Abstract
15-Lipoxygenase 2 (15-LOX2), a lipid-peroxidizing enzyme, is mainly expressed in the luminal compartment of the normal human prostate and often decreased or lost in prostate cancer. Previous studies from our lab implicate 15-LOX2 as a functional tumor suppressor. To better understand the biological role of 15-LOX2 in vivo, we established prostate-specific 15-LOX2 transgenic mice using the ARR2PB promoter. Unexpectedly, transgenic expression of 15-LOX2 or 15-LOX2sv-b, a splice variant that lacks the arachidonic acid metabolizing activity, resulted in age-dependent prostatic hyperplasia and enlargement of the prostate. Prostatic hyperplasia induced by both 15-LOX2 and 15-LOX2sv-b was associated with an increase in luminal and Ki-67+ cells; however, 15-LOX2-transgenic prostates also showed a prominent increase in basal cells. Microarray analysis revealed distinct gene expression profiles that could help explain the prostate phenotypes. Strikingly, 15-LOX2, but not 15-LOX2sv-b, transgenic prostate showed upregulation of several well-known stem/progenitor cell molecules including Sca-1, Trop2, p63, Nkx3.1 and Psca. Prostatic hyperplasia caused by both 15-LOX2 and 15-LOX2sv-b did not progress to prostatic intraprostate neoplasia (PIN) or carcinoma and, mechanistically, prostate lobes (especially those of the 15-LOX2 mice) showed a dramatic increase in senescent cells as revealed by increased SA-βgal, p27Kip1 and HP1γ staining. Collectively, our results suggest that 15-LOX2 expression in mouse prostate leads to hyperplasia and also induces cell senescence, which may, in turn, function as a barrier to tumor development.
Keywords: 15-lipoxygenase 2, prostate, hyperplasia, senescence, tumor suppression, stem cells
INTRODUCTION
15-Lipoxygenase-2 (15-LOX2) is a human-specific, non-heme, and iron-containing enzyme that preferentially metabolizes arachidonic acid (AA) to 15(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid [15(S)-HETE] (Brash et al., 1997). 15-LOX2 has only ~40% sequence homology to human 15-LOX-1 and 12-LOX but displays 78% sequence homology to the murine ortholog, 8-LOX (Jisaka et al., 2000). 15-LOX2 shows a limited tissue distribution and is primarily expressed in the prostate, lung, skin, cornea and esophagus (Brash et al., 1997). Different from 15-LOX2, 8-LOX is not expressed in the murine prostate (Jisaka et al., 1997; Kim et al., 2005; Shappell et al., 2003). The preferential expression of 15-LOX2 in differentiated cells suggests that it may be involved in cellular differentiation and/or secretory functions, although its physiological cellular functions remain poorly characterized.
Strong clinical and experimental evidence has implicated 15-LOX2 as a functional tumor suppressor. FIRST, 15-LOX2 expression and enzymatic activity are frequently downregulated or lost in high-grade prostate intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN) and prostate cancer (PCa) (Jack et al., 2000; Shappell et al., 1999) as well as in the cancers of the skin (Shappell et al., 2001), lung (Gonzalez et al., 2004), breast (Jiang et al., 2006), head and neck (Wang et al., 2006), and esophagus (Xu et al., 2003). SECOND, restoration of 15-LOX2 expression in PCa cells inhibits cell proliferation in vitro and tumor development in vivo (Bhatia et al., 2003; Tang et al., 2002; Tang et al., 2009). THIRD, exogenous 15(S)- HETE, the main 15-LOX2 metabolite, inhibits proliferation or induces apoptosis in PCa (Tang et al., 2002), colon cancer (Chen et al., 2003) and CML (Mahipal et al., 2007) cells. FOURTH, 15-LOX2 functions as a negative cell-cycle regulator in normal human prostate (NHP) epithelial cells (Tang et al., 2002). Moreover, it is cell-autonomously induced prior to NHP cell senescence and its ectopic expression in NHP and PCa cells promotes senescence (Bhatia et al., 2005). Of significance, similar to these tumor-suppressive functions of human 15-LOX2, murine 8-LOX has also been shown to possess anti-tumorigenic and anti-proliferative roles (Kim et al., 2005; Schweiger et al., 2007).
15-LOX2 has at least 6 splice variants (15-LOX2sv-a to 15-LOX2sv-f), which lack appreciable AA-metabolizing activity (Bhatia et al., 2003; Kilty et al., 1999; Tang et al., 2007a; Tang et al., 2002) but, intriguingly, share many biological functions of 15-LOX2. For instance, 15-LOX2sv-b completely lacks AA-metabolizing activity but, like 15-LOX2, could induce cell-cycle arrest in cultured cells (Tang et al., 2002) and inhibits xenograft tumor development (Bhatia et al., 2003), suggesting that 15-LOX2 may possess both enzyme-dependent and -independent biological functions.
Despite our earlier studies implicating 15-LOX2 as a potential tumor suppressor by functioning as an inducer of cell senescence in vitro (Bhatia et al., 2003; Bhatia et al., 2005; Tang et al., 2007a; Tang et al., 2002), it remains unclear whether 15-LOX2 possesses similar functions in a suitable animal model. Furthermore, little is known about the physiological functions of 15-LOX2 in the prostate. To address these deficiencies, we have established prostate-specific 15-LOX2 transgenic mice using the ARR2PB promoter (Zhang et al., 2000). Herein, we report that transgenic expression of 15-LOX2 in mouse prostate induces distinct gene expression profiles and epithelial cell senescence in vivo and induces, unexpectedly, prostatic hyperplasia.
RESULTS
Generation and characterization of 15-LOX2 transgenic mice
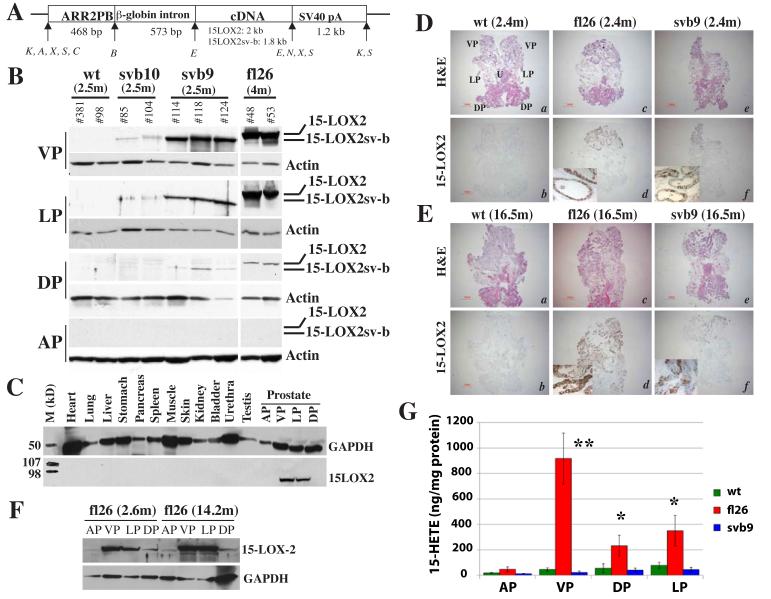
To generate transgenic mice, we cloned full-length 15-LOX2 (fl) or 15-LOX2sv-b (svb) cDNA (Tang et al., 2002) under the control of ARR2PB promoter and microinjected the transgene-containing Kpn1 fragment (Fig. 1A) into the male pronucleus of FVB/N mice. By PCR genotyping, we identified seven fl and six svb potential founder male mice. F1 mice, generated by crossing the positive transgenic founders that passed on the transgene with non-transgenic females, were utilized to characterize the transgene expression using Western blotting (Fig. 1B, C & F), RT-PCR (not shown), and immunohistochemistry (IHC; Fig. 1D & E; fig. S1-S2).
Figure 1. Generation and characterization of 15-LOX2 transgenic mice.
(A) Schematic diagram of transgene constructs, which contain the ARR2PB promoter, rabbit β-globin second intron sequence, 15-LOX2 or 15-LOX2sv-b cDNA, and β-globin-SV40 hybrid polyA tail. The sizes (bp) of each module and restriction enzyme sites (K, Kpn I; A, Apa I; X, Xba I; S, Sal I; C, Cla I; B, BamH I, E, EcoR I; N, Nhe I) are indicated.
(B) Prostatic lobes were dissected from animals of the indicated genotypes and ages (m, month), lysed in RIPA buffer and used in SDS-PAGE (50 μg lysate/lane). Immunoblotting was performed using the rabbit polyclonal anti-15LOX2, which recognizes most splice variants including 15-LOX2sv-b. The blots were stripped and reprobed for β-actin.
(C) Prostate-specific transgene expression. Urogenital and other organs indicated were isolated from 2.5-month fl26 15-LOX2 transgenic mice and protein lysates (50 μg/lane) used in Western blotting for 15 LOX2 and GAPDH (loading control).
(D-E) Transgene expression in young and old animals. Representative images of whole-mount prostate sections (without AP) made from 2.4 (D) or 16.5 (E) month (m) old wt, fl26 and svb9 mice (n>15/genotype), stained for HE or 15-LOX2. Images were taken with a Nikon stereomicroscope (Bar = 1 mm). The orientation of the whole-mount images was illustrated in D, panel a (U, urethra).
(F) Transgene expression in young (2.5 month) and old (14.2 month) prostate lobes of fl26 mice.
(G) 15(S)-HETE levels in wt and transgenic VPs measured in the presence of 50 μM AA. Bars represent the mean ± S.D of the measurements obtained from 5 animals/group. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.
To avoid potential effects of transgene insertion on the prostate phenotype (Kasper et al., 1998; Majumder et al., 2003; Masumori et al., 2001), three fl lines, i.e., fl2 (highest expresser), fl26 (high expresser), and fl15 (low expresser) (Fig. 1B; fig. S1), and three svb lines, i.e., svb9 (high expresser), svb10 (low expresser), and svb16 (lowest expresser) (Fig. 1B; fig. S2) were expanded. All transgenic animals were fertile and overall similar to wild-type (wt) animals in external appearances. The only noticeable change in transgenic animals (compared to age-matched controls) was the increased bladder size and age-associated bladder obstruction (not shown). Western blotting (Fig. 1B, C & F) and IHC on either whole-mount prostate (Fig. 1D-E) or microdissected lobes (fig. S1-S2) revealed that the transgene was expressed, in descending orders, in ventral prostate (VP), lateral prostate (LP), and dorsal prostate (DP) with the anterior prostate (AP) being mostly negative. Genitourinary organs and several other organs examined were negative for transgene expression (Fig. 1C). Overall, the expression patterns of the transgenes, 15-LOX2 or 15-LOX2sv-b, were very similar to those of other transgenes driven by various probasin promoters (i.e., −426/+28 rPB, LPB, and ARR2PB) in several strains of mice (Kasper et al., 1998; Majumder et al., 2003; Masumori et al., 2001). It should be noted that while fl26 animals showed strong and homogeneous 15-LOX2 expression in IHC (Fig. 1Dd & Ed) and Western blot (Fig. 1B), the svb9 prostates frequently exhibited lower and heterogeneous 15-LOX2sv-b staining (Fig. 1B, Fig. 1Df & Ef). This ‘difference’ in transgene expression levels is most likely related to the fact that the polyclonal anti-15-LOX2 antibody used preferentially recognizes 15-LOX2 (i.e., full length) and does not recognize its splice variants very well under harsh denaturing conditions (such as Western blotting and paraffin-embedded IHC) although it does recognize equally well the undenatured proteins of 15-LOX2 splice variants in immunofluorescence staining (Bhatia et al., 2003; Bhatia et al., 2005; see Fig. 6F, below).
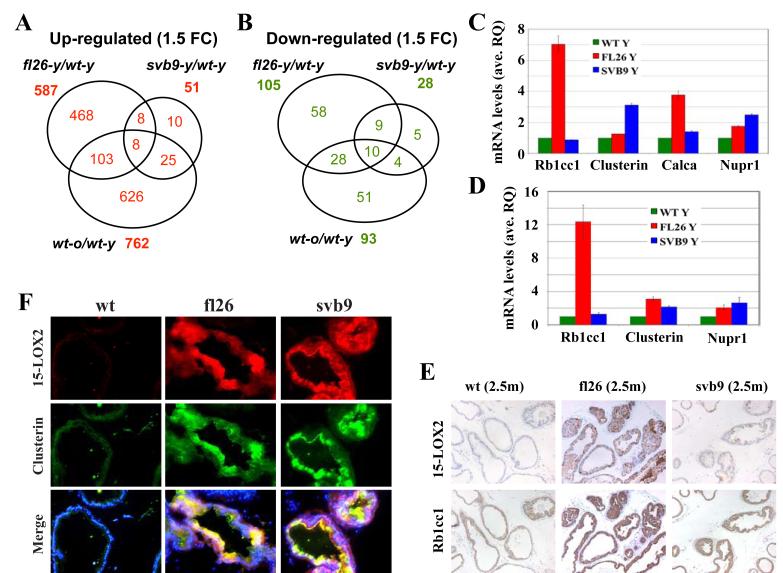
Figure 6. Microarray analysis of gene expression in transgenic VPs.
(A-B) Venn diagram presentations of commonly up- and down-regulated genes. Comparisons were made of those genes that showed ≥1.5 fold changes (1.5 FC) of either upregulation (left) or downregulation (right) in the three hybridization groups, i.e., fl26-y versus wt-y, svb9-y versus wt-y, and wt-o versus wt-y.
(C) qPCR analysis of four randomly picked genes upregulated in microarray. Shown are relative mRNA levels and bars represent mean ± S.D of three independent measurements.
(D) qPCR analysis showing epithelial-specific expression of genes analyzed in (C). Epithelial glands from respective genotypes (at 6 mo.) were microdissected by LCM and qPCR analysis was carried out using RNA isolated from epithelial glands. Shown are relative mRNA levels and bars represent mean ± S.D of 3-4 independent measurements.
(E) Serial whole-mount paraffin sections of wt and transgenic VPs at 2.5 months were used in IHC analysis of 15-LOX2 (upper) and Rb1cc1 (lower). Representative images (100x) of multiple animals analyzed (n>5/group) are presented.
(F) Serial whole-mount cryosections of wt and transgenic VPs at 6 mo. were used in immunofluorescence staining of 15-LOX2 (upper) and clusterin (middle). Lower panel shows a merge with DAPI. Representative images (200x) of multiple animals analyzed (n>3/group) are presented. Note that a more uniform expression of 15-LOX2 can be seen in svb9 animals in cryosections (upper panel in F) compared to in paraffin sections (upper panel in E).
15-LOX2 expression levels in the fl transgenic lines correlated well with the 15(S)-HETE-producing activities (Fig. 1G; tables S1 & S2). However, the svb9 and wt prostate lobes showed similar levels of 15(S)-HETE (Fig. 1G; tables S1 & S2), thus corroborating that 15-LOX2sv-b lacks enzymatic activity (Bhatia et al., 2003). No significant differences in 12(S)-HETE or PGE2 levels were observed between transgenic and wt prostates (table S2; data not shown). Importantly, 8(S)-HETE and 9(S)-HODE, the main AA and LA metabolites of murine 8-LOX, respectively, were undetectable in wt as well as transgenic prostates (not shown), consistent with earlier reports that 8-LOX, although inducible by phorbol esters in the mouse epidermis, was not expressed in mouse prostate (Jisaka et al., 1997; Kim et al., 2005; Shappell et al., 2003). Fully consistent with activity measurement, the polyclonal anti-15-LOX2 antibody we employed, which recognizes 15-LOX2 and its splice variants (Tang et al., 2002; Bhatia et al., 2003) as well as murine 8-LOX (Kim et al., 2005), never detected 8-LOX in wt mouse prostates (e.g., Fig. 1B, D, & E). Altogether, these results suggest that we have successfully established mouse prostate-specific expression of human 15-LOX2 or 15-LOX2sv-b.
For all subsequent studies, the fl26 and svb9 transgenic lines were generally used, which expressed similar levels of protein (e.g., see Fig. 6F, below).
Transgenic expression of 15-LOX2, in particular, 15-LOX2sv-b leads to enlarged VP associated with increased branching morphogenesis
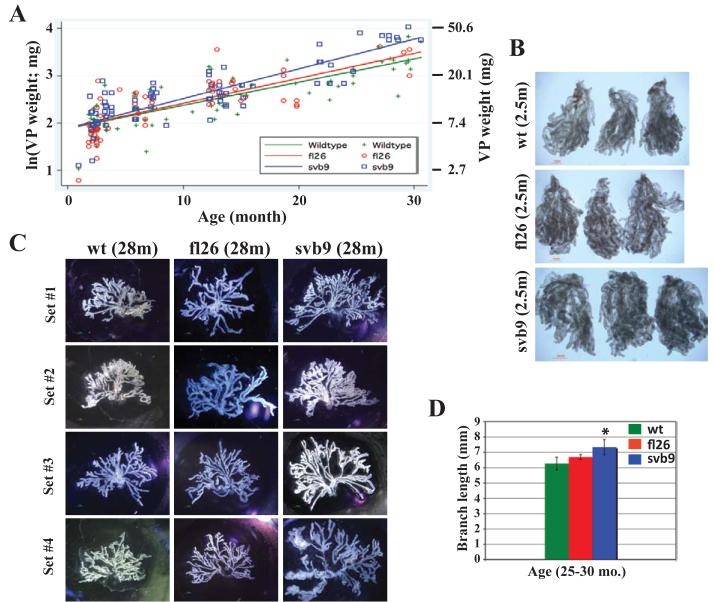
The human prostate is an organ that continues to grow with age and 15-LOX2 expression in the human prostate shows an age-related increase (Bhatia et al., 2005). To determine whether 15-LOX2 expression affected the overall prostate development, we microdissected the VP (highest transgene expression), and, for comparison, the AP (no transgene expression) from wild type (n = 91), fl26 (n = 68), and svb9 (n = 74) animals at 2 to 30 months, plotted the log wet weights (in mg) of the prostate lobes as a function of age, and performed linear regression analysis. Much to our surprise, transgene expression appeared to have accelerated the VP ‘growth’ such that at any given age, the transgenic VPs appeared heavier (Fig. 2A) and larger (Fig. 2B) than wt VPs. This was particularly evident with the svb9 VPs (P < 0.0005). On the contrary, APs harvested from the same cohort of animals did not show any significant difference (not shown). When branching morphogenesis of microdissected VPs from 25-30 month-old animals was carried out, the VPs of fl26 and svb9 in particular, showed more complex branching patterns (Fig. 2C), significantly longer branches (Fig. 2D), and more branching points and branch tips (not shown) than the age-matched wt VPs. Similar patterns of differences were also observed in comparisons of younger (i.e., ~6 months) animals (not shown).
Figure 2. 15-LOX2 or 15-LOXsv-b expression results in enlargement of mouse prostates.
(A) Graph showing wet VP weights (mg; right) or ln (weight) of wt (n = 91), fl26 (n = 68) and svb9 (n = 91) mice as a function of animal age.
(B) Representative images (>5 for each genotype) of microdissected VP lobes of 2.5 month-old wt, fl26, svb9 mice showing increased prostate size in transgenic mice (scale bar = 1 mm).
(C) Branching morphogenesis of representative VP lobes (4 for each genotype) microdissected from wt and transgenic mice depicting the differences in the length of branches and the complexity of branching pattern.
(D) Branch lengths of the microdissected VPs from old (25 – 30 months) wt or transgenic animals (n = 5 per genotype). *P<0.05.
Transgenic prostates exhibit age-related epithelial cell hyperplasia in association with increases in proliferative (Ki-67+) cells
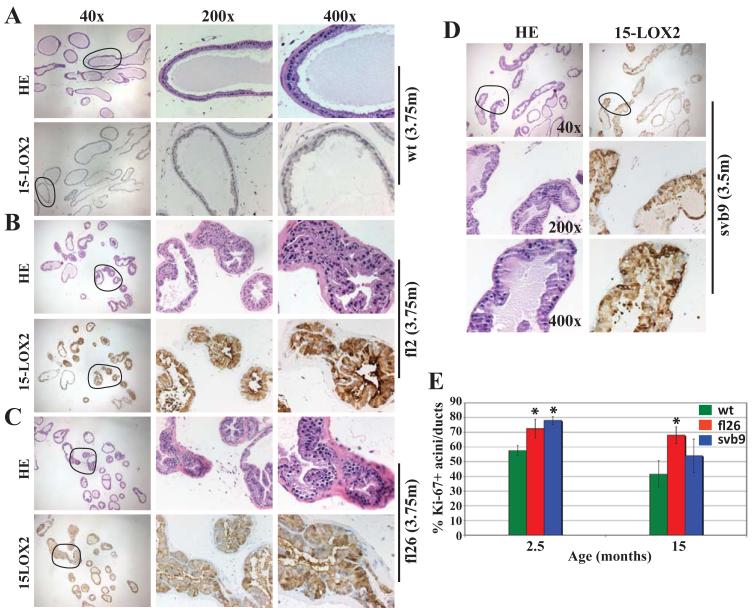
To determine the potential cellular mechanisms underlying the transgene-induced VP enlargement, we conducted thorough IHC analysis in both microdissected (Fig. 3) and whole-mount (fig. S3) VP lobes. Surprisingly (considering potential tumor-suppressive functions of 15-LOX2), we observed widespread hyperplasia that correlated with the transgene expression levels (Fig. 3B - C). The svb9 VPs also exhibited hyperplasia (Fig. 3D). Hyperplasia was observed in the VPs of animals as young as 6-10 weeks (fig. S3A). The VPs in older (e.g., 15-month) transgenic animals showed extensive hyperplasia involving >50% of the acini (fig. S3B). Hyperplastic areas showed crowded cells, stratified nuclei, and formation of intraluminal tufts, though true cribriform structures were rarely seen (Fig. 3B-D; fig. S3). Hyperplastic epithelial cells were tall with abundant cytoplasm and many contained prominent secretory material. In some areas of hyperplasia, cells demonstrated nuclear atypia, with nuclear enlargement and prominent nucleoli. Based on these findings, two pathologists (D.K and D.G.T) independently classified the primary lesions in the transgenic VPs as atypical epithelial hyperplasia with lack of evidence of PIN lesions defined as by the Bar Harbor Classification System (Shappell et al., 2004). The transgenic LPs, as expected, manifested less dramatic, though still obvious hyperplastic changes compared to the transgenic VPs (not shown).
Figure 3. Transgenic VPs demonstrate epithelial hyperplasia.
(A) H&E and 15-LOX2 staining of wt VPs.
(B-D) The VPs of fl2 (B, highest expresser) and fl26 (C, high expresser) display prominent epithelial hyperplasia that correlated with transgene expression levels. The VPs of svb9 (D) also show epithelial hyperplasia. The ages in months (m) and the original magnifications of microphotographs are indicated. Circled areas in the 40x images are enlarged in the corresponding 200x and 400x images.
(E) Ki-67+ acini/ducts as % of the total acini and ducts counted. Whole-mount VP sections stained for Ki-67 were used to quantify the acini and ducts that contained Ki-67+ cells [total numbers of acini/ducts counted: n = 168 for wt (15m), 202 for fl26 (15m), 215 for svb9 (15m), 196 for wt (2.5m), 189 for fl26 (2.5m), 195 for svb9 (2.5m)]. Data were collected from serial whole-mount sections of 3 VPs (* p<0.05).
Consistent with the hyperplastic phenotypes, we observed significantly increased numbers of Ki-67+ acini/ducts in the 2.5-month transgenic VPs (Fig. 3E), which also had increased numbers of Ki-67+ cells per acinus or duct, especially in the svb9 VP (wt, 1.81±0.014; fl26, 2.3±0.5; svb9, 4.45±0.2). At 15 months, the transgenic VPs still had higher Ki-67+ acini/ducts compared to the age-matched wt animals (Fig. 3E). In contrast to increased Ki-67+ proliferative cells, the transgenic VPs did not show significant changes in apoptosis assessed by caspase-3 staining (not shown).
15-LOX2 induced prostatic hyperplasia is accompanied by increased basal cells
Prostatic hyperplasia induced by both 15-LOX2 and 15-LOX2svb9 was characterized by significantly increased numbers of luminal cells that stained positive for androgen receptor (AR; fig. S3) and cytokeratin 8 (CK8) (fig. S4). These changes phenotypically resemble the hyperplastic, PIN, and neoplastic lesions in the human prostate wherein the majority of cells are luminal (Abate-Shen and Shen, 2000). IHC staining for CD45 (pan-leukocyte marker) and α-smooth muscle actin did not reveal significant differences between the transgenic vs. wt VPs and between the fl26 vs. svb9 VPs (not shown).
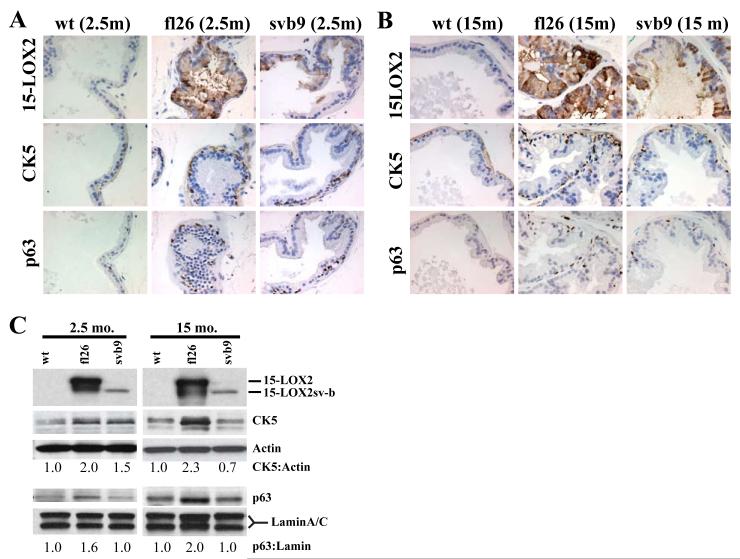
Distinctly, however, the hyperplastic lesions (glands) in the fl26 VPs also showed apparent ‘basal-cell hyperplasia’, characterized by increased numbers of cytokeratin 5 (CK5) and p63 (Signoretti et al., 2000) positive cells, which were observed in young (2.5-month; Fig. 4A) and intensified in older (15-month; Fig. 4B) animals. Western blotting analysis of both 2.5 and 15-month older mice also revealed increased CK5 and p63 protein levels in fl26 VPs compared to age-matched svb9 and wt animals (Fig. 4C). In comparison to fl26 VPs, the svb9 VPs exhibited much less prominent ‘basal-cell hyperplasia’ phenotype (Fig. 4A-C) although the young svb9 VPs did demonstrate slightly increased CK5 protein levels (Fig. 4C).
Figure 4. Increased basal cells in the 15-LOX2 transgenic prostates.
(A-B) Representative IHC images of serial tissue sections of 2.5 (A) and 15 (B) month-old wt and transgenic VPs stained for 15-LOX2, CK5, and p63. Original magnifications: x400.
(C) Microdissected VPs were analyzed by immunoblotting for 15-LOX2, CK5 and p63. Actin was used as loading control for CK5 and lamin A/C was used as loading control for nuclear p63. The relative ratios of CK5:actin and p63:lamin were estimated by densitometry and by setting the corresponding wt values to 1.0.
Prominent induction of cell senescence in young 15-LOX2 hyperplastic VPs
Despite extensive epithelial hyperplasia in transgenic VPs, no progression to PIN and carcinoma was noticed in >500 animals analyzed with the longest survived animals being ~30-month old. Also, the fl26 prostate lobes generally displayed more severe hyperplasia compared to svb9 VPs but the svb9 VPs showed more prominent organ ‘hypertrophy’ (Fig. 2). These two observations suggest that certain cell-intrinsic mechanism(s) activated by transgene expression, especially in fl26 VPs, might have led to the observed results. One such mechanism could be induction of cell senescence (Bhatia et al., 2005; Tang et al., 2007a). We stained the whole-mount cryosections of young (2.5 – 3 month) and old (15 month) wt and transgenic VPs for senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-βgal). As shown in Fig. 5A, the 2.5 month-old fl26 VPs showed stronger SA-βgal staining compared to both wt and svb9 VPs. A strong correlation between transgene expression and SA-βgal staining was observed in the epithelial glands (Fig. 5B). At 15 months, wt VPs, as expected, showed some SA-βgal staining whereas both fl26 and svb9 VPs showed comparable SA-βgal staining, which was overall stronger than that in wt VPs (fig. S5A).
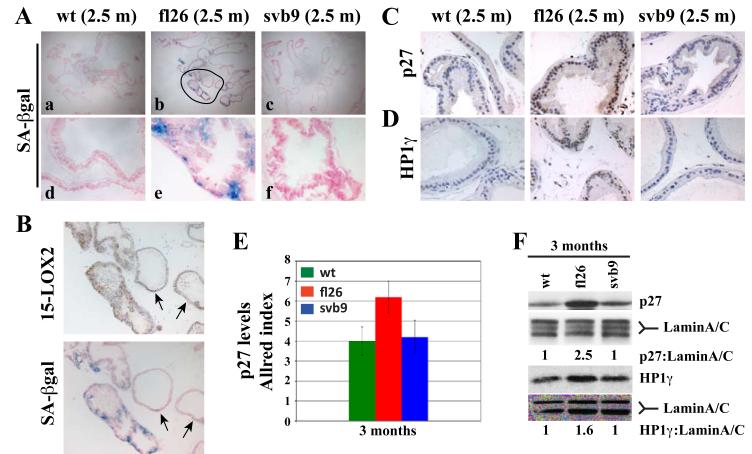
Figure 5. Transgenic expression of 15-LOX2 leads to early induction of senescence.
(A) Fresh whole-mount cryosections of wt and transgenic VPs at 2.5 mo. were stained for SA-βGal. Shown are images (40x, upper panels; 400x, lower panels) representative of 3-5 animals analyzed from each genotype/age group.
(B) SA-βgal staining correlates with the transgene expression. The encircled area in fl26 (2.5m) in A was enlarged to show matched SA-βgal and 15-LOX2 staining. Note a good correlation between SA-βgal positivity and transgene expression. The two arrows indicate the glands that show weak staining for 15-LOX2 and correspondingly the lack of SA-βgal staining.
(C-D) Whole-mount paraffin sections of wt and transgenic VPs at 2.5 mo. were used in IHC analysis of p27 (C) or HP1-γ (D). Representative images (400x) are presented.
(E) Allred method determination of relative p27 levels (as Allred index) in the VPs of wt and transgenic animals at ~ 3 mo. (n=5).
(F) Western blotting analysis of p27 and HP1γ protein levels in the VPs of wt and transgenic animals. Lamin A/C was used as loading control. The relative ratios of p27:lamin and HP1-γ:lamin were shown by setting the corresponding wt values to 1.0.
In prostate-specific AKT transgenic mouse (MPAKT) model (Majumder et al., 2008; Majumder et al., 2003), progression of PIN to PCa was blocked by senescence induction associated with upregulation of p27kip1 (p27), a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor involved in cell-cycle arrest and senescence, and HP1γ, a heterochromatin-associated protein concentrated in senescent cells. We observed that the p27 (Fig. 5C) and HP1γ (Fig. 5D) expression patterns resembled that of SA-βgal, i.e., both proteins were significantly upregulated in 2.5-month fl26 VPs compared to the wt and svb9 VPs. Semi-quantification of p27 levels by the Allred method (Allred et al., 1998) in whole-mount VPs showed significant increase in p27 nuclear staining in the 2.5-month fl26 VPs (Fig. 5E), as further confirmed by Western blotting (Fig. 5F). Both p27 and HP1γ protein levels in 15 month-old transgenic VPs only showed slight increases over those in wt VPs (fig. S5B-E), perhaps due to the increased ‘background’ levels of p27 and HP1γ in the old wt VPs, similar to SA-βgal staining (fig. S5A).
The above observations suggest that 15-LOX2 induces an early and persistent whereas 15-LOX2sv-b seems to induce a late senescence response in the mouse prostate that involves upregulation of p27 and HP1γ. Subsequently, we carried out a pilot correlation study in human PCa (n = 8) serial sections stained for 15-LOX2, p27 and HP1γ. The results revealed that all three molecules were co-expressed in benign prostatic glands with a good correlation, i.e., those glands that showed strong 15-LOX2 staining also showed distinct nuclear localization of p27 and HP1γ (fig. S6A and C). In contrast, PCa cells generally showed weak or no 15-LOX2 staining with reduced and predominantly cytoplasmic labeling of p27 and reduced HP1γ (fig. S6B and D).
Microarray analysis reveals distinct gene expression profiles that help explain the phenotypes in transgenic prostates
We carried out microarray analysis to compare global gene expression profiles in young (y; 2.5-3.0 month) wt, fl26, and svb9 VPs and old (o; 14-15 month) wt VPs using Agilent’s mouse whole genome oligo arrays. We included the old wt VPs because 15-LOX2 expression correlates with age in the human prostate (Bhatia et al., 2005). When a 1.5 fold-change (FC) cutoff was applied, fl26y(vs)wty comparison revealed 587 upregulated and 105 downregulated genes in the young fl26 VPs, of which 252 upregulated and 47 downregulated genes, respectively, were found to be statistically significant (P<0.05) (Fig. 6A-B; tables S3-S4). In contrast, svb9y(vs)wty comparison only showed 51 upregulated and 28 downregulated genes in the svb9y VPs, of which very few genes showed a P value less than 0.05 (Fig. 6A-B; tables S5-S6). On the other hand, 16 genes were commonly upregulated and 19 genes were commonly downregulated in fl26y and svb9y VPs (Fig. 6A-B; table S7). Interestingly, we observed a significant number of genes commonly upregulated or downregulated between the wto(vs)wty and fl26y(vs)wty comparisons as well as between the wto(vs)wty and svb9y(vs)wty comparisons (Fig. 6A-B; table S7).
Among the genes upregulated in the fl26y prostates were p63 and CK5 (Table 1), whose protein levels were also upregulated as revealed in our earlier IHC and Western blotting analyses (Fig. 4A-C). The upregulation of several other randomly picked molecules including Rb1cc1, clusterin, calcitonin and Nupr1 that were upregulated in fl26y VPs in microarray (Table 1; table S3) was also confirmed by quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR) and/or IHC analyses (Fig. 6C-F). Importantly, qPCR analysis of RNA prepared from epithelial glands isolated by laser capture microdissection (LCM) confirmed the epithelial-specific differences in gene expression levels between 6-month-old wt and transgenic VPs (Fig. 6D). Interestingly, two of the four molecules examined, i.e., clusterin and Nupr1, also showed some upregulation in svb9y VPs (Fig. 6C, D & F), in contrast to microarray data (table S5).
Table 1.
Representative genes up regulated in fl26y(vs)wty comparison (genes are grouped according to GO terms)
| Probe name (Agilent’s) |
Gene name | Gene description | P-value | Fold change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stem and progenitor cell/developmental related | ||||
| A_51_P253897 | Psca | Prostate stem cell antigen | 0.006 | 3.2048 |
| A_51_P257938 | Tacstd2 (Trop2) | Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 | 0.06 | 1.5781 |
| A_51_P265495 | Ly6a (Sca-1) | Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus A | 0.009 | 2.569 |
| A_51_P213544 | Klf4 | Krüppel-like factor 4 | 0.04 | 1.6683 |
| A_51_P409408 | Nkx3.1 | NK-3 transcription factor, locus 1 (Drosophila) | 0.13 | 1.5636 |
| A_51_P216550 | Trp63 | Transformation related protein 63 | 0.07 | 1.7779 |
| Cell proliferation/cell growth related | ||||
| A_52_P53906 | Ccnd2 | Cyclin D2 | 0.075 | 1.5736 |
| A_51_P396351 | Pcna | Proliferating cell nuclear antigen | 0.004 | 1.6933 |
| A_51_P240768 | Kras | v-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene | 0.004 | 1.6291 |
| A_52_P542172 | Rb1cc1 | RB1-inducible coiled-coil 1 | 0.002 | 4.1581 |
| A_52_P347826 | Rb1cc1 | RB1-inducible coiled-coil 1 | 0.008 | 5.8899 |
| A_51_P374571 | Igfbp6 | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 6 | 0.0003 | 1.5734 |
| A_51_P367720 | Clu | clusterin | 0.0005 | 8.6252 |
| Signal transduction/G-protein coupled receptor activity | ||||
| A_51_P290826 | Calca | calcitonin/calcitonin-related polypeptide, alpha | 0.01 | 4.9803 |
| A_51_P241074 | Map2k1 | Mitogen activated protein kinase kinase | 0.12 | 1.5118 |
| A_52_P100088 | Mapk1 | Mitogen activated protein kinase 1 | 0.07 | 1.5141 |
| A_51_P325343 | Mapk14 | Mitogen activated protein kinase 14 | 0.01 | 1.6251 |
| A_51_P264388 | Mapk8ip3 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein 3 |
0.06 | 1.6194 |
| A_51_P270339 | Pik3ap1 | Phosphoinositide-3-kinase adaptor protein 1 | 0.07 | 1.646 |
| A_51_P149852 | Pip5k1c | Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase, type 1 gamma |
0.05 | 1.7009 |
| A_51_P301566 | Plat | Plasminogen activator, tissue | 0.005 | 1.6774 |
| Angiogenesis | ||||
| A_51_P391159 | Ang1 | Angiogenin, ribonuclease A family, member 1 | 0.004 | 3.1862 |
| A_51_P349888 | Ang2 | Angiogenin, ribonuclease A family, member 2 | 0.01 | 2.585 |
| A_51_P179504 | Ang3 | Angiogenin, ribonuclease A family, member 3 | 0.006 | 3.7605 |
| A_51_P502906 | Ang4 | Angiogenin, ribonuclease A family, member 4 | 0.001 | 2.5945 |
| A_52_P98778 | Ang4 | Angiogenin, ribonuclease A family, member 4 | 0.002 | 3.3289 |
| A_51_P338443 | Angptl4 | Angiopoietin-like 4 | 0.17 | 1.673 |
| A_52_P480709 | Agtrap | Angiotensin II, type I receptor-associated protein | 0.03 | 1.5613 |
| Metabolism | ||||
| A_51_P337918 | Aldh4a1 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 4 family, member A1 | 0.01 | 1.5853 |
| A_51_P491504 | Aldh5a1 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 5, subfamily A1 | 0.03 | 1.5256 |
| A_51_P509384 | Aldh8a1 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 8 family, member A1 | 0.05 | 2.7516 |
| A_51_P453909 | Cyp2f2 | Cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily f, polypeptide 2 |
0.06 | 2.1186 |
| A_51_P489367 | Cyp3a25 | Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily a polypeptide 25 |
0.01 | 1.5924 |
| A_51_P292008 | Gpx3 | Glutathione peroxidase 3 (Gpx3) | 0.12 | 1.6138 |
| A_51_P359625 | Gsr | Glutathione reductase 1 | 0.015 | 1.6918 |
| A_52_P317653 | Car1 | Carbonic anhydrase 1 (Car1) | 0.01 | 1.8094 |
| A_51_P290986 | Dhcr7 | 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase | 0.01 | 1.6917 |
| Transcription/translation related | ||||
| A_52_P233441 | Gata2 | GATA binding protein 2 (Gata2) | 0.03 | 1.7727 |
| A_52_P63553 | Cebpb | CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), beta | 0.042 | 1.678 |
| A_52_P449871 | Idb4 | Inhibitor of DNA binding 4 | 0.002 | 1.8216 |
| A_51_P254646 | Jundm2 | Jun dimerization protein 2 | 0.008 | 2.0147 |
| A_52_P452689 | Atf3 | Activating transcription factor 3 | 0.27 | 1.7723 |
| A_51_P367866 | Egr1 | Early growth response 1 | 0.12 | 1.6758 |
| A_52_P310981 | Eif4e | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E | 0.001 | 1.6077 |
| A_51_P479659 | Eif5b | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B | 0.19 | 1.504 |
| Extracellular matrix/cytoskeletal/membrane related | ||||
| A_51_P358344 | Col17a1 | Procollagen, type XVII, alpha 1 | 0.04 | 2 |
| A_52_P479262 | Col6a3 | Type VI collagen alpha 3 subunit | 0.004 | 1.7039 |
| A_51_P255395 | Col7a1 | Procollagen, type VII, alpha 1 | 0.04 | 1.5765 |
| A_52_P430886 | Krt1-13 | Keratin complex 1, acidic, gene 13 | 0.03 | 2.4411 |
| A_51_P186856 | Krt2-5 (CK5) | Keratin complex 2, basic, gene 5 (Keratin 5) | 0.05 | 1.6891 |
| A_51_P281673 | Krtap9-1 | Keratin associated protein 9-1 | 0.02 | 1.6734 |
| A_51_P323248 | Sdc4 | Syndecan 4 | 0.05 | 1.5971 |
| A_52_P588483 | Fbln1 | Fibulin 1 | 0.035 | 1.9833 |
| A_52_P101852 | Sparc | Secreted acidic cysteine rich glycoprotein | 0.03 | 1.5572 |
| A_51_P392687 | Vim | Vimentin | 0.05 | 1.5644 |
| A_51_P199354 | Lamc1 | Laminin, gamma 1 | 0.04 | 1.6454 |
| Transport/binding proteins | ||||
| A_51_P179672 | Hbb-bh1 | Hemoglobin Z, beta-like embryonic chain | 0.008 | 1.6784 |
| A_52_P278538 | Hba-a1 | Hemoglobin alpha, adult chain 1 | 0.09 | 1.823 |
| A_51_P374476 | Hbb-b1 | Hemoglobin, beta adult major chain | 0.1 | 1.7915 |
| A_51_P361650 | Saa1 | Serum amyloid A | 0.12 | 2.6951 |
| A_51_P166886 | Saa2 | Serum amyloid A 2 | 0.09 | 2.8992 |
| A_51_P337308 | Saa3 | Serum amyloid A 3 | 0.11 | 1.717 |
| A_51_P290826 | Calca | Calcitonin/calcitonin-related polypeptide, alpha | 0.01 | 4.9803 |
| A_51_P366811 | Apod | Apolipoprotein D | 0.02 | 1.521 |
| A_51_P171999 | Apoe | Apolipoprotein E | 0.07 | 1.6647 |
| A_52_P185907 | Crabp1 | Cellular retinoic acid binding protein I | 0.07 | 2.5061 |
| A_51_P489720 | Slc16a11 | Solute carrier family 16 (monocarboxylic acid transporters), member 11 |
0.01 | 1.629 |
| A_51_P203620 | Slc18a1 | Solute carrier family 18 (vesicular monoamine), member 1 |
0.005 | 2.0968 |
| A_52_P105040 | Slc25a4 | Solute carrier family 25 (mitochondrial carrier, Adenine nucleotide translocator), member 4 |
0.03 | 1.5965 |
| A_52_P485939 | Slc39a8 | Solute carrier family 39 (metal ion transporter), member 8 |
0.01 | 1.8563 |
Listed are several classes of representative genes upregulated by ≥1.5 fold in the young (2.5-3 months) fl26 VPs (fl26y) compared to age-matched wt VPs (wty). The majority of genes presented show statistically significant (P < 0.05) upregulation. A full list of genes up regulated in fl26y(vs)wty comparison is presented in table S3.
Gene ontology (GO) analysis of the upregulated genes revealed interesting differential gene expression patterns (Table 1; table S3) that could help explain the prostate phenotypes in the transgenic animals. First, both CK5 and p63 were upregulated in fl26y (Table 1), corroborating the ‘basal cell hyperplasia’ phenotype in the fl26 VPs (Fig. 4). In addition, at least 5 other well-established (prostate) stem/progenitor cell markers (Lawson and Witte, 2007; Tang et al., 2007b) including Sca-1 (Lawson and Witte, 2007), Trop2 (Goldstein et al., 2008), Klf4 (Okita et al., 2008), Psca (Tran et al., 2002), and Nkx3.1 (Wang et al., 2009) were also upregulated preferentially in fl26y VPs compared to svb9y. Second, the fl26y VPs also upregulated several cell-cycle proteins such as cyclin D2 and Pcna (proliferating cell nuclear antigen) as well as positive regulators of proliferation such as K-ras, MAPK and PI3K pathway molecules (Table 1). Very few of these molecules were upregulated in the svb9y VPs, suggesting that 15-LOX2 and 15-LOX2sv-b promotes cell proliferation in mouse prostate (Fig. 3E) via different molecular mechanisms. Third, the fl26y(vs)wty comparison revealed prominent upregulation of angiogenin molecules (i.e., angiogenin 1-4) (Table 1), which were also upregulated in some other prostate-restricted transgenic models (Dillner et al., 2003; Kindblom et al., 2003; Majumder et al., 2003) and have been recently implicated in PCa development and progression through regulating angiogenesis and proliferation (Ibaragi et al., 2009; Katona et al., 2005; Yoshioka et al., 2006). Interestingly, all 4 angiogenin molecules were significantly upregulated in the wto(vs)wty but none was upregulated in the svb9y(vs)wty VPs (table S5 & table S7). Finally, in addition to these distinct gene expression profiles, many genes were commonly up- or downregulated in fl26y(vs)wty, svb9y(vs)wty, and wto(vs)wty comparisons (table S7; data not shown).
DISCUSSION
The current project was undertaken to probe the in vivo biological activities of the functional tumor suppressor 15-LOX2, whose expression is reduced or lost in PCa. Through establishment and characterization of prostate-specific 15-LOX2 transgenic mice, we report several surprising and interesting findings (Fig. 7). Expression of 15-LOX2 in mouse prostate, unexpectedly, leads to prostatic hyperplasia associated with increased cell proliferation and increased numbers of both luminal and basal cells. Expression of 15-LOX2sv-b, a splice variant that lacks AA-metabolizing activity, results in a moderate epithelial hyperplasia but apparent prostate enlargement associated with increased cell proliferation and luminal cells only (Fig. 7). Prostatic hyperplasia induced by both 15-LOX2 and 15-LOX2sv-b does not progress to PIN or carcinoma, likely due to the induction of cell senescence.
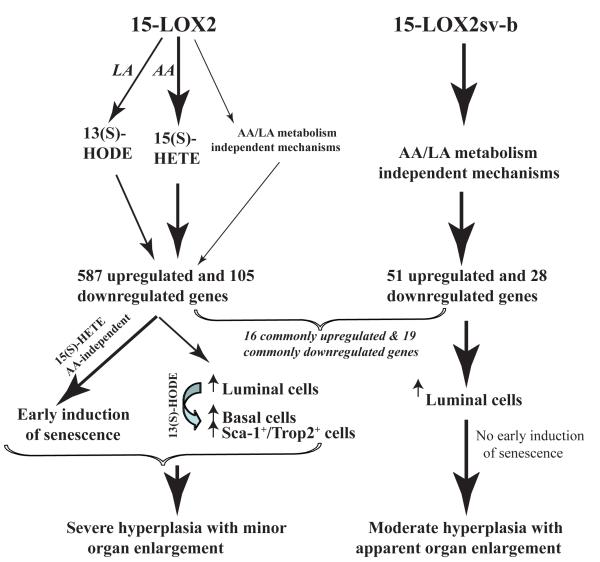
Figure 7. Schematic depicting possible mechanisms of action of 15-LOX2 and 15-LOX2sv-b.
15-LOX2 possesses AA and LA-metabolizing activity to produce 15(S)-HETE and 13(S)-HODE, respectively, and may also possess, to a much lesser extent (depicted by thinner arrows), AA/LA metabolism-independent functions, which together induce ~600 upregulated and ~100 downregulated genes (by ≥1.5 fold) in mouse VPs. These changes in gene expression result in two cellular outcomes, i.e., prominent hyperplasia (with increase in numbers of both luminal and basal cells) associated with enhanced proliferation caused by 13(S)-HODE and early induction of senescence induced by 15(S)- HETE, which may cancel each other out resulting in minor prostate enlargement. In contrast, 15-LOX2sv-b lacks AA and LA-metabolizing activities and only causes alterations of a total of ~80 genes, among which 16 upregulated and 19 downregulated genes are commonly shared with the fl26 VPs. 15-LOX2sv-b expression increases mainly luminal cells without early induction of cell senescence resulting in hyperplasia and pronounced prostate ‘hypertrophy’. Persistent presence of senescence in 15-LOX2 transgenic prostate and late induction of senescence in 15-LOX2sv-b transgenic prostate may both constitute the barrier to hyperplasia-to-tumor progression.
Prostatic hyperplasia induced by 15-LOX2 or 15-LOX2sv-b: Distinct organ phenotypes and cellular basis
15-LOX2 reduces proliferation, induces senescence, and inhibits xenograft tumor development when ectopically expressed in PCa cells. Therefore, it came as a surprise to us that transgenic expression of 15-LOX2, and enzymatically inactive 15-LOX2sv-b in particular, resulted in enlargement of mouse prostate, which, histologically, is characterized by epithelial hyperplasia. The fl VPs consistently display more severe hyperplastic lesions than age-matched svb VPs. One possible explanation is that, compared to svb VPs, the fl VPs demonstrate significantly increased numbers of not only luminal cells but also basal cells that stain positive for CK5 and p63 (Fig. 7). This basal-cell hyperplasia is associated with gene expression changes in CK5, p63, Nkx3.1, and Sca-1 as well as a novel prostate stem cell marker Trop2 (Goldstein et al., 2008), suggesting that 15-LOX2 expression results in increases in both basal cells and perhaps p63+/Sca-1+/Trop2+ stem/progenitor cells in the basal layer, the latter of which in turn could give rise to more luminal cells. Consequently, increased cellularity in both basal and luminal compartments contribute to the more prominent hyperplasia phenotype observed in the fl VPs (Fig. 7).
Why is basal-cell hyperplasia only observed in the fl transgenic VPs and how could we reconcile the seeming contradiction of tumor-suppressive effects of 15-LOX2/15(S)-HETE in vitro (Tang et al., 2007a) versus increased proliferation and hyperplasia in fl VPs? One explanation could be related to the unique biochemical properties of 15-LOX2, which metabolizes predominantly AA to generate 15(S)-HETE but can also metabolize LA to produce some 13(S)-HODE (Kilty et al., 1999). Indeed, in the fl transgenic VPs, we have observed significantly higher levels of not only 15(S)-HETE (table S1) but also 13(S)-HODE (table S2), suggesting that 15-LOX2 in mouse prostate is producing a significant amount of 13(S)-HODE from LA, available from the chow. This increase in 13(S)-HODE could potentially explain the severe hyperplasia in the fl VPs as 13(S)-HODE, the principal metabolite of 15-LOX1, possesses protumorigenic functions in PCa cells (Spindler et al., 1997) and transgenic expression of 15-LOX1 in mouse prostate results in hyperplasia and PIN via over-production of 13(S)-HODE (Kelavkar et al., 2006). Since 15-LOX2 in our transgenic model is directed to the luminal cell compartment by ARR2PB promoter, presumably, the luminal cell-derived 13(S)-HODE acts on the basal (stem/progenitor) cells to promote their proliferation (Fig. 7). The svb9 VPs, on the other hand, do not show increased levels of 13(S)-HODE (table S2) and thus lack the basal-cell hyperplasia phenotype. How 15-LOX2sv-b induces prostatic hyperplasia remains presently unclear.
Distinct and shared gene expression profiles and molecular mechanisms for 15-LOX2 and 15-LOX2sv-b
Genome-wide cDNA microarray analysis has revealed nearly 600 up-regulated and 100 downregulated genes in the fl26 VPs but only ~50 upregulated and 28 downregulated genes in svb9 VPs, compared to the age-matched young wt VPs (Fig. 7). The significantly more upregulated genes in the fl26 VPs are almost certainly related to the ability of 15-LOX2 to produce 15(S)-HETE and 13(S)-HODE (Fig. 7). On the other hand, it is remarkable that 16 of the 51 genes upregulated and 19 of the 28 genes downregulated in the young svb9 VPs are shared with the fl26 VPs, suggesting strongly that as we proposed earlier (Bhatia et al., 2003), 15-LOX2 possesses AA/LA metabolism-independent biological functions (Fig. 7).
Among the genes upregulated in the fl26 VPs, many are positive cell-cycle molecules (e.g., cyclin D2, Pcna) or positive regulators of cell proliferation (e.g., K-ras, Mapk, Pik3) and, strikingly, are also upregulated in two other transgenic prostate models, i.e., MPAKT (Majumder et al., 2003) and PB-PRL (Dillner et al., 2003; Kindblom et al., 2003), both of which also manifest conspicuous hyperplastic lesions (table S8). For example, MPAKT VPs, mainly characterized by PIN lesions (Majumder et al., 2003), and fl26 VPs share ~15% identical (e.g., Ang 2, Ang, 3, Trop2, Psca, Fgfbp1, Saa1 and Saa2) and ~40% similar upregulated genes (table S8). Likewise, PB-PRL VPs, which display stromal hyperplasia with mild epithelial hyperplasia (Dillner et al., 2003; Kindblom et al., 2003), share ~13% identical and ~30% similar upregulated genes with the fl26 VPs (table S8). Among the 17 identical genes are Ang 4, clusterin, and several ECM proteins including vimentin, col3a1, and laminin (table S8). These similarities suggest that transgenic expression of 15-LOX2 may cause not only epithelial hyperplasia but also some stromal alterations. By comparison, the svb9 VPs show many fewer changes in gene expression and the majority of the up- and downregulated genes in fl26 VPs are not observed in svb9 VPs (Fig. 7). On the other hand, increased levels of Clu and Nupr1 in svb9y VPs observed by qPCR suggest that inter-animal variability commonly associated with animal studies might have masked differential expression of at least some genes in the svb9 animals when analyzed by microarray.
15-LOX2 expression elicits early and persistent cell senescence in vivo: Potential barrier to tumor development
How do we explain that although fl26 VPs exhibit more severe hyperplasia than svb9 VPs, the latter appear bigger and display more conspicuous organ ‘hypertrophy’? A possible explanation could be that 15-LOX2, both in vitro (Bhatia et al., 2005) and in vivo (this study), seems to be a stronger inducer of cell senescence than 15-LOX2sv-b. Hence, 2-3 month fl26 VPs already show prevalent senescence, which persists throughout adulthood; in contrast, increased senescence is observed only in old svb9 VPs. Consequently, despite that 15-LOX2 induces prominent cell proliferation and hyperplasia, early induction of senescence presumably cancels out the proliferation-induced increases in both luminal and basal cells. As a result, 15-LOX2 only causes mild prostate enlargement compared to 15-LOX2 svb9 (Fig. 7).
How 15-LOX2 elicits cell senescence at the molecular level is presently unclear. Since 15(S)-HETE can act as a ligand for PPARγ to induce gene transcription (Chen et al., 2003; Subbarayan et al., 2006), we are tempted to speculate that 15-LOX2, partially localized in the nucleus (Bhatia et al., 2003) and perhaps via intranuclear production of 15(S)-HETE, preferentially activates a set of genes such as Rb1cc1 (Table.1; Fig. 6 C-E) in fl26 VPs. Rb1cc1 can in turn induce Rb1 (Chano et al., 2002; Ikebuchi et al., 2009) and p21 by physically interacting with p53 (Melkoumian et al., 2005), all of which are important players of senescence. Microarray analysis also identifies a subset of genes commonly up- and down-regulated in fl26 and svb9 VPs (Fig. 7), some of which might be involved in 15-LOX2-induced but largely responsible for 15-LOX2sv-b-caused cell senescence.
Since cell senescence is a strong suppressor of progression from hyperplastic lesions to overt tumor development (Braig et al., 2005; Chen et al., 2005; Majumder et al., 2008), we hypothesize that 15-LOX2-elicited cell senescence functions as a barrier to hyperplasia-to-tumor progression in our transgenic animals. This hypothesis is strongly buttressed by the fact that the 15(S)-HETE-elicited senescence seems to predominate over the 13(S)-HODE-promoted hyperplasia in ultimately preventing progression of hyperplasia to PIN/tumor (Fig. 7). We are currently testing this hypothesis by crossing fl26 mice to Hi-Myc mice (Ellwood-Yen et al., 2003), which develop invasive adenocarcinoma in the prostate.
MATERIALS & METHODS
Generation of prostate-specific 15-LOX2 transgenic mice
The transgene constructs (see Fig. 1A) were made by placing 15-LOX2 and 15LOX2sv-b cDNA (Tang et al., 2002) under the control of ARR2PB promoter (Zhang et al., 2000), intervened by the rabbit β-globin second intron sequence that increases transgene expression and followed by β-globin-SV40 hybrid polyA sequences (Chen et al., 2009). The ~4.2 kb Kpn I fragments containing the transgenes were gel-purified and microinjected into the male pronucleus of FVB/N mice. Male founder mice were identified by PCR genotyping of tail-clip DNA using primers C (sense, 5′- ACTACCTCCCAAAGAACTTCCCC-3′) and D (antisense, 5′-TTCAATGCCGATGCCTGTG-3′), or using primers F2 (sense, 5′-GGTCATCATCCTGCCTTTC-3′; in the β-globin intron) and R1 (antisense, 5′-CGATGCTGACAGACACTTTG-3′; in the transgene cDNA). PCR of β-actin was used as control. All the procedures involving the usage of animals were approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC).
Prostate microdissection and branching morphogenesis of VP
Detailed procedure was described elsewhere (Sugimura et al., 1986). Briefly, the prostate was removed along with the urogenital tract. The organs were placed immediately in ice cold Hank’s Buffered Salt Solution (HBSS) and microdissected under a dissection microscope. One of the two VP lobes was then incubated in 1% collagenase in HBSS on Maximov depression slide for 10 min and branches were separated using fine forceps. From the branched VP, branch tips were counted and branch lengths were measured.
From a separate group of wt and transgenic mice, the wet weights of both lobes of the VP and AP (as control) were collected at different ages from 2 to 30 months. Weights (in mg) were plotted as a function of animal age and regression analysis was carried out to test the significance of differences in the weights of prostatic lobes between transgenic and wt mice.
Microarray analysis
Basic procedures for microarray experiments were recently described (Bhatia et al., 2008). In brief, VP lobes were removed and submerged in 50 μl of RNALater at 4°C for 1-2 days, RNALater was then removed and the prostate lobes were frozen at −80°C until processed. VP lobes from 6 mice of the same genotype were combined to reduce the inter-animal variability. The combined frozen VP lobes were crushed in a BioPulverizer (Biospec Products, Inc). RNA was isolated using RNA mini prep kit for VPs of 2.5 – 3 months old (young) animals (17-29 mg) and midi prep kit for VPs of 14-16 months (old) animals (38-64 mg) according to the manufacturer’s instructions utilizing syringe homogenization. RNA was quantified using the Nanodrop ND-1000 and RNA integrity analyzed by Agilent Bioanalyzer. Microarray experiments were carried out using the 44K whole mouse genome oligo arrays from Agilent (G4122A). RNA from young (y) and old (o) wt and young transgenic (fl26 & svb9) VPs was hybridized onto dual channel arrays in wt old vs. wt young, fl26 young vs. wt young, and svb young vs. wt young combinations in biological replicates.
The array data were subjected to LOWESS normalization and the normalized data were used for calculating fold changes (FC) of up- and downregulated genes in each individual comparison. A paired t-test was carried out for each comparison to obtain P values. Venn Diagram analysis was carried out by using Venn Diagram analysis module from ArrayTrack microarray analysis suite developed by FDA’s NCTR (Fang et al., 2009). GO analysis was carried out by using WebGestalt (WEB-based GEne SeT AnaLysis Toolkit) developed and maintained by Bioinformatics Resource Center at Vanderbilt. All microarray data have been deposited in NCBI GEO database (accession # GSE158;http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?token=xvmphckuguyoqrm&acc=GSE15827).
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We gratefully thank Dr. R. Matusik (Vanderbilt University) for providing the ARR2PB promoter, D. Holowell for transgenic related studies, Dr. H. Thames and K. Lin for assistance in statistics, the Histology Core for help in IHC, Animal Facility Core for animal related experiments, Molecular Biology Core, especially J. Repass for assistance in qPCR analysis, C. Perez for assistance in LCM, S. Gaddis, L. Shen and S. Tsavachidis for assistance in microarray analysis, Drs. S. Fischer and C. Jeter for critically reading the manuscript, and other members of the Tang lab for support and helpful discussions. This work was supported in part by grants from NIH (R01-AG023374, R01-ES015888, and R21-ES015893-01A1), American Cancer Society (RSG MGO-105961), Department of Defense (W81XWH-07-1-0616 and W81XWH-08-1-0472), and Elsa Pardee Foundation (D.G.T) and by two Center Grants (CCSG-5 P30 CA016672 and ES07784).
Non-standard abbreviations used
- 15-LOX2
15-lipoxygenase 2
- 15(S)-HETE
15(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid
- AA
arachidonic acid
- AP
anterior prostate
- CK5
cytokeratin 5
- DP
dorsal prostate
- ECM
extracellular matrix
- HP1-γ
heterochromatin protein-1 γ
- LP
lateral prostate
- NHP
normal human prostate epithelial cells
- PCa
prostate cancer
- PPARs
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors
- SA-βgal
senescence associated β-galactosidase
- VP
ventral prostate
- wt
wild type
REFERENCES
- Abate-Shen C, Shen MM. Molecular genetics of prostate cancer. Genes Dev. 2000;14:2410–34. doi: 10.1101/gad.819500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allred DC, Harvey JM, Berardo M, Clark GM. Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by immunohistochemical analysis. Mod Pathol. 1998;11:155–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia B, Jiang M, Suraneni M, Patrawala L, Badeaux M, Schneider-Broussard R, et al. Critical and distinct roles of p16 and telomerase in regulating the proliferative life span of normal human prostate epithelial progenitor cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:27957–72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803467200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia B, Maldonado CJ, Tang S, Chandra D, Klein RD, Chopra D, et al. Subcellular localization and tumor-suppressive functions of 15-lipoxygenase 2 (15-LOX2) and its splice variants. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:25091–100. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301920200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia B, Tang S, Yang P, Doll A, Aumueller G, Newman RA, et al. Cell-autonomous induction of functional tumor suppressor 15-lipoxygenase 2 (15-LOX2) contributes to replicative senescence of human prostate progenitor cells. Oncogene. 2005;24:3583–95. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braig M, Lee S, Loddenkemper C, Rudolph C, Peters AH, Schlegelberger B, et al. Oncogene-induced senescence as an initial barrier in lymphoma development. Nature. 2005;436:660–5. doi: 10.1038/nature03841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brash AR, Boeglin WE, Chang MS. Discovery of a second 15S-lipoxygenase in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:6148–52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.12.6148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chano T, Ikegawa S, Kontani K, Okabe H, Baldini N, Saeki Y. Identification of RB1CC1, a novel human gene that can induce RB1 in various human cells. Oncogene. 2002;21:1295–8. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen GG, Xu H, Lee JF, Subramaniam M, Leung KL, Wang SH, et al. 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid arrests growth of colorectal cancer cells via a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-dependent pathway. Int J Cancer. 2003;107:837–43. doi: 10.1002/ijc.11447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X, Schneider-Broussard R, Hollowell D, McArthur M, Jeter C, Benavides F, et al. Abnormal differentiation, hyperplasia and embryonic/perinatal lethality in BK5-T/t transgenic mice. Differentiation. 2009;77:324–34. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2008.10.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z, Trotman LC, Shaffer D, Lin HK, Dotan ZA, Niki M, et al. Crucial role of p53-dependent cellular senescence in suppression of Pten-deficient tumorigenesis. Nature. 2005;436:725–30. doi: 10.1038/nature03918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner K, Kindblom J, Flores-Morales A, Shao R, Tornell J, Norstedt G, et al. Gene expression analysis of prostate hyperplasia in mice overexpressing the prolactin gene specifically in the prostate. Endocrinology. 2003;144:4955–66. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-0415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood-Yen K, Graeber TG, Wongvipat J, Iruela-Arispe ML, Zhang J, Matusik R, et al. Myc-driven murine prostate cancer shares molecular features with human prostate tumors. Cancer Cell. 2003;4:223–38. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00197-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang H, Harris SC, Su Z, Chen M, Qian F, Shi L, et al. ArrayTrack: an FDA and public genomic tool. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;563:379–98. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-175-2_20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein AS, Lawson DA, Cheng D, Sun W, Garraway IP, Witte ON. Trop2 identifies a subpopulation of murine and human prostate basal cells with stem cell characteristics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:20882–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811411106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez AL, Roberts RL, Massion PP, Olson SJ, Shyr Y, Shappell SB. 15-Lipoxygenase-2 expression in benign and neoplastic lung: an immunohistochemical study and correlation with tumor grade and proliferation. Hum Pathol. 2004;35:840–9. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2004.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibaragi S, Yoshioka N, Kishikawa H, Hu JK, Sadow PM, Li M, et al. Angiogenin-stimulated rRNA transcription is essential for initiation and survival of AKT-induced prostate intraepithelial neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7:415–24. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebuchi K, Chano T, Ochi Y, Tameno H, Shimada T, Hisa Y, et al. RB1CC1 activates the promoter and expression of RB1 in human cancer. Int J Cancer. 2009;125:861–7. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack GS, Brash AR, Olson SJ, Manning S, Coffey CS, Smith JA, Jr., et al. Reduced 15-lipoxygenase-2 immunostaining in prostate adenocarcinoma: correlation with grade and expression in high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Hum Pathol. 2000;31:1146–54. doi: 10.1053/hupa.2000.16670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang WG, Watkins G, Douglas-Jones A, Mansel RE. Reduction of isoforms of 15-lipoxygenase (15-LOX)-1 and 15-LOX-2 in human breast cancer. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2006;74:235–45. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2006.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jisaka M, Kim RB, Boeglin WE, Brash AR. Identification of amino acid determinants of the positional specificity of mouse 8S-lipoxygenase and human 15S-lipoxygenase-2. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:1287–93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.2.1287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jisaka M, Kim RB, Boeglin WE, Nanney LB, Brash AR. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a phorbol ester-inducible 8S-lipoxygenase from mouse skin. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:24410–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.39.24410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper S, Sheppard PC, Yan Y, Pettigrew N, Borowsky AD, Prins GS, et al. Development, progression, and androgen-dependence of prostate tumors in probasin-large T antigen transgenic mice: a model for prostate cancer. Lab Invest. 1998;78:i–xv. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katona TM, Neubauer BL, Iversen PW, Zhang S, Baldridge LA, Cheng L. Elevated expression of angiogenin in prostate cancer and its precursors. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:8358–63. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelavkar UP, Parwani AV, Shappell SB, Martin WD. Conditional expression of human 15-lipoxygenase-1 in mouse prostate induces prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia: the FLiMP mouse model. Neoplasia. 2006;8:510–22. doi: 10.1593/neo.06202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilty I, Logan A, Vickers PJ. Differential characteristics of human 15-lipoxygenase isozymes and a novel splice variant of 15S-lipoxygenase. Eur J Biochem. 1999;266:83–93. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim E, Rundhaug JE, Benavides F, Yang P, Newman RA, Fischer SM. An antitumorigenic role for murine 8S-lipoxygenase in skin carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 2005;24:1174–87. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindblom J, Dillner K, Sahlin L, Robertson F, Ormandy C, Tornell J, et al. Prostate hyperplasia in a transgenic mouse with prostate-specific expression of prolactin. Endocrinology. 2003;144:2269–78. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-0187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson DA, Witte ON. Stem cells in prostate cancer initiation and progression. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:2044–50. doi: 10.1172/JCI32810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahipal SV, Subhashini J, Reddy MC, Reddy MM, Anilkumar K, Roy KR, et al. Effect of 15-lipoxygenase metabolites, 15-(S)-HPETE and 15-(S)-HETE on chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line K-562: reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediate caspase-dependent apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007;74:202–14. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumder PK, Grisanzio C, O’Connell F, Barry M, Brito JM, Xu Q, et al. A prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia-dependent p27 Kip1 checkpoint induces senescence and inhibits cell proliferation and cancer progression. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:146–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.06.00. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumder PK, Yeh JJ, George DJ, Febbo PG, Kum J, Xue Q, et al. Prostate intraepithelial neoplasia induced by prostate restricted Akt activation: the MPAKT model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:7841–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1232229100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masumori N, Thomas TZ, Chaurand P, Case T, Paul M, Kasper S, et al. A probasin-large T antigen transgenic mouse line develops prostate adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine carcinoma with metastatic potential. Cancer Res. 2001;61:2239–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melkoumian ZK, Peng X, Gan B, Wu X, Guan JL. Mechanism of cell cycle regulation by FIP200 in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65:6676–84. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita K, Nakagawa M, Hyenjong H, Ichisaka T, Yamanaka S. Generation of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells without viral vectors. Science. 2008;322:949–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1164270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger D, Furstenberger G, Krieg P. Inducible expression of 15-lipoxygenase-2 and 8-lipoxygenase inhibits cell growth via common signaling pathways. J Lipid Res. 2007;48:553–64. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M600311-JLR200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shappell SB, Boeglin WE, Olson SJ, Kasper S, Brash AR. 15-lipoxygenase-2 (15-LOX-2) is expressed in benign prostatic epithelium and reduced in prostate adenocarcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1999;155:235–45. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65117-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shappell SB, Keeney DS, Zhang J, Page R, Olson SJ, Brash AR. 15-Lipoxygenase-2 expression in benign and neoplastic sebaceous glands and other cutaneous adnexa. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;117:36–43. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2001.01378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shappell SB, Olson SJ, Hannah SE, Manning S, Roberts RL, Masumori N. Elevated expression of 12/15-lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase-2 in a transgenic mouse model of prostate carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003;63:2256–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shappell SB, Thomas GV, Roberts RL, Herbert R, Ittmann MM, Rubin MA, et al. Prostate pathology of genetically engineered mice: definitions and classification. The consensus report from the Bar Harbor meeting of the Mouse Models of Human Cancer Consortium Prostate Pathology Committee. Cancer Res. 2004;64:2270–305. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-0946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signoretti S, Waltregny D, Dilks J, Isaac B, Lin D, Garraway L, et al. p63 is a prostate basal cell marker and is required for prostate development. Am J Pathol. 2000;157:1769–75. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64814-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler SA, Sarkar FH, Sakr WA, Blackburn ML, Bull AW, LaGattuta M, et al. Production of 13-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (13-HODE) by prostate tumors and cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;239:775–81. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1997.7471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbarayan V, Krieg P, Hsi LC, Kim J, Yang P, Sabichi AL, et al. 15-Lipoxygenase-2 gene regulation by its product 15-(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid through a negative feedback mechanism that involves peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Oncogene. 2006;25:6015–25. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimura Y, Cunha GR, Donjacour AA. Morphogenesis of ductal networks in the mouse prostate. Biol Reprod. 1986;34:961–71. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod34.5.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang DG, Bhatia B, Tang S, Schneider-Broussard R. 15-lipoxygenase 2 (15-LOX2) is a functional tumor suppressor that regulates human prostate epithelial cell differentiation, senescence, and growth (size) Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2007a;82:135–46. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2006.05.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang DG, Patrawala L, Calhoun T, Bhatia B, Choy G, Schneider-Broussard R, et al. Prostate cancer stem/progenitor cells: identification, characterization, and implications. Mol Carcinog. 2007b;46:1–14. doi: 10.1002/mc.20255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang S, Bhatia B, Maldonado CJ, Yang P, Newman RA, Liu J, et al. Evidence that arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase 2 is a negative cell cycle regulator in normal prostate epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:16189–201. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111936200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang Y, Wang MT, Chen Y, Yang D, Che M, Honn KV, et al. Downregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and induction of tumor dormancy by 15-lipoxygenase-2 in prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 2009;124:1545–51. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran CP, Lin C, Yamashiro J, Reiter RE. Prostate stem cell antigen is a marker of late intermediate prostate epithelial cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2002;1:113–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D, Chen S, Feng Y, Yang Q, Campbell BH, Tang X, et al. Reduced expression of 15- lipoxygenase 2 in human head and neck carcinomas. Tumour Biol. 2006;27:261–73. doi: 10.1159/000094761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X, Kruithof-de Julio M, Economides KD, Walker D, Yu H, Halili MV, et al. A luminal epithelial stem cell that is a cell of origin for prostate cancer. Nature. 2009;461:495–500. doi: 10.1038/nature08361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu XC, Shappell SB, Liang Z, Song S, Menter D, Subbarayan V, et al. Reduced 15S-lipoxygenase-2 expression in esophageal cancer specimens and cells and upregulation in vitro by the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, NS398. Neoplasia. 2003;5:121–7. doi: 10.1016/s1476-5586(03)80003-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka N, Wang L, Kishimoto K, Tsuji T, Hu GF. A therapeutic target for prostate cancer based on angiogenin-stimulated angiogenesis and cancer cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:14519–24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606708103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J, Thomas TZ, Kasper S, Matusik RJ. A small composite probasin promoter confers high levels of prostate-specific gene expression through regulation by androgens and glucocorticoids in vitro and in vivo. Endocrinology. 2000;141:4698–710. doi: 10.1210/endo.141.12.7837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.