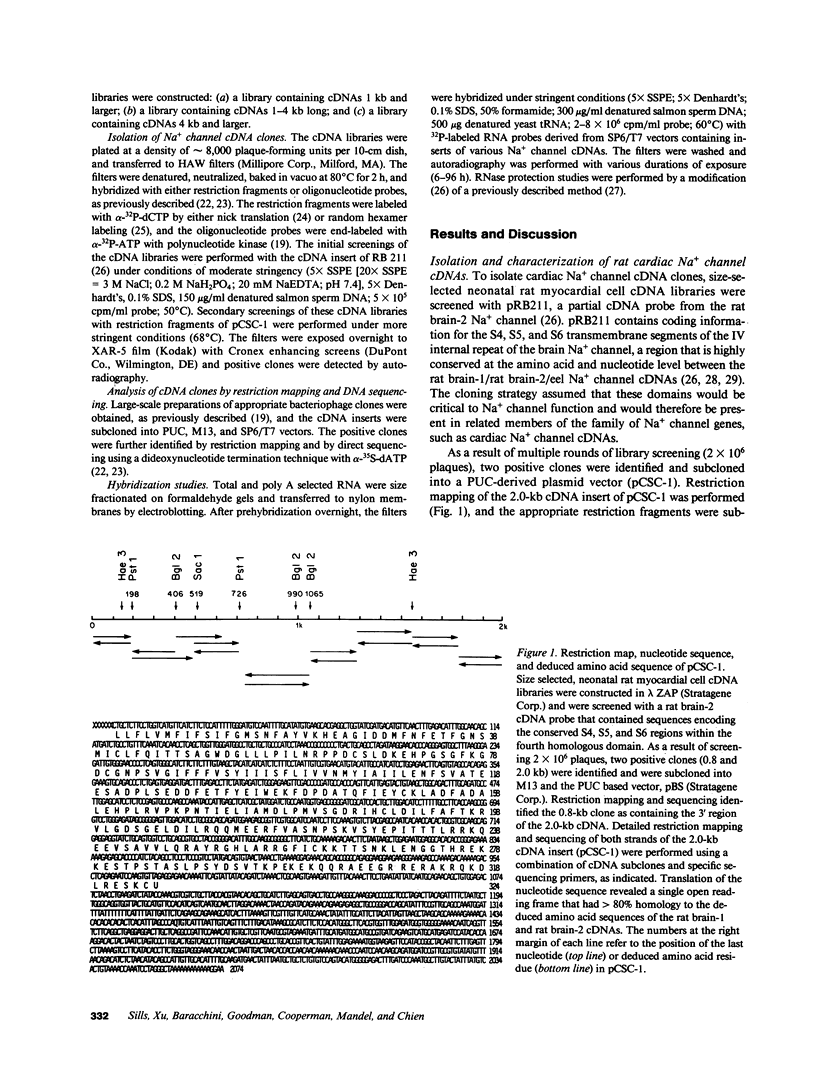
Abstract
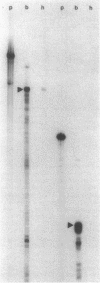
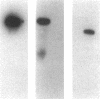
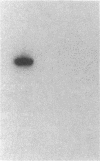
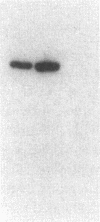
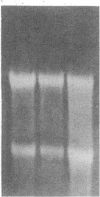
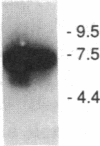
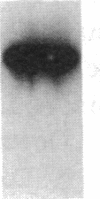
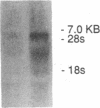
This study examined the diversity of Na+ channel gene expression in intact cardiac tissue and purified myocardial cells. The screening of neonatal rat myocardial cell cDNA libraries with a conserved rat brain Na+ channel cDNA probe, resulted in the isolation and characterization of a putative rat cardiac Na+ channel cDNA probe (pCSC-1). The deduced amino acid sequence of pCSC-1 displayed a striking degree of homology with the eel, rat brain-1, and rat brain-2 Na+ channel, thereby identifying pCSC-1 as a related member of the family of Na+ channel genes. Northern blot analysis revealed the expression of a 7-kb CSC-1 transcript in rat cardiac tissue and purified myocardial cells, but little or no detectable expression of CSC-1 in rat brain, skeletal muscle, denervated skeletal muscle, or liver. Using RNase protection and Northern blot hybridization with specific rat brain Na+ channel gene probes, expression of the rat brain-1 Na+ channel was observed in rat myocardium, but no detectable expression of the rat brain-2 gene was found. This study provides evidence for the expression of diverse Na+ channel mRNAs in rat myocardium and presents the initial characterization of a new, related member of the family of Na+ channel genes, which appears to be expressed in a cardiac-specific manner.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L. Probing the molecular structure of the voltage-dependent sodium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:455–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.002323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Lee K. S., Powell T. Sodium current in single rat heart muscle cells. J Physiol. 1981 Sep;318:479–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Molecular properties of voltage-sensitive sodium channels. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:953–985. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Armon M., Kloog Y., Henis Y. I., Sokolovsky M. Batrachotoxin changes the properties of the muscarinic receptor in rat brain and heart: possible interaction(s) between muscarinic receptors and sodium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3524–3527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooperman S. S., Grubman S. A., Barchi R. L., Goodman R. H., Mandel G. Modulation of sodium-channel mRNA levels in rat skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8721–8725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan T. M., Noble D., Noble S. J., Powell T., Twist V. W. An isoprenaline activated sodium-dependent inward current in ventricular myocytes. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):634–637. doi: 10.1038/328634a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin A. L., Snutch T., Lübbert H., Dowsett A., Marshall J., Auld V., Downey W., Fritz L. C., Lester H. A., Dunn R. Messenger RNA coding for only the alpha subunit of the rat brain Na channel is sufficient for expression of functional channels in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7503–7507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant A. O., Starmer C. F., Strauss H. C. Antiarrhythmic drug action. Blockade of the inward sodium current. Circ Res. 1984 Oct;55(4):427–439. doi: 10.1161/01.res.55.4.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo X. T., Uehara A., Ravindran A., Bryant S. H., Hall S., Moczydlowski E. Kinetic basis for insensitivity to tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin in sodium channels of canine heart and denervated rat skeletal muscle. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7546–7556. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. A., Xu Y. C., Chien K. R. Nucleotide sequence of full length cDNAs encoding rat cardiac myosin light chain-2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4722–4722. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar C. C., Cribbs L., Delaney P., Chien K. R., Siddiqui M. A. Heart myosin light chain 2 gene. Nucleotide sequence of full length cDNA and expression in normal and hypertensive rat. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2866–2872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. R., Henderson S. A., Reynolds R., Dunnmon P., Yuan D., Chien K. R. Alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation of cardiac gene transcription in neonatal rat myocardial cells. Effects on myosin light chain-2 gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7352–7358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. R., Henderson S. A., Reynolds R., Dunnmon P., Yuan D., Chien K. R. Alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation of cardiac gene transcription in neonatal rat myocardial cells. Effects on myosin light chain-2 gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7352–7358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubbe W. F., Opie L. H. Metabolic basis of increased vulnerability to fibrillation in myocardial ischaemia. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1987 Oct;19 (Suppl 5):1–3. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(87)80604-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel G., Cooperman S. S., Maue R. A., Goodman R. H., Brehm P. Selective induction of brain type II Na+ channels by nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):924–928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Ikeda T., Kayano T., Suzuki H., Takeshima H., Kurasaki M., Takahashi H., Numa S. Existence of distinct sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat brain. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):188–192. doi: 10.1038/320188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Shimizu S., Tanabe T., Takai T., Kayano T., Ikeda T., Takahashi H., Nakayama H., Kanaoka Y., Minamino N. Primary structure of Electrophorus electricus sodium channel deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):121–127. doi: 10.1038/312121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Ion channels in cardiac cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:473–484. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.002353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Miller J. C., Reynolds R., Willerson J. T., Buja L. M., Chien K. R. Inhibition of the release of arachidonic acid prevents the development of sarcolemmal membrane defects in cultured rat myocardial cells during adenosine triphosphate depletion. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1333–1338. doi: 10.1172/JCI113735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperelakis N., Shigenobu K. Changes in membrane properties of chick embryonic hearts during development. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Oct;60(4):430–453. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.4.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]