Abstract
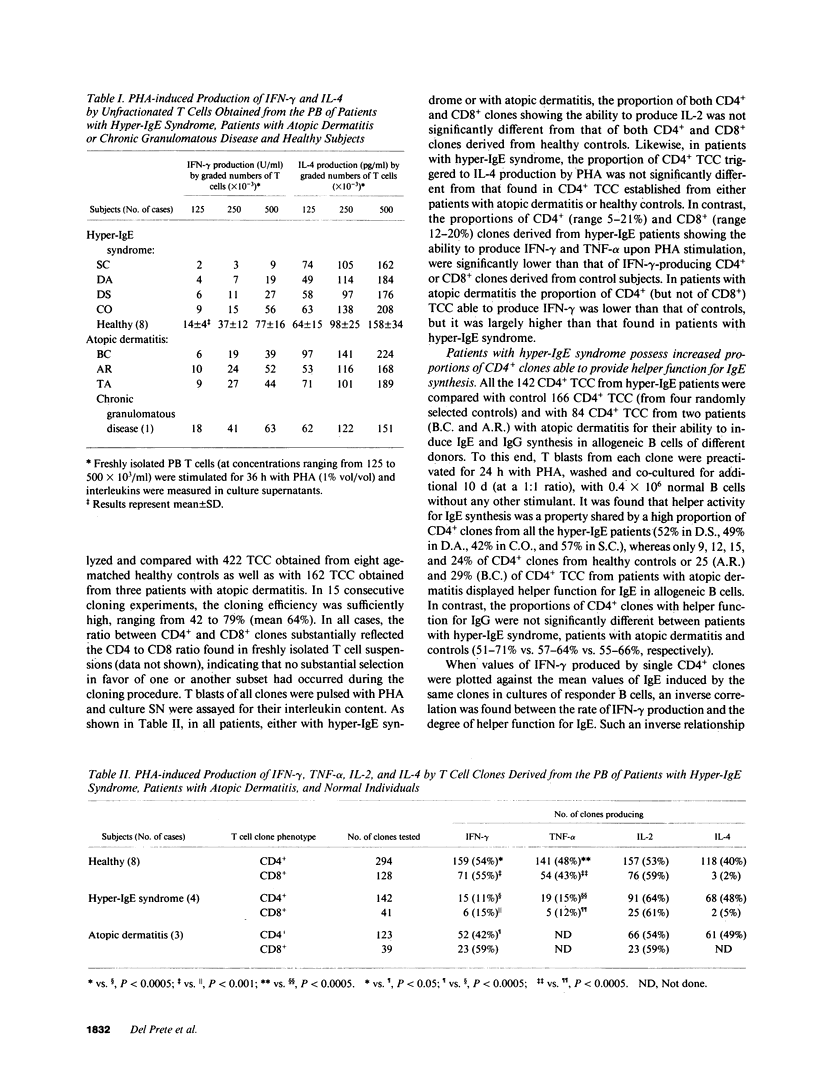
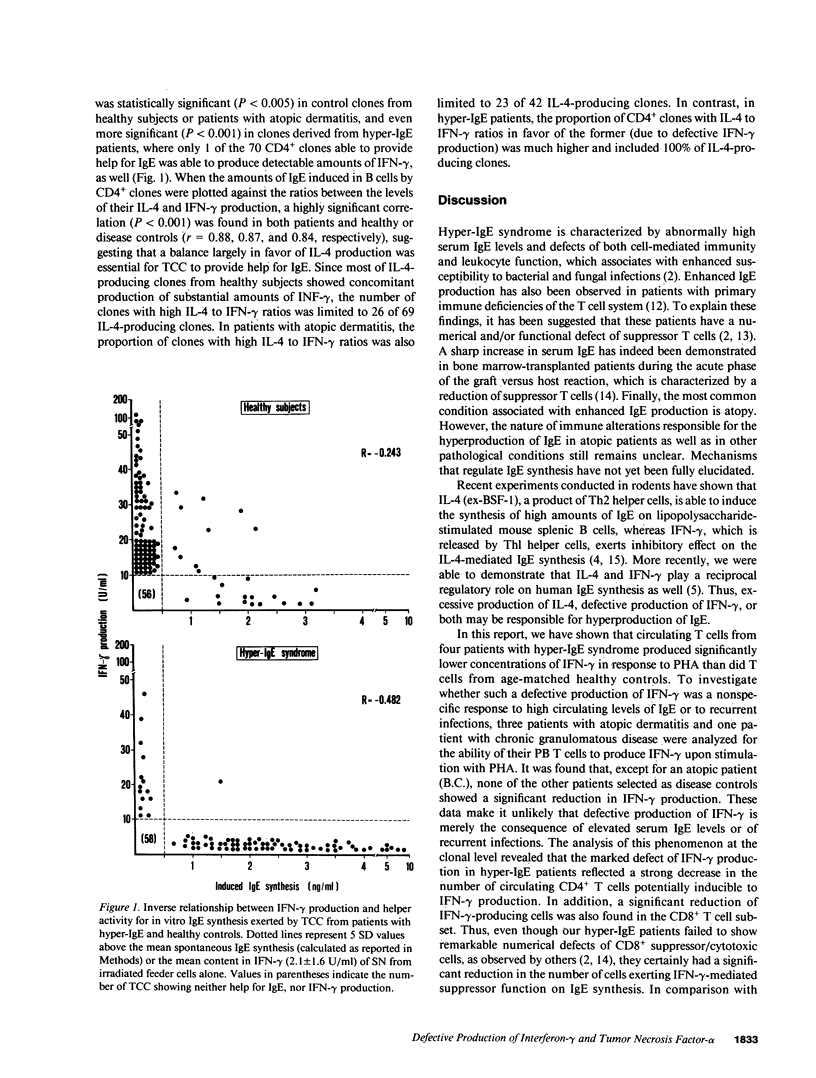
Circulating T cells from four patients with the hyper-IgE syndrome were found to produce significantly lower concentrations of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) in response to stimulation with phytohemagglutinin (PHA) than did T cells from eight age-matched healthy controls, three patients with atopic dermatitis and one patient with chronic granulomatous disease. A clonal analysis revealed that patients with hyper-IgE syndrome had markedly lower proportions of circulating T cells able to produce IFN-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in comparison with controls. In contrast, the proportions of peripheral blood T cells able to produce IL-4 or IL-2 were not significantly different in patients and controls. All the four patients with hyper-IgE syndrome showed high proportions of circulating CD4+ helper T cells able to induce IgE synthesis in allogeneic B cells, as well. Such an activity for IgE synthesis appeared to be positively correlated with IL-4 production by T cells and inversely related to the ability of the same T cells to produce IFN-gamma. Since IFN-gamma exerts an inhibitory effect on the synthesis of IgE and both IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha play an important role in inflammatory reactions, we suggest that the defective production of IFN-gamma may be responsible for hyperproduction of IgE and the combined defect of IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha may contribute to the undue susceptibility to infections seen in patients with hyper-IgE syndrome.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buckley R. H., Becker W. G. Abnormalities in the regulation of human IgE synthesis. Immunol Rev. 1978;41:288–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb01469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Fiscus S. A. Serum IgD and IgE concentrations in immunodeficiency diseases. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):157–165. doi: 10.1172/JCI107906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Wray B. B., Belmaker E. Z. Extreme hyperimmunoglobulinemia E and undue susceptibility to infection. Pediatrics. 1972 Jan;49(1):59–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrétien I., Van Kimmenade A., Pearce M. K., Banchereau J., Abrams J. S. Development of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies for immunoassay and neutralization of human interleukin-4. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Feb 8;117(1):67–81. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Carty J. A T cell activity that enhances polyclonal IgE production and its inhibition by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):949–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G., Maggi E., Macchia D., Tiri A., Parronchi P., Ricci M., Romagnani S. Human T cell clones can induce in vitro IgE synthesis in normal B cells regardless of alloantigen recognition or specificity for peculiar antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Dec;16(12):1509–1514. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G., Maggi E., Parronchi P., Chrétien I., Tiri A., Macchia D., Ricci M., Banchereau J., De Vries J., Romagnani S. IL-4 is an essential factor for the IgE synthesis induced in vitro by human T cell clones and their supernatants. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4193–4198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Stocks N., Zoon K., Stanton G. J., Timonen T., Herberman R. B. Positive self regulation of cytotoxicity in human natural killer cells by production of interferon upon exposure to influenza and herpes viruses. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1222–1234. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Reinherz E., Leung D., McKee K. T., Jr, Schlossman S., Rosen F. S. Deficiency of suppressor T cells in the hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):783–791. doi: 10.1172/JCI110315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi E., Del Prete G., Macchia D., Parronchi P., Tiri A., Chrétien I., Ricci M., Romagnani S. Profiles of lymphokine activities and helper function for IgE in human T cell clones. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jul;18(7):1045–1050. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Pantaleo G., Moretta L., Cerottini J. C., Mingari M. C. Direct demonstration of the clonogenic potential of every human peripheral blood T cell. Clonal analysis of HLA-DR expression and cytolytic activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):743–754. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paliard X., de Waal Malefijt R., Yssel H., Blanchard D., Chrétien I., Abrams J., de Vries J., Spits H. Simultaneous production of IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-gamma by activated human CD4+ and CD8+ T cell clones. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):849–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin J. M., Eales L. J., Galazka A. R., Pinching A. J. Atopic manifestations in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome: response to recombinant interferon gamma. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 May 9;294(6581):1185–1186. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6581.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Dayton E. T., Fanning V., Thiagarajan P., Hoxie J., Trinchieri G. Immune interferon and leukocyte-conditioned medium induce normal and leukemic myeloid cells to differentiate along the monocytic pathway. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2058–2080. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringdén O., Persson U., Johansson S. G., Wilczek H., Gahrton G., Groth C. G., Lundgren G., Lönnqvist B., Möller E. Markedly elevated serum IgE levels following allogeneic and syngeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1983 Jun;61(6):1190–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S., Del Prete G. F., Maggi E., Bellesi G., Biti G., Rossi Ferrini P. L., Ricci M. Abnormalities of in vitro immunoglobulin synthesis by peripheral blood lymphocytes from untreated patients with Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1375–1382. doi: 10.1172/JCI110890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S., Del Prete G., Maggi E., Ricci M. Activation through CD3 molecule leads a number of human T cell clones to induce IgE synthesis in vitro by B cells from allergic and nonallergic individuals. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1744–1749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Paul W. E. Interferon-gamma and B cell stimulatory factor-1 reciprocally regulate Ig isotype production. Science. 1987 May 22;236(4804):944–947. doi: 10.1126/science.3107127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeg P. S., Moore R. N., Johnson H. M., Oppenheim J. J. Regulation of murine macrophage Ia antigen expression by a lymphokine with immune interferon activity. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1780–1793. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taswell C. Limiting dilution assays for the determination of immunocompetent cell frequencies. I. Data analysis. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1614–1619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


