Abstract
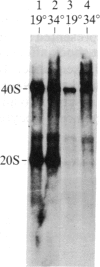
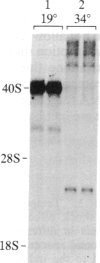
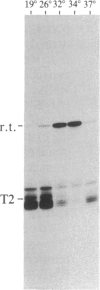
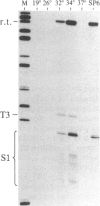
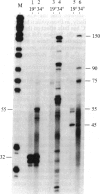
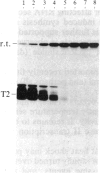
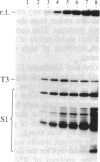
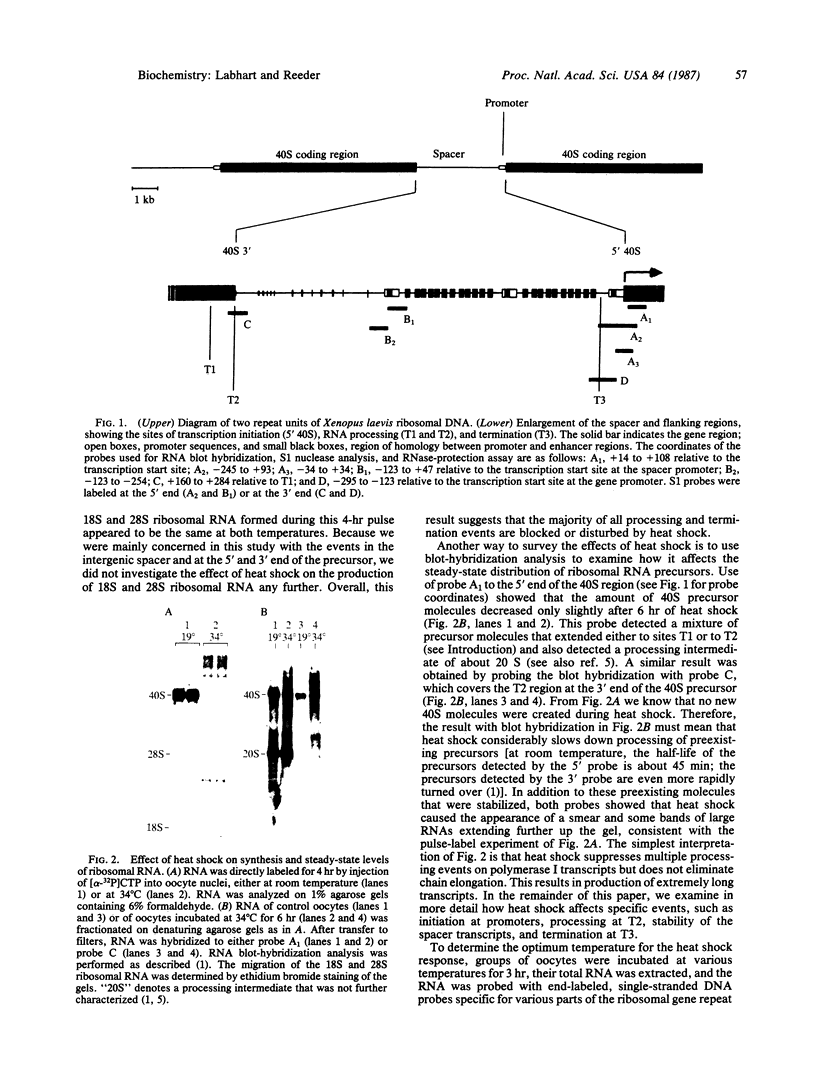
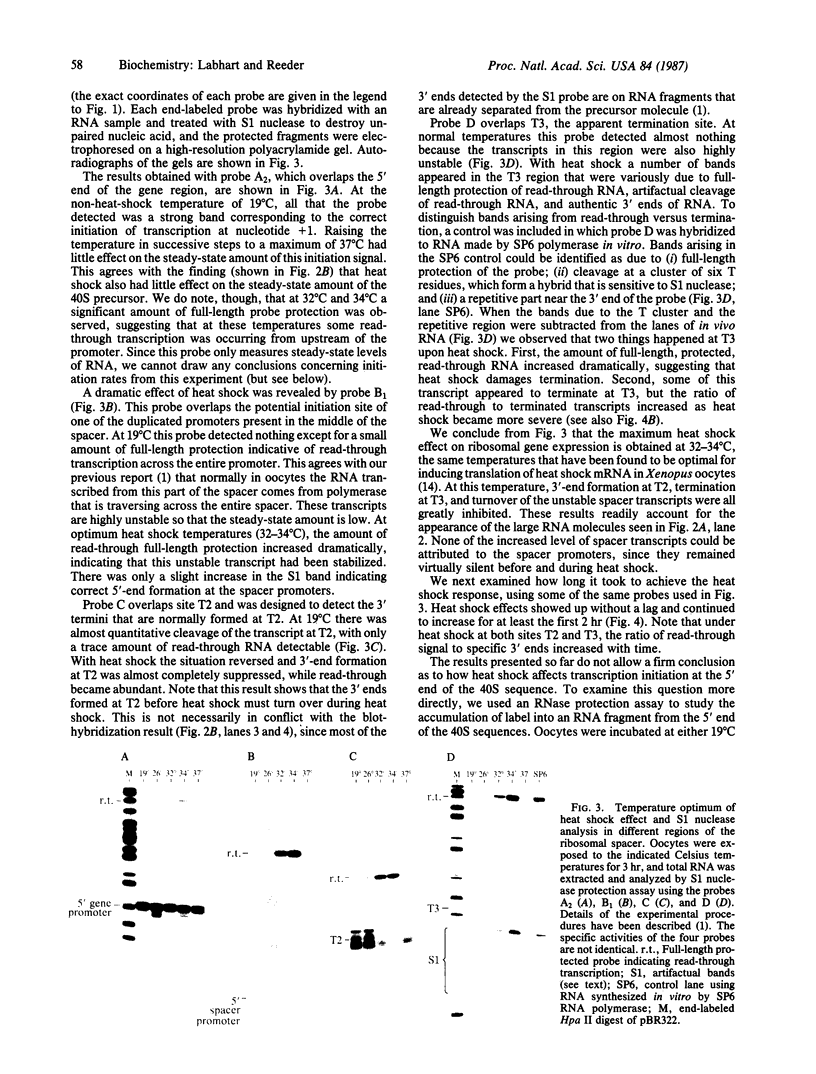
We have shown recently that, in Xenopus laevis oocytes, the 3' end of the longest detectable ribosomal precursor RNA is not formed by transcription termination but by RNA processing and that RNA polymerase I continues to transcribe through the intergenic spacer region. In oocytes, these spacer transcripts are turned over rapidly, and the only apparent transcription termination site is located 215 base pairs upstream of the 5' end of the next transcription unit. In this paper we show that, at heat shock temperature (34 degrees C), processing at the 3' end of the precursor, rapid turnover of spacer transcripts, and termination are all severely impaired. In contrast, transcription initiation and chain elongation are not significantly affected by heat shock. This results in the appearance of large RNA in the range of 10-20 kilobases and longer.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakken A., Morgan G., Sollner-Webb B., Roan J., Busby S., Reeder R. H. Mapping of transcription initiation and termination signals on Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):56–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Gurdon J. B. The heat-shock response in Xenopus oocytes is controlled at the translational level. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):811–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. Spacer promoters are essential for efficient enhancement of X. laevis ribosomal transcription. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90765-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. The ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis is transcribed as part of the primary ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6041–6051. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellgaard E. G., Clever U. RNA metabolism during puff induction in Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1971;36(1):60–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00326422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Characterization of three sites of RNA 3' end formation in the Xenopus ribosomal gene spacer. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):223–228. doi: 10.1038/302223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Hsp70 accelerates the recovery of nucleolar morphology after heat shock. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3095–3100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Hogness D. S. Effect of heat shock on the synthesis of low molecular weight RNAs in drosophilia: accumulation of a novel form of 5S RNA. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subjeck J. R., Shyy T., Shen J., Johnson R. J. Association between the mammalian 110,000-dalton heat-shock protein and nucleoli. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1389–1395. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warocquier R., Scherrer K. RNA metabolism in mammalian cells at elevated temperature. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Sep;10(2):362–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J., Feramisco J. R. Nuclear and nucleolar localization of the 72,000-dalton heat shock protein in heat-shocked mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4501–4513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost H. J., Lindquist S. RNA splicing is interrupted by heat shock and is rescued by heat shock protein synthesis. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):185–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90382-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]