Abstract
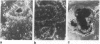
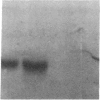
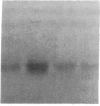
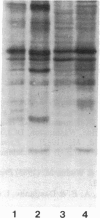
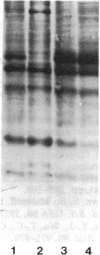
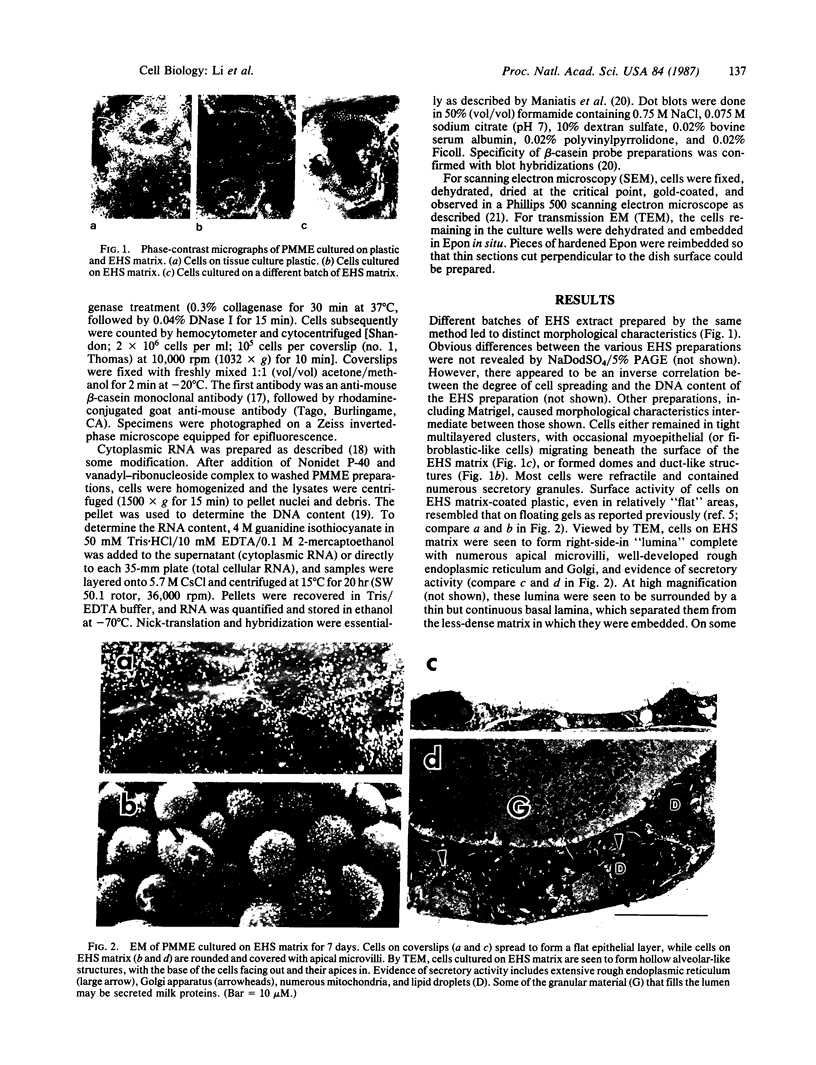
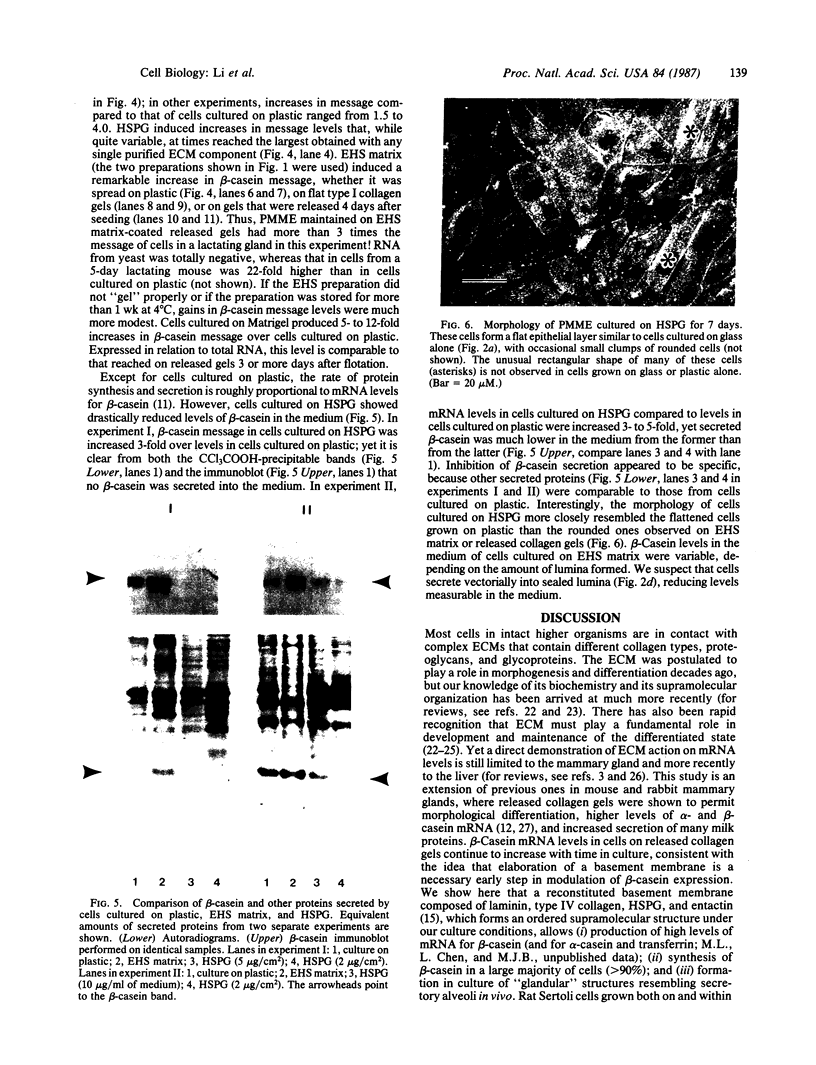
When primary mouse mammary epithelial cells are cultured on plastic, they rapidly lose their ability to synthesize and secrete most milk proteins even in the presence of lactogenic hormones, whereas cells cultured on released type I collagen gels show greatly enhanced mRNA levels and secretion rates of beta-casein and of some other milk proteins. We show here that culture on a reconstituted basement membrane from Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm tumor (EHS) allows greater than 90% of cells to produce high levels of beta-casein. By comparison, 30-40% of cells on released type 1 gels and only 2-10% of cells on plastic express beta-casein after 6 days in culture. Because only 40% of cells from late pregnant gland produced beta-casein before culture, the EHS matrix can both induce and maintain an increased level of casein gene expression. Individual basal lamina components were also evaluated. Type IV collagen and fibronectin had little effect on morphology and beta-casein mRNA levels. In contrast, both laminin and heparan sulfate proteoglycan increased beta-casein mRNA levels (1.5- to 4-fold and 2- to 8-fold, respectively). However, for heparan sulfate proteoglycan, increased message was not accompanied by increased secretion of beta-casein. Profound morphological differences were evident between cells cultured on plastic and on EHS matrix, the latter cells forming ducts, ductules, and lumina and resembling secretory alveoli. These results emphasize the vital role of the extracellular matrix in receiving and integrating structural and functional signals that can direct specific gene expression in differentiated tissues.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggeler J., Takemura R., Werb Z. High-resolution three-dimensional views of membrane-associated clathrin and cytoskeleton in critical-point-dried macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1452–1458. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissell M. J., Hall H. G., Parry G. How does the extracellular matrix direct gene expression? J Theor Biol. 1982 Nov 7;99(1):31–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(82)90388-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissell M. J. The differentiated state of normal and malignant cells or how to define a "normal" cell in culture. Int Rev Cytol. 1981;70:27–100. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. S., Malinoff H. L., Wicha M. S. Connectin: cell surface protein that binds both laminin and actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5927–5930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman J. T., Bartley J. C., Bissell M. J. Glucose metabolite patterns as markers of functional differentiation in freshly isolated and cultured mouse mammary epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Jul;134(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90481-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman J. T., Burwen S. J., Pitelka D. R. Substrate properties influencing ultrastructural differentiation of mammary epithelial cells in culture. Tissue Cell. 1979;11(1):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(79)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman J. T., Pitelka D. R. Maintenance and induction of morphological differentiation in dissociated mammary epithelium on floating collagen membranes. In Vitro. 1977 May;13(5):316–328. doi: 10.1007/BF02616178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadley M. A., Byers S. W., Suárez-Quian C. A., Kleinman H. K., Dym M. Extracellular matrix regulates Sertoli cell differentiation, testicular cord formation, and germ cell development in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1511–1522. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall H. G., Farson D. A., Bissell M. J. Lumen formation by epithelial cell lines in response to collagen overlay: a morphogenetic model in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4672–4676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassell J. R., Leyshon W. C., Ledbetter S. R., Tyree B., Suzuki S., Kato M., Kimata K., Kleinman H. K. Isolation of two forms of basement membrane proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8098–8105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaetzel C. S., Ray D. B. Immunochemical characterization with monoclonal antibodies of three major caseins and alpha-lactalbumin from rat milk. J Dairy Sci. 1984 Jan;67(1):64–75. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(84)81267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., McGarvey M. L., Hassell J. R., Star V. L., Cannon F. B., Laurie G. W., Martin G. R. Basement membrane complexes with biological activity. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):312–318. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie G. W., Bing J. T., Kleinman H. K., Hassell J. R., Aumailley M., Martin G. R., Feldmann R. J. Localization of binding sites for laminin, heparan sulfate proteoglycan and fibronectin on basement membrane (type IV) collagen. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):205–216. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90391-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., Lee W. H., Kaetzel C. S., Parry G., Bissell M. J. Interaction of mouse mammary epithelial cells with collagen substrata: regulation of casein gene expression and secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1419–1423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., Parry G., Bissell M. J. Modulation of secreted proteins of mouse mammary epithelial cells by the collagenous substrata. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):146–155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry G., Lee E. Y., Farson D., Koval M., Bissell M. J. Collagenous substrata regulate the nature and distribution of glycosaminoglycans produced by differentiated cultures of mouse mammary epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Feb;156(2):487–499. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90556-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. M., Matusik R. J., Richards D. A., Gupta P., Rodgers J. R. Multihormonal regulation of casein gene expression at the transcriptional and posttransciptional levels in the mammary gland. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1980;36:157–193. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571136-4.50011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suard Y. M., Haeuptle M. T., Farinon E., Kraehenbuhl J. P. Cell proliferation and milk protein gene expression in rabbit mammary cell cultures. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1435–1442. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topper Y. J., Freeman C. S. Multiple hormone interactions in the developmental biology of the mammary gland. Physiol Rev. 1980 Oct;60(4):1049–1106. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.4.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan Y. J., Wu T. C., Chung A. E., Damjanov I. Monoclonal antibodies to laminin reveal the heterogeneity of basement membranes in the developing and adult mouse tissues. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):971–979. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]