Abstract
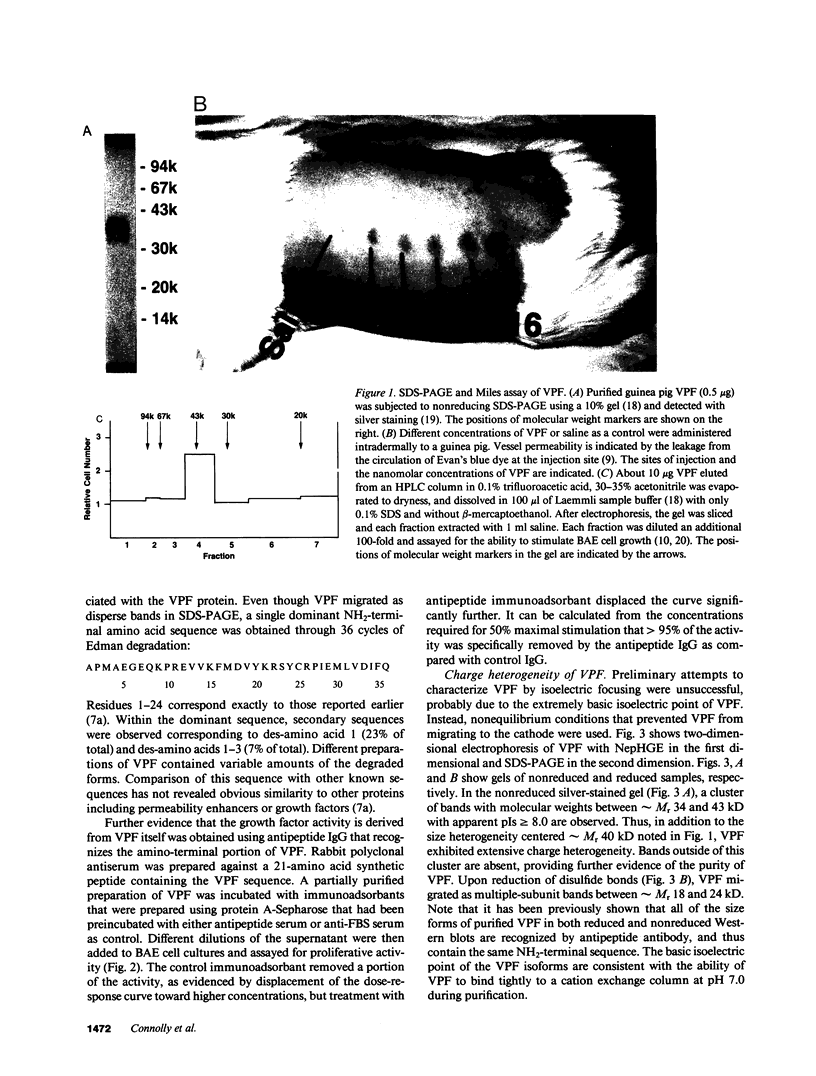
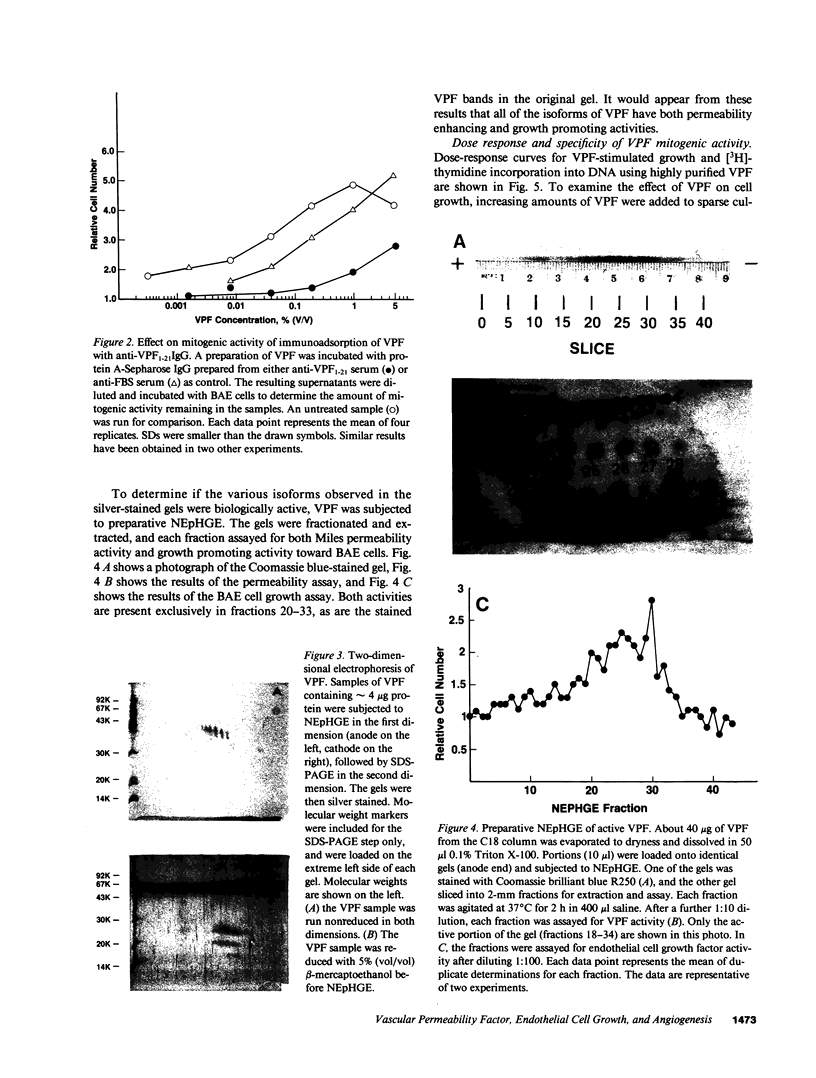
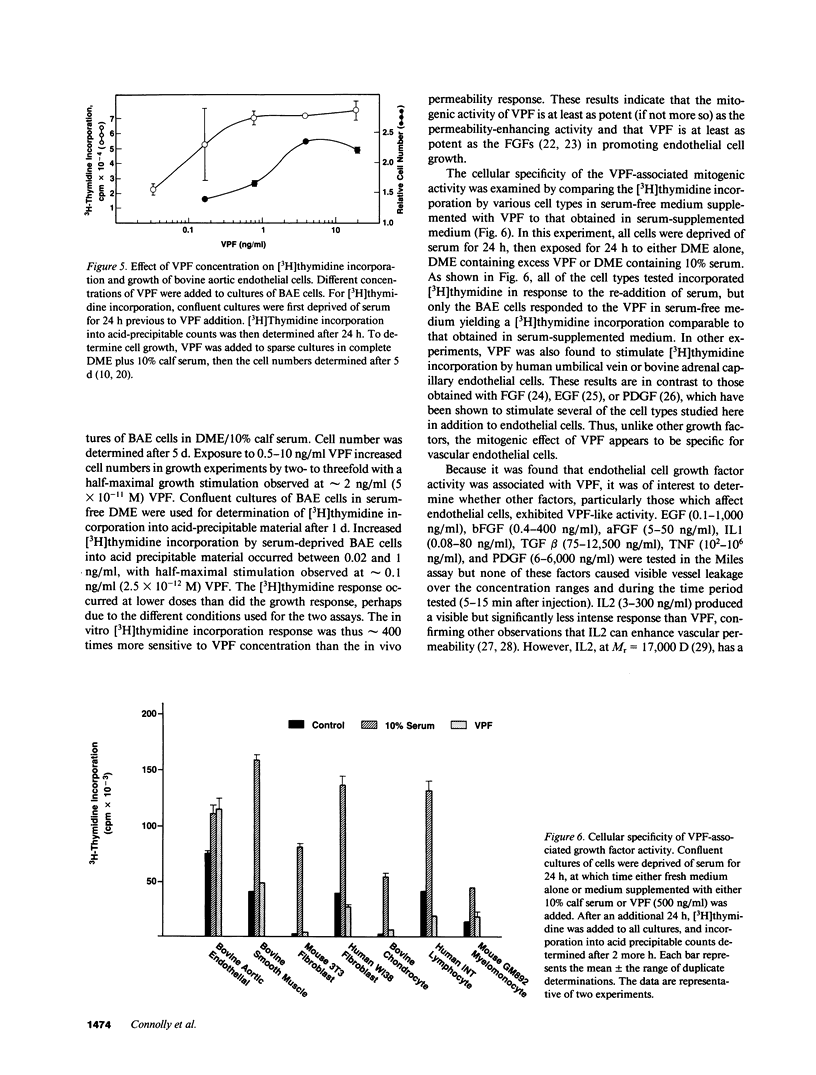
Vascular permeability factor (VPF) is an Mr 40-kD protein that has been purified from the conditioned medium of guinea pig line 10 tumor cells grown in vitro, and increases fluid permeability from blood vessels when injected intradermally. Addition of VPF to cultures of vascular endothelial cells in vitro unexpectedly stimulated cellular proliferation. VPF promoted the growth of new blood vessels when administered into healing rabbit bone grafts or rat corneas. The identity of the growth factor activity with VPF was established in four ways: (a) the molecular weight of the activity in preparative SDS-PAGE was the same as VPF (Mr approximately 40 kD); (b) multiple isoforms (pI greater than or equal to 8) for both VPF and the growth-promoting activity were observed; (c) a single, unique NH2-terminal amino acid sequence was obtained; (d) both growth factor and permeability-enhancing activities were immunoadsorbed using antipeptide IgG that recognized the amino terminus of VPF. Furthermore, 125I-VPF was shown to bind specifically and with high affinity to endothelial cells in vitro and could be chemically cross-linked to a high-molecular weight cell surface receptor, thus demonstrating a mechanism whereby VPF can interact directly with endothelial cells. Unlike other endothelial cell growth factors, VPF did not stimulate [3H]thymidine incorporation or promote growth of other cell types including mouse 3T3 fibroblasts or bovine smooth muscle cells. VPF, therefore, appears to be unique in its ability to specifically promote increased vascular permeability, endothelial cell growth, and angio-genesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. F., Asch B., Harvey V. S., Buchinski B., Dvorak H. F. Fibrinogen influx and accumulation of cross-linked fibrin in mouse carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1920–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly D. T., Knight M. B., Harakas N. K., Wittwer A. J., Feder J. Determination of the number of endothelial cells in culture using an acid phosphatase assay. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jan;152(1):136–140. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Harvey V. S., Estrella P., Brown L. F., McDonagh J., Dvorak A. M. Fibrin containing gels induce angiogenesis. Implications for tumor stroma generation and wound healing. Lab Invest. 1987 Dec;57(6):673–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppley B. L., Doucet M., Connolly D. T., Feder J. Enhancement of angiogenesis by bFGF in mandibular bone graft healing in the rabbit. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1988 May;46(5):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0278-2391(88)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairman R. P., Glauser F. L., Merchant R. E., Bechard D., Fowler A. A. Increase of rat pulmonary microvascular permeability to albumin by recombinant interleukin-2. Cancer Res. 1987 Jul 1;47(13):3528–3532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;43:175–203. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60946-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlowski L. E., Jain R. K. Microvascular permeability of normal and neoplastic tissues. Microvasc Res. 1986 May;31(3):288–305. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(86)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr Culture of vascular endothelium. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1976;3:1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Cheng J., Lui G. M., Baird A., Böhlent P. Isolation of brain fibroblast growth factor by heparin-Sepharose affinity chromatography: identity with pituitary fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6963–6967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Massoglia S., Cheng J., Lui G. M., Böhlen P. Isolation of pituitary fibroblast growth factor by fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC): partial chemical and biological characterization. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Feb;122(2):323–332. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041220223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi H., McKeehan W. L. Isolation, growth requirements, cloning, prostacyclin production and life-span of human adult endothelial cells in low serum culture medium. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1986 Jan;22(1):51–56. doi: 10.1007/BF02623441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa F., Miyazono K., Hellman U., Drexler H., Wernstedt C., Hagiwara K., Usuki K., Takaku F., Risau W., Heldin C. H. Identification of angiogenic activity and the cloning and expression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor. Nature. 1989 Apr 13;338(6216):557–562. doi: 10.1038/338557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A. Culture of human endothelial cells. Transplant Proc. 1980 Sep;12(3 Suppl 1):49–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashima N., Nishi-Takaoka C., Fujita T., Taki S., Yamada G., Hamuro J., Taniguchi T. Unique structure of murine interleukin-2 as deduced from cloned cDNAs. 1985 Jan 31-Feb 6Nature. 313(6001):402–404. doi: 10.1038/313402a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Sasse J., Sullivan R., Smith J. A. Human tumor cells synthesize an endothelial cell growth factor that is structurally related to basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2448–2452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knedler A., Ham R. G. Optimized medium for clonal growth of human microvascular endothelial cells with minimal serum. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1987 Jul;23(7):481–491. doi: 10.1007/BF02628418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILES A. A., MILES E. M. Vascular reactions to histamine, histamine-liberator and leukotaxine in the skin of guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1952 Oct;118(2):228–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. W., Bale W. F. Accessibility of circulating immunoglobulin G to the extravascular compartment of solid rat tumors. Cancer Res. 1984 Sep;44(9):3719–3723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olander J. V., Marasa J. C., Kimes R. C., Johnston G. M., Feder J. An assay measuring the stimulation of several types of bovine endothelial cells by growth factor(s) derived from cultured human tumor cells. In Vitro. 1982 Feb;18(2):99–107. doi: 10.1007/BF02796401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olwin B. B., Hauschka S. D. Identification of the fibroblast growth factor receptor of Swiss 3T3 cells and mouse skeletal muscle myoblasts. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3487–3492. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polverini P. J., Cotran R. S., Sholley M. M. Endothelial proliferation in the delayed hypersensitivity reaction: an autoradiographic study. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):529–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polverini P. J., Leibovich S. J. Induction of neovascularization in vivo and endothelial proliferation in vitro by tumor-associated macrophages. Lab Invest. 1984 Dec;51(6):635–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstein M., Ettinghausen S. E., Rosenberg S. A. Extravasation of intravascular fluid mediated by the systemic administration of recombinant interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1735–1742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senger D. R., Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Perruzzi C. A., Harvey V. S., Dvorak H. F. Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science. 1983 Feb 25;219(4587):983–985. doi: 10.1126/science.6823562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senger D. R., Perruzzi C. A., Feder J., Dvorak H. F. A highly conserved vascular permeability factor secreted by a variety of human and rodent tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1986 Nov;46(11):5629–5632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C. W., Levitt S. H. Quantitative study of vascularity in Walker carcinoma 256. Cancer Res. 1971 May;31(5):587–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A., Rios-Candelore M., Fitzpatrick S. Purification and characterization of acidic fibroblast growth factor from bovine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):357–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]











