Abstract
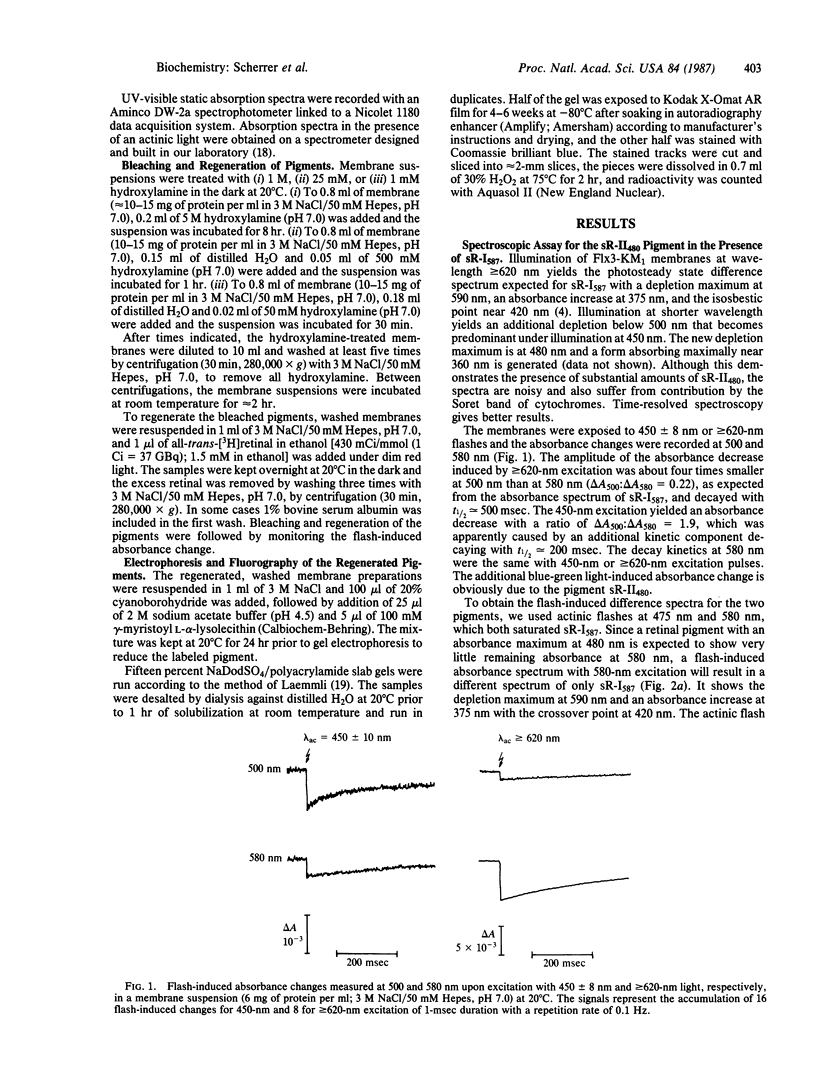
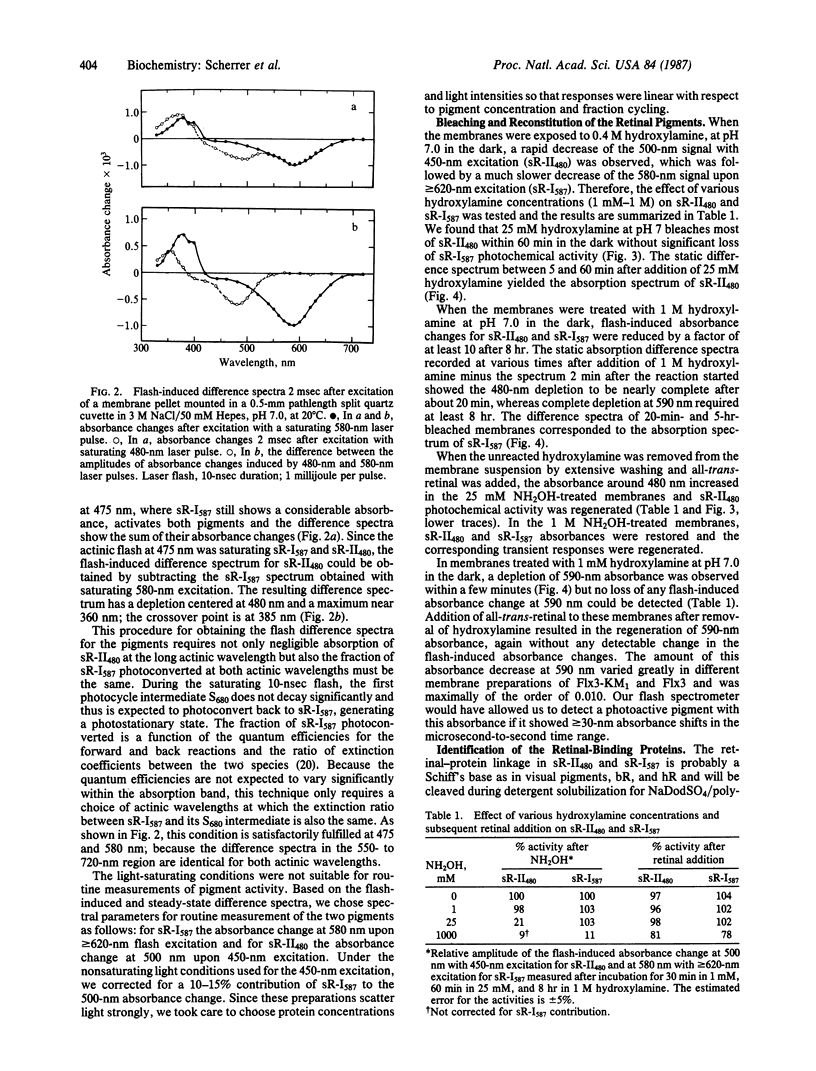
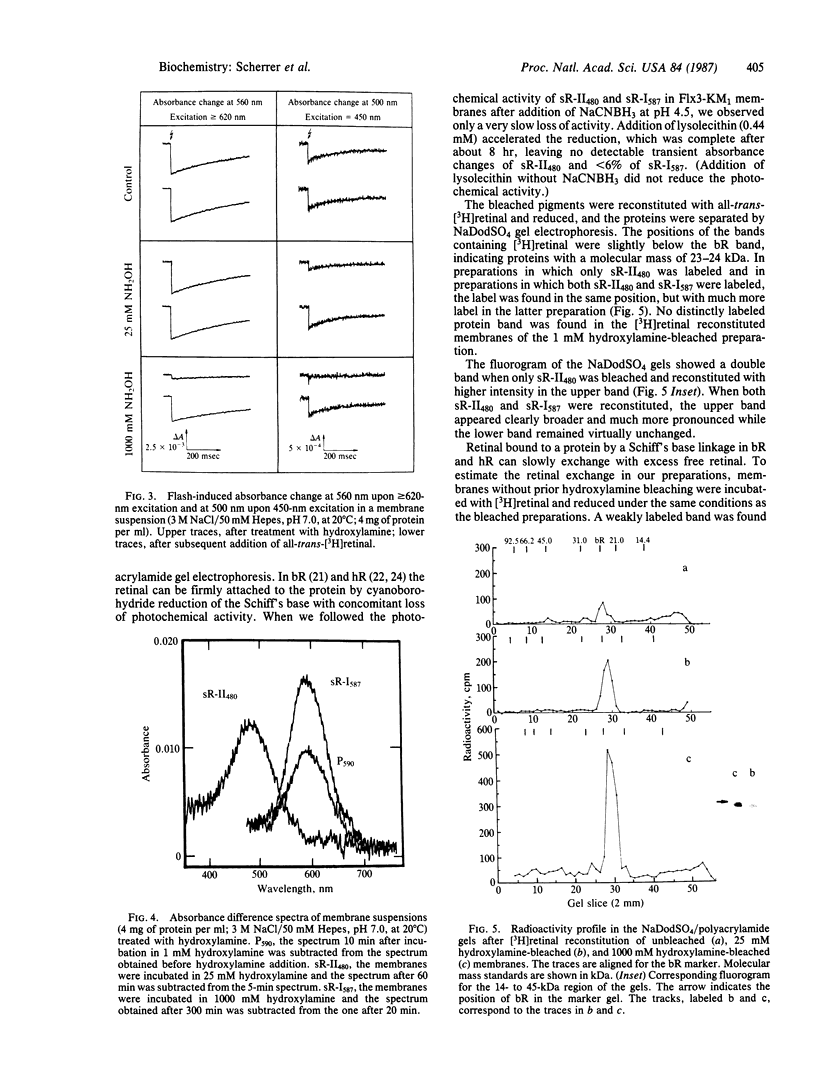
Spectroscopic evidence indicates the presence of a second sensory receptor sR-II in Halobacterium halobium, which causes a repellent response to blue-green light. Reactions with hydroxylamine and NaCNBH3 and reconstitution of the bleached pigment with retinal show that it is very similar to the other retinylidene pigments bacteriorhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and especially the earlier-discovered phototaxis receptor, sensory rhodopsin, renamed sR-I587. The second sensory receptor, sR-II480, has an absorbance maximum at 480 nm and undergoes a cyclic photoreaction with a half-time of approximately 200 msec. Its predominant photocycle intermediate absorbs maximally near 360 nm. The receptor can be detected spectroscopically in the presence of sR-I587 and quantitated through its transient response to 450-nm excitation. It is selectively bleached by low hydroxylamine concentrations that are insufficient to bleach sR-I587 significantly. Its photochemical and phototactic activities can be restored by addition of retinal. The mobility of the receptor, on NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gels, was similar or identical to that of sR-I587 and slightly faster than bacteriorhodopsin, yielding an apparent molecular mass of 23-24 kDa.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogomolni R. A., Spudich J. L. Identification of a third rhodopsin-like pigment in phototactic Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6250–6254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand E., Dencher N. Two photosystems controlling behavioural responses of Halobacterium halobium. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):46–48. doi: 10.1038/257046a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katre N. V., Wolber P. K., Stoeckenius W., Stroud R. M. Attachment site(s) of retinal in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4068–4072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Bogomolni R. A., Stoeckenius W. Photoconversion from the light-adapted to the dark-adapted state of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1985 Aug;48(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83773-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Halorhodopsin: a light-driven chloride ion pump. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:11–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.000303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Oesterhelt D. Identification of the retinal-binding protein in halorhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2674–2677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Niederberger W. The photochemical cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Fed Proc. 1977 May;36(6):1805–1809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Spudich J. L. Control of transmembrane ion fluxes to select halorhodopsin-deficient and other energy-transduction mutants of Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4308–4312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Sundberg S. A., Manor D., Spudich J. L. Properties of a second sensory receptor protein in Halobacterium halobium phototaxis. Proteins. 1986 Nov;1(3):239–246. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Bogomolni R. A. Mechanism of colour discrimination by a bacterial sensory rhodopsin. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):509–513. doi: 10.1038/312509a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Bogomolni R. A. Spectroscopic discrimination of the three rhodopsinlike pigments in Halobacterium halobium membranes. Biophys J. 1983 Aug;43(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84345-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and related pigments of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:587–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W. The rhodopsin-like pigments of halobacteria: light-energy and signal transducers in an archaebacterium. Trends Biochem Sci. 1985 Dec;10(12):483–486. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(85)90210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg S. A., Alam M., Spudich J. L. Excitation signal processing times in Halobacterium halobium phototaxis. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):895–900. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83530-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg S. A., Bogomolni R. A., Spudich J. L. Selection and properties of phototaxis-deficient mutants of Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):282–287. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.282-287.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. E., Bogomolni R. A., Weber H. J. Purification of photochemically active halorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6172–6176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomioka H., Takahashi T., Kamo N., Kobatake Y. Flash spectrophotometric identification of a fourth rhodopsin-like pigment in Halobacterium halobium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 14;139(2):389–395. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff E. K., Bogomolni R. A., Scherrer P., Hess B., Stoeckenius W. Color discrimination in halobacteria: spectroscopic characterization of a second sensory receptor covering the blue-green region of the spectrum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7272–7276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


