolarized by preincubation in high potassium medium followed by dilution into potassium-free medium. Membrane potential measurements using the cyanine dye, Di(S)-C3-5 verified a striking hyperpolarization of IMCD cells using this protocol. Hyperpolarization increased the apparent initial rate of sodium uptake fourfold. Amiloride and ANP inhibited potential-stimulated sodium uptake 73% and 65%, respectively; the two agents together were not additive. Addition of 5 mM sodium to hyperpolarized cells resulted in a significant amiloride-sensitive depolarization. Half-maximal inhibition of potential-driven sodium uptake occurred at 3 X 10(-7) M amiloride, and 5 X 10(-11) M ANP. We conclude that sodium enters IMCD cells via a conductive, amiloride-sensitive sodium channel, which is regulated by ANP. ANP inhibition of luminal sodium entry in the IMCD appears to contribute to the marked natriuretic effect of this hormone in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benos D. J. Amiloride: a molecular probe of sodium transport in tissues and cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Mar;242(3):C131–C145. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.3.C131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantiello H. F., Ausiello D. A. Atrial natriuretic factor and cGMP inhibit amiloride-sensitive Na+ transport in the cultured renal epithelial cell line, LLC-PK1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):852–860. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80498-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cupples W. A., Sonnenberg H. Load dependency of sodium chloride reabsorption by medullary collecting duct in rat. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 2):F642–F648. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.4.F642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison D. H., Velázquez H., Wright F. S. Thiazide-sensitive sodium chloride cotransport in early distal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 2):F546–F554. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.3.F546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goligorsky M. S., Duncan R. L., Westbrook S., Reinach P., Hruska K. A. Demonstration of a direct effect of atrial natriuretic factor on epithelium: study in cultured pig kidney cells. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1987;13(1):51–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamison R. L., Sonnenberg H., Stein J. H. Questions and replies: role of the collecting tubule in fluid, sodium, and potassium balance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Oct;237(4):F247–F261. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.237.4.F247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch T. J., Matthes H., Keller S. K., Wiederholt M. Electrical properties of sodium bicarbonate symport in kidney epithelial cells (BSC-1). Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 2):F954–F968. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.6.F954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppen B. M. Conductive properties of the rabbit outer medullary collecting duct: inner stripe. Am J Physiol. 1985 Apr;248(4 Pt 2):F500–F506. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.4.F500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez R. E., Dunn B. R., Troy J. L., Brenner B. M. Modulation of the natriuretic response to atrial natriuretic peptide by alterations in peritubular Starling forces in the rat. Circ Res. 1986 Dec;59(6):605–611. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.6.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoguchi H., Knepper M. A., Manganiello V. C. Effects of atrial natriuretic factor on cyclic guanosine monophosphate and cyclic adenosine monophosphate accumulation in microdissected nephron segments from rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):500–507. doi: 10.1172/JCI112840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Grady S. M., Palfrey H. C., Field M. Characteristics and functions of Na-K-Cl cotransport in epithelial tissues. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 1):C177–C192. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.2.C177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prigent A., Bichara M., Paillard M. Hydrogen transport in papillary collecting duct of rabbit kidney. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):C241–C246. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.3.C241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Montecucco C., Hesketh T. R., Tsien R. Y. Lymphocyte membrane potential assessed with fluorescent probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;595(1):15–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom S. C., Weinman E. J., O'Neil R. G. Microelectrode assessment of chloride-conductive properties of cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 2):F291–F302. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.2.F291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. C. The use of fluorescent dyes to measure membrane potentials: a response. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Aug;112(2):302–305. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041120222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff S. P., Mandel L. J. Active ion transport in the renal proximal tubule. I. Transport and metabolic studies. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Oct;84(4):601–622. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg H., Cupples W. A., de Bold A. J., Veress A. T. Intrarenal localization of the natriuretic effect of cardiac atrial extract. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;60(9):1149–1152. doi: 10.1139/y82-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg H., Honrath U., Chong C. K., Wilson D. R. Atrial natriuretic factor inhibits sodium transport in medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 2):F963–F966. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.6.F963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B. Ion transport by the cortical and outer medullary collecting tubule. Kidney Int. 1982 Nov;22(5):473–484. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K. J., Papavassiliou F. Sodium reabsorption in the papillary collecting duct of rats. Effect of adrenalectomy, low Na+ diet, acetazolamide, HCO-3-free solutions and of amiloride. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Feb 14;379(1):49–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00622904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner A. Optical probes of membrane potential. J Membr Biol. 1976 Jun 30;27(4):317–334. doi: 10.1007/BF01869143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. R., Honrath U., Sonnenberg H. Furosemide action on collecting ducts: effect of prostaglandin synthesis inhibition. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jun;244(6):F666–F673. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.6.F666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. R., Honrath U., Sonnenberg H. Thiazide diuretic effect on medullary collecting duct function in the rat. Kidney Int. 1983 May;23(5):711–716. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Seifter J. L., Lear S., Brenner B. M., Silva P. Atrial peptides inhibit oxygen consumption in kidney medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 2):F379–F383. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.2.F379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Silva P., Brenner B. M., Seifter J. L. cGMP mediates effects of atrial peptides on medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 2):F551–F559. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.3.F551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Silva P., Seifter J. L. Intracellular pH regulation and proton transport by rabbit renal medullary collecting duct cells. Role of plasma membrane proton adenosine triphosphatase. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):113–120. doi: 10.1172/JCI112264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Silva P., Seifter J. L. Intracellular pH regulation in rabbit renal medullary collecting duct cells. Role of chloride-bicarbonate exchange. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1682–1688. doi: 10.1172/JCI112486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


