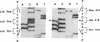Abstract
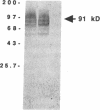
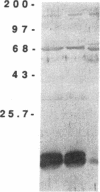
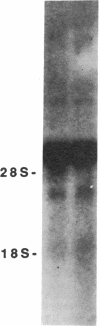
A membrane-bound cytochrome b, a heterodimer formed by a 91-kD glycoprotein and a 22-kD polypeptide, is a critical component of the phagocyte NADPH-oxidase responsible for the generation of superoxide anion. Mutations in the gene for the 91-kD chain of this cytochrome result in the X-linked form of chronic granulomatous disease (CGD), in which phagocytes are unable to produce superoxide. Typically, there is a marked deficiency of the 91-kD subunit and the cytochrome spectrum is absent (X- CGD). In a variant form of CGD with X-linked inheritance, affected males have a normal visible absorbance spectrum of cytochrome b, yet fail to generate superoxide (X+ CGD). The size and abundance of the mRNA for the 91-kD subunit and its encoded protein were examined and appeared normal. To search for a putative mutation in the coding sequence of the 91-kD subunit gene, the corresponding RNA from an affected X+ male was amplified by the polymerase chain reaction and sequenced. A single nucleotide change, a C----A transversion, was identified that predicts a nonconservative Pro----His substitution at residue 415 of the encoded protein. Hybridization of amplified genomic DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes demonstrated the mutation to be specific to affected X+ males and the carrier state. These results strengthen the concept that all X-linked CGD relates to mutations affecting the expression or structure of the 91-kD cytochrome b subunit. The mechanism by which the Pro 415----His mutation renders the oxidase nonfunctional is unknown, but may involve an impaired interaction with other components of the oxidase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehner R. L., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Haines J. L., Conneally P. M., Palmer C., Heerema N., Orkin S. H. DNA linkage analysis of X chromosome-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3398–3401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohler M. C., Seger R. A., Mouy R., Vilmer E., Fischer A., Griscelli C. A study of 25 patients with chronic granulomatous disease: a new classification by correlating respiratory burst, cytochrome b, and flavoprotein. J Clin Immunol. 1986 Mar;6(2):136–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00918746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borregaard N., Cross A. R., Herlin T., Jones O. T., Segal A. W., Valerius N. H. A variant form of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease with normal nitroblue tetrazolium slide test and cytochrome b. Eur J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;13(3):243–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1983.tb00095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Babior B. M. Chronic granulomatous disease. Adv Hum Genet. 1987;16:229–297. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0620-8_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Scott P. J., Mayo L. A. Cytosolic components of the respiratory burst oxidase: resolution of four components, two of which are missing in complementing types of chronic granulomatous disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):825–829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Orkin S. H., Brown R., Jesaitis A. J., Parkos C. A. The glycoprotein encoded by the X-linked chronic granulomatous disease locus is a component of the neutrophil cytochrome b complex. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):717–720. doi: 10.1038/327717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Ochs H. D., de Martinville B., Giacalone J., Lindgren V., Distèche C., Pagon R. A., Hofker M. H., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Minor Xp21 chromosome deletion in a male associated with expression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa, and McLeod syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):250–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamers M. N., de Boer M., Meerhof L. J., Weening R. S., Roos D. Complementation in monocyte hybrids revealing genetic heterogeneity in chronic granulomatous disease. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):553–555. doi: 10.1038/307553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa T., Suzuki K., Suzuki S., Andrews P. C., Babior B. M. A possible role for protein phosphorylation in the activation of the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. Evidence from studies with cells from patients with chronic granulomatous disease. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9109–9115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth P. G., Segal A. W. Further evidence for the involvement of a phosphoprotein in the respiratory burst oxidase of human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):723–731. doi: 10.1042/bj2390723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunoi H., Rotrosen D., Gallin J. I., Malech H. L. Two forms of autosomal chronic granulomatous disease lack distinct neutrophil cytosol factors. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1298–1301. doi: 10.1126/science.2848319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Curnutte J. T., Roberts R. L., Babior B. M. Relationship of protein phosphorylation to the activation of the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. Defects in the phosphorylation of a group of closely related 48-kDa proteins in two forms of chronic granulomatous disease. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6777–6782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Malawista S. E., Roberts R. L., Rosen H., Ochs H. D., Babior B. M., Curnutte J. T. Phosphorylation of the oxidase-related 48K phosphoprotein family in the unusual autosomal cytochrome-negative and X-linked cytochrome-positive types of chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):811–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkos C. A., Allen R. A., Cochrane C. G., Jesaitis A. J. Purified cytochrome b from human granulocyte plasma membrane is comprised of two polypeptides with relative molecular weights of 91,000 and 22,000. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):732–742. doi: 10.1172/JCI113128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkos C. A., Dinauer M. C., Walker L. E., Allen R. A., Jesaitis A. J., Orkin S. H. Primary structure and unique expression of the 22-kilodalton light chain of human neutrophil cytochrome b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3319–3323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer-Pokora B., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Goff S. C., Newburger P. E., Baehner R. L., Cole F. S., Curnutte J. T., Orkin S. H. Cloning the gene for an inherited human disorder--chronic granulomatous disease--on the basis of its chromosomal location. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):32–38. doi: 10.1038/322032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W. Absence of both cytochrome b-245 subunits from neutrophils in X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):88–91. doi: 10.1038/326088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Cross A. R., Garcia R. C., Borregaard N., Valerius N. H., Soothill J. F., Jones O. T. Absence of cytochrome b-245 in chronic granulomatous disease. A multicenter European evaluation of its incidence and relevance. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 3;308(5):245–251. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302033080503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber A. I., Borregaard N., Simons E., Wright J. Chronic granulomatous disease: a syndrome of phagocyte oxidase deficiencies. Medicine (Baltimore) 1983 Sep;62(5):286–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teahan C., Rowe P., Parker P., Totty N., Segal A. W. The X-linked chronic granulomatous disease gene codes for the beta-chain of cytochrome b-245. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):720–721. doi: 10.1038/327720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpp B. D., Nauseef W. M., Clark R. A. Two cytosolic neutrophil oxidase components absent in autosomal chronic granulomatous disease. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1295–1297. doi: 10.1126/science.2848318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weening R. S., Corbeel L., de Boer M., Lutter R., van Zwieten R., Hamers M. N., Roos D. Cytochrome b deficiency in an autosomal form of chronic granulomatous disease. A third form of chronic granulomatous disease recognized by monocyte hybridization. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):915–920. doi: 10.1172/JCI111792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]