Abstract
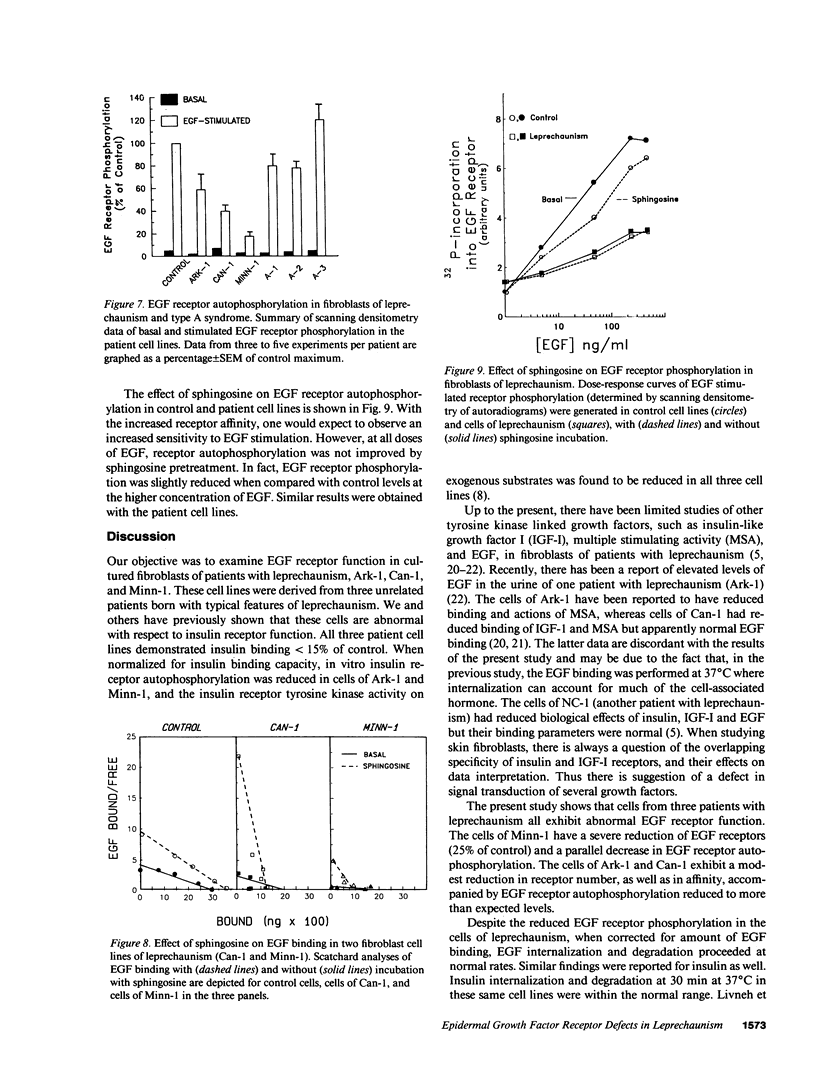
Leprechaunism is a rare genetic disorder characterized by severe growth retardation and insulin resistance. Maximal epidermal growth factor (EGF) binding was reduced in fibroblasts from three unrelated patients with leprechaunism (Ark-1, Can-1, and Minn-1) compared with control (0.8-2.2%/mg protein vs. 5.5%/mg protein). This was due to a decrease in receptor affinity in Ark-1 and Can-1 and a decrease in receptor number in Minn-1. In all cell lines, EGF-stimulated receptor autophosphorylation was also decreased to 18-60% of control, whereas EGF internalization and degradation was normal. Sphingosine (40 microM), a protein kinase C inhibitor, increased EGF receptor affinity twofold in control cells and six- to nine-fold in cells of leprechaunism. However, sphingosine did not enhance EGF-stimulated receptor autophosphorylation in either the controls or the patients' cells. By contrast, only one of the three cell lines of patients with the type A syndrome demonstrated a decrease in EGF binding and all demonstrated normal or near normal EGF-stimulated receptor autophosphorylation. These data indicate that in patients with leprechaunism, there are functional abnormalities of the EGF receptor, as well as of the insulin receptor, that may contribute to the severity of the syndrome. These data also suggest a role for the insulin receptor in maintaining normal EGF receptor function in these cells.
Full text
PDF
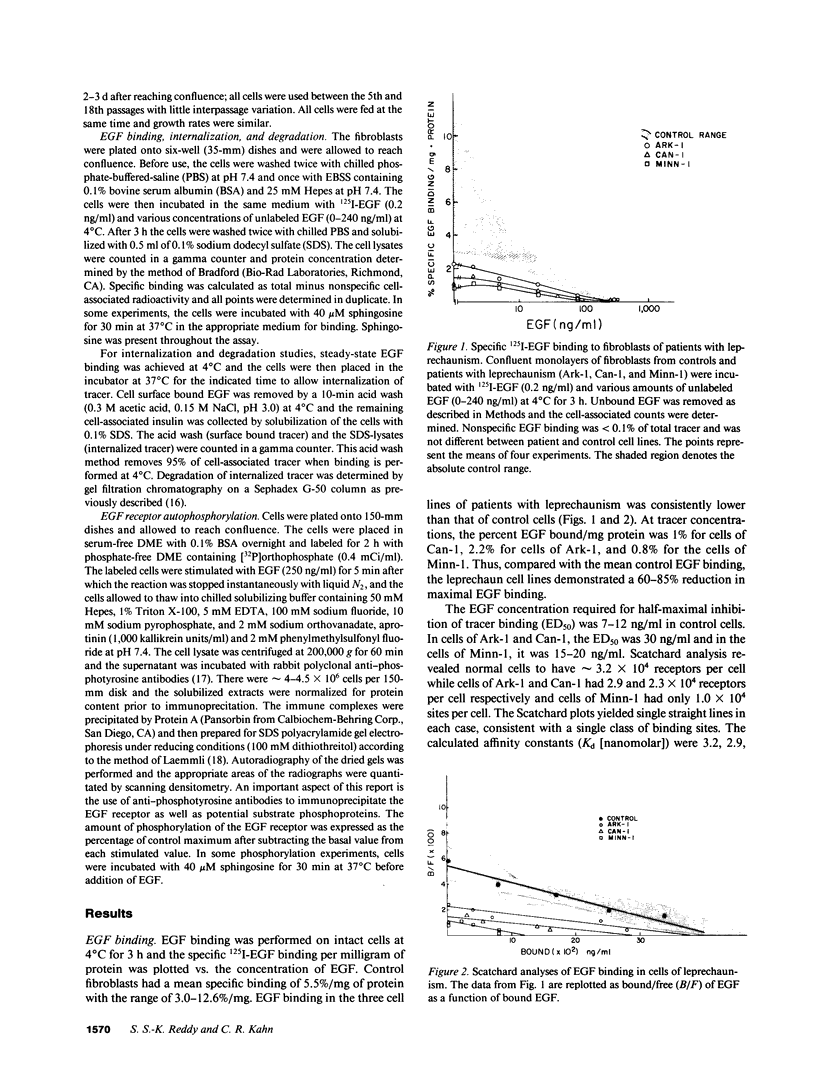
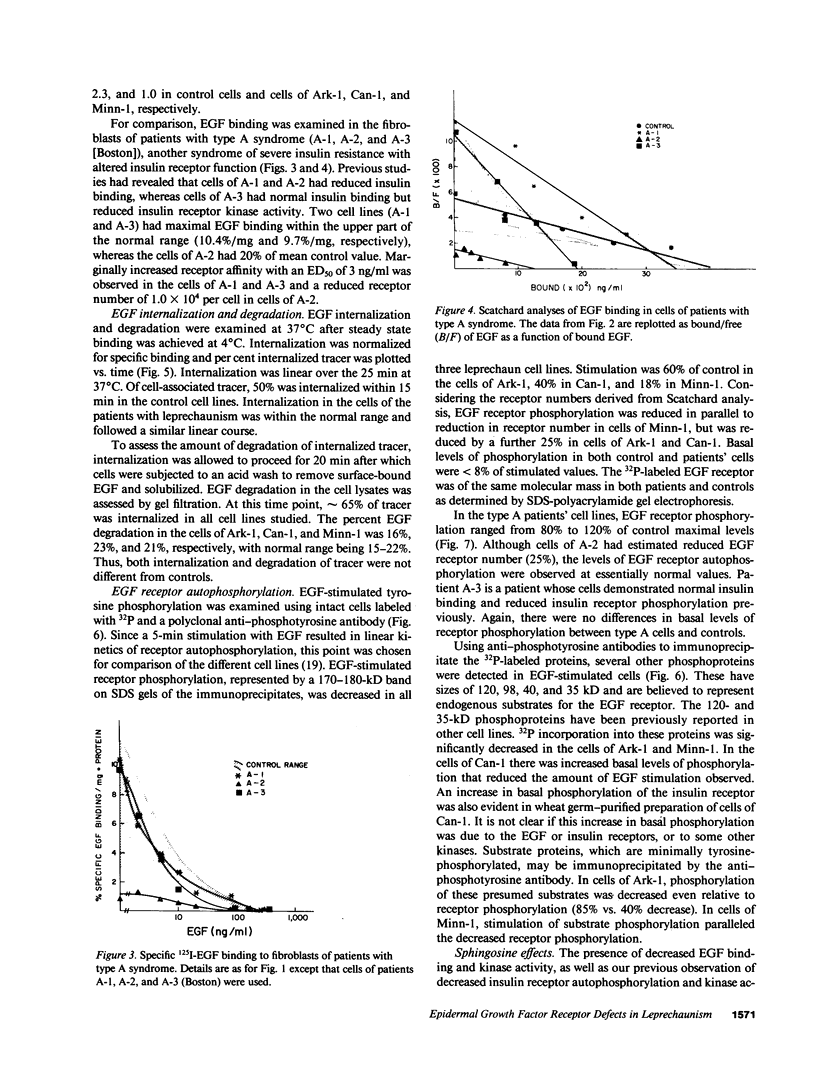
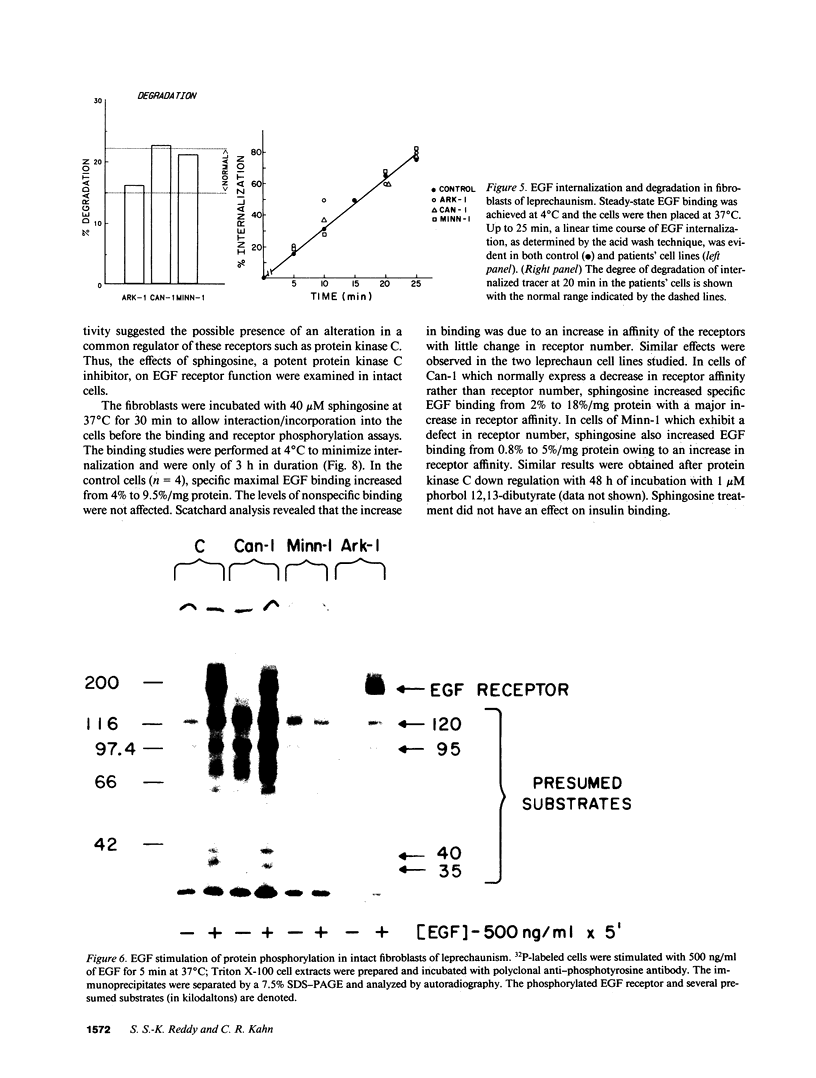



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazzi M. D., Nelsestuen G. L. Mechanism of protein kinase C inhibition by sphingosine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 15;146(1):203–207. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90711-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Stumpo D. J., Kennington E. A., Tuttle J. S., Orth D. N., Thompson K. L., Hung M. C., Rosner M. R. Decreased levels of hepatic epidermal growth factor receptors in obese hyperglycemic rodents. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12356–12364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag G. E., Roth R. A., Beaudoin J., Mochly-Rosen D., Koshland D. E., Jr Protein kinase C directly phosphorylates the insulin receptor in vitro and reduces its protein-tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5822–5824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. W., Larner J., Locker E. F., Widom B., Elders M. J. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in cultured fibroblasts from a patient with leprechaunism: impaired post-binding actions of insulin and multiplication-stimulating activity. Metabolism. 1984 Dec;33(12):1084–1096. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(84)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONOHUE W. L., UCHIDA I. Leprechaunism: a euphemism for a rare familial disorder. J Pediatr. 1954 Nov;45(5):505–519. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(54)80113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Gironès N., Faucher M. Two alternative mechanisms control the interconversion of functional states of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5373–5379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. J. Effects of epidermal growth factor and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate on metabolism of the epidermal growth factor receptor in normal human fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1718–1724. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Waterfield M. D., Parker P. J. Autophosphorylation and protein kinase C phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Effect on tyrosine kinase activity and ligand binding affinity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14538–14546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frindik J. P., Kemp S. F., Fiser R. H., Schedewie H., Elders M. J. Phenotypic expression in Donohue syndrome (leprechaunism): a role for epidermal growth factor. J Pediatr. 1985 Sep;107(3):428–430. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80527-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigorescu F., Flier J. S., Kahn C. R. Characterization of binding and phosphorylation defects of erythrocyte insulin receptors in the type A syndrome of insulin resistance. Diabetes. 1986 Feb;35(2):127–138. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.2.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigorescu F., Herzberg V., King G., Meistas M., Elders J., Frazer T., Kahn C. R. Defects in insulin binding and autophosphorylation of erythrocyte insulin receptors in patients with syndromes of severe insulin resistance and their parents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Mar;64(3):549–556. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-3-549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigorescu F., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Insulin binding and insulin-dependent phosphorylation of the insulin receptor solubilized from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13708–13716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachiya H. L., Takayama S., White M. F., King G. L. Regulation of insulin receptor internalization in vascular endothelial cells by insulin and phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6417–6424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammons G. T., Smith R. M., Jarett L. Inhibition by bacitracin of rat adipocyte plasma membrane degradation of 125I-insulin is associated with an increase in plasma membrane bound insulin and a potentiation of glucose oxidation by adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11563–11570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M. Lysosphingolipids inhibit protein kinase C: implications for the sphingolipidoses. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):670–674. doi: 10.1126/science.3101176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Greenberg C. S., Bell R. M. Sphingosine inhibition of agonist-dependent secretion and activation of human platelets implies that protein kinase C is a necessary and common event of the signal transduction pathways. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13620–13626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Loomis C. R., Merrill A. H., Jr, Bell R. M. Sphingosine inhibition of protein kinase C activity and of phorbol dibutyrate binding in vitro and in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12604–12609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Bevins C. L., Cama A., Ojamaa K., Marcus-Samuels B., Kadowaki H., Beitz L., McKeon C., Taylor S. I. Two mutant alleles of the insulin receptor gene in a patient with extreme insulin resistance. Science. 1988 May 6;240(4853):787–790. doi: 10.1126/science.2834824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplowitz P. B., D'Ercole A. J. Fibroblasts from a patient with leprechaunism are resistant to insulin, epidermal growth factor, and somatomedin C. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Oct;55(4):741–748. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-4-741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight A. B., Rechler M. M., Romanus J. A., Van Obberghen-Schilling E. E., Nissley S. P. Stimulation of glucose incorporation and amino acid transport by insulin and an insulin-like growth factor in fibroblasts with defective insulin receptors cultured from a patient with leprechaunism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh E., Prywes R., Kashles O., Reiss N., Sasson I., Mory Y., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Reconstitution of human epidermal growth factor receptors and its deletion mutants in cultured hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12490–12497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh E., Reiss N., Berent E., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. An insertional mutant of epidermal growth factor receptor allows dissection of diverse receptor functions. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2669–2676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02558.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill A. H., Jr, Sereni A. M., Stevens V. L., Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M., Kinkade J. M., Jr Inhibition of phorbol ester-dependent differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemic (HL-60) cells by sphinganine and other long-chain bases. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12610–12615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. H., Murray D. K. Sphingolipids inhibit insulin and phorbol ester stimulated uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 16;138(1):463–467. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90303-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang D. T., Sharma B. R., Shafer J. A., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Predominance of tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptors during the initial response of intact cells to insulin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7131–7136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittet D., Krause K. H., Wollheim C. B., Bruzzone R., Lew D. P. Nonselective inhibition of neutrophil functions by sphinganine. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10072–10076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podskalny J. M., Kahn C. R. Cell culture studies on patients with extreme insulin resistance. II. Abnormal biological responses in cultured fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Feb;54(2):269–275. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy S. S., Lauris V., Kahn C. R. Insulin receptor function in fibroblasts from patients with leprechaunism. Differential alterations in binding, autophosphorylation, kinase activity, and receptor-mediated internalization. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1359–1365. doi: 10.1172/JCI113739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling E. E., Rechler M. M., Grunfeld C., Rosenberg A. M. Primary defect of insulin receptors in skin fibroblasts cultured from an infant with leprechaunism and insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5877–5881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinnett-Smith J. W., Rozengurt E. Diacylglycerol treatment rapidly decreases the affinity of the epidermal growth factor receptors of Swiss 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jul;124(1):81–86. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041240114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sissom J. F., Stenzel W. K., Warshaw J. B. Decreased binding of epidermal growth factor in placentas from streptozotocin-diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):242–247. doi: 10.1172/JCI113054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Samuels B., Roth J., Kasuga M., Hedo J. A., Gorden P., Brasel D. E., Pokora T., Engel R. R. Decreased insulin binding in cultured lymphocytes from two patients with extreme insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 May;54(5):919–930. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-5-919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. M., Gill G. N. The EGF receptor: structure, regulation and potential role in malignancy. Cancer Surv. 1985;4(4):767–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E. E., Rechler M. M., Romanus J. A., Knight A. B., Nissley S. P., Humbel R. E. Receptors for insulinlike growth factor I are defective in fibroblasts cultured from a patient with leprechaunism. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1356–1365. doi: 10.1172/JCI110383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E., Olcott M. C., Bell R. M., Merrill A. H., Jr, Lambeth J. D. Inhibition of the oxidative burst in human neutrophils by sphingoid long-chain bases. Role of protein kinase C in activation of the burst. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12616–12623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]