Abstract
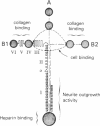
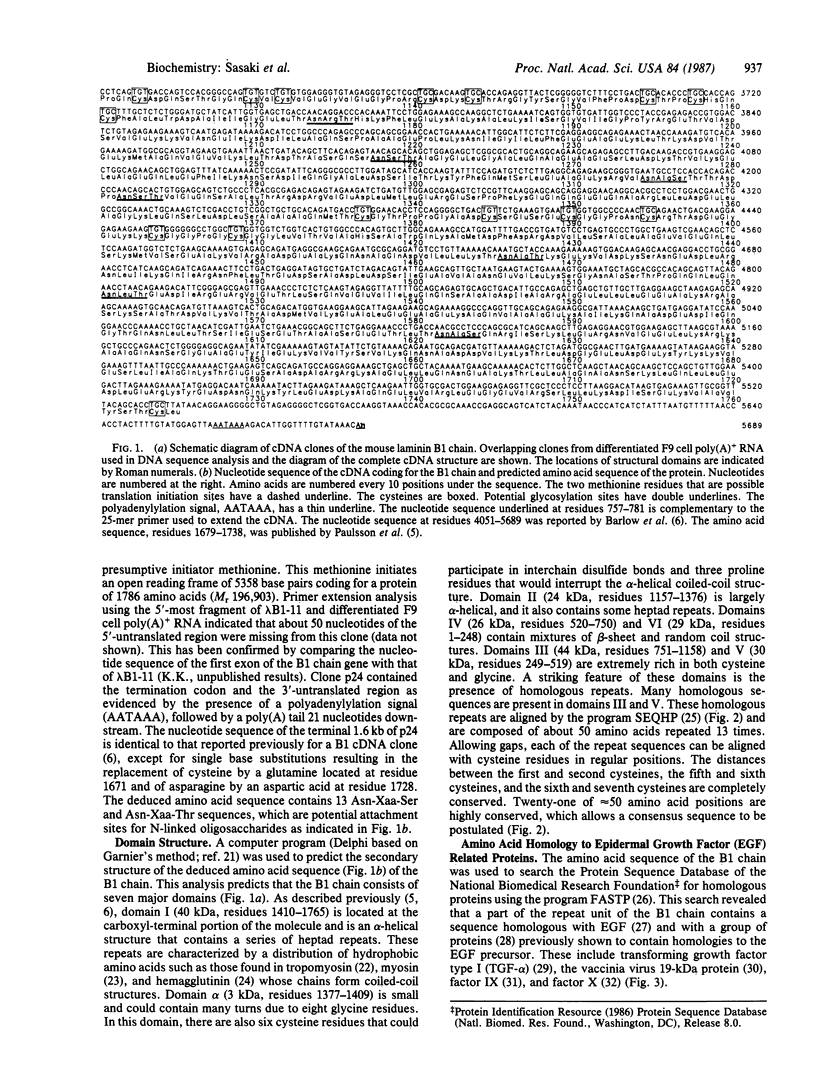
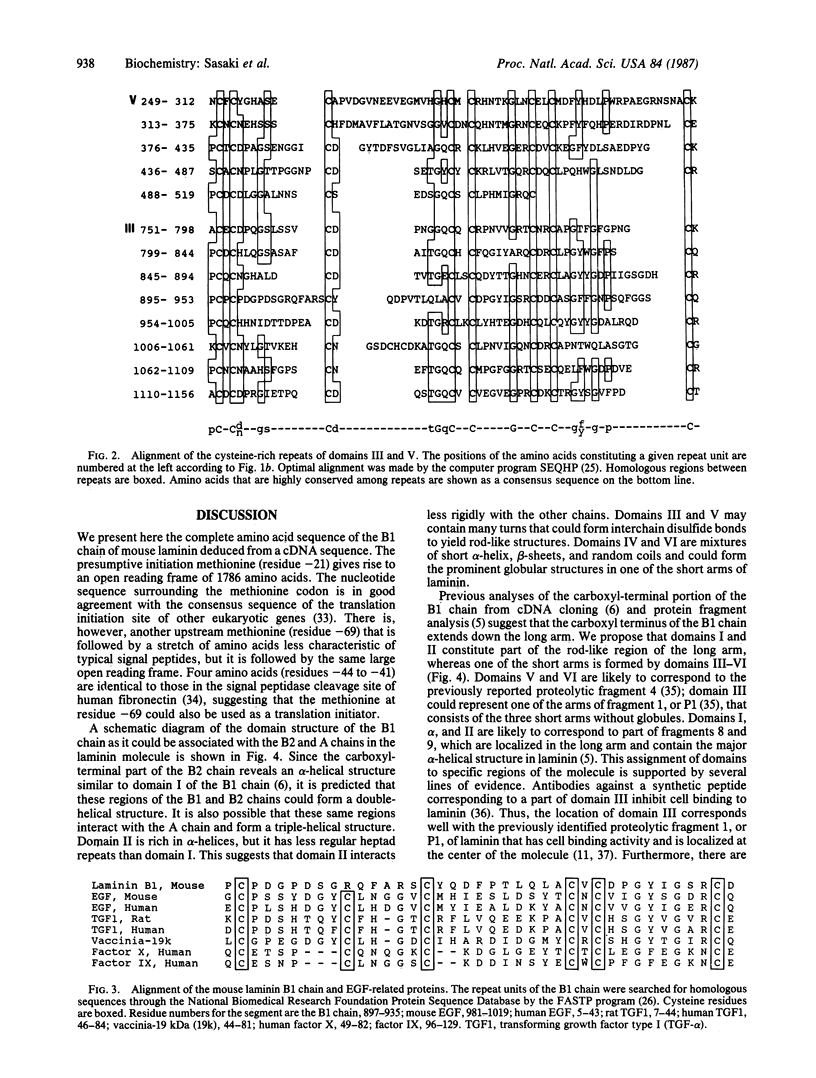
Laminin is a basement membrane-specific glycoprotein (800 kDa) consisting of three chains: A, B1, and B2. Laminin has diverse biological functions, which include stimulating epithelial cell growth and differentiation. We have isolated two overlapping cDNA clones that span 5.9 kilobases and code for the entire B1 chain of mouse laminin. The nucleotide sequence of the clones reveals a 5358-base pair open reading frame that potentially codes for 1786 amino acids, including 20 amino acids of a presumptive signal peptide. Analysis of the deduced protein sequence predicts that the B1 chain has seven distinct domains that include cysteine-rich repeats, alpha-helical, and globular structures. Part of the cysteine-rich region is homologous to epidermal growth factor and other proteins that contain epidermal growth factor-like repeats.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlow D. P., Green N. M., Kurkinen M., Hogan B. L. Sequencing of laminin B chain cDNAs reveals C-terminal regions of coiled-coil alpha-helix. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2355–2362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron-Van Evercooren A., Kleinman H. K., Ohno S., Marangos P., Schwartz J. P., Dubois-Dalcq M. E. Nerve growth factor, laminin, and fibronectin promote neurite growth in human fetal sensory ganglia cultures. J Neurosci Res. 1982;8(2-3):179–193. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490080208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassel-Duby R., Jayasuriya A., Chatterjee D., Sonenberg N., Maizel J. V., Jr, Fields B. N. Sequence of reovirus haemagglutinin predicts a coiled-coil structure. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):421–423. doi: 10.1038/315421a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomquist M. C., Hunt L. T., Barker W. C. Vaccinia virus 19-kilodalton protein: relationship to several mammalian proteins, including two growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7363–7367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. R., MacQueen H. A. Subunits of laminin are differentially synthesized in mouse eggs and early embryos. Dev Biol. 1983 Apr;96(2):467–471. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornbrooks C. J., Carey D. J., McDonald J. A., Timpl R., Bunge R. P. In vivo and in vitro observations on laminin production by Schwann cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3850–3854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., McCarthy B. J., Wadsworth S. C. Sequence organization of two recombinant plasmids containing genes for the major heat shock-induced protein of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):575–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L. Random subcloning of sonicated DNA: application to shotgun DNA sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):216–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Roberts A. B., Winkler M. E., Chen E. Y., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-alpha: precursor structure and expression in E. coli. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90550-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doege K., Hassell J. R., Caterson B., Yamada Y. Link protein cDNA sequence reveals a tandemly repeated protein structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3761–3765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar D., Timpl R., Thoenen H. The heparin-binding domain of laminin is responsible for its effects on neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1463–1468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J., Odermatt E., Engel A., Madri J. A., Furthmayr H., Rohde H., Timpl R. Shapes, domain organizations and flexibility of laminin and fibronectin, two multifunctional proteins of the extracellular matrix. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray A., Dull T. J., Ullrich A. Nucleotide sequence of epidermal growth factor cDNA predicts a 128,000-molecular weight protein precursor. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):722–725. doi: 10.1038/303722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington W. F., Rodgers M. E. Myosin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:35–73. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa M. I. Los Alamos sequence analysis package for nucleic acids and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):183–196. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komoriya A., Hortsch M., Meyers C., Smith M., Kanety H., Schlessinger J. Biologically active synthetic fragments of epidermal growth factor: localization of a major receptor-binding region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1351–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Umezawa K., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Primary structure of human fibronectin: differential splicing may generate at least 10 polypeptides from a single gene. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1755–1759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor IX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6461–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie G. W., Bing J. T., Kleinman H. K., Hassell J. R., Aumailley M., Martin G. R., Feldmann R. J. Localization of binding sites for laminin, heparan sulfate proteoglycan and fibronectin on basement membrane (type IV) collagen. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):205–216. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90391-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullen B. A., Fujikawa K., Kisiel W., Sasagawa T., Howald W. N., Kwa E. Y., Weinstein B. Complete amino acid sequence of the light chain of human blood coagulation factor X: evidence for identification of residue 63 as beta-hydroxyaspartic acid. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 7;22(12):2875–2884. doi: 10.1021/bi00281a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin R. W., Gehron P., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R., Valentine T., Swarm R. A murine tumor producing a matrix of basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):204–220. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott U., Odermatt E., Engel J., Furthmayr H., Timpl R. Protease resistance and conformation of laminin. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Mar;123(1):63–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Deutzmann R., Timpl R., Dalzoppo D., Odermatt E., Engel J. Evidence for coiled-coil alpha-helical regions in the long arm of laminin. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):309–316. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03630.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. N., Margulies I. M., Tralka T. S., Terranova V. P., Madri J. A., Liotta L. A. Isolation of a subunit of laminin and its role in molecular structure and tumor cell attachment. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9740–9744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. L., Letourneau P. C., Palm S. L., McCarthy J., Furcht L. T. Neurite extension by peripheral and central nervous system neurons in response to substratum-bound fibronectin and laminin. Dev Biol. 1983 Jul;98(1):212–220. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Smith K. K., Marotti K. R. Hormonal induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells: generation of parietal endoderm by retinoic acid and dibutyryl cAMP. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90471-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroobant P., Rice A. P., Gullick W. J., Cheng D. J., Kerr I. M., Waterfield M. D. Purification and characterization of vaccinia virus growth factor. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):383–393. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Rao C. N., Kalebic T., Margulies I. M., Liotta L. A. Laminin receptor on human breast carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):444–448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Johansson S., van Delden V., Oberbäumer I., Hök M. Characterization of protease-resistant fragments of laminin mediating attachment and spreading of rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8922–8927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]