Abstract
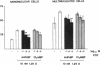
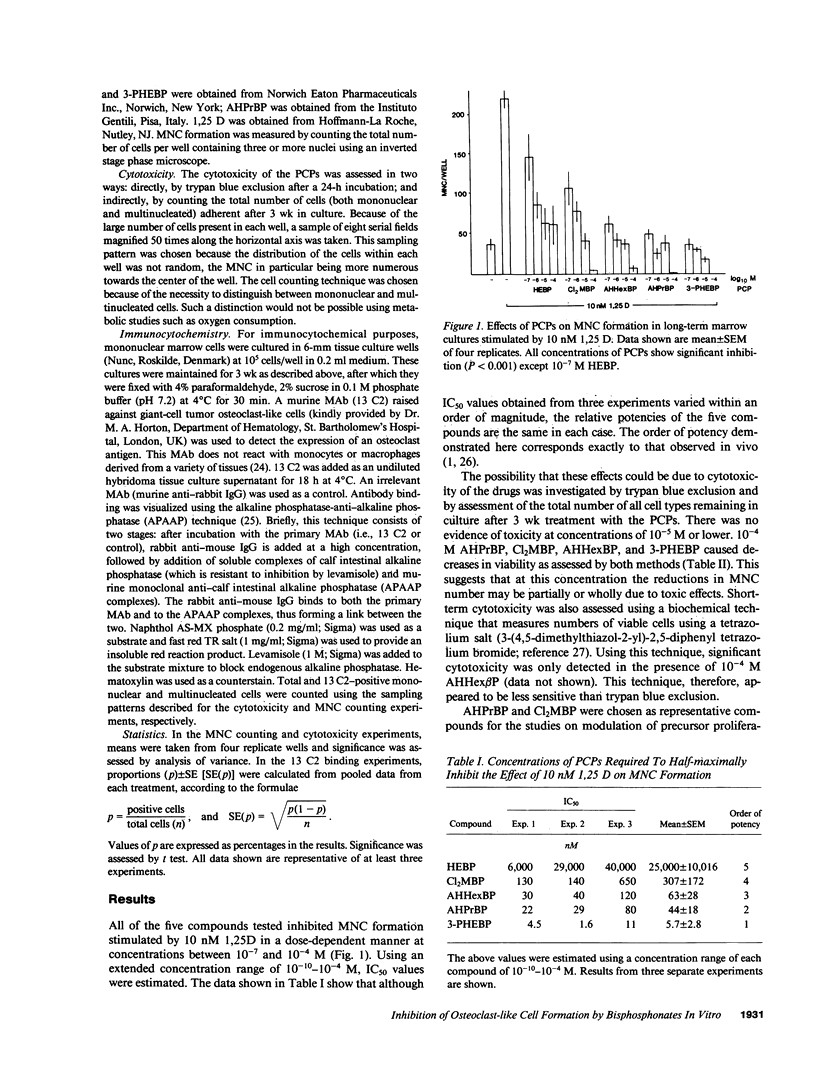
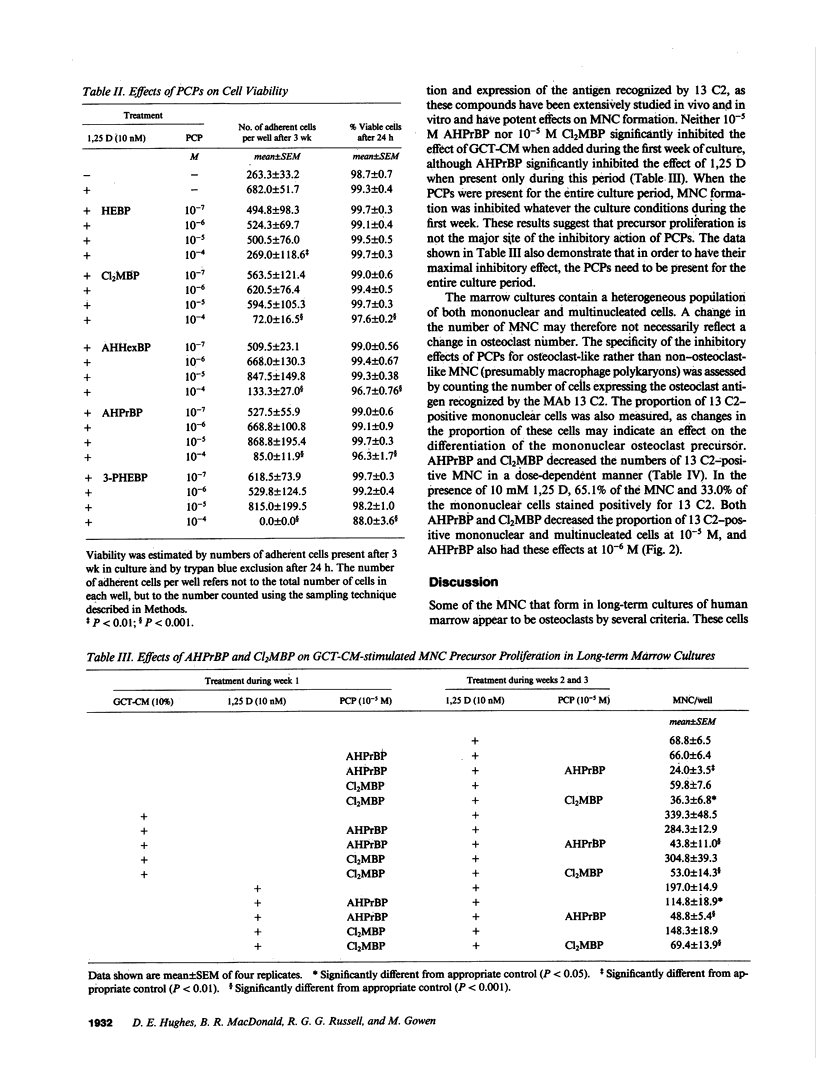
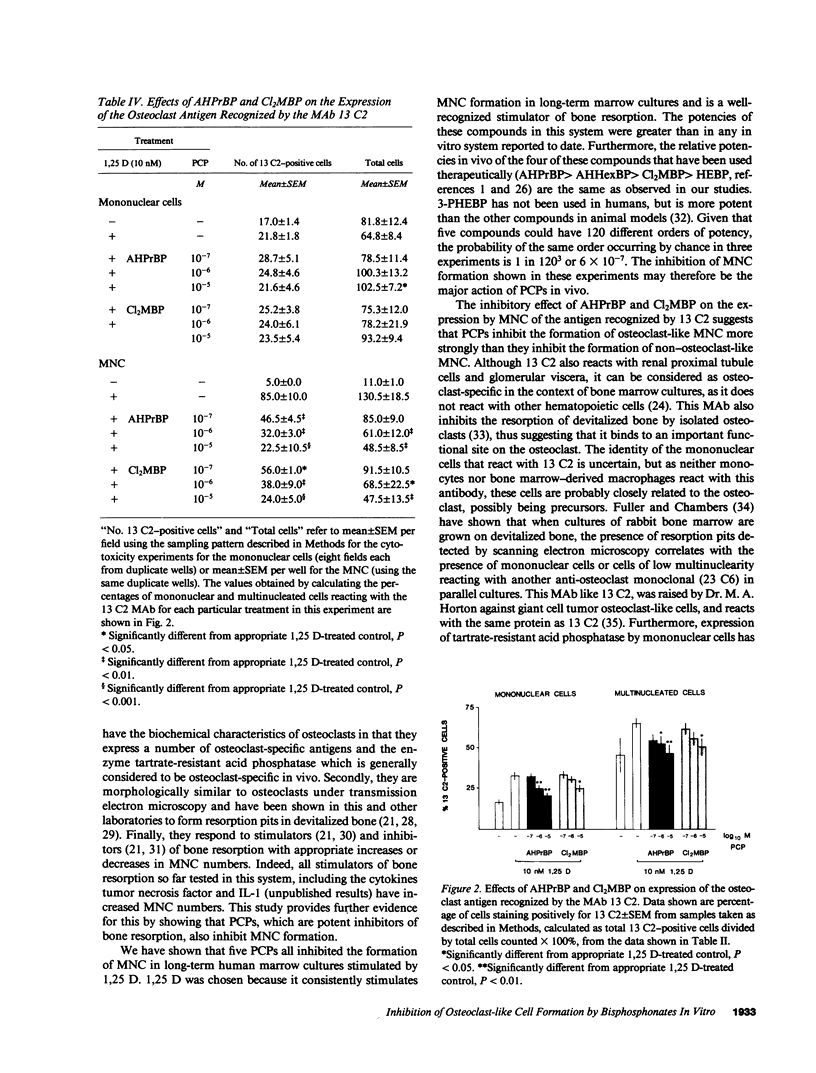
Bisphosphonates inhibit bone resorption in vivo and in vitro by unknown mechanisms. The effect of bisphosphonates on the formation of osteoclasts from their mononuclear hematopoietic precursors was investigated using human long-term marrow cultures in which multinucleated cells form that express most of the known features of the osteoclast phenotype (e.g., bone resorption, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase, calcitonin responsiveness, and reactivity with specific MAbs). The five bisphosphonates that were tested strongly inhibited 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-stimulated formation of these cells with the same relative potencies as they inhibit bone resorption in vivo. Two representative compounds (3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene-1,1-bisphosphonate and dichloromethylene bisphosphonate) failed to inhibit the proliferation of precursors of the osteoclast-like cells. However, these compounds decreased the proportion of mononuclear and multinucleated cells expressing an osteoclast antigen, thus suggesting a degree of specificity for cells of the osteoclast lineage. We conclude that bisphosphonates are potent inhibitors of osteoclast-like cell formation in long-term human marrow cultures, and that this may be related to their ability to inhibit bone resorption in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman R. D., Johnston C. C., Khairi M. R., Wellman H., Serafini A. N., Sankey R. R. Influence of disodium etidronate on clinical and laboratory manifestations of Paget's disease of bone (osteitis deformans). N Engl J Med. 1973 Dec 27;289(26):1379–1384. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197312272892601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ash P., Loutit J. F., Townsend K. M. Osteoclasts derived from haematopoietic stem cells. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):669–670. doi: 10.1038/283669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron R., Neff L., Tran Van P., Nefussi J. R., Vignery A. Kinetic and cytochemical identification of osteoclast precursors and their differentiation into multinucleated osteoclasts. Am J Pathol. 1986 Feb;122(2):363–378. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonekamp P. M., Löwik C. W., van der Wee-Pals L. J., van Wijk-van Lennep M. L., Bijvoet O. L. Enhancement of the inhibitory action of APD on the transformation of osteoclast precursors into resorbing cells after dimethylation of the amino group. Bone Miner. 1987 Feb;2(1):29–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonekamp P. M., van der Wee-Pals L. J., van Wijk-van Lennep M. M., Thesing C. W., Bijvoet O. L. Two modes of action of bisphosphonates on osteoclastic resorption of mineralized matrix. Bone Miner. 1986 Feb;1(1):27–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield R., Rosner W., Skinner J., McWhorter J., Resnick L., Feldman F., Kammerman S., Ryan K., Kunigonis M., Bohne W. Diphosphonate therapy of paget's disease of bone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Jan;44(1):96–106. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-1-96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecchini M. G., Felix R., Fleisch H., Cooper P. H. Effect of bisphosphonates on proliferation and viability of mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages. J Bone Miner Res. 1987 Apr;2(2):135–142. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650020209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Fuller K., Darby J. A., Pringle J. A., Horton M. A. Monoclonal antibodies against osteoclasts inhibit bone resorption in vitro. Bone Miner. 1986 Apr;1(2):127–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das S. K., Stanley E. R., Guilbert L. J., Forman L. W. Human colony-stimulating factor (CSF-1) radioimmunoassay: resolution of three subclasses of human colony-stimulating factors. Blood. 1981 Sep;58(3):630–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vries H. R., Bijvoet O. L. Results of prolonged treatment of Paget's disease of bone with disodium ethane-1-hydroxy-1, 1-diphosphonate (EHDP). Neth J Med. 1974;17(6):281–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Persio J. F., Brennan J. K., Lichtman M. A., Speiser B. L. Human cell lines that elaborate colon-stimulating activity for the marrow cells of man and other species. Blood. 1978 Mar;51(3):507–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas D. L., Duckworth T., Russell R. G., Kanis J. A., Preston C. J., Preston F. E., Prenton M. A., Woodhead J. S. Effect of dichloromethylene diphosphonate in Paget's disease of bone and in hypercalcaemia due to primary hyperparathyroidism or malignant disease. Lancet. 1980 May 17;1(8177):1043–1047. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91496-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHMAN D. A., HAY E. D. Origin of osteoclasts from mononuclear leucocytes in regenerating newt limbs. Anat Rec. 1962 Aug;143:329–337. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091430402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast D. K., Felix R., Dowse C., Neuman W. F., Fleisch H. The effects of diphosphonates on the growth and glycolysis of connective-tissue cells in culture. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):97–107. doi: 10.1042/bj1720097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frijlink W. B., Bijvoet O. L., te Velde J., Heynen G. Treatment of Paget's disease with (3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene)-1, 1-bisphosphonate (A.P.D.). Lancet. 1979 Apr 14;1(8120):799–803. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91318-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller K., Chambers T. J. Generation of osteoclasts in cultures of rabbit bone marrow and spleen cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Sep;132(3):441–452. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041320306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton M. A., Lewis D., McNulty K., Pringle J. A., Chambers T. J. Monoclonal antibodies to osteoclastomas (giant cell bone tumors): definition of osteoclast-specific cellular antigens. Cancer Res. 1985 Nov;45(11 Pt 2):5663–5669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A. J., Simmons D. J. Investigation of cell lineage in bone using a chimaera of chick and quial embryonic tissue. Nature. 1975 Nov 27;258(5533):325–327. doi: 10.1038/258325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khairi M. R., Altman R. D., DeRosa G. P., Zimmermann J., Schenk R. K., Johnston C. C. Sodium etidronate in the treatment of Paget's disease of bone. A study of long-term results. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Dec;87(6):656–663. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-6-656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald B. R., Mundy G. R., Clark S., Wang E. A., Kuehl T. J., Stanley E. R., Roodman G. D. Effects of human recombinant CSF-GM and highly purified CSF-1 on the formation of multinucleated cells with osteoclast characteristics in long-term bone marrow cultures. J Bone Miner Res. 1986 Apr;1(2):227–233. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650010210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald B. R., Takahashi N., McManus L. M., Holahan J., Mundy G. R., Roodman G. D. Formation of multinucleated cells that respond to osteotropic hormones in long term human bone marrow cultures. Endocrinology. 1987 Jun;120(6):2326–2333. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-6-2326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minaire P., Berard E., Meunier P. J., Edouard C., Goedert G., Pilonchery G. Effects of disodium dichloromethylene diphosphonate on bone loss in paraplegic patients. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):1086–1092. doi: 10.1172/JCI110331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya K., Yamada S., Felix R., Fleisch H. Effect of bisphosphonates on prostaglandin synthesis by rat bone cells and mouse calvaria in culture. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Oct;69(4):403–411. doi: 10.1042/cs0690403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival R. C., Paterson A. D., Yates A. J., Beard D. J., Douglas D. L., Neal F. E., Russell R. G., Kanis J. A. Treatment of malignant hypercalcaemia with clodronate. Br J Cancer. 1985 May;51(5):665–669. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston S. H., Gardner M. D., Dryburgh F. J., Jenkins A. S., Cowan R. A., Boyle I. T. Comparison of aminohydroxypropylidene diphosphonate, mithramycin, and corticosteroids/calcitonin in treatment of cancer-associated hypercalcaemia. Lancet. 1985 Oct 26;2(8461):907–910. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90848-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitsma P. H., Teitelbaum S. L., Bijvoet O. L., Kahn A. J. Differential action of the bisphosphonates (3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene)-1,1-bisphosphonate (APD) and disodium dichloromethylidene bisphosphonate (Cl2MDP) on rat macrophage-mediated bone resorption in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):927–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI110704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. G., Smith R., Preston C., Walton R. J., Woods C. G. Diphosphonates in Paget's disease. Lancet. 1974 May 11;1(7863):894–898. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90347-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleeboom H. P., Bijvoet O. L., van Oosterom A. T., Gleed J. H., O'Riordan J. L. Comparison of intravenous (3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene)-1, 1-bisphosphonate and volume repletion in tumour-induced hypercalcaemia. Lancet. 1983 Jul 30;2(8344):239–243. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson P. H., Stevenson J. R. Cytotoxic and migration inhibitory effects of bisphosphonates on macrophages. Calcif Tissue Int. 1986 Apr;38(4):227–233. doi: 10.1007/BF02556715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., MacDonald B. R., Hon J., Winkler M. E., Derynck R., Mundy G. R., Roodman G. D. Recombinant human transforming growth factor-alpha stimulates the formation of osteoclast-like cells in long-term human marrow cultures. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):894–898. doi: 10.1172/JCI112677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Mundy G. R., Roodman G. D. Recombinant human interferon-gamma inhibits formation of human osteoclast-like cells. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3544–3549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]