Abstract
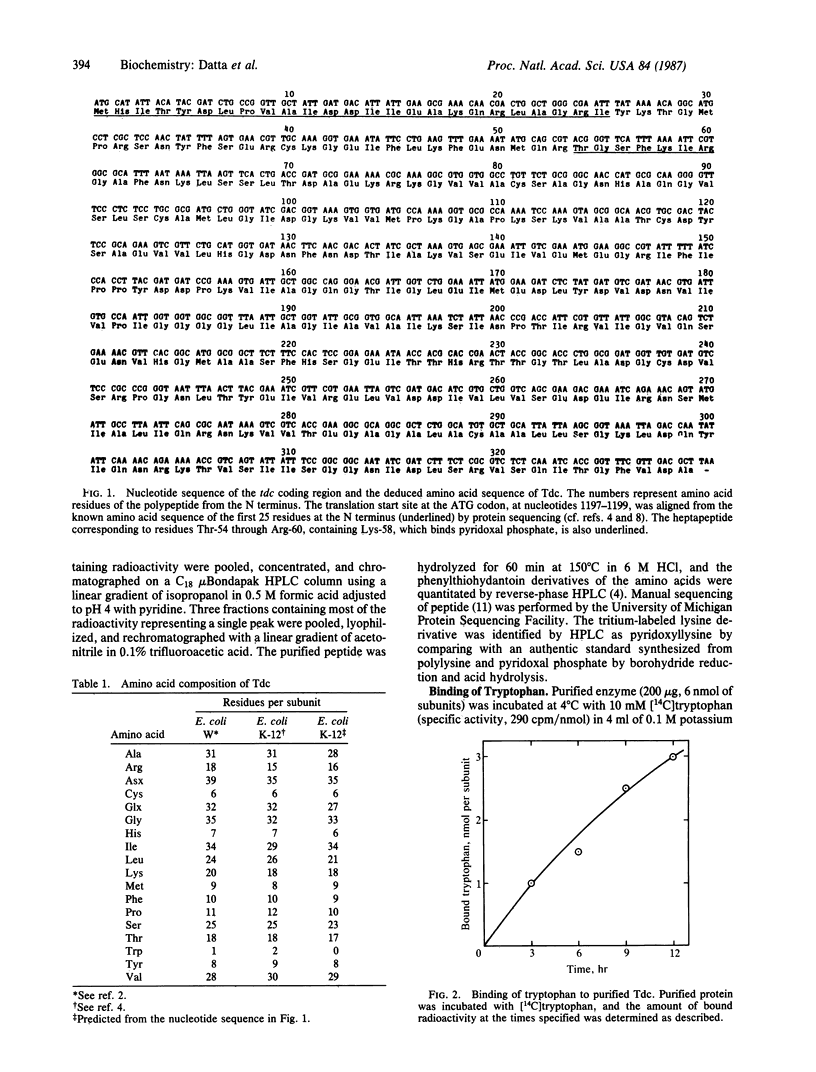
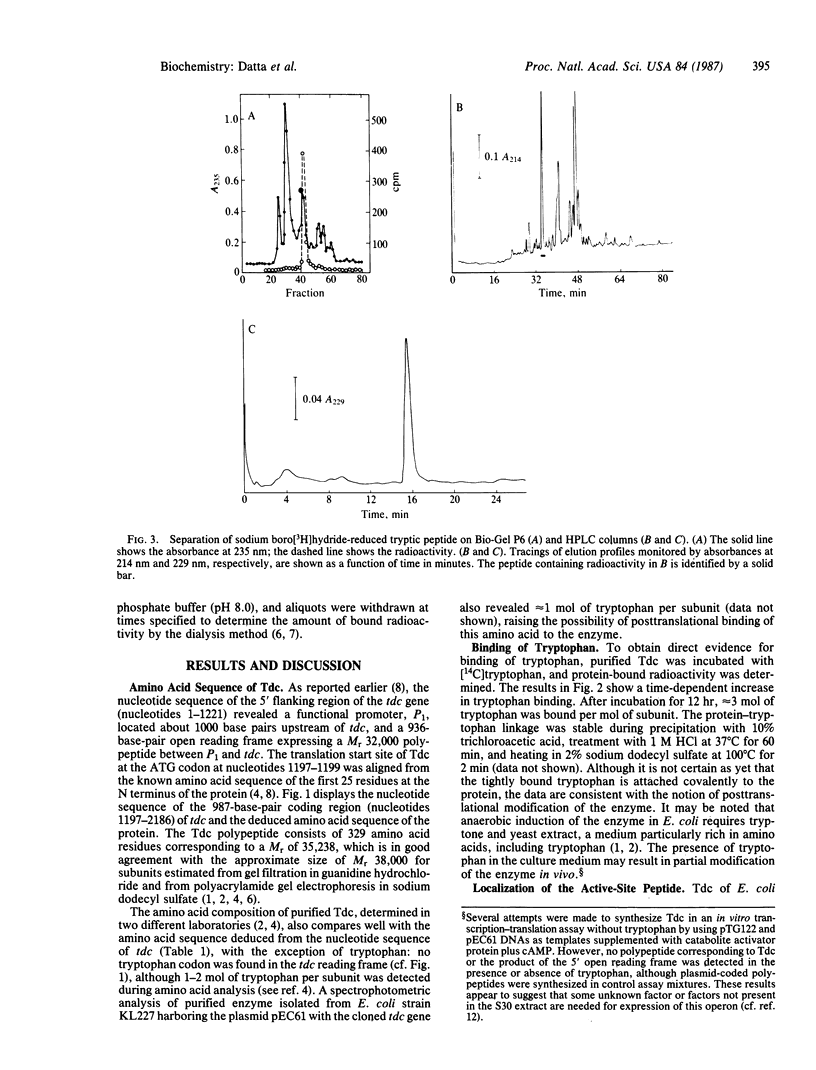
The 987-base-pair coding region of the tdc gene of Escherichia coli K-12 encoding biodegradative threonine dehydratase [Tdc; L-threonine hydro-lyase (deaminating), EC 4.2.1.16], previously cloned in this laboratory, was sequenced. The deduced polypeptide consists of 329 amino acid residues with a calculated Mr of 35,238. Although the purified enzyme was shown to contain tryptophan, no tryptophan codon was found in the tdc reading frame. Incubation of purified Tdc with [14C]tryptophan revealed apparent "covalent" binding of tryptophan, indicating posttranslational modification of the enzyme. A heptapeptide, 54Thr-55Gly-56Ser-57Phe-58Lys-59Ile- 60Arg, was found to contain Lys-58, which binds pyridoxal phosphate coenzyme. A comparison of amino acid sequences between the Tdc polypeptide and the biosynthetic threonine dehydratases of yeast (encoded by ILV1) and E. coli (encoded by ilvA) and the E. coli D-serine dehydratase (DsdA, encoded by dsdA) revealed various extents of homology: five domains of the Tdc polypeptide were 63-93% homologous with the yeast enzyme, and three of these same regions were 80% homologous with the biosynthetic E. coli dehydratase; two different domains showed 67% and 83% homology with DsdA. In addition, two other sequences were highly conserved in all four proteins, one of which was shown to contain the conserved lysine residue that binds pyridoxal phosphate in the Tdc and DsdA polypeptides. These observations suggest that, despite their diverse origin and metabolic significance, these enzymes may have evolved from a common ancestral protein.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne C. P., Wood W. A. L-threonine dehydrase as a model of allosteric control involving ligand-induced oligomerization. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1975;9:65–101. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152809-6.50010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman D. A., Datta P. Catabolite inactivation of biodegradative threonine dehydratase of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1760–1767. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluri R., Jackson L. E., Lee W. E., Crawford I. P. Tryptophan synthetase 2 subunit. Primary structure of the pyridoxyl peptide from the Escherichia coli enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6620–6624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss T. J., Datta P. Escherichia coli K-12 mutation that inactivates biodegradative threonine dehydratase by transposon Tn5 insertion. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):826–831. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.826-831.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss T. J., Datta P. Molecular cloning and expression of the biodegradative threonine dehydratase gene (tdc) of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(2):308–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00425676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobert E. H., Datta P. Synthesis of biodegradative threonine dehydratase in Escherichia coli: role of amino acids, electron acceptors, and certain intermediary metabolites. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):586–592. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.586-592.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. S., Datta P. Chemical characterization of biodegradative threonine dehydratases from two enteric bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 23;706(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90371-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park L. S., Datta P. Inhibition of Escherichia coli biodegradative threonine dehydratase by pyruvate. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):1026–1028. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.1026-1028.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park L. S., Datta P. Mechanism of catabolite inactivation of Escherichia coli biodegradative threonine dehydratase by glyoxylate. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5362–5367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park L. S., Datta P. The role of glyoxylate in the regulation of biodegradative threonine dehydratase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7927–7934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos F., Wiame J. M. Occurrence of a catabolic L-serine (L-threonine) deaminase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr;123(3):571–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röder H., Mundt B., Wagner A., Pöschel E. Probleme der topographischen Diagnostik doppelseitiger Abduzensparesen. Psychiatr Neurol Med Psychol (Leipz) 1986 Apr;38(4):215–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiltz E., Schmitt W. Sequence of Escherichia coli D-serine dehydratase. Location of the pyridoxal-phosphate binding site. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 2;134(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80550-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shizuta Y., Hayaishi O. Regulation of biodegradative threonine deaminase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;11:99–146. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152811-9.50010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


