Abstract
A carboxypeptidase activity was recently identified in highly purified human lung mast cells and dispersed mast cells from skin. Using affinity chromatography with potato-tuber carboxypeptidase inhibitor as ligand, mast cell carboxypeptidase was purified to homogeneity from whole skin extracts. The purified enzyme yielded a single staining band of approximately 34,500 D on SDS-PAGE. Carboxypeptidase enzyme content estimated by determination of specific activity, was 0.5, 5, and 16 micrograms/10(6) mast cells from neonatal foreskin, adult facial skin, and adult foreskin, respectively. Human mast cell carboxypeptidase resembled bovine carboxypeptidase A with respect to hydrolysis of synthetic dipeptides and angiotensin I, but was distinguished from carboxypeptidase A in its inability to hydrolyze des-Arg9 bradykinin. The amino acid composition of human mast cell carboxypeptidase was similar to the composition of rat mast cell carboxypeptidase. The amino-terminal amino acid sequence of mast cell carboxypeptidase demonstrated 65% positional identity with human pancreatic carboxypeptidase B, but only 19% with human carboxypeptidase A. Thus, human mast cell carboxypeptidase is a novel member of the protein family of zinc-containing carboxypeptidases, in that it is functionally similar but not identical to bovine carboxypeptidase A, but has structural similarity to bovine and human pancreatic carboxypeptidase B.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
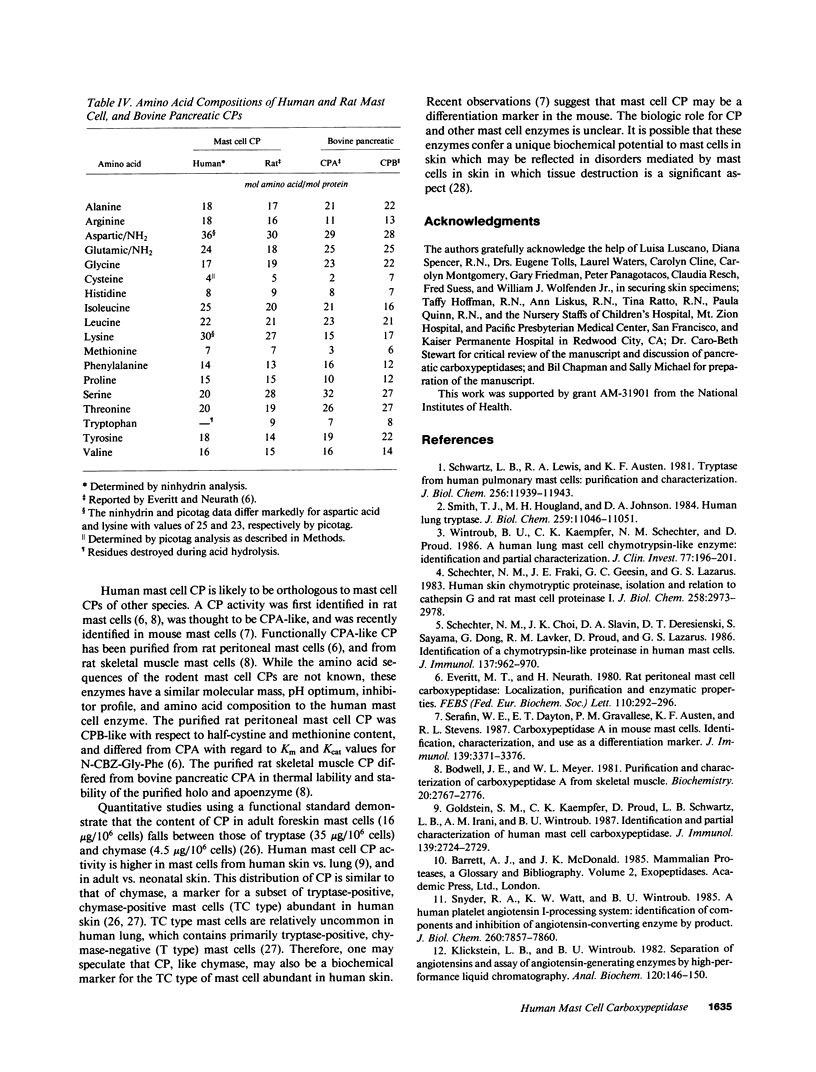
- Bodwell J. E., Meyer W. L. Purification and characterization of carboxypeptidase A from rat skeletal muscle. Biochemistry. 1981 May 12;20(10):2767–2777. doi: 10.1021/bi00513a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw R. A. The amino acid sequence of bovine carboxypeptidase A. 3. Biochemistry. 1969 Sep;8(9):3871–3877. doi: 10.1021/bi00837a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everitt M. T., Neurath H. Rat peritoneal mast cell carboxypeptidase: localization, purification, and enzymatic properties. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 11;110(2):292–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardell S. J., Craik C. S., Clauser E., Goldsmith E. J., Stewart C. B., Graf M., Rutter W. J. A novel rat carboxypeptidase, CPA2: characterization, molecular cloning, and evolutionary implications on substrate specificity in the carboxypeptidase gene family. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17828–17836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S. M., Kaempfer C. E., Proud D., Schwartz L. B., Irani A. M., Wintroub B. U. Detection and partial characterization of a human mast cell carboxypeptidase. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2724–2729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson R. L., Meredith S. C. Amino acid analysis by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography: precolumn derivatization with phenylisothiocyanate. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hewick R. M., Dreyer W. J., Hood L. E. High-sensitivity sequencing with a gas-phase sequenator. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:399–413. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani A. A., Schechter N. M., Craig S. S., DeBlois G., Schwartz L. B. Two types of human mast cells that have distinct neutral protease compositions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4464–4468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Sheikh I., Frendscho M. H. Assessment of histamine release and kinin formation in man: identification of kinin degradation products and characterization of a lymphocyte-dependent histamine releasing factor. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;77(1-2):64–68. doi: 10.1159/000233754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klickstein L. B., Wintroub B. U. Separation of angiotensins and assay of angiotensin-generating enzymes by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 Feb;120(1):146–150. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90329-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence I. D., Warner J. A., Cohan V. L., Hubbard W. C., Kagey-Sobotka A., Lichtenstein L. M. Purification and characterization of human skin mast cells. Evidence for human mast cell heterogeneity. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3062–3069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinkovic D. V. N-terminal amino acid sequences of human carboxypeptidases A, B1, and B2. Biochem Med. 1979 Aug;22(1):11–26. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(79)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter N. M., Choi J. K., Slavin D. A., Deresienski D. T., Sayama S., Dong G., Lavker R. M., Proud D., Lazarus G. S. Identification of a chymotrypsin-like proteinase in human mast cells. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):962–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter N. M., Fräki J. E., Geesin J. C., Lazarus G. S. Human skin chymotryptic proteinase. Isolation and relation to cathepsin g and rat mast cell proteinase I. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2973–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Irani A. M., Roller K., Castells M. C., Schechter N. M. Quantitation of histamine, tryptase, and chymase in dispersed human T and TC mast cells. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2611–2615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Tryptase from human pulmonary mast cells. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11939–11943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Hougland M. W., Johnson D. A. Human lung tryptase. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):11046–11051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder R. A., Watt K. W., Wintroub B. U. A human platelet angiotensin I-processing system. Identification of components and inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme by product. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7857–7860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Neurath H. Amino-acid sequence of bovine carboxypeptidase B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1666–1670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTERSBERGER E., COX D. J., NEURATH H. Bovine pancreatic procarboxypeptidase B. I. Isolation, properties, and activation. Biochemistry. 1962 Nov;1:1069–1078. doi: 10.1021/bi00912a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintroub B. U., Kaempfer C. E., Schechter N. M., Proud D. A human lung mast cell chymotrypsin-like enzyme. Identification and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):196–201. doi: 10.1172/JCI112276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintroub B. U., Klickstein L. B., Kaempfer C. E., Austen K. F. A human neutrophil-dependent pathway for generation of angiotensin II: purification and physicochemical characterization of the plasma protein substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintroub B. U., Mihm M. C., Jr, Goetzl E. J., Soter N. A., Austen K. F. Morphologic and functional evidence for release of mast-cell products in bullous pemphigoid. N Engl J Med. 1978 Feb 23;298(8):417–421. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197802232980803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]